The largest eruptions come from volcanoes called rhyolite calderas, and these huge eruptions (which we haven't really witnessed since 186 AD in New Zealand) may occur at intervals of 10,000 to 30,000 years. Yellowstone, the largest caldera in the U.S.A. seems to erupt on average every 600,000 years!
How often do volcanoes erupt in the world?
The largest eruptions come from volcanoes called rhyolite calderas, and these huge eruptions (which we haven't really witnessed since 186 AD in New Zealand) may occur at intervals of 10,000 to 30,000 years. Yellowstone, the largest caldera in the U.S.A. seems to erupt on average every 600,000 years!
How many caldera eruptions have there been in the world?
At least 20 catastrophic caldera -forming eruptions have occurred in the past 10,000 years; the awesome eruption of 1912 at Novarupta in what is now Katmai National Park and Preserve is the most recent.
What is an example of a caldera eruption?
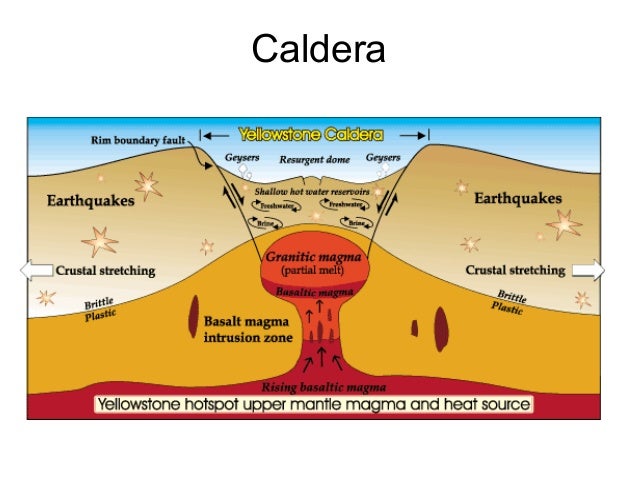
Mount Mazama 's eruption timeline, an example of caldera formation. A caldera is a large cauldron -like hollow that forms shortly after the emptying of a magma chamber in a volcanic eruption. When large volumes of magma are erupted over a short time, structural support for the rock above the magma chamber is lost.
How often do caldera eruptions occur in Hawaii?
Compared to the thousands of volcanic eruptions that occur each century, the formation of a caldera is a rare event, occurring only a few times per century. Only seven caldera-forming collapses are known to have occurred between 1911 and 2016. More recently, a caldera collapse occurred at Kīlauea, Hawaii in 2018.
Do caldera volcanoes erupt?
A caldera is a large depression formed when a volcano erupts and collapses.
When was the last time a caldera volcano erupted?
approximately 640,000 years agoYellowstone CalderaAge of rock2,100,000–70,000 yearsMountain typeCaldera and supervolcanoVolcanic fieldYellowstone PlateauLast eruptionapproximately 640,000 years ago (caldera-forming); 70,000 years ago (in the caldera)11 more rows
How often does Yellowstone caldera erupt?
about 600,000 to 800,000 yearsHow often do volcanic eruptions occur at Yellowstone? Three extremely large explosive eruptions have occurred at Yellowstone in the past 2.1 million years with a recurrence interval of about 600,000 to 800,000 years.
Is a caldera-forming eruption very likely?
Another caldera-forming eruption is theoretically possible, but it is very unlikely in the next thousand or even 10,000 years. Scientists have also found no indication of an imminent smaller eruption of lava in more than 30 years of monitoring.
Is Yellowstone overdue for an eruption?
Yellowstone is not overdue for an eruption. Volcanoes do not work in predictable ways and their eruptions do not follow predictable schedules. Even so, the math doesn't work out for the volcano to be “overdue” for an eruption.
Is Yellowstone ready to erupt?
In its 2.2-million-year history, the Yellowstone caldera system has erupted catastrophically only three times, while producing many localized lava flows. “Yellowstone is not going to erupt again anytime soon, and when it does, it's much more likely to be a lava flow than an explosive event,” Poland said.
