
What best describes the structures of DNA?
DNA structure DNA is the molecule that holds the instructions for growth and development in every living thing. Its structure is described as a double-stranded helix held together by complementary ...
What are the primary and secondary structures of DNA?
Primary structure: sequence of bases in a strand (e.g., ATTTTCGTAAAGGCGTAAAGGCCTTTGTC….)Secondary structure: Interactions between bases to form more complex structures.DNA's secondary structure tends to be a double helix, while RNA often has intramolecular bondind that forms things like hairpin loops, etc.. Then, what is the primary structure of DNA?
What term is used to describe the structure of DNA?
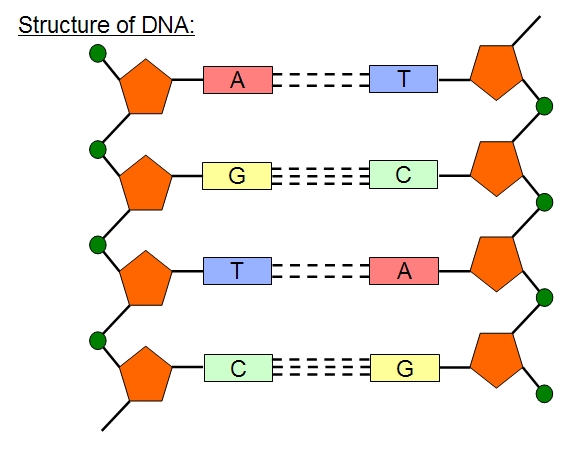
What is the Structure of DNA?
- nucleotides. Each nucleotide contains a phosphate group, a sugar molecule (called deoxyribose ), and a nitrogenous base.
- genetic code. The genetic code determines which instructions are encoded in the DNA molecule; for example, how to make a certain type of protein.
- double helix. ...
- base pairs. ...
What is the overall structure of DNA?
DNA is made of four types of nucleotides, which are linked covalently into a polynucleotide chain (a DNA strand) with a sugar-phosphate backbone from which the bases (A, C, G, and T) extend. A DNA molecule is composed of two (more...) The way in which the nucleotidesubunits are lined together gives a DNAstrand a chemical polarity.

What is the structure of DNA?
DNA is a double helical structure composed of nucleotides. The two helices are joined together by hydrogen bonds. The DNA also bears a sugar-phosph...
What are the three different types of DNA?
The three different types of DNA include: A-DNA B-DNA Z-DNA
How is Z-DNA different from other forms of DNA?
Z-DNA is a left-handed double helix. The helix winds to the left in a zig-zag manner. On the contrary, A and B-DNA are right-handed DNA.
What are the functions of DNA?
The functions of DNA include: Replication Gene expression Mutation Transcription Translation
What type of DNA is found in humans?
B-DNA is found in humans. It is a right-handed double-helical structure.
What are the different parts of DNA?
DNA comprises a sugar-phosphate backbone and the nucleotide bases (guanine, cytosine, adenine and thymine).
What is the A-DNA?
A-DNA: It is a right-handed double helix similar to the B-DNA form. Dehydrated DNA takes an A form that protects the DNA during extreme condition such as desiccation. Protein binding also removes the solvent from DNA and the DNA takes an A form.
Who Discovered DNA?
DNA was first recognized and identified by the Swiss biologist, Johannes Friedrich Miescher in 1869 during his research on white blood cells.
Why is DNA called a polynucleotide?
The DNA is called a polynucleotide because the DNA molecule is composed of nucleotides – deoxyadenylate (A) deoxyguanylate (G) deoxycytidylate (C) and deoxythymidylate (T), which are combined to create long chains called a polynucleotide. As per the DNA structure, the DNA consists of two chains of the polynucleotides.
How are proteins formed?
Polypeptide chains are further folded in secondary, tertiary and quaternary structure to form different proteins. As every organism contains many genes in their DNA, different types of proteins can be formed. Proteins are the main functional and structural molecules in most of the organisms. Apart from storing genetic information, DNA is involved in: 1 Replication process: Transferring the genetic information from one cell to its daughters and from one generation to the next and equal distribution of DNA during the cell division 2 Mutations: The changes which occur in the DNA sequences 3 Transcription 4 Cellular Metabolism 5 DNA Fingerprinting 6 Gene Therapy
How are nucleic acids formed?
