What are the 10 stages of meiosis?
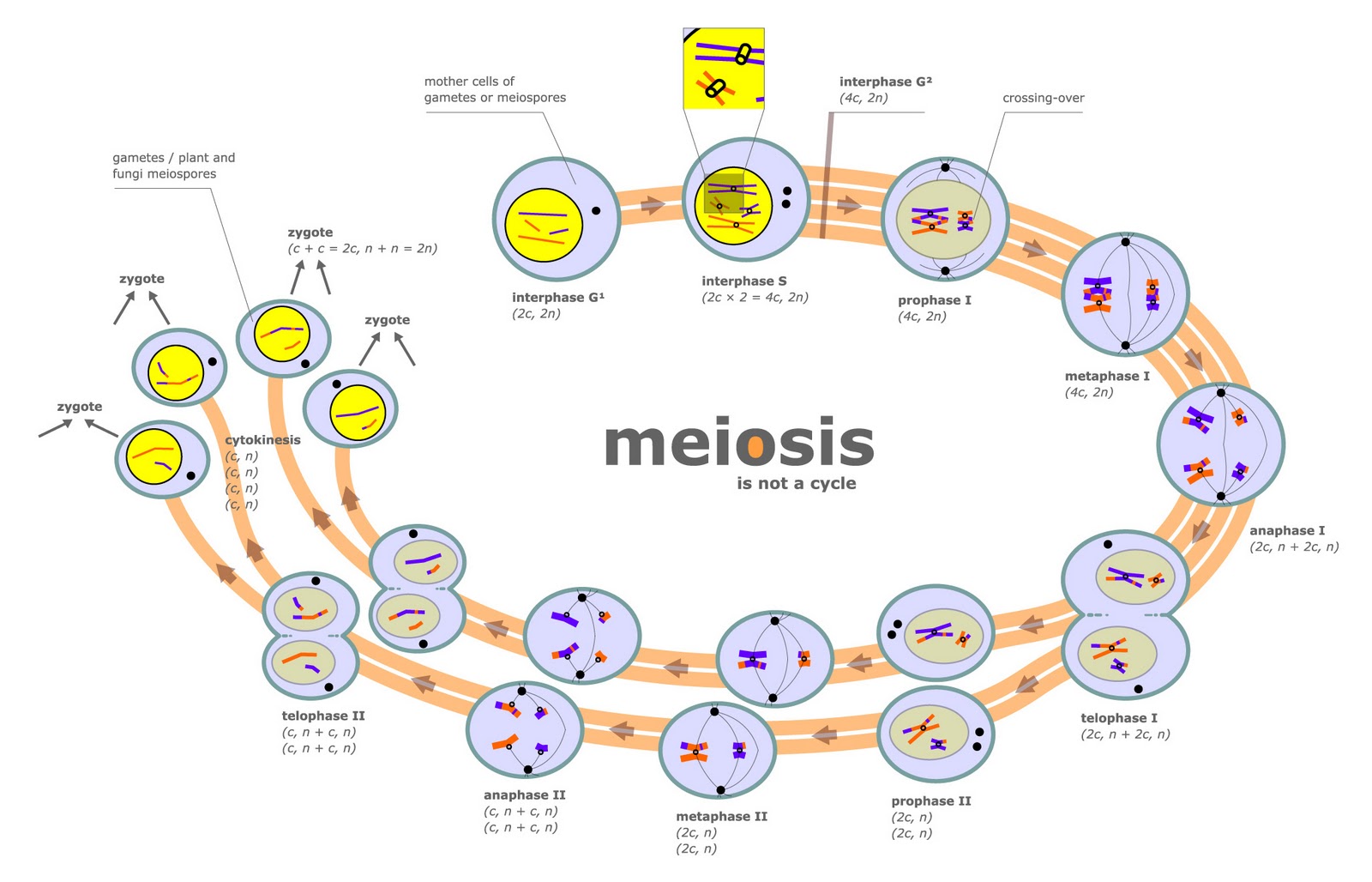
Meiosis consists of two divisions, both of which follow the same stages as mitosis (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase) Meiosis is preceded by interphase, in which DNA is replicated to produce chromosomes consisting of two sister chromatids. A second growth phase called interkinesis may occur between meiosis I and II, however no DNA ...
How to identify the stages of meiosis?
- First, the DNA replicates, just like it does in mitosis.
- Then, 1 cell divides into 2 cells, which also looks the same as it does with mitosis. The homologous pairs divide in the first round of cell divisions (Meiosis I). ...
