Where are ligaments located in the neck?
Similarly, ligaments tend to be located contralaterally, on the other side of the joint from the direction of limited motion. For example, if the neck resists moving into flexion, the taut ligaments that would restrict this motion are located posteriorly (where antagonist neck extensor muscles are located).
What are the three ligaments of the spine?
Three of the more important ligaments in the spine are the Ligamentum Flavum, Anterior Longitudinal Ligament and the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament.
What are the ligaments of the upper cervical spine?
The upper cervical ligament system is especially important in stabilizing the upper cervical spine from the skull to C2. Although the cervical vertebrae are the smallest, the neck has the greatest range of motion. Occipitoatlantal Ligament Complex (Atlas) These four ligaments run between the Occiput and the Atlas:
What are the muscles of the neck?
The muscles of the neck are muscles that cover the area of the neck. These muscles are mainly responsible for the movement of the head in all directions. They consist of 3 main groups of muscles: anterior, lateral and posterior groups, based on their position in the neck.

What ligaments are in the neck?
Three major cervical spine ligaments are:Anterior longitudinal ligament. This ligament extends from the base of your skull, down the front of the cervical vertebra. ... Posterior longitudinal ligament. This ligament starts at C2 and extends down the back of your cervical vertebrae. ... Ligamentum flava.
How many ligaments are in the spine?
threeThe three major ligaments of the spine are the ligamentum flavum, anterior longitudinal ligament (ALL), and posterior longitudinal ligament (PLL) (Fig. 7). The ALL and PLL are continuous bands that run from the top to the bottom of the spinal column along the vertebral bodies.
What are the 5 ligaments of the spine?
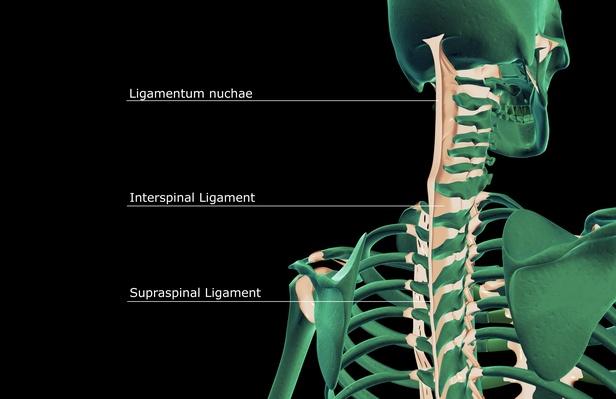
There are five main ligamentous structures seen throughout the spinal column:Anterior Longitudinal Ligament (ALL)Posterior Longitudinal Ligament (PLL)Ligamentum Flavum.Interspinous ligaments.Supraspinous ligament[1]
How do you treat a torn ligament in your neck?
Your doctor may prescribe a soft collar worn around the neck to help support the head and relieve pressure on ligaments, tendons and muscles while they heal. Other treatment options include massaging the tender area, ultrasound, cervical (neck) traction, and aerobic or isometric exercise.
How many ligaments are in the human body?
900 ligamentsLigaments are made of fibrous collagen tissue that connects bones together at the joint to stabilize the joint, support the bones and prevent the bones from grinding into each other. Ligaments have a limited amount of stretching ability, which protects joints from injury. The human body has approximately 900 ligaments.
Are there ligaments in your head?
The alar ligaments reach up from the C2 vertebra and attach strongly to the skull, while the transverse ligaments hold the pivot point of the C2 vertebra tightly to the C1 bone, allowing the head to turn without getting a spinal cord injury.
What are the 6 vertebral ligaments?
Ligaments of the vertebral archesLigamenta flava. Ligamenta flava. ... Interspinous ligaments. The interspinous ligaments connect adjacent vertebral spinous processes. ... Supraspinous ligament. ... Nuchal ligament (ligamentum nuchae) ... Intertransverse ligaments.
What is the strongest ligament in the spine?
