
What are the 4 main lobes of the cerebral cortex?
Lobes of the brain
- Frontal lobe. The frontal lobe is separated from the parietal lobe by a space called the central sulcus, and from the temporal lobe by the lateral sulcus.
- Parietal lobe. The parietal lobe is behind the frontal lobe, separated by the central sulcus. ...
- Temporal lobe. ...
- Occipital lobe. ...
What are the parts of the cerebrum and their functions?
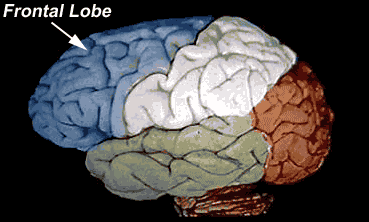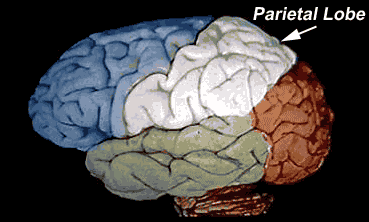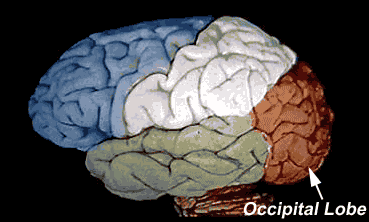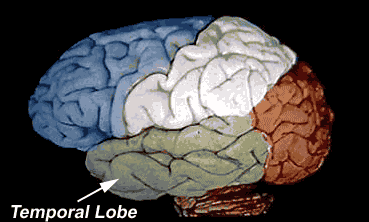
- Frontal lobe. The largest lobe of the brain, located in the front of the head, the frontal lobe is involved in personality characteristics, decision-making and movement. ...
- Parietal lobe. ...
- Occipital lobe. ...
- Temporal lobe. ...
What are the four cerebral lobes?
What Are The Eight Lobes Of The Brain
- Frontal lobe. Boundaries and landmarks. Precentral gyrus.
- Insular lobe. Boundaries and landmarks.
- Parietal lobe. Boundaries and landmarks. Inferior parietal lobule.
- Temporal lobe. Boundaries and landmarks.
- Occipital lobe. Boundaries and landmarks.
- Limbic lobe. Subcallosal gyrus.
- Clinical notes. Anterior cerebral artery syndrome.
What are the effects of a damaged cerebrum?
These symptoms include, but not are limited to, the following:
- Difficulty in planning basic tasks, such as making a cup of coffee or restocking toilet paper.
- Apathy or a complete loss of interest in life.
- Loss of thinking flexibility.
- Difficulty focusing or a complete lack of attention.
- Difficulty speaking in social settings.
- Often repeating actions without any awareness of doing so.
See more
Does the cerebrum have 4 lobes?
The cerebrum consists of two cerebral hemispheres the outer layer called the cortex (gray matter) and the inner layer (white matter). There are four lobes in the cortex, the frontal lobe, parietal lobe, temporal lobe, occipital lobe.
Does the brain have 4 or 5 lobes?
Each cerebral hemisphere is divided into five lobes, four of which have the same name as the bone over them: the frontal lobe, the parietal lobe, the occipital lobe, and the temporal lobe. A fifth lobe, the insula or Island of Reil, lies deep within the lateral sulcus.
What are the 4 lobes of the cerebellum?
The four lobes of the brain are the frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital lobes (Figure 2).
Is the cerebrum a lobe?
The lobes of the cerebrum are actually divisions of the cerebral cortex based on the locations of the major gyri and sulci. The cerebral cortex is divided into six lobes: the frontal, temporal, parietal, occipital, insular and limbic lobes.
What are the five functional lobes of the cerebrum?
Each cerebral hemisphere is divided into five lobes: the frontal lobe, the parietal lobe, the occipital lobe and the temporal lobe, four of which have the same name as the bone above them. Deep within the lateral sulcus lies a fifth lobe, the insula or Island of Reil.
What are the 4 lobes of the cerebrum and their functions?
The four lobes include the occipital, temporal, frontal, and parietal lobes. Each lobe is responsible for a specific task. The frontal lobe functions in solving problems, controlling body movements, sentence formation, and personality traits. The occipital lobe functions in processing visual images.
How many lobes does the cerebellum have?
threeWithin the cerebellum, there are thought to be three anatomical lobes which are dividied by two fissures (large furrows)– the primary fissure and the posterolateral fissure: The anterior lobe (anterior meaning 'to the front') The posterior lobe (posterior meaning 'to the back')
What are the 3 parts of the cerebellum?
