
Beef quality grading is voluntary and administered by the USDA
United States Department of Agriculture
The United States Department of Agriculture, also known as the Agriculture Department, is the U.S. federal executive department responsible for developing and executing federal laws related to farming, forestry, and food. It aims to meet the needs of farmers and ranchers, promote agricult…
What are the quality grades of meat?
They are:
- Prime
- Choice
- Select
- Standard
- Commercial
- Utility
- Cutter
- Canner
What are the 3 grades of meat?
These are the most popular grades of beef found in grocery stores, warehouses and butcher shops:
- USDA Prime beef: contains the greatest degree of marbling and is generally sold to fine restaurants and some selected meat markets. ...
- USDA Choice beef: less marbling than Prime, but is still very high quality. ...
- USDA Select beef: generally a lower priced grade of beef with less marbling than Choice. ...
What are the 4 quality grades of beef?
Beef carcass quality grading is based on (1) degree of marbling and (2) degree of maturity. USDA beef quality grades are Prime, Choice, Select, Standard, Commercial, Utility, Cutter and Canner. Since quality grading is voluntary, not all carcasses are quality graded. Packers may apply their own “house brand” to merchandise their beef.
What grade of beef is the best?
The Eight US Beef Grades and What They Mean
- Prime Beef: Prime beef is the highest grade of beef available in the US. ...
- Choice Beef: Choice is the grade below prime, and will have less visible marbling than prime. ...
- Select Beef: The select grade of beef is mild-tasting beef from young cows that is less flavorful and much more tender than either choice or prime meat.
See more
Who determines the grade of the meat?
the USDABeef quality grading is voluntary and administered by the USDA and paid for by beef packers. The grade is primarily determined by the degree of marbling — the small flecks of fat within the beef muscle. Marbling provides flavor, tenderness and juiciness to beef and improves overall palatability.
Who grades beef and what are the grades?
There are eight total quality grades: Prime, Choice, Select, Standard, Commercial, Utility, Cutter and Canner. They have been used by the beef industry since 1927. The first three quality grades — Prime, Choice and Select — are the most commonly recognized by consumers and are considered food-grade labels by USDA.
What are the 2 main factors used to determine beef quality grades?
Quality Grade Quality grading on beef carcasses is determined by two subjectively scored factors in all cases where color, texture and firmness of lean are normal.
How do meat grades go?
There are eight different USDA beef grades: prime, choice, select, standard, commercial, utility, cutter and canner. Prime being the highest beef quality and canner being the lowest.
What grade of beef does McDonald's use?
McDonald's, the single-largest purchaser of beef, moved up from a F in last year's beef scorecard to a C, given its December 2018 policy that echoes the 2017 WHO guidelines on use of antibiotics in livestock.
What grade meat is Taco Bell?
We use 100 percent USDA premium beef in our seasoned beef.
How is meat graded and what is its importance?
Grading helps the processor to adopt or decide methods and procedures for disposing animals and carcasses. Grading helps the consumers to purchase assured quality of meat and gives satisfaction over the money spent on purchasing the meat.
What is the primary determination of beef quality grade?
Beef quality grading uses the marbling score assigned to the ribeye muscle of a carcass to predict palatability and sort carcasses into like categories. Degree of marbling is the primary determination of quality grade.
How is beef graded after slaughter?
Quality Grade: Slaughter cattle quality grades are based on palatability factors. Quality is evaluated primarily by finish, age & quality (marbling, maturity, color, firmness & texture of lean). Estimate to nearest 1/3 of grade (Prime or Choice), 1/2 grade (Select or Standard) & Utility.
What is the highest quality beef in the world?
Wagyu beefWhat is Wagyu beef? Wagyu beef originates from Japan and is considered by many the best beef on the planet. With the name meaning “Japanese Cow” (wa = Japanese, gyu = cow), it can be found in four different types of Japanese cattle.
What is the highest grade of meat?
PrimePrime is the highest quality of beef available. They have the most marbling and are sure to provide a wonderfully juicy and extremely tasty eating experience.
Is Wagyu better than prime?
This is because those who are looking for maximum marbling in their meats will pick Wagyu every time. Both of these different types of beef are extremely different. From the difference in buttery marbling to their price tag, Wagyu beef will always seem to be better than Prime grade beef.
Which is better USDA Choice or Select?
USDA Select graded meat is generally leaner and has a significantly less amount of marbling than prime or choice. Tender select cuts such as rib, loin, and sirloin are best to use when cooking on a BBQ grill. It is highly recommended to marinate all other cuts before grilling to bring out as much flavor as possible.
What is the difference between AA and AAA beef?