Ligamentum FlavumLigamentum Flavum This yellow ligament is the strongest. It runs from the base of the skull to the pelvis, in front of and between the lamina, and protects the spinal cord and nerves. The ligamentum flavum also runs in front of the facet joint capsules.
Which is stronger ligament or tendon?
Tendons contain bundles of fiber, which a type of tissue called endotenon surrounds. This tissue enables bundles of tendon fibers to move against one another, supporting body movement. Ligaments are typically more elastic than tendons.
Do neck ligaments heal?
Neck sprains, like other sprains, will usually heal gradually, given time and appropriate treatment. You may have to wear a soft collar around your neck to help support the head and relieve pressure on the ligaments so they have time to heal.
What does a torn ligament in the neck feel like?
A torn neck muscle may feel like a sharp, stabbing pain in the neck area. You may have a limited range of motion or feel a dull, achy pain in the neck area. Other common symptoms of a torn neck muscle include localized swelling, soreness, “knots”, stiffness, or weakness.
How long do neck ligaments take to heal?
With proper treatment and rest, most patients will recover from a neck strain or sprain within four to six weeks. If the strain or sprain is severe, it can take three months or more to fully recover.
What are the 6 vertebral ligaments?
Ligaments of the vertebral archesLigamenta flava. Ligamenta flava. ... Interspinous ligaments. The interspinous ligaments connect adjacent vertebral spinous processes. ... Supraspinous ligament. ... Nuchal ligament (ligamentum nuchae) ... Intertransverse ligaments.
Are there ligaments in your back?
Overview. The back is a complex structure of bone and muscle, supported by cartilage, tendons and ligaments, and fed by a network of blood vessels and nerves. The back—especially the lumbar, or lower back—bears much of the body's weight during walking, running, lifting and other activities.
Where are the ligaments in your back?
The Anterior Longitudinal Ligament connects the front of each vertebra to each other. This ligament runs up and down the spine. 3. The Posterior Longitudinal Ligament extends up and down behind the spine and inside the spinal canal.
What is the strongest ligament in the spine?
Ligamentum FlavumLigamentum Flavum This yellow ligament is the strongest. It runs from the base of the skull to the pelvis, in front of and between the lamina, and protects the spinal cord and nerves. The ligamentum flavum also runs in front of the facet joint capsules.
What is the synovial hinge joint?
a synovial hinge joint; it is separated into two joint spaces by an intracapsular fibrous articular disc; gliding action occurs superior to the articular disc and hinge action occurs inferior to the disc
What is paired pterygoid?
paired; it is a specialization of the pterygoid fascia and is a remnant of the mesenchymal core of the first pharyngeal arch (Meckel's cartilage)
What is the term for a remnant of the mesenchymal core of the second pharynge?
a syndesmosis; paired; a remnant of the mesenchymal core of the second pharyngeal arch (Reichert's cartilage)
Which ligaments limit forward bending?
The supraspinous and interspinous ligaments both limit flexion (forward bending). Located in back, the supraspinous ligament is a strong rope like tissue that connects the tips of the spinous processes from your sacrum up to C7 (otherwise known as the base of the neck).
Which ligaments are more fibrous?
In the thoracic (mid-back) area, the intertransverse ligaments are tougher and more fibrous. Now you know your ligament ABCs. These are the spinal ligaments that affect all or at least large portions of the spine. Other spinal ligaments are specific to an area such as the neck or the sacrum and sacroiliac joints.
What ligaments provide stability to the column?
Spinal ligaments also provide stability to the column. They do this by limiting the degree of movement in the direction opposite their location. For example, your anterior longitudinal ligament (see below for details) is located in front of your vertebral bodies. When you arch back, it prevents you from going too far.
What is the intertransverse ligament?
Intertransverse ligaments go from a superior (remember, superior refers to an above location, relatively speaking) transverse process of a vertebra to the transverse process of the vertebra below it . The intertransverse ligaments connect these processes together and help limit the action of side bending (lateral flexion). They also form a sort of border between the bodies in front and the bony rings in the back of the vertebrae.
