
The diagnosis of mitochondrial myopathy is reliant on the combination of numerous techniques including traditional histochemical, immunohistochemical, and biochemical testing combined with the fast-emerging molecular genetic techniques, namely next-generation sequencing (NGS).
What is the prognosis of mitochondrial myopathies?
The symptoms of mitochondrial myopathies include muscle weakness or exercise intolerance, heart failure or rhythm disturbances, dementia, movement disorders, stroke-like episodes, deafness, blindness, droopy eyelids, limited mobility of the eyes, vomiting, and seizures. The prognosis for these disorders ranges in severity from progressive ...
How do you test for mitochondrial disorders?
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or spectroscopy (MRS) for neurological symptoms.
- Retinal exam or electroretinogram (ERG) for vision symptoms.
- Electrocardiogram (EKG) or echocardiogram for symptoms of heart disease.
- Audiogram or auditory-brainstem evoked responses (ABER) for hearing symptoms.
What does mitochondrial myopathy stand for?
Mitochondrial myopathy is an umbrella term used to refer to a family of conditions caused by disorders which involve the mitochondria. Mitochondria are organelles found within the cells of living beings. They are essentially the power generation facilities of the cell, converting various compounds into ATP, a chemical which is used for energy ...
What does mitochondrial myopathies mean?
Mitochondrial myopathy: A group of neuromuscular diseases caused by damage to the mitochondria, energy-producing structures in cells that serve as power plants. Nerve and muscle cells require a great deal of energy and are particularly impaired by mitochondrial dysfunction. Some of the more common mitochondrial myopathies include the Kearns-Sayre syndrome, myoclonic epilepsy with ragged-red ...
How do you know if you have mitochondrial myopathy?
The symptoms of mitochondrial myopathies include muscle weakness or exercise intolerance, heart failure or rhythm disturbances, dementia, movement disorders, stroke-like episodes, deafness, blindness, droopy eyelids, limited mobility of the eyes, vomiting, and seizures.
How do they test for mitochondrial myopathy?
One of the most important tests for mitochondrial disease is the muscle biopsy, which involves removing and examining a small sample of muscle tissue.
What types of tests are done to diagnose Mitochondrial diseases?
Genetic testing is essential for the diagnosis of mitochondrial diseases. Next generation sequencing with gene dosage of nDNA and mtDNA in blood or affected tissues (muscle, buccal swab, urine sediment, liver biopsy) is recommended over testing for specific point mutations in cases of suspected mitochondrial disease.
Is there a blood test for mitochondrial disease?
Blood and urine studies are often the first step in diagnosing mitochondrial disease. These studies typically include measurements of lactate and pyruvate in plasma, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), and urine, as well as measuring specific amino and organic acids.
How do you get tested for Mito?
Your doctor might ask for a blood sample, urine sample or arrange for a muscle or tissue biopsy. Initially, your doctor will arrange for genetic testing to be performed on a blood sample. However, sometimes urine or tissue samples can give more information about potential genetic changes.
How long can you live with mitochondrial myopathy?
A small study in children with mitochondrial disease examined the patient records of 221 children with mitochondrial disease. Of these, 14% died three to nine years after diagnosis. Five patients lived less than three years, and three patients lived longer than nine years.
At what age is mitochondrial disease diagnosed?
The median age at diagnosis was 2.5 years (0.3–13.5). The median number of affected systems was two (range 1–6).
What causes mitochondrial myopathy?
Mitochondrial myopathies may be caused by mutations in the body's nuclear DNA (the DNA found in the nucleus of cells) or by mutations or deletions in the body's mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA, the DNA found in cells' mitochondria).
Is there a cure for mitochondrial myopathy?
Available Treatments Unfortunately, there is no cure for Mitochondrial Disease at present. Treatment is usually supportive, relieving the symptoms that can develop, for example, treating seizures with medication. Doctors can also try to make energy production more efficient, using co-factors and vitamins.