These nucleic acids are formed by the combination of nitrogenous bases, sugar molecules and the phosphate groups that are linked by different bonds in a series of sequences. The DNA structure defines the basic genetic makeup of our body. In fact, it defines the genetic makeup of nearly all life on earth.
Where does DNA replication begin?
The replication of DNA begins at a point known as the origin of replication . The two DNA strands are separated by the DNA helicase. This forms the replication fork.
What are the two rings that make up a pyrimidine?
Cytosine and thymine (and uracil in RNA) are pyrimidines, containing one ring. Adenine and guanine are purines, containing two rings. The pyrimidines pair with the purines: cytosine and guanine form three hydrogen bonds, and adenine and thymine form two. 4.
How many strands does DNA have?
DNA. A molecule of DNA has two strands, composed of nucleotides, that form a double helix shape. Download DNA Lab Activities. 2. Each DNA strand is composed of nucleotides—units made up of a sugar (deoxyribose), a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base.
How do genes separate from each other?
Genes are separated from one another by sequences of nitrogenous bases that don’t provide instructions for RNA synthesis. These are called intergenic regions. Even within genes, there are regions of noncoding DNA called introns.
What are nitrogenous bases called?
Specific sequences of nitrogenous bases that code for particular proteins or regulatory RNA molecules are called genes. Each strand of DNA is like a recipe book for synthesizing proteins. Certain sequences of nitrogenous bases along the strand encode particular RNA molecules.
What are the components of DNA?
A nucleotide has three components: a sugar molecule, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. The sugar in DNA’s nucleotides is called deoxyribose—DNA is an abbreviation for deoxyribonucleic acid. RNA molecules use a different sugar, called ribose.
What is the structure of DNA?
1. A molecule of DNA consists of two strands that form a double helix structure. DNA is a macromolecule consisting of two strands that twist around a common axis in a shape called a double helix. The double helix looks like a twisted ladder—the rungs of the ladder are composed of pairs of nitrogenous bases ( base pairs ), ...
How many genes are in a chromosome?
Chromosome 21, the shortest human chromosome, consists of 48 million base pairs and contains between 200 and 300 genes. Overall, prokaryotic cells have shorter chromosomes with fewer genes. For example, the bacterium Carsonella rudii has only 159,662 base pairs and 182 genes in its entire genome.
How to understand the biological function of DNA?
The molecular structure of DNA. In order to understand the biological function of DNA, you first need to understand its molecular structure. This requires learning the vocabulary for talking about the building blocks of DNA, and how these building blocks are assembled to make DNA molecules.
Which direction does DNA run in?
One strand runs in a 3' to 5' direction while the other runs in a 5' to 3' direction . The nucleotides forming each DNA strand are connected by noncovalent bonds, called hydrogen bonds. Considered individually, hydrogen bonds are much weaker than a single covalent bond, such as a phosphodiester bond.
How many letters are in the DNA alphabet?
The English language has a 26 letter alphabet. In contrast, the DNA “alphabet” has only four “letters,” the four nucleotide monomers. They have short and easy to remember names: A, C, T, G. Each nucleotide monomer is built from three simple molecular parts: a sugar, a phosphate group, and a nucleobase.
What is a polymer?
Polymers are large molecules that are built up by repeatedly linking together smaller molecules, called monomers . Think of how a freight train is built by linking lots of individual boxcars together, or how this sentence is built by sticking together a specific sequence of individual letters (plus spaces and punctuation). In all three cases, the large structure—a train, a sentence, a DNA molecule—is composed of smaller structures that are linked together in non-random sequences— boxcars, letters, and, in the biological case, DNA monomers .
What is the fifth carbon atom in a nucleotide?
A fifth carbon atom is attached to the fourth carbon of the ring. Deoxyribose also contains a hydroxyl group (-OH) attached to the third carbon in the ring. A diagram showing the three main components of a nucleotide: the phosphate group, the deoxyribose sugar, and the nitrogenous base. The phosphate group is a phosphorous atom with four oxygen ...
Why is DNA a good biological molecule?
DNA is well-suited to perform this biological function because of its molecular structure, and because of the development of a series of high performance enzymes that are fine-tuned to interact with this molecular structure in specific ways . The match between DNA structure and the activities of these enzymes is so effective and well-refined that DNA has become, over evolutionary time, the universal information-storage molecule for all forms of life. Nature has yet to find a better solution than DNA for storing, expressing, and passing along instructions for making proteins.
Why are nucleobases called nitrogenous bases?
All four of these nucleobases are relatively complex molecules, with the unifying feature that they all tend to have multiple nitrogen atoms in their structures. For this reason, nucleobases are often also called nitrogenous bases.
What is DNA made of?
The early x-ray diffraction results indicated that DNA was composed of two strands of the polymer wound into a helix. The observation that DNA was double-stranded was of crucial significance and provided one of the major clues that led to the Watson-Crick structure of DNA.
How does DNA structure help us?
The Structure of DNA Provides a Mechanism for Heredity. Genes carry biological information that must be copied accurately for transmission to the next generation each time a cell divides to form two daughter cells.
How is DNA arranged in a double helix?
Because these two chains are held together by hydrogen bonding between the bases on the different strands, all the bases are on the inside of the double helix, and the sugar-phosphate backbones are on the outside (see Figure 4-3). In each case, a bulkier two-ring base(a purine; see Panel 2-6, pp. 120–121) is paired with a single-ring base (a pyrimidine); A always pairs with T, and Gwith C (Figure 4-4). This complementarybase-pairingenables the base pairsto be packed in the energetically most favorable arrangement in the interior of the double helix. In this arrangement, each base pairis of similar width, thus holding the sugar-phosphate backbones an equal distance apart along the DNA molecule. To maximize the efficiency of base-pair packing, the two sugar-phosphate backbones wind around each other to form a double helix, with one complete turn every ten base pairs (Figure 4-5).
How many types of beads are in DNA?
Because only the base differs in each of the four types of subunits, each polynucleotide chain in DNA is analogous to a necklace (the backbone) strung with four types of beads (the four bases A, C, G, and T).
How is genetic information stored in DNA?
Duplication of the genetic information occurs by the use of one DNA strand as a templatefor formation of a complementary strand. The genetic information stored in an organism's DNA contains the instructions for all the proteins the organism will ever synthesize. In eucaryotes, DNA is contained in the cell nucleus.
How many turns does the DNA double helix have?
The DNA double helix. (A) A space-filling model of 1.5 turns of the DNA double helix. Each turn of DNA is made up of 10.4 nucleotide pairs and the center-to-center distance between adjacent nucleotide pairs is 3.4 nm. The coiling of the two strands around (more...)
What is the relationship between DNA and proteins?
The relationship between genetic information carried in DNA and proteins. The complete set of information in an organism's DNAis called its genome, and it carries the information for all the proteins the organism will ever synthesize. (The term genomeis also used to describe the DNA that carries this information.)
Why did Watson and Crick succeed in deducing the structure of DNA?
Watson and Crick succeeded in deducing the structure of DNA because of their passion to solve the problem and their ability to collaborate well together. They were as complementary as the two strands of a DNA double helix.
What is the significance of the double helix?
The DNA double helix, one of the most influential discoveries in the history of science, revealed how information is stored and replicated in living organisms. Francis Crick and Jim Watson did not exaggerate when they proclaimed that they had found "the secret of life" at the Eagle Pub in 1953. The double helix has since become the foundation of modern biology and its most iconic image. However, DNA is much more than a molecule to be memorized; it is a portal for understanding science and scientific strategy. In this Narrative, we will unravel the DNA helix in our minds and go back to a time when the structure was unknown and DNA was not even known to be the molecule of heredity. What did it take to catapult DNA into the modern era? What seems obvious now was not then. The quest to understand DNA was marked by mistakes by brilliant people, insights by underdogs, clues that lay forsaken, and flashes of brilliance. The path to the double helix also reveals the complementary roles of modeling (Watson and Crick) and experimentation (Rosalind Franklin, Maurice Wilkins, and Florence Bell, an unsung heroine whose early discoveries on DNA are featured here). Springing forward to modern times, we will explore how contemporary bio-engineers use DNA as a building material to create nanoscale devices. The DNA double helix continues to be a source of enormous creativity and inspiration.
Which model proposed an incorrect triple helix?
Failed models of DNA preceded the correct one. The first (unpublished) Watson and Crick model and the published Pauling model both proposed an incorrect DNA triple helix.
What is the ratio of guanine and cytosine?
He found that guanine and cytosine are present at a 1:1 ratio, as are adenine and thymine. The implication of this finding was not understood at first. Several scientists were chasing after the DNA structure (structure meaning understanding how the DNA chain adopts a three-dimensional shape).
Does DNA nanorobot inhibit cancer?
The investigators found that the DNA nanorobot inhibited the proliferation of cancer cells in tissue culture.
How to make a model of DNA?
To make a model of DNA, you need to ascertain (1) how many chains of DNA are present in the biological form of DNA, and, if more than one chain, (2) whether those chains run in the same or opposite directions, (3) whether they pack straight or twist around one another, and (4) how the chains interact.
What did Mendel's experiments with peas reveal?
Gregor Mendel’s experiments with peas in the mid-19th century revealed that different traits are conferred by discrete heritable entities that later were called genes. By the early 20th century, evidence suggested that genes reside on chromosomes, which are fibrous nuclear elements composed of DNA and protein.
What are the four nitrogen bases in DNA?
Nitrogen Base – DNA uses four kinds of nitrogenous bases: adenine (A), guanine (G) cytosine (C), and thymine (T). RNA – also contains adenine, guanine and cytosine bases. But instead of thymine, they have another base called uracil (U). DNA uses nitrogen base like the letters in the alphabet to form a word.
How are the two ladders bonded together?
The two ladders are bonded together by hydrogen bonds. These explain how the two ladders form a double helix. It also describes how the language of DNA works. If we zoom into to look at how the bases form it looks like this. Adenine (A) joins with Thymine (T) Guanine (G) joins with cytosine (C).
Why does DNA have a double helix?
DNA forms a double helix because the two ladders run opposite to each other. They rotate around a central axis to form a spiraling helix. This is called an anti-parallel structure. Each strand has a 5′ end and a 3′ end. The bases on one ladder (or strand) pair with the bases on the other ladder.
What does DNA stand for?
DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid. It’s a class of molecule called a nucleic acid.
How does DNA use nitrogen bases?
The order of nitrogen bases in a DNA sequence forms genes, which in the language of the cell, tells cells how to make proteins.
Why is DNA important?
It’s important because it helps explain how DNA functions to create cells. The next step is to understand how the chemical structure of DNA works. DNA molecules arrange themselves in a model called the DNA double helix. It’s a 3-D structure that is stored in the nucleus of all cells.
Why do cells look different?
Cells from different tissues and organs look and behave differently. The reason is that only some of the DNA of each cell is used to make proteins. DNA plays a role as a traffic cop for the types of proteins a cell will make. It does this with proteins in the cells that cause only specific genes to express themselves.
How is mRNA translated into amino acids?
Translation: The mRNA is translated into amino acids by transfer RNA (tRNA). mRNA is read in three-letter sections called codons. Each codon codes for a specific amino acid or building block of a protein. For instance, the codon GUG codes for the amino acid valine.
What is the coiled state of a chromosome?
In this coiled state, it is called chromatin. Chromatin is further condensed, through a process called supercoiling, and it is then packaged into structures called chromosomes. These chromosomes form the familiar “X” shape as seen in the image above. Each chromosome contains one DNA molecule.
How many chromosomes are there in a human body?
Each chromosome contains one DNA molecule. Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes or 46 chromosomes in total. Interestingly, fruit flies have 8 chromosomes. Trusted Source. , and pigeons have 80. Chromosome 1 is the largest and contains around 8,000 genes. The smallest is chromosome 21 with around 3,000 genes.
What is the master plan for life on earth?
In a nutshell. Chromosomes are tightly coiled strands of DNA . Genes are sections of DNA that code individual proteins. Put another way, DNA is the master plan for life on earth and the source of the wonderful variety we see around us. Last medically reviewed on January 11, 2018.
What is DNA made of?
Each of the two strands is a long sequence of nucleotides or individual units made of: a phosphate molecule. a sugar molecule called deoxyribose, containing five carbons. a nitrogen-containing region.
What percentage of DNA is genetic?
Our genes only account for around 3 percent of our DNA, the remaining 97 percent is less well understood. The outstanding DNA is thought to be involved in regulating transcription and translation.
Why is DNA packaged so neatly?
Because we have so much DNA ( 2 meters in each cell) and our nuclei are so small, DNA has to be packaged incredibly neatly.
What happens when your cells divide?
The cells of your body divide as a normal part of growth and development. When this happens, each new cell must have a complete copy of DNA.
How does DNA get split?
In order to achieve this, your DNA must undergo a process called replication. When this occurs, the two DNA strands split apart. Then, specialized cellular proteins use each strand as a template to make a new DNA strand. When replication is completed, there are two double-stranded DNA molecules.
What part of DNA is responsible for aging?
Another part of DNA that may be involved in aging are telomeres. Telomeres are stretches of repetitive DNA sequences that are found at the ends of your chromosomes. They help to protect DNA from damage, but they also shorten with each round of DNA replication.
Why are mutations bad?
They can sometimes be bad. This is because a change in the DNA code can have a downstream impact on the way a protein is made. If the protein doesn’t work properly, disease can result.
Why do cells read the code 3 bases at a time?
Your cells read this code three bases at a time in order to generate proteins that are essential for growth and survival. The DNA sequence that houses the information to make a protein is called a gene. Each group of three bases corresponds to specific amino acids, which are the building blocks of proteins.
Why is DNA damaged?
In fact, it’s estimated that tens of thousands of DNA damage events occur every day in each of our cells. Damage can occur due to things like errors in DNA replication, free radicals, and exposure to UV radiation. But never fear!
What is DNA made of?
DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid. It’s made up of units of biological building blocks called nucleotides. DNA is a vitally important molecule for not only humans, but for most other organisms as well. DNA contains our hereditary material and our genes — it’s what makes us unique.
How is DNA shape dictated?
The spiral shape of DNA is dictated by the space available in a cell much like the way the shape of a spiral staircase is dictated by the size of an apartment.
Why is the interior of DNA hydrophobic?
However, the hydrophobic interior is essential because it stabilizes and protects the hydrogen bonds between the bases. These hydrogen bonds would not form if they were surrounded by water molecules since each of them could just as easily be replaced by hydrogen bonds with water.
What is the name of the molecule that contains the instructions an organism needs to develop, live and reproduce?
Deoxyribonucleic acid or DNA is a molecule that contains the instructions an organism needs to develop, live and reproduce. These instructions are found inside every cell and are passed down from parents to their children.
Why are helices helical?
The classic answer is that helices are helical because the shape is dictated by bonds between molecules. But that only answers how a helix is formed and not why they are that shape. It turns out that a helix, essentially, is a great way to bunch up a very long molecule, such as DNA, in a crowded place, such as a cell.
What are the four types of nitrogen bases in DNA?
The four types of nitrogen bases are adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G) and cytosine (C). The order of these bases is what determines DNA's instructions, or genetic code. Human DNA has around 3 billion bases, and more than 99 per cent of those bases are the same in all people, according to the U.S. National Library of Medicine (NLM).
How does a double stranded helix form?
The double-stranded helix forms as a result of interactions between adjacent base pairs. This interaction consists of van der Waals attractions and it causes the base pairs to come together so that they are in close contact. The result is a stack of base pairs, one on top of the other, with hardly any space between t
What is the result of a double stranded helix?
The double-stranded helix forms as a result of interactions between adjacent base pairs. This interaction consists of van der Waals attractions and it causes the base pairs to come together so that they are in close contact. The result is a stack of base pairs, one on top of the other, with hardly any space between them. The usual term for these interactions are stacking interactions and they are the main force that holds the two strands together in a helical form.
Who Discovered The Structure of DNA?
- The double helix structure of DNA was first discovered in 1953 by James Watson (an American Biologist), Francis Crick (an English Physicist), and Rosalind Franklin (an English Chemist). Though only Watson and Crick were credited with the discovery of the double helix, they are beli…
DNA vs. RNA: What’s The difference?
- DNA and RNA are very similar molecules. Both are types of nucleic acid, both contain genetic information, and both can be found in the nuclei of cells. The structure of RNA nucleotides are also similar to those of DNA; both contain a phosphate group, a sugar molecule, and a nitrogenous base. However, there are some key differences between DNA and RNA molecules. …
What Is DNA Replication?
- DNA replication is a process in which two identical DNA replicas are produced from a single DNA molecule. It is an essential part of cell division, which is necessary for the growth and repair of damaged tissues. DNA replication ensures that each new daughter cell receives a complete copy of the organism’s genetic information. This allows each new cell to function correctly, and the or…