There are three functional areas of the cerebellum – the cerebrocerebellum, the spinocerebellum and the vestibulocerebellum. Cerebrocerebellum – the largest division, formed by the lateral hemispheres.
Where are the 4 lobes of the brain?
The four lobes of the brain are the frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital lobes (Figure 2). The frontal lobe is located in the forward part of the brain, extending back to a fissure known as the central sulcus . The frontal lobe is involved in reasoning, motor control, emotion, and language.
How many frontal lobes are there?
You have two frontal lobes: one in the right hemisphere of your brain and one in the left hemisphere of your brain. They're located in the area of the brain that's directly behind your forehead. Your frontal lobes are vital for many important functions.
What are lobes?
Medical Definition of lobe : a curved or rounded projection or division: as. a : a more or less rounded projection of a body organ or part the lobe of the ear. b : a division of a body organ (as the brain, lungs, or liver) marked off by a fissure on the surface.
What lobe is cerebellum in?
The cerebellum (“little brain”) is a structure that is located at the back of the brain, underlying the occipital and temporal lobes of the cerebral cortex (Figure 5.1).
Which lobes are involved in receiving and processing sensory information?
Parietal Lobes: These lobes are positioned posteriorly to the frontal lobes and above the occipital lobes. They are involved in receiving and processing of sensory information. The somatosensory cortex is found within the parietal lobes and is essential for processing touch sensations.
Which lobes of the brain are responsible for processing and interpreting input from various sources?
Structures of the limbic system, including the olfactory cortex, amygdala, and the hippocampus are located within the temporal lobes. In summary, the cerebral cortex is divided into four lobes that are responsible for processing and interpreting input from various sources and maintaining cognitive function. Sensory functions interpreted by the ...
What is the most developed part of the brain?
The cortex encompasses about two-thirds of the brain mass and lies over and around most of the structures of the brain. It is the most highly developed part of the human brain and is responsible for thinking, perceiving, producing and understanding language. The cerebral cortex is also the most recent structure in the history of brain evolution.
Which lobe controls the right side of the body?
The right frontal lobe controls activity on the left side of the body and the left frontal lobe controls activity on the right side. Occipital Lobes: Located just below the parietal lobes, the occipital lobes are the main center for visual processing. The visual information is sent to the parietal lobes and temporal lobes for further processing.
Which lobes are responsible for processing visual information?
The visual information is sent to the parietal lobes and temporal lobes for further processing. Temporal Lobes: These lobes are located directly below the frontal and parietal lobes. They are involved with memory, emotion, hearing, and language. Structures of the limbic system, including the olfactory cortex, amygdala, ...
Where does the brain process information?
Most of the actual information processing in the brain takes place in the cerebral cortex. The cerebral cortex is located in the division of the brain known as the forebrain. It is divided into four lobes that each have a specific function.
How many lobes are there in the cerebral cortex?
Lobes of the Cerebrum. The cerebral cortex is classified into four lobes, according to the name of the corresponding cranial bone that approximately overlies each part. Each lobe contains various cortical association areas – where information from different modalities are collated for processing.
What is the cerebrum made of?
Internal Structure. The cerebrum is comprised of two different types of tissue - grey matter and white matter: Grey matter forms the surface of each cerebral hemisphere (known as the cerebral cortex), and is associated with processing and cognition. White matter forms the bulk of the deeper parts of the brain.
What is the largest part of the brain?
The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain, located superiorly and anteriorly in relation to the brainstem. It consists of two cerebral hemispheres (left and right), separated by the falx cerebri of the dura mater. Embryologically, the cerebrum is derived from the prosencephalon.
What is the structure of the cerebral hemisphere?
The two cerebral hemispheres are connected by a white matter structure, called the corpus callosum. Central sulcus - groove separating the frontal and parietal lobes. Lateral sulcus - groove separating the frontal and parietal lobes from the temporal lobe. Lunate sulcus - groove located in the occipital cortex.
Which lobe is responsible for memory and language?
The cortical association areas of the temporal lobe are accountable for memory and language - this includes hearing as it is the location of the primary auditory cortex. Occipital Lobe. The occipital lobe is the most posterior part of the cerebrum situated below the occipital bone of the calvaria.
Where is the parietal lobe?
The parietal lobe is found below the parietal bone of the calvaria, between the frontal lobe anteriorly and the occipital lobe posteriorly , from which it is separated by the central sulcus and parieto-occipital sulcus, respectively. It sits superiorly in relation to the temporal lobe, being separated by the lateral sulcus.
Where is the frontal lobe located?
Frontal Lobe. The frontal lobe is located beneath the frontal bone of the calvaria and is the most anterior region of the cerebrum. It is separated from the parietal lobe posteriorly by the central sulcus and from the temporal lobe inferoposteriorly by the lateral sulcus.