Which volcano will destroy the world?
the Yellowstone CalderaEffects of a major eruption: When the Yellowstone Caldera, or "supervolcano," in Yellowstone National erupts again, it will render a huge swath of North America, from Vancouver to Oklahoma City, uninhabitable. It would have incalculable human and economic consequences.
Which supervolcano is most likely to erupt?
ANSWER: Yes. Over the past 640,000 years since the last giant eruption at Yellowstone, approximately 80 relatively nonexplosive eruptions have occurred and produced primarily lava flows. This would be the most likely kind of future eruption.
Is Yellowstone a threat?
Yellowstone offers a dual threat to the public including the threat of a large earthquake with the additional threat of volcanic activity.
What's the biggest supervolcano?
1 – La Garita Caldera.2 – Lake Toba.3 – Cerro Guacha.4 – Yellowstone Caldera.5 – Lake Taupo.6 – Cerro Galán.7 – Island Park Caldera.8 – Vilama.More items...•
What is the largest caldera on Earth?
The Apolaki CalderaThe Apolaki Caldera is a volcanic crater with a diameter of 150 kilometers (93 mi), making it the world's largest caldera. It is located within the Benham Rise (Philippine Rise) and was discovered in 2019 by Jenny Anne Barretto, a Filipina marine geophysicist and her team.
What will happen if Yellowstone erupts?
If another large, caldera-forming eruption were to occur at Yellowstone, its effects would be worldwide. Such a giant eruption would have regional effects such as falling ash and short-term (years to decades) changes to global climate.
How many caldera volcanoes are there in the world?
There are six known, active super volcanoes in the world today.
What is the largest caldera in the world?
The Apolaki CalderaThe Apolaki Caldera is a volcanic crater with a diameter of 150 kilometers (93 mi), making it the world's largest caldera. It is located within the Benham Rise (Philippine Rise) and was discovered in 2019 by Jenny Anne Barretto, a Filipina marine geophysicist and her team.
What would happen if Yellowstone erupted?
If another large, caldera-forming eruption were to occur at Yellowstone, its effects would be worldwide. Such a giant eruption would have regional effects such as falling ash and short-term (years to decades) changes to global climate.
What happens when a caldera collapse?
“During a caldera collapse, a massive block of rock near the top of the volcano slides down into the volcano. As it slides, gets stuck on the jagged walls around it, and slides some more, the block of rock squeezes out more magma than would ordinarily be expelled.”
What is caldera in volcanoes?
Calderas. A caldera is a large depression formed when a volcano erupts and collapses. During a volcanic eruption, magma present in the magma chamber underneath the volcano is expelled, often forcefully. When the magma chamber empties, the support that the magma had provided inside the chamber disappears. As a result, the sides and top of the ...
How big is a caldera?
Calderas vary in size from one to 100 kilometers (0.62 to 62 miles) in diameter. Some calderas form a lake as the bowl-shaped depression fills with water. A famous example is Crater Lake, in Oregon. This caldera formed about 7,000 years ago when a stratovolcano, Mt. Mazama, violently erupted.
What is a resurgent caldera?
Noun. depression caused by the collapse of an underground magma chamber not affiliated with a particular volcano; the largest volcanic structures on Earth. stratovolcano. Noun. steep volcano made of hardened lava, rock, and ash. Also known as a composite volcano. volcano.
What are the causes of calderas in Yellowstone National Park?
Calderas such as Crater Lake and those in Yellowstone National Park result from dramatic eruptions, but slower eruptions can also create calderas. This often occurs with shield volcanoes, which are typically flatter and more gradually sloped. Lava flows from shield volcanoes more slowly and often at regular intervals.
Why is the caldera called a resurgent?
Over time, the refilling of the magma chamber pushes up the caldera floor. This upward movement is why the caldera is called resurgent, which means “risen again.”. Laguna de Quiltoa a caldera in Ecuador. large depression resulting from the collapse of the center of a volcano.
Which state has the youngest volcano?
youngest, most-active volcano in the U.S. state of Hawaii.