Is mitochondrial myopathy painful?
Chronic pain is common in patients with mitochondrial disease. Pain due to mitochondrial disease is primarily of neuropathic nature. Distribution, intensity and type of pain are genetically determined.
How does mitochondrial myopathy affect the body?
Muscular and neurological problems — such as muscle weakness, exercise intolerance, hearing loss, trouble with balance and coordination, seizures, and learning deficits — are common features of mitochondrial disease because muscle cells and nerve cells have especially high energy needs.
Is mitochondrial myopathy fatal?
Mitochondria take in sugars and proteins from the food we eat and produce energy called ATP that our bodies use to function properly. Mitochondrial disease (mito) is a debilitating and potentially fatal disease that reduces the ability of the mitochondria to produce this energy.
Is mitochondrial myopathy painful?
Chronic pain is common in patients with mitochondrial disease. Pain due to mitochondrial disease is primarily of neuropathic nature. Distribution, intensity and type of pain are genetically determined.
What causes mitochondrial myopathy?
Mitochondrial myopathies may be caused by mutations in the body's nuclear DNA (the DNA found in the nucleus of cells) or by mutations or deletions in the body's mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA, the DNA found in cells' mitochondria).
Can you develop mitochondrial disease later in life?
Adult-onset mitochondrial disease often presents in more subtle ways. The disease may manifest for the first time in adulthood or may be first recognized in adulthood after a history of symptoms dating back to childhood. Adult-onset mitochondrial disease is typically a progressive multisystem disorder.
Does myopathy affect the eyes?
description. Ocular muscular dystrophy, or myopathy, predominantly affects muscles moving the eyes.
What is the test for mitochondrial disease?
Diagnostic tests in mitochondrial diseases. A physical exam typically includes tests of strength and endurance, such as an exercise test, which can involve activities like repeatedly making a fist, or climbing up and down a small flight of stairs.
How to determine if someone has mitochondrial disease?
Finally, a genetic test can determine whether someone has a genetic mutation that causes mitochondrial disease. Ideally, the test is done using genetic material extracted from blood or from a muscle biopsy. It is important to realize that although a positive test result can confirm diagnosis, a negative test result is not necessarily conclusive.
What is the procedure used to examine muscle without taking a tissue sample?
In addition to the muscle biopsy, noninvasive techniques can be used to examine muscle without taking a tissue sample. For instance, a technique called muscle phosphorus magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) can measure levels of phosphocreatine and ATP (compounds that are often depleted in muscles affected by mitochondrial disease).
What does a dye stain in a muscle show?
When treated with a dye that stains mitochondria, muscles affected by mitochondrial disease often show ragged red fibers — muscle cells (fibers) that have excessive mitochondria. Other stains can detect the absence of essential mitochondrial enzymes in the muscle.
When should genetic testing be done before a muscle biopsy?
In most cases, genetic studies should be obtained before invasive testing such as muscle biopsy, thus, muscle biopsy is suggested when genetic testing cannot confirm the diagnosis or when required to rule out other conditions in the differential diagnosis.
What is an example of a test that can detect kidney malfunction?
For example, an electrocardiogram (EKG) can monitor the heart’s activity, and a blood test can detect signs of kidney malfunction.
What is neurological exam?
A neurological exam can include tests of reflexes, vision, speech, and basic cognitive (thinking) skills. Depending on information found during the medical history intake and exams, a physician might proceed with more specialized tests that can detect abnormalities in muscles, brain, and other organs. 1.
What are the clinical features of mitochondrial myopathy?
