
What causes van der Waals force?
It results from the distortion of a molecule…. Van der Waals forces may arise from three sources. First, the molecules of some materials, although electrically neutral, may be permanent electric dipoles.
Why are solids held together by van der Waals forces?
Solids that are held together by van der Waals forces characteristically have lower melting points and are softer than those held together by the stronger ionic, covalent, and metallic bonds. Van der Waals forces may arise from three sources. First, the molecules of some materials, although electrically neutral, may be permanent electric dipoles.
Is van der Waals force the same as London force?
The term van der Waals force is sometimes used loosely for all intermolecular forces. The term always includes the London dispersion force between instantaneously induced dipoles. It is sometimes applied to the Debye force between a permanent dipole and a corresponding induced dipole or to the Keesom force between permanent molecular dipoles.
Where does van der Waals forces occur?
van der Waals forces, relatively weak electric forces that attract neutral molecules to one another in gases, in liquefied and solidified gases, and in almost all organic liquids and solids.
Why does Van der Waals force exist?
Van der Waals forces occur because while neutral molecules have no net charge or permanent dipole moment, they do have a dynamic distribution of charge. As two molecules approach, this charge distribution can become favorable for interaction between the two molecules (Figure 15.8A).
What is van der Waals forces easy definition?
Definition of van der Waals forces : the relatively weak attractive forces that act on neutral atoms and molecules and that arise because of the electric polarization induced in each of the particles by the presence of other particles.
Do all molecules have van der Waals?
The given statement is (a) True. All molecules are known to exhibit Van der Waals forces. These forces are formed due to specific interactions between the neighboring molecules that can have either attractive or repulsive forces.
What are the factors that affect van der Waals forces?
The Van Der Waals forces between two atoms are affected by a number of factors, including the distance between the atoms, the nature of the atoms involved, and the environment around the atoms. The closer two atoms are to each other, the stronger the Van Der Waals forces between them.
What are van der Waals forces called?
Van der Waals forces' is a general term used to define the attraction of intermolecular forces between molecules. There are two kinds of Van der Waals forces: weak London Dispersion Forces and stronger dipole-dipole forces.
How do you increase van der Waals forces?
If there are surface asperities, or protuberances, that result in a greater total area of contact between two particles or between a particle and a wall, this increases the van der Waals force of attraction as well as the tendency for mechanical interlocking.
How do van der Waals forces hold molecules together?
Answer and Explanation: Van der Waals forces hold molecules together by their opposite-charged areas when they become closer together. This is called a dipole-dipole type of bonding between the molecules. An example of this type of bond is a hydrogen bond.
What are hydrogen bonds simple definition?
Hydrogen bonding is a special type of dipole-dipole attraction between molecules, not a covalent bond to a hydrogen atom. It results from the attractive force between a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to a very electronegative atom such as a N, O, or F atom and another very electronegative atom.
What is vanderwall force and its types?
Van der Waals forces' is a general term used to define the attraction of intermolecular forces between molecules. There are two kinds of Van der Waals forces: weak London dispersion forces and stronger dipole-dipole forces. Suggest Corrections. Similar questions.
1. How Do You Define Hydrogen Bonds?
Hydrogen bonds are a type of dipole interaction and are unique. When a hydrogen atom binds to an atom of a strongly electronegative element such as...
2. What are the Types of Van Der Waals Forces?
There are three types of Van Der Waal forces- Dispersion Forces or London Dispersion forces Dipole-Dipole ForcesHydrogen Bond
3. What Kind of Force is there Between Nonpolar Molecules?
Between nonpolar molecules, you will find dispersion forces.
4. Write the Relative Strengths of the Intermolecular Forces.
Intermolecular Force Relative Strength Dipole-Dipole forceMedium London Dispersion forceWeakest Hydrogen Bond Strongest
5. What Factors Can Affect the Van Der Waals Forces?
There are 3 factors that can have an effect on Van Der Waals forces such as - Number of electrons present in an atomSize and shape of the atom Natu...
What are Van der Waals forces?
In simple words, Van Der Waals Forces are those bonds that play the role of attracting both molecules and atoms. These interactions include weak electrostatic forces lying in a close range within molecules lacking charges. Moreover, they are the weakest intermolecular forces, comprising of dipole-dipole and dispersion forces.
What is Van der Waals dispersion force?
Van Der Waals dispersion forces are close-knit interactions depending on distance resulting in intermolecular attractions or repulsions. These bonds get stronger when they lie in a range of 0.4 kilojoules per mole (kJ/mol) and 4 kJ/mol. Moreover, they are active within a distance of fewer than 0.6 nanometers (nm).
What are the factors that affect Van der Waals forces?
The factors affecting Van Der Waals forces are as follows: Number of Electrons Present In An Atom: The amount of electrons present is responsible for the creation of temporary dipoles. The strength of the Waals forces depends on the number of dipoles. Therefore, an increase in the number of dipoles increases the bonds of Van Der Waals.
Why do polar molecules freeze?
They often freeze into solids when the temperature falls quickly. According to the Van Der Waals definition, these forces depend on the polarization ability of the molecules or atoms. The dispersion interactions are also present within two molecules, even the polar ones when they are extremely close to each other.
