Common Causes
Related Conditions

How do you confirm xerostomia?
Sometimes you may need blood tests, imaging scans of your salivary glands or tests that measure how much saliva you produce to identify the cause of your dry mouth.
Can a doctor diagnose dry mouth?
Diagnosis of dry mouth is often based on a patient's history and physical examination. An ENT specialist can help figure out the cause of the dry mouth and see if the salivary glands are producing enough saliva. Lab work and potentially a minor salivary gland biopsy to evaluate for Sjogren's disease may be recommended.
What is the most common cause of xerostomia?
There are numerous causes of xerostomia; the most common cause is medication side effects, followed by Sjogren syndrome (SS) and radiotherapy and other autoimmune diseases in no particular order.
What is the difference between xerostomia and dry mouth?
Dry mouth, also called xerostomia (ZEER-oh-STOH-mee-ah), is the condition of not having enough saliva to keep the mouth wet. Dry mouth can happen to anyone occasionally—for example, when nervous or stressed. However, when dry mouth persists, it can make chewing, swallowing, and even talking difficult.
What kind of doctor do you go to for dry mouth?
Make an appointment to see your family physician or dentist if you always feel as though you have cotton inside your mouth or experience more than minor daily discomfort due to dry mouth symptoms. A health care professional can make a firm diagnosis of dry mouth and determine the best course of treatment for you.
Is dry mouth a serious symptom?
Medical conditions: Dry mouth can be a sign of a more serious condition, such as diabetes, Alzheimer's disease, stroke and Sjogren's syndrome. Sjogren's syndrome (SHOW-grins) is an autoimmune disease that causes the body to attack the glands that produce moisture.
Is xerostomia curable?
Dry mouth is usually a temporary and treatable condition. In most cases, you can prevent and relieve symptoms of dry mouth at home by doing one or more of the following: sipping water throughout the day.
What nerve damage causes dry mouth?
Some cases of dry mouth originate from nerve damage that prevents saliva production signals from reaching the salivary glands. Diabetic neuropathy is a classic example of this because the nerves around the salivary glands are very susceptible to changes in blood pressure.
Why is my mouth so dry even after drinking water?
It's normal to occasionally have a dry mouth if you're dehydrated or feeling nervous, but a persistently dry mouth can be a sign of an underlying problem. You should see your dentist or GP if you have an unusually dry mouth (known as xerostomia) so they can try to determine the cause.
What disease causes lack of saliva?
Dry mouth can be due to certain health conditions, such as diabetes, stroke, yeast infection (thrush) in your mouth or Alzheimer's disease, or due to autoimmune diseases, such as Sjogren's syndrome or HIV/AIDS. Snoring and breathing with your mouth open also can contribute to dry mouth.
Does anxiety cause dry mouth?
Stress can affect your body in numerous ways and increase your likelihood of developing a large array of conditions, and dry mouth is no exception. Stress and anxiety can affect the flow of your saliva and cause dry mouth, according to the Journal of Dental Research, Dental Clinics, Dental Prospects.
How can I stimulate my salivary glands naturally?
If you can still make saliva, the actions of chewing and sucking stimulate production of saliva. Try chewing sugarless gum with xylitol or sucking on lozenges. For lozenges, Dr. Hou suggests those containing slippery elm and/or marshmallow root.
What doctor can diagnose Sjogren's syndrome?
Diagnosis of Sjögren's Syndrome A rheumatologist (a specialist in autoimmune diseases) may diagnose the disease. However, an ophthalmologist (eye doctor) or a dentist may also perform certain tests to help make the diagnosis.
Can dry mouth be cured?
Sip water regularly. Try over-the-counter saliva substitutes — look for products containing xylitol, such as Mouth Kote or Oasis Moisturizing Mouth Spray, or ones containing carboxymethylcellulose (kahr-bok-see-meth-ul-SEL-u-lohs) or hydroxyethyl cellulose (hi-drok-see-ETH-ul SEL-u-lohs), such as Biotene Oral Balance.
How long can dry mouth last?
You may also notice cracks and cuts on your lips at the corners of your mouth, or you could experience a burning sensation on your tongue. “Dry mouth usually resolves on its own one to two months after completing chemotherapy, but it can last six months to a year after radiation to the head and neck,” says Dr. Vyas.