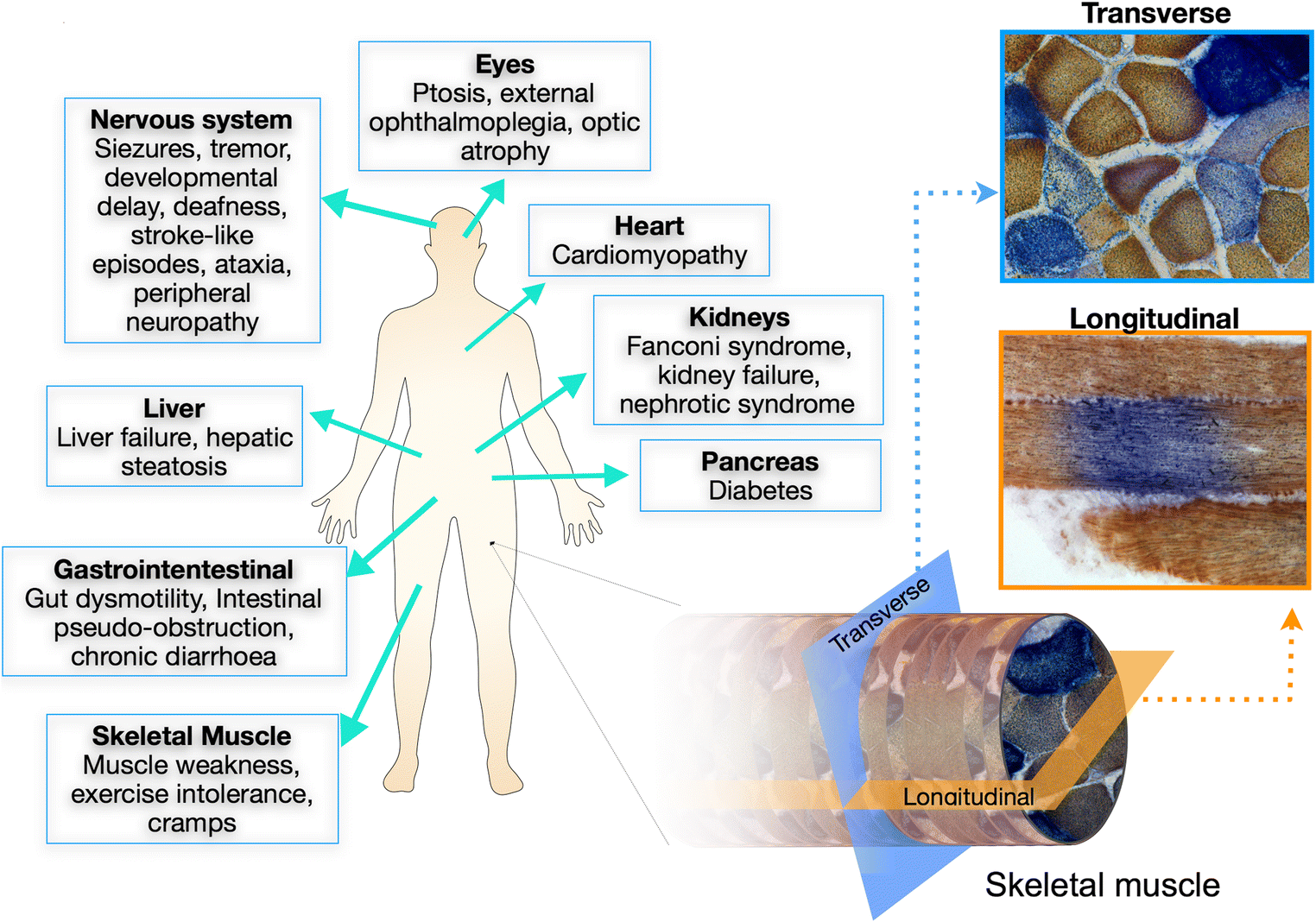
In virtually all patients with mitochondrial myopathy, there is potential involvement of other systems which may well be the prominent and life-threatening feature—for example, cardiomyopathy, epilepsy, or stroke-like episodes (Fig. (Fig.1)1) [1]. Indeed the most frequent presentation of mitochondrial myopathy is in combination with other symptoms which is often the clue to likely mitochondrial involvement. While beyond the scope of this review to cover these features, it is essential that they are considered when evaluating all patients.