Where does the interspinous ligament connect to the spinous process?
The interspinous ligaments connect the whole of each spinous process vertically. The interspinous ligament starts at the root of the spinous process, where it emerges from the ring of bone located at the back of the body of its respective vertebra, and extends all the way out to the tip.
Where is the ligament flavum located?
It is located between the laminae of the vertebra. At each vertebral level, fibers originate from a superior lamina (the term superior refers to a location above, relatively speaking) and connect to the inferior lamina (i.e. the lamina just below). The ligamentum flavum limits spinal flexion (bending forward), especially abrupt flexion. This function enables the ligamentum flavum to protect your discs from injury.
Where is the nuchal ligament located?
Ligamentum Nuchae. Also known as the nuchal ligament, this ligament is located at the back of your neck. It merges with the supraspinous ligament, which as we’ve discussed, is that long, strong cord that connects the tips of most (i.e. the lumbar and thoracic) of your spinous processes.
How many muscles are there in the neck?
You have more than 20 neck muscles, extending from the base of your skull and jaw down to your shoulder blades and collarbone. These muscles support and stabilize your head, neck and the upper part of your spine. They help you move your head in different directions and assist with chewing, swallowing and breathing.
What are the different types of neck muscles?
There are three types of neck muscles: anterior (front), posterior (back) and lateral (side) muscles.
What is the neck muscle?
The muscles in your neck are skeletal muscles, meaning they’re attached to bones by tendons. They’re voluntary muscles, so you control how they move and work. Other types of muscles in the body – cardiac (in the heart) and smooth (in hollow organs like your stomach) – are involuntary, which means they work without you having to think about it.
What are the fibers in the neck?
Like all other skeletal muscles in the body, neck muscles contain lots of tiny, elastic fibers that allow the muscles to contract. Sheaths of tough connective tissue hold the fibers together. Skeletal muscle fibers are red and white, so the muscles look striated (striped or streaked).
How long does it take for a neck injury to heal?
Most neck muscle injuries heal over the course of a few days or weeks with at-home treatments. Your provider may recommend:
How many people have neck pain?
Studies estimate that about 14% of the population has some form of chronic neck pain. Approximately 45% of those cases (about 15.5 million Americans) may be due to whiplash.
Where are the muscles in the neck located?
Your neck muscles are at the front, back and sides of your neck. From the back, they begin just beneath the base of your skull and extend down near the middle of your back, around your shoulder blades. From the front, these muscles begin at your jaw and extend to your collarbone at the top of your chest.
Which bones are articulated between the sphenoid bone, frontal bone, parietal?
the articulation between four bones: the greater wing of the sphenoid bone, the frontal bone, the parietal bone, the squamous part of the temporal bone
What is the synovial hinge joint?
a synovial hinge joint; it is separated into two joint spaces by an intracapsular fibrous articular disc; gliding action occurs superior to the articular disc and hinge action occurs inferior to the disc
What is paired pterygoid?
paired; it is a specialization of the pterygoid fascia and is a remnant of the mesenchymal core of the first pharyngeal arch (Meckel's cartilage)
What is the term for a remnant of the mesenchymal core of the second pharynge?
a syndesmosis; paired; a remnant of the mesenchymal core of the second pharyngeal arch (Reichert's cartilage)
Which bone participates in the formation of the anterior end of the squamosal suture?
a suture; the greater wing of the sphenoid bone participates in the formation of the anterior end of the squamosal suture
What is a suture in the palate?
a suture; it is a midline feature of the hard palate and marks the line of fusion of the two palatine shelves (secondary palate) during development
What are the two ligaments of the cervical spine?
Ligaments of the Back of the Cervical and Upper Thoracic Spine. 1. Supraspinous Ligament (flexion) 2. Ligamentum Nuchae (fibrous membrane) Ligament Systems – Atlas and Axis. As mentioned in the Vertebral Column, the Atlas (C1) and Axis (C2) are different from the other spinal vertebrae.