How many lobes are there in the brain?
5 lobes of the brain. Each cerebral hemisphere is divided into five lobes: the frontal lobe, the parietal lobe, the occipital lobe and the temporal lobe, four of which have the same name as the bone above them. Deep within the lateral sulcus lies a fifth lobe, the insula or Island of Reil.
Which lobe of the brain is the largest?
Let us therefore see the characteristics of each brain lobe. 1. Frontal lobe. Marked in blue in the image. In humans, it is the largest of the lobes of the brain.
What part of the brain is hidden between the rest of the lobes?
Insula . The insula is a part of the cortex that is hidden between the rest of the lobes of the brain and, to see it, it is necessary to separate the temporal and parietal lobes from each other. That is why it is often not considered as just another lobe.
Which lobe of the brain controls movement?
Each side of your brain contains four lobes. The frontal lobe is important for cognitive functions and control of voluntary movement or activity. The parietal lobe processes information about temperature, taste, touch and movement, while the occipital lobe is primarily responsible for vision.
Which lobe is responsible for the processing of sensory information from all areas of the body?
Parietal lobe. Marked in yellow in the image. It is situated between the frontal and occipital lobes and is primarily responsible for the processing of sensory information from all areas of the body, such as touch, temperature stimuli, pain and pressure, which can be related to the recognition of numbers.
What is the most visible part of the brain?
Each hemisphere is covered by a layer called the cerebral cortex (which is the most visible part of the brain and seems to be full ...
What is the function of the lobes of the brain?
It is characterized by its role in the processing of high-level cognitive functions such as planning, coordination, execution and control of behavior. By extension, it also enables goal setting, anticipation, articulation of language, and regulation of emotions.
What are the lobes of the brain?
The cerebral cortex is divided lengthways into two cerebral hemispheres connected by the corpus callosum. Traditionally, each of the hemispheres has been divided into four lobes: frontal, parietal, ...
Which lobe of the brain receives auditory information from the ears and secondary areas?
Auditory information. The temporal lobe contains the primary auditory cortex, which receives auditory information from the ears and secondary areas, and processes the information so we understand what we’re hearing (e.g. words, laughing, a baby crying).
What is the most famous case of frontal lobe dysfunction?
The most famous case of frontal lobe dysfunction is the story of railway worker Phineas Gage. In 1848, Gage was using a tamping iron to pack in gunpowder for blasting a tunnel through rock.
Which lobe is responsible for emotional regulation?
The frontal lobe is separated from the parietal lobe by a space called the central sulcus, and from the temporal lobe by the lateral sulcus. The frontal lobe is generally where higher executive functions including emotional regulation, planning, reasoning and problem solving occur.
Which lobe is responsible for integrating sensory information?
The parietal lobe is behind the frontal lobe, separated by the central sulcus. Areas in the parietal lobe are responsible for integrating sensory information, including touch, temperature, pressure and pain.
Which lobe of the brain is responsible for visual processing?
The occipital lobe is the major visual processing centre in the brain. The primary visual cortex, also known as V1, receives visual information from the eyes. This information is relayed to several secondary visual processing areas, which interpret depth, distance, location and the identity of seen objects.
What test can be used to check the parietal lobe?
Using callipers or a folded paperclip, and asking a subject to keep their eyes closed , this test can be used to check parietal lobe function. (Image: Lawrence House: Public Domain)
What are the lobes of the cerebral cortex?
The lobes of the cerebral cortex include the frontal (blue), temporal (green), occipital (red), and parietal (yellow) lobes . The cerebellum (unlabeled) is not part of the telencephalon. Diagram depicting the main subdivisions of the embryonic vertebrate brain. Details.
What is the uppermost part of the cerebrum?
Above this, and forming the lateral part of the cerebrum, is the paleopallium, while the uppermost (or dorsal) part is referred to as the archipallium. The cerebrum remains largely devoted to olfactory sensation in these animals, in contrast to its much wider range of functions in amniotes.
What is the cerebrum?
In the human brain, the cerebrum is the uppermost region of the central nervous system. The cerebrum develops prenatally from the forebrain (prosencephalon). In mammals, the dorsal telencephalon, or pallium, develops into the cerebral cortex, and the ventral telencephalon, or subpallium, becomes the basal ganglia.
Where is the cerebrum located?
The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain. Depending upon the position of the animal it lies either in front or on top of the brainstem. In humans, the cerebrum is the largest and best-developed of the five major divisions of the brain. The cerebrum is made up of the two cerebral hemispheres ...
What is the function of the cerebrum?