What is the diagnostic approach for mitochondrial disease?
While histochemical and biochemical studies pave the way for appropriate molecular genetic testing, the diagnostic procedure in mitochondrial diseases has shifted towards the “genetic first approach” because of the advances made with next-generation sequencing (NGS) [15]. The application of NGS techniques including targeted multi-gene panels of candidate genes, unbiased exome sequencing and whole genome sequencing, has revolutionized the diagnostic approach, replacing the sequential method of sequencing candidate genes through Sanger sequencing as the first diagnostic approach. The high-throughput analysis of many genes has led to an increase in the pace of diagnosis and reducing costs. Moreover, unlike Sanger sequencing, NGS can be used for determination of mtDNA heteroplasmy and deletions, although real-time PCR, pyrosequencing, and long-range PCR are still commonly used. The identification of a causative molecular defect facilitates a diagnosis of mitochondrial myopathy in the patient and family members, permitting disease management, genetic counselling, and a variety of reproductive options.
How many genes are in mitochondrial myopathy?
Molecular genetics of mitochondrial myopathy. A search of OMIM, ClinVar, and Mitomap from genes causing mitochondrial myopathy yielded 60 genes. Of these, 31 are mitochondrial genes, including 8 protein-encoding and 23 tRNA mutations. The remaining 29 genes are encoded by the nucleus and have a variety of functions, including subunits and assembly factors of the respiratory chain, mtDNA replication and maintenance, mitochondrial shape, mitochondrial translation, transport, proteases, lipid metabolism, and iron sulphur (Fe-S) cluster formation. Due to the speed at which needed genes are identified, this is likely to be an underestimate of causative genes.
What is mitochondrial myopathy?
Mitochondrial myopathies are an important group of progressive muscle conditions, caused primarily by the impairment of oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS ). OXPHOS is the biochemical process by which mitochondria produce energy in mammalian cells in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Myopathy is one of the most common manifestations of adult-onset mitochondrial disorders due to the high cellular energy demand of skeletal muscle. However, patients with mitochondrial myopathy often have dysfunction in multiple organ systems resulting in variability in clinical phenotype and prognosis [1].
Is skeletal muscle a mitochondrial disease?
Skeletal muscle is commonly affected in mitochondrial disease and is the most frequently biopsied tissue, although the increasing use of genetic tests is likely to reduce the need for muscle biopsies in the future [7]. Patients with mitochondrial myopathy may show histochemical alterations in their skeletal muscle which indicate mitochondrial dysfunction, although in some patients, the muscle biopsy can appear normal. These mitochondrial abnormalities can be identified using several routine histological and immunological studies.
Can mitochondrial myopathy be associated with rhabdomyolysis?
Exercise-induced muscle painis a common feature, limiting exercise tolerance. Rarely, this can be associated with rhabdomyolysis, which should be included in the differential diagnosis of mitochondrial myopathies.
Where is pathogenic mutation located?
When the compilation of various information from the clinical history and histochemical and biochemical tests indicate that the pathogenic mutation is located in the nDNA, whole exome sequencing (WES), whole genome sequencing (WGS) or a targeted multigene panel of candidate genes can be employed to identify the causative gene using DNA extracted from blood. Due to the large number of nuclear-encoded mitochondrial genes the benefits of NGS are obvious [18, 19].
What tests can be done to determine if you have mitochondrial myopathy?
He or she can order tests including specific genetic tests to determine if you have a mitochondrial myopathy.
What is the defining symptom of mitochondrial myopathy?
Muscle pain or weakness: The defining symptom of mitochondrial myopathies is muscle pain (myalgia) or weakness. The muscle symptoms more often affect the upper arms or thighs but can also affect the forearms or lower legs. These symptoms can develop rapidly or gradually.
What organs do mitochondrial myopathies affect?