What are the primary spinal ligaments?
Primary Spinal Ligaments Include: Limits…. 1. Supraspinous Ligament (flexion) 2. Ligamentum Nuchae (fibrous membrane) As mentioned in the Vertebral Column, the Atlas (C1) and Axis (C2) are different from the other spinal vertebrae.
Which ligament connects the facet joints to the posterior openings of the vertebrae?
The Ligamentum Flavum forms a cover over the dura mater: a layer of tissue that protects the spinal cord. This ligament connects under the facet joints to create a small curtain over the posterior openings between the vertebrae. The Anterior Longitudinal Ligament attaches to the front (anterior) of each vertebra.
Which ligaments prevent movement in certain directions?
Further, some ligaments prevent movement in certain directions. Three of the more important ligaments in the spine are the Ligamentum Flavum, Anterior Longitudinal Ligament and the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament . The Ligamentum Flavum forms a cover over the dura mater: a layer of tissue that protects the spinal cord.
What is a ligament?
Peer Reviewed. Ligaments are fibrous bands or sheets of connective tissue linking two or more bones, cartilages, or structures together. One or more ligaments provide stability to a joint during rest and movement. Excessive movements such as hyper–extension or hyper–flexion, may be restricted by ligaments.
Where is the anterior longitudinal ligament located?
The Anterior Longitudinal Ligament attaches to the front (anterior) of each vertebra. This ligament runs up and down the spine (vertical or longitudinal). The Posterior Longitudinal Ligament runs up and down behind (posterior) the spine and inside the spinal canal.
Which vertebrae have the greatest range of motion?
Although the cervical vertebrae are the smallest, the neck has the greatest range of motion. Occipitoatlantal Ligament Complex (Atlas) These four ligaments run between the Occiput and the Atlas: Anterior Occipitoatlantal Ligament. Posterior Occipitoatlantal Ligament.
What are the muscles of the neck?
These muscles are mainly responsible for the movement of the head in all directions. They consist of 3 main groups of muscles: anterior, lateral and posterior groups, based on their position in the neck.
What is the position of a muscle in the neck?
The position of a muscle or group of muscles in the neck generally relates to the function of the muscles. For example, the muscles in the posterior neck are responsible for extension of the neck. The muscles of the neck are closely related to a number of important structures that pass between the thorax and the head, ...
What muscles are located in the mandible?
These muscles include the digastric, mylohyoid, geniohyoid and stylohyoid muscles .
Which muscle is most superficial in the anterior neck?
The superficial muscles are the most superficial in the anterior neck, and include the platysma and sternocleidomastoid . The suprahyoid muscles, as the name suggests, are found superior to the hyoid bone , and include the digastric , mylohyoid , geniohyoid and stylohyoid .
Where does the geniohyoid muscle come from?
The geniohyoid is a short muscle that arises from the inferior mental spine of the mandible and runs posteroinferiorly to insert into the superior border of the body of the hyoid bone.
What are the three main groups of muscles?
They consist of 3 main groups of muscles: anterior, lateral and posterior groups, based on their position in the neck. The musculature of the neck is further divided into more specific groups based on a number of determinants; including depth, precise location and function. The position of a muscle or group of muscles in ...
Which spinal nerves supply the sternocleidomastoid muscle?
The sternocleidomastoid muscle is innervated by the accessory nerve (CN XI) and anterior rami of spinal nerves C2 and C3. Vascular supply to this muscle is derived from branches of the occipital , posterior auricular , superior thyroid and suprascapular artery.

Function
Clinical significance
Epidemiology
Risks
Overview
Variations
Structure
Definition
Causes
- Also known as the nuchal ligament, this ligament is located at the back of your neck. It merges with the supraspinous ligament, which as weve discussed, is that long, strong cord that connects the tips of most (i.e. the lumbar and thoracic) of your spinous processes.
Location