The economy of Russia has gradually transformed from a planned economy into a market-oriented economy. It has enormous natural resources, particularly oil and natural gas. As of 2021, it was the fifth-largest economy in Europe, the world's eleventh-largest economy by nominal GDP, and the sixth-largest by PPP.
Full Answer
What is the current economic situation in Russia?
The Russian leadership did not expect Germany to play the role it played in securing a functional sanctions’ regime against Russia, nor did they assume that the German backing of the sanctions’ regime, both among German political elites as well as among the influential German business community, would last for so long.
How good is the Russian economy?
The Russian banking sector has been resilient so far, but medium-term impacts remain to be seen. Credit growth has been supported by a slow economic recovery and public credit support programs. Employment in Russia is still below pre-pandemic levels, however the labor market began showing some signs of improvement by the end of 2020.
What is the GDP growth rate in Russia?
ISET-PI has updated its real GDP growth forecast for the fourth ... The Lari Real Exchange Rate (RER) depreciated monthly with respect to Turkish Lira (TRY) (by 0.6%), Russian Ruble (RUB) (by 1.3%) and Euro (EUR) (0.3%), and remained unchanged against ...
How strong is Russian economy?
Walmart gained ground on its financial outlook and dividend hike. US stocks fell Thursday as investors sorted through heightened tensions between Russia and Ukraine and downbeat economic data alongside strong earnings reports including from retail behemoth Walmart.

Is Russia's economy increasing?
The real economy is surprisingly resilient too. True, Russian consumer prices have risen by more than 10% since the beginning of the year, as the rouble's initial depreciation made imports more expensive and many Western companies pulled out, reducing supply.
Is Russia GDP increasing or decreasing?
Russia Q1 GDP Economy Growth Slows Down More Than Expected - Bloomberg.
Is Russia's economy declining?
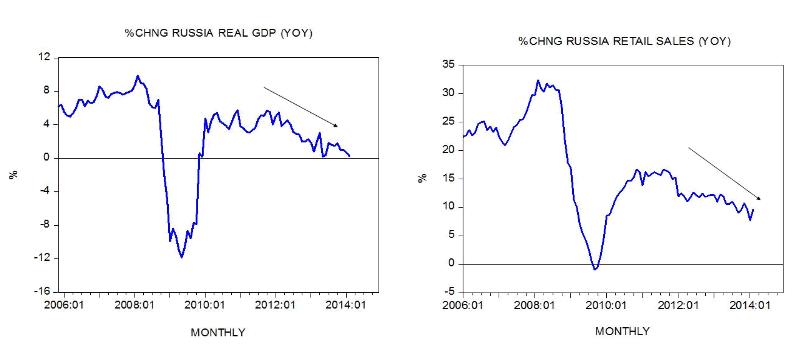
Like many emerging economies dependent on raw material exports, Russia has had other sharp contractions before: The country's output experienced a 3% decline during the 2020 pandemic and a 7.8% drop in 2009 following the global financial crisis.
How is Russia's economy 2021?
Economic Developments Russia's economy saw a strong rebound in the first half of 2021 and is expected to grow by 4.3 percent this year. However, the momentum weakened in the second half of the year.
Is Russian economy growing 2022?
Russia forecasts 7.8% GDP contraction in 2022; unemployment rate at 6.7% | Business Standard News.
How is the Russian economy 2022?
On April 6, 2022, the White House stated, “Experts predict Russia's GDP will contract up to 15 percent this year, wiping out the last fifteen years of economic gains. Inflation is already spiking above 15 percent and forecast to accelerate higher … Supply chains in Russia have been severely disrupted.
Is Russia in recession now?
Nevertheless, Russia can only be so savvy. It remains a commodity play, and not much else. The economy is already in a recession. According to a Bloomberg forecast, Russian GDP will fall by 9.6% in 2022 with a peak quarterly GDP decline reaching –15.7% versus a year ago.
What has Putin done for Russia's economy?
During Putin's first two terms as president, he signed into law a series of liberal economic reforms, such as the flat income tax of 13 percent, reduced profits-tax and new land and civil codes. Within this period, poverty in Russia reduced by more than half and real GDP has grown rapidly.
Is the Russian economy contracting?
The economy will contract by no more than 5% in 2022, a presidential adviser said earlier in May, weeks after the economy ministry said gross domestic product was on track to contract by more than 12%, in what would be the biggest GDP drop since the aftermath of the fall of the Soviet Union.
What are some current issues in Russia?
The poisoning of Russian political opposition leader Alexei Navalny in August led to a further deterioration in Russia's relations with the European Union.Covid-19 Response. ... Freedom of Expression. ... Freedom of Assembly. ... Human Rights Defenders. ... Freedom of Association. ... Chechnya. ... Counterterrorism.More items...
What is Russia's economy?
The economy of Russia is an upper-middle income mixed economy, with enormous natural resources, particularly oil and natural gas. It is the fifth-largest economy in Europe, the world's eleventh-largest economy by nominal GDP and the sixth-largest by PPP .
What are the characteristics of the Russian economy?