How many types of Van der Waals forces are there?
Initially, there are three types of Van Der Waals forces. These include:
What determines the strength of a dipole-dipole force?
Ans. The strength of a dipole-dipole force depends on the bond length and distinction between the electronegative effects of the atoms.
What is the Debye force?
Debye. It is a force responsible for generating attractions within a permanent polarity of a molecule and an induced polarity of the other.
How do Van der Waals forces work?
Van der Waals forces may arise from three sources. First, the molecules of some materials, although electrically neutral, may be permanent electric dipoles. Because of fixed distortion in the distribution of electric charge in the very structure of some molecules, one side of a molecule is always somewhat positive and the opposite side somewhat negative. The tendency of such permanent dipoles to align with each other results in a net attractive force. Second, the presence of molecules that are permanent dipoles temporarily distorts the electron charge in other nearby polar or nonpolar molecules, thereby inducing further polarization. An additional attractive force results from the interaction of a permanent dipole with a neighbouring induced dipole. Third, even though no molecules of a material are permanent dipoles (e.g., in the noble gas argon or the organic liquid benzene ), a force of attraction exists between the molecules, accounting for condensing to the liquid state at sufficiently low temperatures.
What is the van der Waals bond?
Learn More in these related Britannica articles: mineral: Van der Waals bonds. Neutral molecules may be held together by a weak electric force known as the van der Waals bond. It results from the distortion of a molecule so that a small positive charge develops on one end and a corresponding negative charge….
Who is the author of the theory of intermolecular forces?
The forces are named for the Dutch physicist Johannes Diderik van der Waals, who in 1873 first postulated these intermolecular forces in developing a theory to account for the properties of real gases.
What is van der Waals force?
The van der Waals force is a short-range force existing in both gas and liquid phases due to the fluctuation in electron clouds surrounding the nucleus, which can be determined by London–van der Waals theory (microscopic theory) or Lifshitz–van der Waals theory (macroscopic theory).
Which van der Waals force has a lower boiling point?
van der Waals forces also depend on molecular shape. For example, 2,2-dimethylpropane (neopentane) has a lower boiling point than pentane. Neopentane is more spherical than pentane; therefore, it has less surface area than the more cylindrical pentane molecule.
What is VDW in chemistry?
6.8.1 van der Waals (vdW) forces and interactions. Van der Waals forces exist among all kinds of atoms and molecules. The origin of vdW force stems from the instantaneous dipole-induced dipole interactions among adjacent apolar atoms and molecules, which can be repulsive or attractive. Among polar molecules, there are three components ...
Why is van der Waals stronger in hexane than pentane?
The van der Waals forces are stronger in hexane than in pentane because hexane has a larger surface area to interact with neighboring molecules. The stronger intermolecular attraction holds molecules together more tightly, decreasing the vapor pressure of hexane and giving it a higher boiling point than pentane.
How does van der Waals affect the structure of a protein?
The van-der-Waals interaction is another important phenomenon that contributes to stabilize of the tridimensional protein structure. Taken individually van-der-Waals interactions are weak attractions between molecules that are in close proximity to each other. They are also known as London dispersion forces. Basically, as two atoms come closer to each other, this attraction increases until they are separated by the van-der-Waals contact distance. When two molecules are too close to each other, the potential energy due to repulsion becomes very high; therefore the assembly becomes unstable, and repulsion occurs even when these molecules are neutral. As the molecules move further apart, the potential energy due to repulsion decreases.
What are the energies associated with van der Waals interactions?
Energies associated with van-der-Waals interactions are generally small. However, when the surfaces of two large molecules come together, a large number of atoms can be in close contact and the net effect can be substantial. Macromolecules such as proteins contain numerous sites of potential van-der-Waals interactions.
What are the components of VDW?
Among polar molecules, there are three components that contribute to the total vdW forces: the induction force, the orientation force and the dispersion force. For neutral molecules, the last is the most important. The one-sixth power of vdW forces suggests they drop substantially over a long distance.
What are Van der Waals Forces?
Van der Waals forces are weak intermolecular forces that are dependent on the distance between atoms or molecules. These forces arise from the interactions between uncharged atoms/molecules.
What are the factors that affect Van der Waals forces?
Factors Affecting Van der Waals Forces. 1. Number of Electrons Held by the Atoms/Molecules. While traversing down a group in the modern periodic table, the atomic radii of the elements increase along with the number of electrons held by their respective nuclei.
What causes debye forces?
Debye forces are caused by the interactions between permanent dipoles and other atoms/molecules, which results in the formation of induced dipoles. For example, an induced dipole can be formed from the repulsive forces between electrons (belonging to a molecule) and a permanent dipole.
Why do dispersion forces occur?
London dispersion forces arise due to the interactions between an instantaneous dipole and an atom/molecule. These forces are named after the German physicist Fritz London and are also known as instantaneous dipole – induced dipole forces.
What is the weakest force?
In the group of forces that fall under the category of ‘ weak chemical forces’, Van der Waals forces are the weakest. They are known to rapidly vanish when the distance between the interacting molecules increases. The strengths of Van der Waals forces typically range from 0.4 kJ.mol-1 to 4 kJ.mol-1.