Why is my mouth always dry?
Dry mouth is a side effect of numerous medications, including antihistamines, decongestants, painkillers, and diuretics. Dry mouth can be a symptom of an underlying illness, including diabetes, stroke, Alzheimer's Disease, HIV/AIDS, and other conditions.
What is the best treatment for xerostomia?from ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Either agent is tried for up to 3 months to ascertain efficacy. These medications do require some residual salivary gland function as it stimulates the patent gland to secrete saliva. The application of topical physostigmine has also been a therapy option in the treatment of xerostomia. Physostigmine is a cholinesterase inhibitor, thus increasing the amount of acetylcholine available to stimulate salivary glands. It increases the production of saliva by stimulating mucin-producing glands.[15] A gel containing 1.8 mg of physostigmine may provide relief for about 120 minutes.[15] Additionally, malic acid has demonstrated some benefit if xerostomia is drug-induced.[10] Anethole trithionate (cholagogue-bile secretion stimulant) is another drug that has proven to be beneficial for xerostomia. [16]
Why is Xerostomia delayed?from ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Xerostomia has many causes, including medications and radiation. Despite being a common disorder, its diagnosis usually gets delayed, and the treatment is not satisfactory. For this reason, an interprofessional team is the best management strategy.
What is Xerostomia in medical terms?from ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Xerostomia is defined as "a subjective feeling of oral dryness." These symptoms might present as dry mouth, difficulty swallowing, or dry oral mucosa/skin. There are numerous causes of xerostomia; the most common cause is medication side effects, followed by Sjogren syndrome (SS) and radiotherapy and other autoimmune diseases in no particular order. Irrespective of a specific etiology, the patient's primary complaint is dry mouth. Because it is such a debilitating condition without any particular treatment, there are major psychosocial factors that come into play, ranging from mild anxiety to major depressive disorder. This activity outlines the evaluation, pathophysiology, and treatment of xerostomia and highlights the role of the interprofessional team to aid in managing patients with xerostomia.
What is the interprofessional approach to xerostomia?from ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Because it can have both benign and pathological etiologies, xerostomia requires an interprofessional team approach, including physicians, specialists, dentists, specialty-trained nurses, and pharmacists, all collaborating across disciplines to achieve optimal patient results. [Level V]
What are the three major salivary glands?from ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
The three major salivary glands responsible for saliva production are the parotid gland, submandibular gland, and sublingual gland . The anatomy of all three glands is quite similar, consisting of a duct that opens into the oral cavity.[2] Hyposalivation due to radiation shows fibrosis while hyposalivation due to an autoimmune disease could show an infiltrate of B and T-cells, leading to gland destruction.
What is 3D MR sialography?from ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Sialography:An imaging technique that can be used to identify salivary stones or masses.[12] Three-dimensional (3D) MR sialography looks to be a promising diagnostic approach in patients with radiation exposure as the salivary gland flow can be visualized.[13] A small trial on 3D MR sialography in pre and post-radiation patients has shown promise. Imaging performed at 6 weeks pre-radiation and 6 months post-radiation showed a decrease in salivary flow.
What is the most important thing to know about xerostomia?from ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
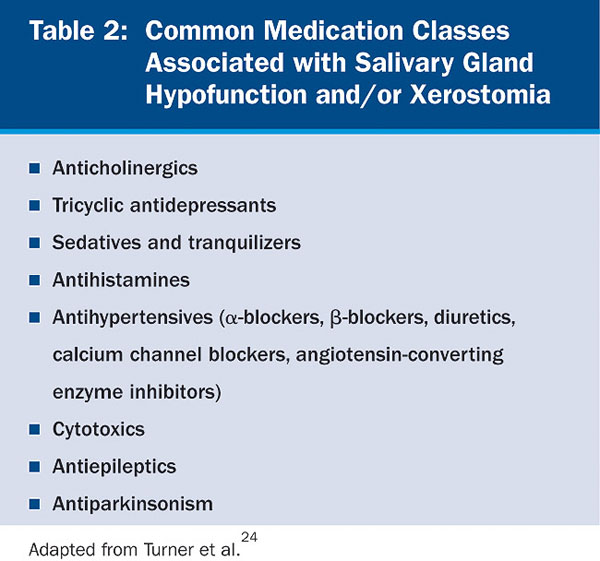
The most important thing is the recognition of the symptoms of xerostomia and taking action. A simple history and physical exam can help with the diagnosis.[18] It is crucial that healthcare professional reviews the patient's medication list. Anti-hypertensives, Parkinson drugs, diuretics, and many others have implications as a cause of xerostomia. If a medication is the suspected cause and alteration of regimen is straightforward, it should merit consideration and a mutual decision made regarding ongoing therapy. A pharmacy consult is often necessary to discuss alternative regimens and to avoid drug-drug interactions.