The Russian economy is volatile. Since 1989 its institutional environment was transformed from a socialist command economy to a capitalistic market system. Its industrial structure dramatically shifted from over-investment in manufacturing and agriculture to market services and mining, especially oil and gas. Richard Connolly argues that for the last four centuries, there are four main characteristics of the Russian economy that have shaped the system and persisted despite the political upheavals. First of all the weakness of the legal system means that impartial courts do not rule and contracts are problematic. Second is the underdevelopment of modern economic activities, with very basic peasant agriculture dominant into the 1930s. Third is technological underdevelopment, eased somewhat by borrowing from the West in the 1920s. And fourth lower living standards compared to Western Europe and North America.
What was the Soviet Union's economy like in the 1950s?
Beginning in 1928, the course of the Soviet Union 's economy was guided by a series of five-year plans. By the 1950s, the Soviet Union had rapidly evolved from a mainly agrarian society into a major industrial power. By the 1970s the Soviet Union entered the Era of Stagnation. The complex demands of the modern economy and inflexible administration overwhelmed and constrained the central planners. The volume of decisions facing planners in Moscow became overwhelming. The cumbersome procedures for bureaucratic administration foreclosed the free communication and flexible response required at the enterprise level for dealing with worker alienation, innovation, customers, and suppliers.
What percentage of Russia's GDP is natural resources?
In 2019, the Natural Resources and Environment Ministry estimated the value of natural resources to 60% of the country's GDP. Russia has one of the lowest external debts among major economies, and ranked among the "very easy" countries in the Ease of Doing Business Index.
What is Russia's largest industry?
Russia's large automotive industry ranks as the world's tenth-largest by production. It has a large and sophisticated arms industry, capable of designing and manufacturing high-tech military equipment, and is the world's second-largest exporter of arms, behind only the United States.
How did Russia bounce back from the financial crash?
Russia bounced back from the August 1998 financial crash with surprising speed. Much of the reason for the recovery was the devaluation of the ruble, which made domestic producers more competitive nationally and internationally.
Why did Russia go into recession?
The Russian economy risked going into recession from early 2014, mainly due to falling oil prices, sanctions, and the subsequent capital flight. While in 2014 GDP growth remained positive at 0.6%, in 2015 the Russian economy shrunk by 3.7% and was expected to shrink further in 2016.
What is Russia's economic policy?
For the last five years, economic stability has been the dominant goal of Russia’s economic policy. Pension cuts and tax increases have helped to turn Russia’s budget deficit into a surplus, but the population is paying a high toll. In early 2019, real disposable incomes of the Russian population were still 13 percent lower than in 2014. Russians are unlikely to regain their pre-crisis living standards until 2024, the year when Putin is expected to leave the Kremlin.
What are the threats to Russia's economy?
First of all, the structure of Russia’s economy is a bet against technological change.
What is the effect of the Dutch disease on the Russian economy?
This effect, sometimes called the “Dutch disease”, means that the natural resource industry vacuums up qualified labor and strengthens the ruble, which makes it difficult for other sectors of the economy to compete with imports and on foreign markets. The Russian oil industry will not drive growth either.
Why should the Russian leadership reduce the state's footprint in the economy?
The Russian leadership could also try to reduce the state’s footprint in the economy to spur competition and create more incentives for the right kind of investments. However, in the last 10 years the Russian state didn’t give up control over a single of its bigger state-owned enterprises.
When did Russia go into recession?
It became apparent in 2013 when energy prices were at an all-time high. Soon after, the double shock of tumbling oil prices and economic sanctions sent Russia into a severe recession.
Will Russia regain its pre-crisis living standards?
Russians are unlikely to regain their pre-crisis living standards until 2024, the year when Putin is expected to leave the Kremlin. While it lacks drivers for growth, Russia’s economy is currently not at risk of becoming unstable. The constant flow of oil and gas dollars will remain an important pillar of Russia’s current account surplus.
Is Russia's economic woes mitigated?
Russia’s economic woes could be mitigated with the right economic policies, but most options remain rather hypothetical, because they are not compatible with the country’s political economy. Russia could invest heavily in education and healthcare to increase the productivity and longevity of its shrinking workforce.
What was the economic impact of the Russian republic?
Economy of Russia. The Russian republic, by virtue of its great size and abundant natural resources, played a leading role in the economy of the Soviet Union. In the first decades of the Soviet regime, these resources made possible great economic advances, including the rapid development of mining, metallurgy, and heavy engineering, ...
How much of Russia's GDP is agriculture?
Overall, agriculture contributes little more than 5 percent to Russia’s gross domestic product (GDP), though the sector employs about one-eighth of the total labour force. The main product of Russian farming has always been grain, which occupies considerably more than half of the cropland.
What was the impact of Chernobyl on Ukraine?
The most visible aspects of this situation—such as the Chernobyl accident at a nuclear power plant in Ukraine in 1986, widespread industrial pollution, and the drastic reduction in the volume of the Aral Sea as a result of inflow diversions —were only symptomatic of decades of wasteful resource exploitation.
What were the consequences of the Russian reforms in the 1990s?
