How much DNA is needed for a transformation?
For successful chemical transformation, 50–100 µL of competent cells and 1–10 ng of DNA are recommended. When a ligation mixture is used as the transforming DNA (often 1–5 µL is sufficient), purification prior to chemical transformation is generally not required.
How much volume in microliters of plasmid should you transfer to your cells?
1-5 µl of DNA (plasmid or ligation product) is recommended for 50 µl of competent cells.
How much ligation product do I need for transformation?
between 1-5 µlTransformation. Add between 1-5 µl of ligation mixture to competent cells for transformation.
How many plasmids can transform a single E coli cell?
one plasmid moleculecoli cell can only be transformed by one plasmid molecule, which is then propigated to make a clonal population of bacterial that contains only a single plasmid species.
What should be the minimum weight of DNA that is required for successful transformation?
For successful chemical transformation, 50–100 µL of competent cells and 1–10 ng of DNA are recommended.
How does plasmid size affect transformation efficiency?
The transformation efficiency (transformants per microgram plasmid DNA) decreased with increases of size of the DNA. However that of 2.0 x 10(3) transformants per microgram of DNA were done routinely, by using a plasmid with a large molecular size of 12.6 kbp.
What is the best ligation ratio?
To determine the best ratio of insert:vector to use for cloning, you may have to try different ratios ranging from 1:1 to 15:1, but a 3:1 ratio is a good place to start. For blunt-end ligation, be sure to adjust the insert:vector ratio and increase to 10:1 to optimize your result.
Why do we use 42 degree Celsius heat shock in a transformation?
One model is that the heat shock (0 → 42°C) causes changes in membrane fluidity, resulting in the formation of zones of adhesion, where the outer and inner cell membranes fuse with pores in the cell wall, and through which DNA may pass (9-12).
How is ligation ratio calculated?
0:050:58How do I calculate how much DNA to add to a ligation reaction? - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipWhich will be 25 to 30 femtomole x' depending on your vector. Size for inserts of similar size toMoreWhich will be 25 to 30 femtomole x' depending on your vector. Size for inserts of similar size to the vector we recommend a one-to-one molar ratio of insert to vector.
Can a single E. coli take up 2 plasmids?
Double transformations, in which a single cell (typically an Escherichia coli bacterium) is transformed simultaneously with two different plasmids, are deemed by most researchers to be very low frequency events, in particular when both plasmids carry the same antibiotic resistance gene, and/or origin of replication, or ...
Can a single E. coli take up more than one plasmid?
coli bacteria readily accept multiple plasmids, resulting in widespread aclonality and reveal a complex pattern of colony development. Cotransformation of plasmids occurs by either CaCl2 or by electroporation methods.
How many plasmids can a bacteria have?
The copy number is the number of copies of the plasmid in each bacterial cell. For most plasmids, it is 1 or 2 copies per chromosome, but it may be as many as 50 or more for certain small plasmids such as the ColE plasmids.
How are plasmids transferred into bacteria?
This is commonly done using calcium chloride which permeabilizes the cell membrane so the bacteria can easily uptake your plasmid of interest. Scientists can also use electroporation, the application of an electrical charge to cells, to increase cell membrane permeability and thus transformation efficiency.
How are plasmids transferred?
When a bacterium divides, all of the plasmids contained within the cell are copied such that each daughter cell receives a copy of each plasmid. Bacteria can also transfer plasmids to one another through a process called conjugation.
How do you calculate transformation efficiency?
The equation for calculating Transformation Efficiency (TE) is: TE = Colonies/µg/Dilution. Efficiency calculations can be used to compare cells or ligations.
How much DNA does it take to transfect in a 96 well plate?
We recommend at least 50ng of plasmid DNA per well for 96-well experiments and 30ng of plasmid DNA per well for 384-well experiments. Tip: The following table lists the volumes to be added per well.
How much optmemem to add to plasmid X?
1. Take 4ug of plasmid X and add 250ul of optmemem (label tube as 1)
How long does it take to harvest a 293F cell?
We use 1:6 DNA:PEI ratio to transfect 293F cell to generate VLP cull culture. We harvest cell from 3 days to 6 days.
What are the factors that influence the efficiency of plasmid DNA transfection?
The topology (linear or supercoiled) and the size of the vector construct, the quality of the plasmid DNA, and the promoter choice are major factors that influence the efficiency of plasmid DNA transfection.
What is the best quality of plasmid DNA?