What causes xerostomia?
Symptoms of xerostomia are caused by changes in composition and amount of saliva produced , and may include full dysfunction of salivary glands. 1–3 The causes of xerostomia are multifactorial and may not be identifiable in all cases. Many cases of mild to moderate (temporary or intermediate) dry mouth can be attributed to anxiety, smoking, and alcohol consumption. Causes of more severe symptoms include polypharmacy (ingestion of multiple medications at once), chemotherapy or radiotherapy that damages salivary glands, and systemic or autoimmune diseases that result in salivary gland dysfunction. 1–3
How to treat xerostomia?
Their purpose is to reduce symptoms and/or increase salivary flow, thus reducing the incidence of oral disease. The patient can consider increasing fluid intake and decreasing use of caffeine, alcohol, and tobacco. Patients may also be advised to increase humidity at night, avoid using toothpastes that contain sodium lauryl sulphate, which may be irritating, and stop consuming crunchy/hard foods. They should use soft toothbrushes, mouthrinses with fluoride or prescription-strength fluoride, and sugar-free chewing gums/candy to stimulate salivary flow. 7 While chewing stimulates salivary flow, only gums that list xylitol as their first ingredient should be used. 12,13 There are several over-the-counter mucosal lubricants , saliva substitutes, and saliva stimulants with xylitol, including in oral-adhering discs, that help maintain the feeling of moisture in the mouth.
What causes dry mouth?
True dry mouth is related to salivary gland hypofunction (SGH) and may be caused by medication usage, alcohol or tobacco use, dehydration, medical treatment, or systemic/autoimmune disorders. Categorized as temporary, intermediate or severe, xerostomia is characterized by the subjective reporting of symptoms caused by low salivary flow.
What causes salivary gland dysfunction?
Causes of more severe symptoms include polypharmacy (ingestion of multiple medications at once), chemotherapy or radiotherapy that damages salivary glands, and systemic or autoimmune diseases that result in salivary gland dysfunction. 1–3.
Why do you need a dental hygienist for xerostomia?
Patients with xerostomia require dental hygienists to detect this common disorder early and provide coordinated management for positive health outcomes.
Why does dry mouth worsen at night?
5 Dry mouth symptoms may worsen at night due to reduced salivary output, as the human body reaches its lowest circadian levels during sleep, which can also be exacerbated by mouth breathing. 4,7
Why is dry mouth growing in adolescents?
1–3 In fact, the prevalence of dry mouth among adolescents is growing due to their increased use of inhalers, medications used to treat diabetes and attention deficit disorders, mouth breathing, and dehydration. 5,6.
What is xerostomia in the mouth?
Xerostomia is defined as the subjective complaint of dry mouth. 1Interestingly, patients complaining of xerostomia frequently do not show any objective sign of hyposalivation and their symptoms may be secondary to qualitative and/or quantitative changes in the composition of saliva.2,3The normal stimulated salivary flow rate averages 1.5–2.0 mL/min while the unstimulated salivary flow rate is approximately 0.3–0.4 mL/min.4,5A diagnosis of hyposalivation is made when the stimulated salivary flow rate is ≤0.5–0.7 mL/min and the unstimulated salivary flow rate is ≤0.1 mL/min.5–7Xerostomia in patients with objective hyposalivation is diagnosed when the rate of saliva flow is less than the rate of fluid absorption across the oral mucosa plus the rate of fluid evaporation from the mouth.8
How prevalent is xerostomia?
The prevalence of xerostomia in the population ranges from 5.5% to 46%. Studies have shown differences in the prevalence between the sexes and xerostomia appears to increase with increasing age. A possible explanation is that older individuals take several xerogenic drugs for their chronic conditions and this may lead to an overall reduction of the unstimulated salivary flow rate.1,10,12,14–18Xerostomia remains an unresolved common complaint especially among the geriatric population, despite seeking medical or dental consultation.19The aim of this review is to explore the current state of knowledge on management and treatment of patients affected by xerostomia and hyposalivation.
What is the subjective complaint of dry mouth?
Xerostomia, the subjective complaint of dry mouth, and hyposalivation remain a significant burden for many individuals. Diagnosis of xerostomia and salivary gland hypofunction is dependent upon a careful and detailed history and thorough oral examination. There exist many options for treatment and symptom management: salivary stimulants, ...
What are the effects of xerostomia?
In particular, it may affect speech, chewing, swallowing, denture-wearing, and general well-being .9Xerostomia secondary to hyposalivation may also result in rampant dental caries, oral fungal infections (eg, candidiasis), taste changes, halitosis, or burning mouth .5,10,11The most frequent cause of hyposalivation is the use of certain medications (such as anticoagulants, antidepressants, antihypertensives, antiretrovirals, hypoglycemics, levothyroxine, multivitamins and supplements, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and steroid inhalers) (Villa et al, unpublished data, 2014), followed by radiotherapy to the head and neck, and Sjögren’s syndrome.12Other factors include depression, anxiety and stress, or malnutrition.13
What is subjective grade 3?
Subjective grade 3= dryness causing dietary alterations or interference with sleep, speaking, or other activities
Is Anethole trithione a cholagogue?
Other sialogogues. Anethole trithione is a cholagogue that has been shown to improve oral symptoms and increase the salivary flow in patients with xerostomia and hyposalivation.47More studies are necessary to prove the efficacy of this medication.
Can salivary glands cause dry mouth?
Patients with salivary gland hypofunction typically complain of dry mouth, difficulty swallowing and/or speaking; they hardly tolerate spicy, acidic, and crunchy food and often times report taste changes or difficulty wearing dentures.20
What is the best treatment for xerostomia?
Either agent is tried for up to 3 months to ascertain efficacy. These medications do require some residual salivary gland function as it stimulates the patent gland to secrete saliva. The application of topical physostigmine has also been a therapy option in the treatment of xerostomia. Physostigmine is a cholinesterase inhibitor, thus increasing the amount of acetylcholine available to stimulate salivary glands. It increases the production of saliva by stimulating mucin-producing glands.[15] A gel containing 1.8 mg of physostigmine may provide relief for about 120 minutes.[15] Additionally, malic acid has demonstrated some benefit if xerostomia is drug-induced.[10] Anethole trithionate (cholagogue-bile secretion stimulant) is another drug that has proven to be beneficial for xerostomia. [16]
Why is Xerostomia delayed?
Xerostomia has many causes, including medications and radiation. Despite being a common disorder, its diagnosis usually gets delayed, and the treatment is not satisfactory. For this reason, an interprofessional team is the best management strategy.
What is Xerostomia in medical terms?
Xerostomia is defined as "a subjective feeling of oral dryness." These symptoms might present as dry mouth, difficulty swallowing, or dry oral mucosa/skin. There are numerous causes of xerostomia; the most common cause is medication side effects, followed by Sjogren syndrome (SS) and radiotherapy and other autoimmune diseases in no particular order. Irrespective of a specific etiology, the patient's primary complaint is dry mouth. Because it is such a debilitating condition without any particular treatment, there are major psychosocial factors that come into play, ranging from mild anxiety to major depressive disorder. This activity outlines the evaluation, pathophysiology, and treatment of xerostomia and highlights the role of the interprofessional team to aid in managing patients with xerostomia.
What is the interprofessional approach to xerostomia?
Because it can have both benign and pathological etiologies, xerostomia requires an interprofessional team approach, including physicians, specialists, dentists, specialty-trained nurses, and pharmacists, all collaborating across disciplines to achieve optimal patient results. [Level V]
What are the three major salivary glands?
The three major salivary glands responsible for saliva production are the parotid gland, submandibular gland, and sublingual gland . The anatomy of all three glands is quite similar, consisting of a duct that opens into the oral cavity.[2] Hyposalivation due to radiation shows fibrosis while hyposalivation due to an autoimmune disease could show an infiltrate of B and T-cells, leading to gland destruction.
What is the most important thing to know about xerostomia?