- Last, the 2 cells divide again. ...
How long does each of the stages in meiosis take?
The complete meiosis process in human males takes about 74 hours. Spermatogenesis usually begins at 12-13 years of age and continues throughout life. Several hundred million sperm cells are produced daily by healthy young adult males. Between 200 and 600 million sperm cells are normally released in each ejaculation.
What occurs during the different stages of meiosis?
What are the 8 stages of meiosis in order?
- prophase I. the chromosomes condense, and the nuclear envelope breaks down.
- Metaphase I. pairs of homologous chromosomes move to the equator of the cell.
- Anaphase I.
- Telophase I and Cytokinesis.
- Prophase II.
- Metaphase II.
- Anaphase II.
- Telophase II and Cytokinesis.
Does meiosis have 4 or 8 phases?
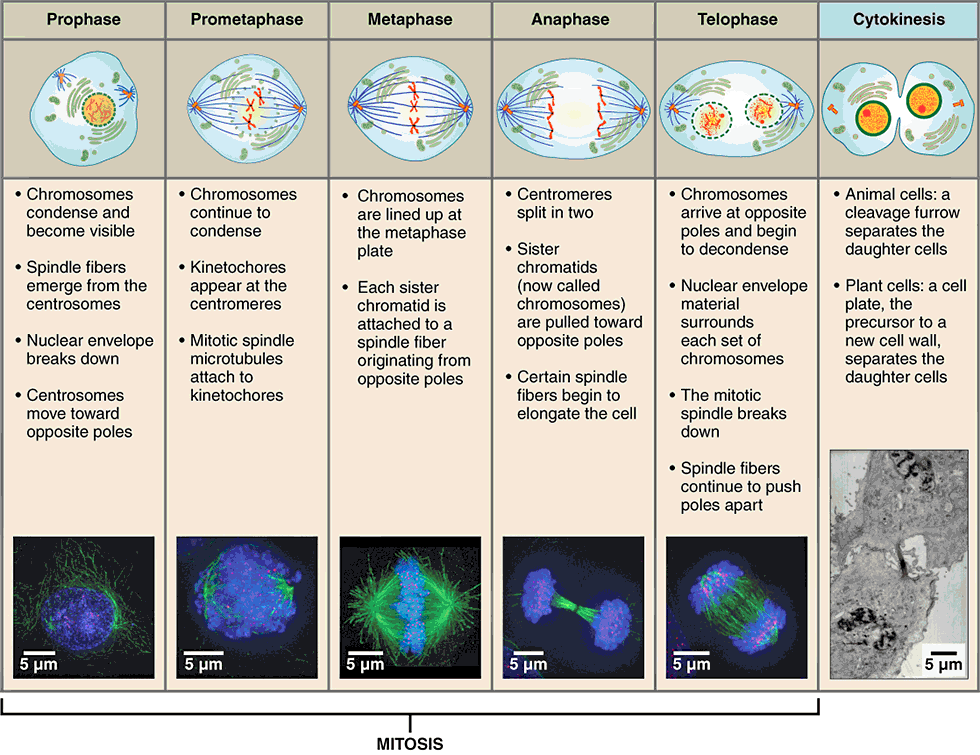
The Eight Phases Meiosis I begins after DNA replicates during interphase of the cell cycle. In both meiosis I and meiosis II, cells go through the same four phases as mitosis - prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. However, there are important differences between meiosis I and mitosis.
What are the 8 phases for meiosis?
In this video Paul Andersen explains the major phases of meiosis including: interphase, prophase I, metaphase I, anaphase I, telophase I, cytokinesis, interphase II, metaphase II, anaphase II, and telophase II. He explains how variation is created in the next generation through meiosis and sexual reproduction.
What are the 4 phases of meiosis?
Since cell division occurs twice during meiosis, one starting cell can produce four gametes (eggs or sperm). In each round of division, cells go through four stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
What are the 6 phases of meiosis?
There are six stages within each of the divisions, namely prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase and cytokinesis.
What are the 8 phases of mitosis?
prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, and cytokinesis. metaphase, prometaphase, prophase, anaphase, telophase, and cytokinesis.
What are the 5 stages of meiosis 1?
Meiotic prophase I is subdivided into five stages: leptotene, zygotene, pachytene, diplotene, and diakinesis.
What are 4 phases of mitosis?
These phases are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
What are the 7 stages of meiosis?