Therefore, mitochondrial myopathies most commonly affect organs that consume a lot of oxygen such as muscles, the brain, and the heart. Symptoms may vary, but typically include muscle pain or weakness, double vision or blurry vision, droopy eyelids, difficulty breathing, and, in some forms, blindness, and seizures.
Why do mitochondria have their own DNA?
Mitochondrial myopathies caused by mutations in mitochondrial DNA can only be transmitted from the mother to her child because this type of DNA only comes from mothers. Mutations in mitochondrial DNA are responsible for disorders such as MELAS and Myoclonic Epilepsy with Ragged Red Fibers. Mutations in mitochondrial DNA can also cause Chronic Progressive External Ophthalmoplegia and Kearns-Sayre Syndrome.
What supplements help with mitochondrial myopathies?
Supplements to improve mitochondrial function and currently being studied include: Coenzyme Q10 : An important protein in mitochondrial function.
What is mitochondrial myopathy?
Mitochondrial myopathies are a set of disorders involving abnormalities in mitochondria, which are structures within cells that are responsible for using oxygen to produce energy — often described as the powerhouses of the cells. Therefore, mitochondrial myopathies most commonly affect organs that consume a lot of oxygen such as muscles, the brain, ...
What is the treatment for myopathy?
Specific treatments options include exercise, supplements, medications to prevent seizures, and surgery and various assistive devices for associated eye and breathing issues.
Why is it so difficult to diagnose mitochondrial disease?
Because mitochondrial diseases affect so many different organs and tissues of the body, and patients have so many different symptoms, mitochondrial diseases can be difficult to diagnose. There is no single laboratory or diagnostic test that can confirm the diagnosis of a mitochondrial disease.
What is mitochondrial disease?
Mitochondrial diseases are chronic (long-term), genetic, often inherited disorders that occur when mitochondria fail to produce enough energy for the body to function properly. (Inherited means the disorder was passed on from parents to children.) Mitochondrial diseases can be present at birth, but can also occur at any age.
How many people have mitochondrial disease?
One in 5,000 individuals has a genetic mitochondrial disease. Each year, about 1,000 to 4,000 children in the United States are born with a mitochondrial disease. With the number and type of symptoms and organ systems involved, mitochondrial diseases are often mistaken for other, more common, diseases.
How many chances do children inherit mitochondrial disease?
There is a 50% chance that each child in the family will inherit a mitochondrial disease. Mitochondrial inheritance: In this unique type of inheritance, the mitochondria contain their own DNA. Only mitochondrial disorders caused by mutations in the mitochondrial DNA are exclusively inherited from mothers.
What are the parts of the body that are affected by mitochondrial diseases?
Mitochondrial diseases can affect almost any part of the body, including the cells of the brain, nerves, muscles, kidneys, heart, liver, eyes, ears or pancreas.
What type of inheritance is mitochondrial disease?
Inheritance types are: Autosomal recessive inheritance: This child receives one mutated copy of a gene from each parent. There is a 25% chance that each child in the family will inherit a mitochondrial disease. Autosomal dominant inheritance : This child receives one mutated copy of a gene from either parent.
What is the function of mitochondria?
Several thousand mitochondria are in nearly every cell in the body. Their job is to process oxygen and convert substances from the foods we eat into energy. Mitochondria produce 90% of the energy our body needs to function.
Overview
Myopathy refers to diseases that affect skeletal muscles (muscles that connect to your bones). These diseases attack muscle fibers, making your muscles weak.
Diagnosis and Tests
You should first contact your primary care doctor to alert them to the symptoms you’re concerned about. Depending on the nature of your symptoms, you might be referred to a specialist such as a neurologist or a rheumatologist.
Management and Treatment
After determining your specific type of myopathy, your healthcare provider will develop a treatment plan specific to your symptoms.
Living With
Although myopathy is a long-term (chronic) disease whether inherited or acquired, you can take steps to improve your health to help control your illness. These might include:
