
When are epimers called diastereomers?
Diastereomers are a type of a stereoisomer. Diastereomerism occurs when two or more stereoisomers of a compound have different configurations at one or more of the equivalent stereocenters and are not mirror images of each other.. Also when two diastereoisomers differ from each other at only one stereocenter they are epimers.
Are epimers diastereomers?
Yes. Epimers differ in only one stereogenic center, and all the others are the same, so they are diastereomers (at least one same center and at least one different center: diastereomers) Yes.
Is glucose a homopolymer?
If all the monomers are identical the polymer is a homopolymer. For example starch is made solely of glucose molecules so starch is a homopolymer. If the monomers are not identical the polymer is a heteropolymer. Proteins are made up of up to 20 different amino acids, so proteins are heteropolymers.
Is the presence of glucose in urine normal?
Under normal circumstances there will be little or no glucose in urine. When this condition does occur, it is called glucosuria. When glucose is present in the urine, a measure of anything under (including 0) 15 milligrams of glucose per deciliter of urine is considered to be in the normal range.
What are Epimers?
What are stereoisomers that are not mirror images of each other?
What are optical isomers?
What is mutarotation in chemistry?
Which epimers are used in drugs?
What is stereoisomer?
Which is the simplest carbohydrate?
See 4 more
About this website
Epimers – Definitions, Examples, Enantiomers and Diastereomers
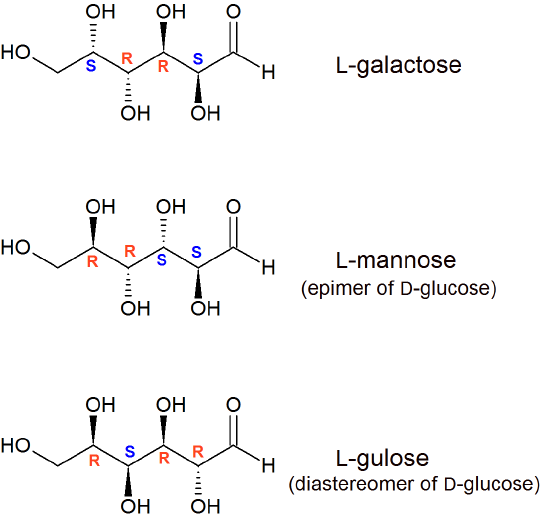
The Epimers of glucose involve some formations, some examples are starch, glycogen, glucose, polysaccharides, and oligosaccharides. The stereoisomers β-D-mannopyranose and β-D-glucopyranose are known as epimers because they differ only in the C-2 position of stereochemistry.
What is an Epimer? - Definition in Chemistry & Examples
Some specific examples of epimers are the two stereoisomers of glucose. In the alpha version of glucose, the -OH group is pointing down, and in the beta version the same -OH group is pointing up ...
What are Epimers?
Epimer in stereochemistry specifies one of a pair of stereoisomers. At stereogenic centre, two isomers present in the molecules differ, while the rest remains identical. A molecule may contain numerous stereocenters leading to several stereocenters.
What are stereoisomers that are not mirror images of each other?
Diastereomers are stereoisomers that are not mirror images of each other in that they are not linked with reflection operation unlike of enantiomers. They possess the same physical properties. One of the example include meso compounds. The below structure is mesotartaric acid.
What are optical isomers?
Optical isomers or Enantiomers are 2 isomers that are relevant to each other by reflection. They are non – super imposable. They are comprised of the same physical properties except in a way they interact with several optical isomers of other compounds.
What is mutarotation in chemistry?
Mutarotation, as the corresponding stereocenters interconvert, is the change in optical rotation due to the change in equilibrium between two anomers. As x-alpha and β anomeric forms interconvert, cyclic sugars exhibit mutarotation.
Which epimers are used in drugs?
Below example illustrates, formation of enantiomeric pair, where mesotartaric acid forms diastereomeric pair with dextro tartaric acids and levo. Epirubicin and Doxorubicin are epimers that are used in drugs.
What is stereoisomer?
Stereoisomers are isomeric molecules that posses the same constitution and molecular formula, but they vary in three-dimensional orientations of their atoms in the space.
Which is the simplest carbohydrate?
Monosaccharides, or basic sugars, are considered the simplest carbohydrates. Glucose is an example. To make bigger molecules, monosaccharides may be united. Two monosaccharides contain disaccharides.
What are Epimers?
Epimer in stereochemistry specifies one of a pair of stereoisomers. At stereogenic centre, two isomers present in the molecules differ, while the rest remains identical. A molecule may contain numerous stereocenters leading to several stereocenters.
What are stereoisomers that are not mirror images of each other?
Diastereomers are stereoisomers that are not mirror images of each other in that they are not linked with reflection operation unlike of enantiomers. They possess the same physical properties. One of the example include meso compounds. The below structure is mesotartaric acid.
What are optical isomers?
Optical isomers or Enantiomers are 2 isomers that are relevant to each other by reflection. They are non – super imposable. They are comprised of the same physical properties except in a way they interact with several optical isomers of other compounds.
What is mutarotation in chemistry?
Mutarotation, as the corresponding stereocenters interconvert, is the change in optical rotation due to the change in equilibrium between two anomers. As x-alpha and β anomeric forms interconvert, cyclic sugars exhibit mutarotation.
Which epimers are used in drugs?
Below example illustrates, formation of enantiomeric pair, where mesotartaric acid forms diastereomeric pair with dextro tartaric acids and levo. Epirubicin and Doxorubicin are epimers that are used in drugs.
What is stereoisomer?
Stereoisomers are isomeric molecules that posses the same constitution and molecular formula, but they vary in three-dimensional orientations of their atoms in the space.
Which is the simplest carbohydrate?
Monosaccharides, or basic sugars, are considered the simplest carbohydrates. Glucose is an example. To make bigger molecules, monosaccharides may be united. Two monosaccharides contain disaccharides.