Comparison to mitosisMeiosisStepsProphase I, Metaphase I, Anaphase I, Telophase I, Prophase II, Metaphase II, Anaphase II, Telophase IIGenetically same as parent?NoCrossing over happens?Yes, normally occurs between each pair of homologous chromosomesPairing of homologous chromosomes?Yes5 more rows
What are the phases of meiosis 1 and 2?
Both Meiosis I and II have the same number and arrangement of phases: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Both produce two daughter cells from each parent cell.
What is meiosis and its stages?
Meiosis is the process in which a single cell divides twice to form four haploid daughter cells. These cells are the gametes – sperms in males and egg in females. The process of meiosis is divided into 2 stages. Each stage is subdivided into several phases.
What is the phase of mitosis?
What Are the Phases of Mitosis? Mitosis consists of five morphologically distinct phases: prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Each phase involves characteristic steps in the process of chromosome alignment and separation.
What are the stages of meiosis and mitosis?
In meiosis, prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase occur twice. The first round of division is special, but the second round is more like mitosis. In mitosis, prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase occur once. Chromosomes condense and the centrosomes begin to form an early spindle.
How many cell divisions are there in meiosis?
Before meiosis, the DNA is replicated, as in mitosis. Meiosis then consists of two cell divisions, known as meiosis I and meiosis II. In the first division, which consists of different phases, the duplicated DNA is separated into daughter cells. In the next division, which immediately follows the first, the two alleles of each gene are separated ...
How many cells are there in meiosis 2?
At the end of meiosis II, there are 4 cells, each haploid, and each with only 1 copy of the genome. These cells can now be developed into gametes, eggs in females and sperm in males.
What happens in metaphase 1 of meiosis?
In metaphase I of meiosis, the alleles are separated, allowing for this phenomenon to happen. In meiosis II, they will be separated into individual gametes. In mitosis, all the chromosomes line up on their centromeres, and the sister chromatids of each chromosome separate into new cells.
What is the first step in meiosis?
Prophase I , the first step in meiosis I, is similar to prophase in mitosis in that the chromosomes condense and move towards the middle of the cell. The nuclear envelope degrades, which allows the microtubules originating from the centrioles on either side of the cell to attach to the kinetochores in the centromeres of each chromosome.
Why is meiosis necessary?
Meiosis is necessary for many sexually-reproducing animals to ensure the same number of chromosomes in the offspring as in the parents. The act of fertilization includes two cells fusing together to become a new zygote. If the number of alleles of each gene is not reduced to 1 in the gametes that produce the zygote, ...
What is the process of reducing the number of chromosomes in a cell before reproduction?
What is Meiosis ? Meiosis is the process in eukaryotic, sexually-reproducing animals that reduces the number of chromosomes in a cell before reproduction. Many organisms package these cells into gametes, such as egg and sperm.
Where do homologous chromosomes line up in meiosis?
In metaphase I of meiosis I, the homologous pairs of chromosomes line up on the metaphase plate, near the center of the cell. This step is referred to as a reductional division. The homologous chromosomes that contain the two different alleles for each gene are lined up to be separated. As seen in the diagram above, while the chromosomes line up on the metaphase plate with their homologous pair, there is no order upon which side the maternal or paternal chromosomes line up. This process is the molecular reason behind the law of segregation.
What is the process of meiosis?
To put that another way, meiosis in humans is a division process that takes us from a diploid cell—one with two sets of chromosomes—to haploid cells—ones with a single set of chromosomes. In humans, the haploid cells made in meiosis are sperm and eggs.
What phase of meiosis is haploid?
In meiosis II, the sister chromatids separate, making haploid cells with non-duplicated chromosomes. Phases of meiosis II. Prophase II: Starting cells are the haploid cells made in meiosis I. Chromosomes condense. Metaphase II: Chromosomes line up at the metaphase plate.
What happens to homologues in anaphase I?
In anaphase I, the homologues are pulled apart and move apart to opposite ends of the cell. The sister chromatids of each chromosome, however, remain attached to one another and don't come apart. Finally, in telophase I, the chromosomes arrive at opposite poles of the cell.
How are sister chromatids captured?
The two sister chromatids of each chromosome are captured by microtubules from opposite spindle poles. In metaphase II, the chromosomes line up individually along the metaphase plate. In anaphase II, the sister chromatids separate and are pulled towards opposite poles of the cell.
Why do chromosomes become haploid in meiosis?
The number of chromosomes becomes haploid in meiosis I, because the actual sister chromatids are not pulled apart by spindle fibers. For example, if a cell was undergoing meiosis, and had a total of 4 chromosomes in it, then 2 of them would go to one daughter cell, and 2 of them would go to the other daughter cell.