The main difference between the grades is the amount of marbling. Prime beef has slightly abundant marbling; AAA has small marbling; AA has slight marbling; A has traces of marbling. The more marbling the more flavorful and juicy the meat will be. Hence, a premium is frequently paid for AAA cuts over AA cuts.
What grade of beef is best?
Prime is the highest quality of beef available. They have the most marbling and are sure to provide a wonderfully juicy and extremely tasty eating experience.
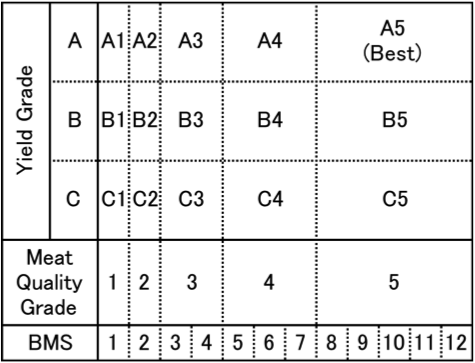
What are the 5 yield grades of beef?
December 2013 SP 755 Page 2 University of Tennessee Institute of Agriculture 2 There are five yield grades: USDA yield grades 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5. The lower the numerical value of the USDA yield grade, the higher the expected yield of closely trimmed, boneless retail cuts.
What are the two things that beef graders look for in a beef grade?
When beef graders are assigning beef grades, they look at two things: 1) quality and 2) yield.
What are the three grades of beef?
However, in the retail world, you only hear of three of them — Prime, Choice and Select. Top 3 grades of beef: Prime. Choice. Select. Prime Graded Beef comes from well-fed beef cattle and it has lots of marbling (i.e. white flecks of fat within the beef). You usually find Prime Beef at restaurants and hotels.
Who decides if beef is Prime, Choice or Select?
All meat for public consumption in the U.S. must be inspected by the US Department of Agriculture (USDA). In some states, like Missouri, you can also have an inspector from a state inspection agency inspect meat. However, state inspected meat cannot cross state lines for sale.
What does USDA grade mean?
The USDA Grades beef to signify that it’s high quality beef that is safe to eat. The beef grades also tell you the amount of tenderness and amount of marbling to expect in the beef. Technically, there are eight grades. However, in the retail world, you only hear of three of them — Prime, Choice and Select. USDA Meat Grading Scale.
What is the purpose of USDA inspection of beef?
When beef is inspected, USDA inspectors first inspect the live animal to make sure they’re healthy from head to hoof and treated humanely. They also inspect things like the slaughtering process, all of the animal’s parts and organs, the temperature of the meat, and they make sure the carcass stays as clean as possible during the entire process.
How to determine if a cow is prime or select?
Based on that one location of the cow, they can then determine if the beef in the entire cow is Prime, Choice or Select.
What does a second area grader look for in a beef carcass?
If the animal is too old when it’s slaughtered, it will be tough. The second area graders look at is yield, or the usable lean meat on the carcass. Consumers rarely hear about this portion of the beef grading, but beef processors are very familiar with it.
What is the USDA grades of meat?
The grades given to meat by USDA are known as a symbol of high-quality, safe, and healthy American beef. Quality grades, within the cattle production industry, are used as a language to make business transactions easier. Using this grading system, manufacturers, as well as consumers, enjoy several benefits.
What are the two ways beef is graded?
There are two ways in which beef is graded. Quality grades that are for juiciness, tenderness and flavor and yield grades that stand for the amount of usable meat that is obtained from a carcass.
Why is beef considered a high grade?
It is primarily based on the fat marbling level and the maturity of the meat. These two factors are responsible for the tenderness of beef. Meat that is obtained from a young cattle holds a high grade as it has greater fat marbling. Cattle producers are required to pay an amount to have a trained inspector grade their beef.
What is the highest grade of beef?
U.S Prime is the highest grade in all of the eight grades, as it has a high level of fat marbling and is rich in flavor. After prime, comes Choice, Select, Standard, Commercial, Utility, Cutter, and Canner. The cutter, utility, and canner grades are lowest grades of beef as they have no fat marbling hence lack tenderness and flavor.
What is the problem with USDA grading?
The first and the major issue that the USDA grading system has is its narrow criteria for grading meat. This system is solely based on the idea that the most important factor that determines the quality of the meat is ‘marbling’. This is an approach that, in the present age, is less accepted.
How many grades of beef are there?
Eight grades of beef are defined by the United States Department of Agriculture beef grading system. They are:
What is prime beef?
United States Prime beef. This is the first and highest grade in all beef grades. It has greater fat marbling and this grade’s beef is almost tender. This beef is obtained from young cattle who are very well fed. This grade’s beef is found in abundance in high-end and posh steak houses, hotels or restaurants.
What is the beef grading system?