The best results are achieved with plasmid DNA of the highest purity that is free from phenol, sodium chloride, and endotoxins.
What is the most common vector for transfection?
Classic transfection technologies have initially been developed for introducing plasmid DNA into cells, and plasmid DNA still remains the most common vector for transfection. DNA plasmids containing recombinant genes and regulatory elements can be transfected into cells to study gene function and regulation, mutational analysis ...
Why is it important to perform control transfections?
Regardless of the transfection method used, it is important to perform control transfections to check for cell health, to determine whether the reported assay is working properly, and to establish any insert-related problems. To check for optimal cell growth conditions, include a negative control (no DNA, no transfection reagent).
Why is linear DNA more efficient?
Stable transfections are more efficient when using linear DNA due to its optimal integration into the host genome. Linear DNA with free ends is more recombinogenic and more likely to be integrated into the host chromosome to yield stable transformants, even though it is taken up by the cell less efficiently.
Can too strong a promoter cause transient transfection?
However, using too strong a promoter to drive the expression of a potentially toxic gene can cause problems in transient transfection of plasmid DNA. For the potentially toxic gene products, use of weak promoters are recommended. Toxic gene products are also a problem for selection of stably transfected cells.
Does nuclear delivery of plasmids evade degradation?
This effect is observed using equivalent mass or molar concentrations of different-sized constructs, suggesting that nuclear delivery of plasmids may be limited by the rate of intracellular transit and that small plasmids evade degradation by rapid transit through the cytoplasm, rather than through the saturation of cellular defenses (Lukacs, et al., 2000; McLenachan et al., 2007).
How to mix plasmid DNA?
Add 2 µl of the plasmid DNA (2 ng) to the cells in the tube labeled “Gene _”; mix gently by swirling the pipette tip around in the mixture (“stirring”). Similarly, add 2 µl of TE buffer to the cells in the tube labeled “negative” and mix. DO NOT mix by pipetting up and down. DO NOT ‘pulse-spin’ in the microcentrifuge.
What is the process of introducing plasmid DNA into host cells?
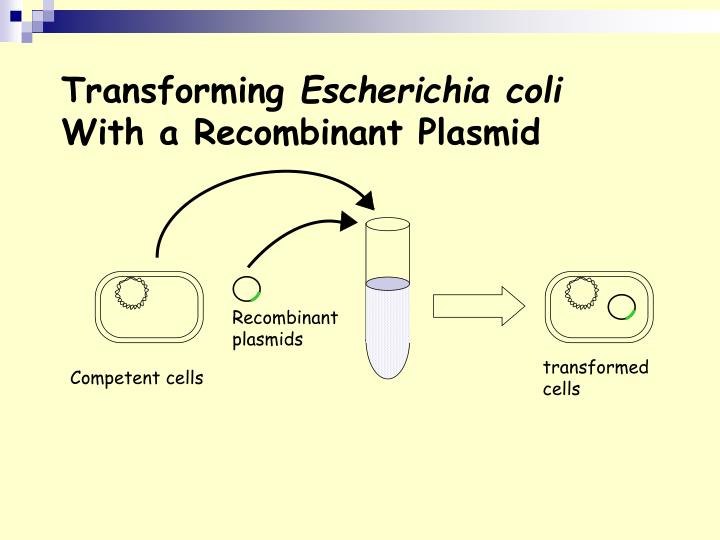
For our purposes today, it describes the process of introducing plasmid DNA (with engineered genes of interest) into host bacterial cells that have been prepared (usually with CaCl 2 solution) to uptake the DNA, making them ‘competent’ . Without this prior treatment, uptake of foreign DNA by bacteria would be an extremely rare event. Even with the treatment, it is still a relatively inefficient process, requiring selection of the smaller number of ‘transformants’ from a larger background of untransformed cells. Antibiotic resistance is a common selection mechanism, which is why plasmids that are engineered for cloning purposes typically have one or more genes that will confer antibiotic resistance in their bacterial hosts. (Think of the LB agar plates that we just poured, containing the antibiotic Ampicillin.)
How to label sterile microcentrifuge tubes?
Obtain and label 2 sterile microcentrifuge tubes: one is “negative” and one is “Gene _” (A, F, T, M, etc); include your team name (or a logo) on the tubes, so that you will be able to recognize them among the others. Place these tubes on ice to pre-chill them.
How long to incubate DNA in ice?
Incubate on ice for 30 minutes. This step allows the cells and the DNA to complex together in the presence of the CaCl 2 solution that the cells are in.
How long to incubate a bacterial tube?
Cap and place the tubes at a 45 0 angle in the shaking (~225 rpm) bacterial incubator, room 408, which is set to 37 0 Incubate for 30 minutes.
Is GFP a monomeric protein?
In the following 2 clones, the “GFP” tag is another version of GFP termed “monomeric” GFP, or “mGFP”. For our purposes, ‘mGFP’ and turbo GFP (‘tGFP’) are functionally equivalent, and we only need to keep in mind that they are different proteins and therefore have different gene sequences. The clones below were not commercially available from Origene directly in their mGFP vectors; #4 was a ‘custom subclone’ given to us as a sample from Origene, and #5 was subcloned by SAC, from an “Entry vector”. Therefore, we don’t have a ‘single link’ to the clones as we do for the first three:
How to save time when you have a tube of plasmid DNA?
If you are not concerned with transformation efficiency (such as when you have a tube of plasmid DNA and just need to transform bacteria so that you can grow up more of the plasmid) you can save a lot of time by shortening or skipping many steps and will still get enough colonies for your next step.
How much DNA do you need for ligation?
If you used 100-1000 ng of total DNA in a ligation you will often get more colonies if you use 1 μl of a 1:5 or 1:10 dilution rather than 1 μl directly.
Why is transformation important in bacteria?
Transformation of bacteria with plasmids is important not only for studies in bacteria but also because bacteria are used as the means for both storing and replicating plasmids. Because of this, nearly all plasmids (even those designed for mammalian cell expression) ...
How do genetic modifications help bacteria?
Scientists have made many genetic modifications to create bacterial strains that can be more easily transformed and that will help to maintain the plasmid without rearrangement of the plasmid DNA. Additionally, specific treatments have been discovered that increase the transformation efficiency and make bacteria more susceptible to either chemical or electrical based transformation, generating what are commonly referred to as 'competent cells.'
How long to incubate competent cell/DNA mixture on ice?
Incubate the competent cell/DNA mixture on ice for 20-30 mins.
How to mix DNA in a falcon tube?
GENTLY mix by flicking the bottom of the tube with your finger a few times.
How long does it take for a cell to thaw?
Take competent cells out of -80°C and thaw on ice (approximately 20-30 mins).
How long does it take to digest a plasmid?
We recommend using your entire PCR reaction and 1μg of recipient plasmid. It is also critical that as much of the recipient plasmid as possible be cut with both enzymes, and therefore it is important that the digest goes at least 4 hours and as long as overnight.
How much DNA can you use for cloning?
For most standard cloning, you can transform 1-2μl of your ligation reaction into competent cells such as DH5alpha or TOP10. If using much less total DNA (<1ng) or if you are having trouble getting colonies, you might want to use higher competency cells. Additionally, if your final product is going to be very large (>10kb) you might want to use electro-competent cells instead of the more common chemically-competent cells.
What sequence is used for cloning ORF?
Therefore, our Forward Primer will use the sequence 5'-ATGTGGCATATCTCGAAGTAC-3' for the region that binds the ORF and we will add the EcoRI restriction site (GAATTC) to the 5’ end of this primer, making our Forward Primer 5'-GAATTCATGTGGCATATCTCGAAGTAC-3'.
What are the primers used for cloning?
The basic PCR primers for molecular cloning consist of: 1 Leader Sequence: Extra base pairs on the 5' end of the primer assist with restriction enzyme digestion (usually 3-6bp) 2 Restriction Site: Your chosen restriction site for cloning (usually 6-8bp) 3 Hybridization Sequence: The region of the primer that binds to the sequence to be amplified (usually 18-21bp)
What is PCR cloning?
PCR based cloning is incredibly versatile and allows for nearly any piece of DNA to be placed into a backbone vector of choice with minimal limitations.
How to isolate insert and vector?
Isolate your insert and vector by gel purification: Run your digest DNA on an agarose gel and conduct a gel purification to isolate the DNA. When running a gel for purification purposes it is important to have nice crisp bands and to have space to cut out the bands.
How to check the size of a vector after purifying DNA?
After purifying the DNA, conduct a diagnostic restriction digest of 100-300ng of your purified DNA with the enzymes you used for the cloning. Run your digest on an agarose gel. You should see two bands, one the size of your vector and one the size of your new insert.