Which molecules tend to have stronger dispersion forces?
2. Shape of the Molecule. Long, unbranched molecules tend to feature stronger dispersion forces than branched, short-chain molecules. For example, the structural isomers butane and isobutane (2-methyl propane) have different boiling points despite having the same chemical formulae.
What happens after one atom forms a dipole?
After one atom forms a random dipole, the next atom forms an induced dipole. Van Der Waals Bonding is the form of bonding seen in N2 molecules.
Van der Waals forces in DNA structure Definition
DNA is a genetic material that stores and passes on the information to the next generation. It comprises nitrogenous bases, a sugar molecule, and a phosphate group. It comprises two strands that are arranged in a double helix manner. The two strands act as templates and give rise to a new daughter strand.
Overview of Van der Waals forces in DNA structure
DNA is regarded as the information storage molecule. The basic unit of DNA is a nucleotide that is composed of a nitrogenous base, a five-carbon sugar, and an ion of phosphoric acid. The nitrogenous bases can be classified into purines and pyrimidines. Purines include adenine and guanine and pyrimidines include cytosine and thymine.
Van der Waal forces and their Role in DNA
Van der Waal forces like ionic bonds, hydrogen bonds, and hydrophobic bonds are non-covalent bonds. They cause attraction and repulsion between molecules and surfaces and act by causing a change in the polarization of the nearby particles.
Other Forces Acting on DNA
Apart from the Van der Waals force that forms the major stabilizing force, hydrogen bonding also contributes to DNA stabilization. Hydrogen bonds are formed between complementary strands. In nature, hydrogen bonds are formed when hydrogen interacts with the molecules of higher electronegativity; thus, they are electrostatic.
What is van der Waals force?
Van der Waals forces, also known as the van der Waals interactions, are the weak interactions existing at a molecular or atomic level. These are the short term attractive forces that exist between uncharged molecules of substances. The bonds formed due to the Van Der Waals interaction are the secondary bonds, while ionic and covalent bonds act as primary bonds. Van der Waals force is named after a Dutch scientist Johannes Diderik van der Waals. He discovered these forces in 1873 while working on the characteristics of real gases. He observed that the electrons distributed unevenly throughout an atom or molecule tend to move continuously and form a temporary dipole. The temporary dipole formed in an atom forms another temporary dipole in the neighbouring atom, and the process goes on and on. The domino effect existing between the temporary dipoles establishes a force of attraction known as the van der Waals force. The force of attraction exists between atoms or molecules of a substance or two different substances, thereby helping two objects stick to each other. The strength of van der Waals force typically lies between 0.4 kJ/mole and 4 kJ/mole and they tend to act over a distance less than or equal to 0.4 nm.
Which forces have a low boiling point?
7. The solids that are held together with the help of van der Waals forces have a low boiling point, while the solids held together by covalent, ionic, or metallic bonds tend to have a high boiling point.
What force do geckos use?
Geckos lizards make use of van der Waals forces to climb flat surfaces such as walls and roofs. This is a result of the force of attraction between the footpads of the lizard and the surface. A similar type of attraction helps some of the animals walk on the surface of the water.
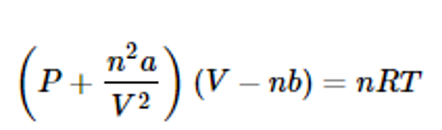
What Are Van Der Waals Forces?
Characteristics of Van Der Waals Forces
- Covalent bondsand ionic bonds are significantly stronger than Van der Waals forces
- These forces are additive in nature, they are made up of several individual interactions
- These forces cannot be saturated
- No directional characteristic can be attributed to these forces
Types of Van Der Waals Forces
- 1. Keesom Interactions
Keesom interactions can arise due to the following interactions (all of which are electrostatic in nature): 1. The electrostatic interaction between the charges in ionic molecules. 2. Interaction between dipoles in polar molecules. 3. Quadrupole interactions in the molecules whose symmet… - 2. Debye Forces
Debye forces are caused by the interactions between permanent dipoles and other atoms/molecules, which results in the formation of induced dipoles. For example, an induced dipole can be formed from the repulsive forces between electrons (belonging to a molecule) an…
Factors Affecting Van Der Waals Forces
- 1. Number of Electrons Held by the Atoms/Molecules
While traversing down a group in the modern periodic table, the atomic radii of the elements increase along with the number of electrons held by their respective nuclei. The presence of a relatively large number of electrons (along with the additional space for these electrons to dispe… - 2. Shape of the Molecule
Long, unbranched molecules tend to feature stronger dispersion forces than branched, short-chain molecules. For example, the structural isomers butane and isobutane (2-methyl propane) have different boiling points despite having the same chemical formulae. The boiling point of bu…
Applications of Van Der Waals Forces
- It is widely believed that Geckos exploit Van der Waals forces hanging on to smooth surfaces with only their toes.
- The attractive forces that arise between the spatulae of the Gecko’s footpads and the smooth surface enable the lizard to effectively climb these surfaces. Similar biological designs can be observe...