What happens before entering meiosis?
Before entering meiosis I, a cell must first go through interphase. As in mitosis, the cell grows during G phase, copies all of its chromosomes during S phase, and prepares for division during G phase.
How many genes are in a homologous chromosome?
Two homologous chromosomes carry different versions of three genes. One has the A, B, and C versions, while the other has the a, b, and c versions. A crossover event in which two chromatids—one from each homologue—exchange fragments swaps the C and c genes. Now, each homologue has two dissimilar chromatids.
What are the stages of meiosis?
Stages of Meiosis 1 and 2 (With Pictures) Meiosis is the type of cell division that is seen during the formation of gametes (sex cells). It consists of two successive divisions which are meiosis 1 and meiosis 2. In meiosis 1, the number of chromosomes is reduced by one-half and for this reason, it is called reduction division.
What are the two divisions of meiosis?
Each of the two meiotic divisions is divided into interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. Each stage is followed by 1 or 2 indicating whether it belongs to meiosis 1 or 2. Here are list of stages of meiosis 1 and meiosis 2 as below:
How do homologous chromosomes form?
This stage is manifested by the chromosomes becoming visible as distinct bodies as they get shorter and thicker and centrioles become arranged at opposite sides of the nucleus. As prophase progresses, homologous chromosomes lie side by side and become intertwined rather like a zipper forming pairs called bivalents in a process called synapsis. Chromosomes may become coiled around each other and their chromatids may remain in contact at points called chiasmata. During synapsis, homologous chromosomes exchange genetic material between one another. This exchange is called crossing over.
Why do homologous chromosomes migrate to the opposite poles?
This is because the spindle fibres shorten and thus the chromosomes are pulled. It is important to note that sister chromatids do not separate at this stage.
What is the difference between meiosis 1 and 2?
In meiosis 1, the number of chromosomes is reduced by one-half and for this reason, it is called reduction division. Meiosis 2 results in separation the sister chromatids and for this reason, it is known as equatorial division. Each of the two meiotic divisions is divided into interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase.
What happens to the chromosomes in the nuclear membrane?
Nuclear membrane disappears completely making the chromosomes free in the cytoplasm. The spindles are already fully formed. Each pair of the homologous chromosomes moves to the equator of the spindle and attach to the spindles by their centromeres such that the two homologous chromosomes orientate towards opposite poles.
How many daughter cells are there in meiosis?
The cytoplasm divides across the middle. Thus meiosis results into four daughter cells each having a haploid number of chromosomes.
What are the two stages of meiosis?
The two stages of meiosis are meiosis I and meiosis II. Each stage is further divided into another four phases, details of which we will discuss in this article. Meiosis is a type of cell division that occurs only in eukaryotes (organisms with membrane-bound cell organelles). The process of meiosis is exhibited by higher forms ...
What is the difference between meiosis and other types of cell division?
Let's Work Together! A significant difference between meiosis and other types of cell division like mitosis or binary fission is that, in meiosis, the parent cell divides and produces four gametes that are not capable of further division; whereas in other types of cell division, the parent cell produces identical daughter cells, ...
What happens to the chromosomes during fertilization?
During the process of fertilization, two gametes fuse, which results in the doubling of the number of chromosomes. The fusion of gametes leads to the production of a zygote that has the same chromosome number as that of the parents. The haploids are unique and distinct from each other due to the crossing over process in meiosis I.
How many chromatids are in a cell during prophase?
The pair of chromosomes within a cell is called homologous chromosomes. Thus, there are a total of four chromatids in a cell, which are collectively called a tetrad. During prophase I, the homologous chromosomes begin to condense ...
How are haploids formed?
Telophase II. Four nuclei (two each in a daughter cell) are formed by the process of cytokinesis. Each of the four nuclei develops a nuclear envelope. Four daughter cells or gametes are formed. The resulting four gametes contain half the number of chromosomes, and are therefore called haploids, each having a single set of chromosome.
How many daughter cells are produced in meiosis II?
Meiosis II takes place in the same manner as mitosis. The two daughter cells produced at the end of meiosis I (in most cases) undergo further division and produce four daughter cells at the end of meiosis II.
How many haploid cells are there in meiosis?
During meiosis I, a cell is divided into two, and in meiosis II, even further division takes place, resulting into a total of four haploid cells. Before the start of the process, the parent cell goes through a stage of preparation called the interphase.