The reforms beginning in the 1990s caused considerable hardships for the average Russian citizen; in the decade after the dissolution of the Soviet Union, the Russian economy contracted by more than two-fifths. The monetary system was in disarray: the removal of price controls caused a huge escalation in inflation and prices;
What did the Russian government do to encourage privatization?
To encourage privatization, the government issued vouchers to Russian citizens that enabled them to purchase of shares in privatized firms, though in practice these vouchers frequently were sold for cash and were accumulated by entrepreneurs. A commodity- and stock-exchange system also was established.
What happened to Russia before the collapse of the Soviet Union?
In the years before the dissolution of the Soviet Union, however, the economy of Russia and of the entire country was in a state of decline, and official statistics masked industrial inefficiencies. After the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991, the Russian government implemented a series of radical reforms designed to transform ...
Where is Russia's energy found?
Most, if not all, of the raw materials required by modern industry are found within its borders. Its coal reserves are particularly extensive. The biggest fields lie in the remote Tunguska and Lena basins of East Siberia and the Far East, but these are largely untapped, and the bulk of output comes from more southerly fields along the Trans- Siberian Railroad. About three-fourths of Russia’s coal is produced in Siberia—some two-fifths from the Kuznetsk Basin alone and the remainder from the Kansk-Achinsk, Cheremkhovo, and South Yakut basins and numerous smaller sources. The production of hard (anthracite) coal in European Russia takes place mainly in the eastern Donets Basin and, in the Arctic, in the Pechora Basin around Vorkuta.
Under the tsars
Russia had long been an autocracy, subject to absolute rule by the tsar. Bound by a strict social hierarchy, serfs (peasants of feudal Russian) had been owned by their masters, forced to work the lands and receiving nothing in return. Serfdom had been abolished in 1861, but many Russians continued to live in conditions which were little better.
Lenin and the revolution
The Bolsheviks, leaders of the 1917 Russian Revolution, promised the people of Russia equality, opportunity and better living conditions. But Lenin was not a miracle worker. Russia was engulfed in civil war for several more years, and things would get worse before they got better.
Subsequent Five Year Plans
Five Year Plans became a standard feature of Soviet economic development and before 1940, they proved relatively successful. Throughout the 1930s, as it became clear war was on the horizon, heavy industry was built up further.
The devastation of war
For all of the advancements of the 1920s and 1930s, World War Two ruined much of Russia’s economic progress. The Red Army suffered the loss of millions of soldiers and millions more died of hunger or disease.
Overview
The Economy of Russia has gradually transformed from a planned economy into a market-oriented economy. It has enormous natural resources, particularly oil and natural gas. As of 2021, it was the fifth-largest economy in Europe, the world's eleventh-largest economy by nominal GDP, and the sixth-largest by PPP.
Russia's vast geography is an important determinant of its economic activity, …
Economic history
The Russian economy is volatile. Since 1989 its institutional environment was transformed from a socialist command economy to a capitalistic market system. Its industrial structure dramatically shifted away from heavy investment in manufacturing and agriculture toward market services, oil, gas, and mining. Richard Connolly argues that for the last four centuries, there are four main ch…
Public policy
Russia was expected to have a Government Budget deficit of $21 billion in 2016. The budget deficit narrowed to 0.6% of GDP in 2017 from 2.8% in 2016.
On 1 January 2004, the Government of Russia established the Stabilization fund of the Russian Federation as part of the federal budget to balance it if price of oil falls. On 1 February 2008 the Stabilization fund was divided into two parts. Th…
Sectors
The mineral-packed Ural Mountains and the vast fossil fuel (oil, gas, coal), and timber reserves of Siberia and the Russian Far East make Russia rich in natural resources, which dominate Russian exports. Oil and gas exports, specifically, continue to be the main source of hard currency.
Russia has been widely described as an energy superpower; as it has the world…
External trade and investment
Russia recorded a trade surplus of US$15.8 billion in 2013. Balance of trade in Russia is reported by the Central Bank of Russia. Historically, from 1997 until 2013, Russia balance of trade averaged US$8338.23 million reaching an all-time high of US$20647 million in December 2011 and a record low of −185 USD million in February 1998. Russia runs regular trade surpluses primarily due to e…
Mergers and acquisitions
Between 1985 and 2018 almost 28,500 mergers or acquisitions have been announced in Russia. This cumulates to an overall value of around 984 bil. USD which translates to 5.456 bil. RUB. In terms of value, 2007 has been the most active year with 158 bil. USD, whereas the number of deals peaked in 2010 with 3,684 (964 compared to the value record year 2007). Since 2010 value and numbers have decreased constantly and another wave of M&A is expected.
See also
• Commonwealth of Independent States
• History of post-Soviet Russia
• List of companies of Russia
• List of Russian federal districts by GDP
Further reading
• Alexeev, Michael, and Shlomo Weber, eds. The Oxford handbook of the Russian economy (Oxford UP, 2013) excerpt.
• Åslund, Anders. Russia's Crony Capitalism: The Path from Market Economy to Kleptocracy (Yale University Press, 2019). excerpt
• Connolly, Richard. The Russian economy: a very short introduction (2020) excerpt