The most important thing is the recognition of the symptoms of xerostomia and taking action. A simple history and physical exam can help with the diagnosis.[18] It is crucial that healthcare professional reviews the patient's medication list. Anti-hypertensives, Parkinson drugs, diuretics, and many others have implications as a cause of xerostomia. If a medication is the suspected cause and alteration of regimen is straightforward, it should merit consideration and a mutual decision made regarding ongoing therapy. A pharmacy consult is often necessary to discuss alternative regimens and to avoid drug-drug interactions.
Why is xerostomia increasing?
The prevalence of xerostomia is increasing due to the increasing aging population. [6] Age by itself is not a cause of xerostomia, but older patients tend to be on multiple medications and have a higher incidence of comorbid conditions.
Treatments For A Dry Mouth: Xerostomia
Do you have Xerostomia? Xerostomia is the medical term for a dry mouth caused by salivary gland dysfunction, medication, radiation therapy, or Sjogren's syndrome. There are many treatments you can explore to stimulate saliva production and quality of life.
What Are The Causes Of Dry Mouth?
It is important to figure out the root causes of dry mouth to prevent tooth decay and stop the problem due to which salivary secretion is adversely affecting.
Treatments Via Surgery
Surgical dry mouth treatments can include a minor surgical procedure to create ducts from the gland to bring saliva into the mouth or replace salivary glands altogether with excess glands taken from inside the mouth or from the lower lip.
What is xerostomia?
Xerostomia is another name for dry mouth caused by reduced or absent saliva flow.
How is xerostomia diagnosed?
If you have symptoms of xerostomia, see your doctor. Your doctor will ask you about your symptoms and your medical and medication history. Your doctor will look inside your mouth and may measure the flow rate of your saliva.
How to tell if you have dry mouth?
To determine if you have Dry Mouth, your doctor or dentist will. likely conduct a routine exam. Here are some things they may do: Review your medications, both over-the-counter. and prescription medications, including. antihistamines, decongestants, and diuretics. Inspect your lips, tongue, and mouth for. dryness and cracking.
Why is it important to speak to your dentist about dry mouth?
about Dry Mouth—if not to alleviate the discomfort, then to. protect against the associated health risks, such as gingivitis , tooth decay, gum disease, and fungal infections.
When to use a saline bath?
in the morning and at night for soothing dryness relief.
What is the best saliva substitute?
Try over-the-counter saliva substitutes that contain xylitol, such as Mouth Kote or Oasis Moisturizing Mouth Spray, or that contain carboxymethylcellulose (kahr-bok-see-meth-ul-SEL-u-lohs) or hydroxyethyl cellulose (hi-drok-see-ETH-ul SEL-u-lohs), such as Biotene OralBalance Moisturizing Gel.
Why is saliva important for teeth?
Also avoid spicy or salty food because they can cause irritation. Saliva is important to maintain the health of your teeth and mouth . Taking these steps to protect your teeth may also help your dry mouth condition: Brush with a fluoride toothpaste and floss your teeth.
What is the best mouthwash for dry mouth?
Mouthwashes designed for dry mouth, especially ones with xylitol, can be effective, such as Biotene Dry Mouth Oral Rinse or Act Dry Mouth Mouthwash, which also offer protection against tooth decay. If you have severe dry mouth, your doctor or dentist may: Prescribe medication that stimulates saliva.
What to do when your lips are cracked?
Moisturize your lips to soothe dry or cracked areas.
How to get rid of bacteria in your teeth?
Brush with a fluoride toothpaste and floss your teeth. Ask your dentist if you might benefit from prescription fluoride toothpaste, toothpaste containing betaine, or a tooth gel to neutralize bacteria acids. Use a fluoride rinse or brush-on fluoride gel before bedtime.
What to do if your mouth is dry?
Your doctor or dentist may: Change medications that cause dry mouth. If your doctor believes medication to be the cause, he or she may adjust your dosage or switch you to another medication that doesn't cause a dry mouth. Recommend products to moisturize your mouth.
How to diagnose dry mouth?
Diagnosis. To determine the cause of your dry mouth, your doctor likely will review your medical history and all medications you're taking, including over-the-counter medications, and examine your mouth. Sometimes you may need blood tests, imaging scans of your salivary glands or tests that measure how much saliva you produce to identify ...