Commercial. Utility, Cutter, and Canner Grades. Back to Top. The beef grading system developed by the United States Department of Agriculture is a voluntary grading system based on the meat's maturity and level of fat marbling.
How to get USDA graded beef?
To receive a USDA grading on beef, manufacturers must pay for a trained inspector to grade the beef at the slaughterhouse. Once the beef is graded, the manufacturer must comply with the labeling requirements set by the Food Safety and Inspection Service. Consumers can find the USDA grading on the meat package label.
What is a lower grade beef?
Lower grades are most often used for processing and use in canned goods. The different beef grades are found in specific cuts of meat; each has its own unique uses and recommended cooking methods.
Is commercial grade beef tender?
Standard and Commercial grades are very low in fat content and may be considerably less tender. When sold in the retail market they typically go ungraded or are labeled under the store brand name and sold for lower prices. Consider using moist heat methods to cook this beef. They are suitable for stew and slow cooker recipes that will make them less tough; grilling or frying may result in dry and chewy meat.
Is select beef good?
Select beef is also widely available in the retail market. It is much leaner than U.S. Choice and tends to be less tender or juicy. U.S. Select was formerly labeled as “Good.” Due to the low-fat content in this meat, it should be reserved for moist heat cooking methods to prevent drying. Moist heat methods include braising, stewing, steaming, and poaching. Cooking in a slow cooker is one example. These methods help break down tough fibers that are usually present in this meat.
Is beef good for dry heat?
Because this grade of beef has such a high level of fat marbling, it is excellent for dry-heat cooking methods. These include roasting, grilling, frying, broiling, and baking.
Is Choice beef better than Prime?
Choice beef is widely available to consumers in supermarkets and restaurants. This beef has a good amount of fat marbling, although less than U.S. Prime. U.S. Choice accounts for roughly 50 percent of all graded beef. It can typically be cooked with either dry or moist heat methods without causing excessive dryness. U.S. Choice is an excellent economic alternative to U.S. Prime. You can grill, fry, roast, or bake this beef as well as stew it or braise it.
How many different grades of beef are there?
Meat Grades of Beef. There are actually eight different U.S.D.A. Grades of beef. The cattle are graded from a hanging carcass that is cut between the 12th and 13th rib, right at the end of the Ribeye. Years ago the cattle was graded primarily by the individual grader.
What is the most commonly found grade of beef in supermarkets?
2) CHOICE. Choice grade cattle have moderate marbling and make up of about 65 percent of all graded cattle. This is the most commonly found grade of beef in supermarkets. Choice roasts and steaks from the rib or loin will be very tender, juicy, and flavorful.
What does the circular label mean on a meat?
First, look for the circular label, which means the meat has been inspected for wholesomeness from the U.S. Department of Agriculture. The product went through an inspection process and is safe to cook and consume.
What is the best grade of chicken?
Meat Grades of Chicken. There are three grades of chicken. A, B, and C. Grade A is the best quality and most commonly found in butcher shops and grocery stores. This bird has good meat to bone ratio, is clean with no torn skin, no bruising, no broken bones, and is not discolored.
How many grades of lamb are there?
There are five grades of lamb. You will only find Prime and Choice in butcher shops or grocery stores. The other three are Good, Utility, and Cull are older and used in processed products.
What is prime cattle?
1) PRIME. Prime cattle are young, well-fed, and are highly-marbled with an abundant of white flecks of fat running through the meat. Prime grade is most commonly found in high-end steak houses, fine restaurants or hotels, and from time to time, my butcher shop!!
When was the USDA Meat Grade Shield created?
Second, look for the USDA Meat Grade shield, which is paid for by the producer or meat processor. It began voluntarily in 1926 and was created to get a better handle on the livestock market and quality of the animals.
What is meat and Poultry Inspection?
Meat inspection assures the consumer that the meat and poultry products are clean, safe, and wholesome for human consumption at the time of purchase. This involves inspection of the live animal, carcass, internal organs, plant facilities, equipment, personnel, and transportation system.
What is the difference between grading and inspection?
Remember that there is a difference between inspection and grading. Inspection is mandatory on meat products that are for sale to the public and may be conducted by the State Department of Agriculture or the U.S. Department of Agriculture. Grading is a voluntary program that segregates meat products on the basis of their expected palatability or yield attributes . The service is provided by the U.S. Department of Agriculture.
What is the Oklahoma meat inspection?