It functions as the center of sensory perception, memory, thoughts and judgement; the cerebrum also functions as the center of voluntary motor activities.
Which layer of the cerebrum is found only in mammals?
The cerebral cortex, the outer layer of grey matter of the cerebrum, is found only in mammals. In larger mammals, including humans, the surface of the cerebral cortex folds to create gyrus gyri (ridges) and sulci (furrows) which increase the surface area.
Which part of the brain controls the sense of emotion?
The cerebrum is a major part of the brain, controlling emotions, hearing, vision, personality and much more. It controls all precision of voluntary actions. Upper motor neurons in the primary motor cortex send their axons to the brainstem and spinal cord to synapse on the lower motor neurons, which innervate the muscles.
Cerebrum
The cerebrum is the largest part of the mammalian brain, and it contains two hemispheres. Furthermore, the cerebrum contains four cerebral lobes that are important for functions of sensory perception, controlling voluntary movement, and higher cognitive functions.
Structure of Cerebrum
The cerebrum consists of two types of tissue, grey and white matter. Grey matter is composed of neural fibers and cells that are not myelinated, and it covers the surface of the cerebral cortex. Due to the high density of neurons, grey matter is associated with cognition and processing.
Cerebrum Function
The cerebrum has several important functions: sensory processing, olfaction, language, communication, and learning and memory. Other functions include our ability to move around and understand who we are voluntarily.
How many neurons are in the cerebellum?
There are about 3.6 times as many neurons in the cerebellum as in the neocortex, a ratio that is conserved across many different mammalian species. The unusual surface appearance of the cerebellum conceals the fact that most of its volume is made up of a very tightly folded layer of gray matter: the cerebellar cortex.
Where is the cerebellum located?
The cerebellum is located in the posterior cranial fossa. The fourth ventricle, pons and medulla are in front of the cerebellum. It is separated from the overlying cerebrum by a layer of leathery dura mater, the tentorium cerebelli; all of its connections with other parts of the brain travel through the pons. Anatomists classify the cerebellum as part of the metencephalon, which also includes the pons; the metencephalon is the upper part of the rhombencephalon or "hindbrain". Like the cerebral cortex, the cerebellum is divided into two cerebellar hemispheres; it also contains a narrow midline zone (the vermis ). A set of large folds is, by convention, used to divide the overall structure into 10 smaller "lobules". Because of its large number of tiny granule cells, the cerebellum contains more neurons than the total from the rest of the brain, but takes up only 10% of the total brain volume. The number of neurons in the cerebellum is related to the number of neurons in the neocortex. There are about 3.6 times as many neurons in the cerebellum as in the neocortex, a ratio that is conserved across many different mammalian species.
How does the cerebellum function?
The strongest clues to the function of the cerebellum have come from examining the consequences of damage to it. Animals and humans with cerebellar dysfunction show, above all, problems with motor control, on the same side of the body as the damaged part of the cerebellum. They continue to be able to generate motor activity but lose precision, producing erratic, uncoordinated, or incorrectly timed movements. A standard test of cerebellar function is to reach with the tip of the finger for a target at arm's length: A healthy person will move the fingertip in a rapid straight trajectory, whereas a person with cerebellar damage will reach slowly and erratically, with many mid-course corrections. Deficits in non-motor functions are more difficult to detect. Thus, the general conclusion reached decades ago is that the basic function of the cerebellum is to calibrate the detailed form of a movement, not to initiate movements or to decide which movements to execute.
How does the cerebellum change with age?
The cerebellum is the youngest brain region (and body part) in centenarians according to an epigenetic biomarker of tissue age known as epigenetic clock: it is about 15 years younger than expected in a centenarian. Further, gene expression patterns in the human cerebellum show less age-related alteration than that in the cerebral cortex. Some studies have reported reductions in numbers of cells or volume of tissue, but the amount of data relating to this question is not very large.
What is the role of the cerebellum in human behavior?
In humans, the cerebellum plays an important role in motor control. It may also be involved in some cognitive functions such as attention and language as well as emotional control such as regulating fear and pleasure responses, but its movement-related functions are the most solidly established.
What is the smaller part of the brain called?
This article is about the smaller region in the lower part of the brain. For the large region of the brain, see Cerebrum. The cerebellum (Latin for "little brain") is a major feature of the hindbrain of all vertebrates. Although usually smaller than the cerebrum, in some animals such as the mormyrid fishes it may be as large as or even larger.
Which part of the brain contains more neurons than the rest of the brain?
Because of its large number of tiny granule cells, the cerebellum contains more neurons than the total from the rest of the brain, but takes up only 10% of the total brain volume. The number of neurons in the cerebellum is related to the number of neurons in the neocortex.