Meat inspection became law under the Federal Meat Inspection Act of 1906. It required inspection of red meat products sold in interstate and foreign commerce. The Act established strict sanitation requirements for plants and called for examination of all labels for truthfulness and accuracy. In 1967, the Federal Meat Inspection Act was amended with the Wholesome Meat Act. This amendment established the Federal-State Cooperative inspection program, which required State Inspection programs to be “at least equal to” the Federal inspection program. The 1968 Wholesome Poultry Products Acts extended the same provisions to poultry inspection. In Oklahoma, we have both State and Federal inspection services available.
Why is meat inspection important?
Meat inspection and grading are those activities related to meat products that are important in assuring the best product in the world for the consumer . The purpose of this fact sheet is to broaden your knowledge of meat inspection and grading and reinforce your confidence in the wholesome meat products you are buying.
What is an inspection stamp?
Inspection stamps are the consumer’s assurance that a product is wholesome and accurately labeled. The plant where the product was slaughtered or produced is identified by the number on the inspection stamp.
Why are meat stores inspected?
Retail stores are most often inspected because of consumer complaints.
When is meat inspection required?
Inspection is mandatory when meat is being slaughtered and processed for sale. Those plants that custom slaughter for the owners of animals are exempt from daily inspection since the owner of the animal assumes responsibility for the wholesomeness of the product.
How many grades of beef are there?
There are eight total quality grades: Prime, Choice, Select, Standard, Commercial, Utility, Cutter and Canner. They have been used by the beef industry since 1927.
What is the quality of beef?
When it comes to quality grade, it is all about the eating experience of beef. According to USDA, quality grades are based on two main criteria: the degree of marbling or intramuscular fat in the beef, and the maturity or estimated age of the animal at slaughter.
What is hot carcass weight?
Hot carcass weight (HCW). The hot carcass weight consists of an uncooled carcass minus the hide, head and all internal organs. In most fed cattle, this dressing percentage will be about 63% of the live cattle weight.
What is the difference between a yield grade of 1 and a yield grade of 5?
After assessment, the yield grade is determined and given a USDA yield grade from 1 to 5. A yield grade of 1 offers the largest amount of beef, whereas a yield grade of 5 offers the least.
What is yield grade?
Yield grade is an estimate of the percent retail yield of the four primal cuts of beef, including the chuck, rib, loin and round. Morris shares how the following traits are used to determine yield grade:
Why is beef steak different from steak at a high end restaurant?
Why is it that a beef steak at a food-chain restaurant tastes different than one at a high-end restaurant? It could be because of the quality grade purchased by the owner.
Is select beef leaner than higher grades?
Select. Select beef is very uniform in quality and normally leaner than higher grades. It is fairly tender, but because it has less marbling, it may lack some of the juiciness and flavor of the higher grades.
Why is the grade of a beef cut important?
Likewise, the grade of a beef carcass is critical to the beef producer, since the dollar value received is directly dependent upon the grade. Yet consumers and producers alike often are confused as to what grades mean, and how they are determined.
What are the two types of beef grades?
Summary. Consumers and producers often do not have a clear understanding of beef grading. Beef grades are of two types, Quality Grades and Yield Grades. Most consumers are familiar with the names of several Quality Grades and may use them as a selection criterion when purchasing at retail.
What is USDA yield grade?
USDA Yield Grades estimate beef carcass cutability, which is defined as the combined yield of closely trimmed, boneless retail cuts (%CTBRC) from the round, loin, rib and chuck. This is an estimate of the relative amount of lean, edible meat from a carcass. The five Yield Grades for slaughter cattle and beef carcasses are:
How to determine beef carcass maturity?
Beef carcass maturity is determined by evaluating (a) the size, shape and ossification of the bones and cartilages in the carcass, and (b) the color and texture of the ribeye muscle. In youthful animals, there is a “button” of cartilage on the top of each bone in the vertebral column (backbone).
What is marbling in ribeye?
Within a maturity group, marbling (the amount and distribution of intramuscular fat) within the ribeye is the primary determinant of USDA Quality Grade . Visual evaluations of marbling in the ribeye (at the 12th rib cross-section) are related to differences in eating quality of beef. Beef cuts with high levels of marbling are more likely to be tender, juicy and flavorful than cuts with low levels of marbling. Studies suggest that beef from carcasses grading at least USDA Select is likely to be acceptable in eating quality for most consumers.
How much is ribeye area?
Ribeye area normally ranges from about 9 to 17 square inches among carcasses of common weights and can be measured using a plastic grid (Figure 5).
What are the USDA standards for slaughter cattle?
Beef carcass grading is a voluntary service of the USDA, and the user (the packer) is charged a fee for the service. Grades are determined by an employee of the USDA, working independently of both the producer and packer. The USDA Standards include two separate grade designations – Quality Grades and Yield Grades – and are designated by the stamps shown in Figure 1. A carcass may be either Quality graded, or Yield graded, or both Quality and Yield graded at the same time.