What type of volcano flows from shield volcanoes?
Lava flows from shield volcanoes more slowly and often at regular intervals. Over time, this creates a series of nested depressions. The Kilauea caldera on Kilauea, one of the volcanoes that make up Hawai’i, is one example. Another type of caldera is a resurgent caldera.
What happens to the volcano during an eruption?
During an eruption, the surface of a volcano deforms, or changes shape. The color bands in the lower-right animation box show those changes from before to midway through Kilauea’s 2018 eruption. The closer the color bands are to one another, the more severe the deformation in that area – much like the contour lines on a topographic map denote rapidly changing altitude. The upper-left animation box shows the caldera over the same time period. By June 2018, the caldera had collapsed. As the collapse occurred, the deformation from the eruption increased extensively (indicated by the increase in color bands in close proximity to one another in the lower-right animation box). The white dots represent earthquakes. Earthquakes are a known precursor to volcanic eruptions. The distinct cluster of earthquakes around the caldera were also an indication that the caldera collapse process was underway.
What happens when rock falls in caldera?
The rock from the caldera can then collapse into the magma chamber. As the rock falls, it pressurizes the magma chambers – for Kilauea, the research team identified two of them – increasing the magma flow to the distant vents as well as the total volume of the eruption.
What volcano is the largest in the world?
Scientists have figured out what triggers large-scale volcanic eruptions and what conditions likely lead to them. Hawaii’s Kilauea is one of the most active volcanoes in the world.
How does magma escape from a volcano?
A large quantity of magma can be expelled quickly from the chamber (or chambers) beneath the volcano through these vents, leaving the rocky floor and walls of the caldera above the chamber without sufficient support. The rock from the caldera can then collapse into the magma chamber.
What was the largest eruption in 200 years?
Kilauea’s 2018 eruption, however, was especially massive. In fact, it was the volcano’s largest eruption in over 200 years. Scientists at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California used the abundance of data collected from this rare event to shed light on the cause of large-scale eruptions like this one and, perhaps more importantly, what mechanisms trigger them.
What do the white dots on the caldera mean?
The white dots represent earthquakes. Earthquakes are a known precursor to volcanic eruptions. The distinct cluster of earthquakes around the caldera were also an indication that the caldera collapse process was underway. Credits: NASA/JPL-Caltech. But what the science team really wanted to know was what caused the caldera to collapse in ...
Can a volcano erupt at a low elevation vent?
Even though the model doesn’t predict when a volcano is going to erupt, it can provide crucial insight into the likely severity of an eruption once it begins. “If we see an eruption at a low-elevation vent, that is a red flag or warning that caldera collapse is possible,” said Roman.
How big is the crater of the Calderas volcano?
The blast is thought to have ejected about 800 cubic kilometers of ash into the atmosphere, producing a crater that is 100 kilometers long and 35 kilometers wide. The crater is now the site of the world's largest volcanic lake. Calderas on Other Planets.
What is a Caldera?
Calderas are some of the most spectacular features on Earth. They are large volcanic craters that form by two different methods: 1) an explosive volcanic eruption; or, 2) collapse of surface rock into an empty magma chamber.
How deep is the caldera in Alaska?
The caldera is 10 kilometers in diameter and 500-1,000 meters deep.
What is the caldera chain at Yellowstone?
Yellowstone Caldera Chain: The current caldera at Yellowstone is the most recent in a series of eruptions that span millions of years. The North American Plate is moving west over a stationary hot spot. As the plate moves, the hotspot produces an enormous eruption (and a large caldera) every few million years.
How was Crater Lake formed?
Crater Lake was formed about 7700 years ago when an enormous volcanic eruption of Mount Mazama emptied a large magma chamber below the mountain. The fractured rock above the magma chamber collapsed to produce a massive crater over six miles across. Centuries of rain and snow filled the caldera, creating Crater Lake.
What volcanoes produced ash deposits?
Explosive Eruptions at Kilauea: Many of Kilauea's pre-1924 explosive eruptions that produced significant ash deposits probably happened when the volcano's summit crater was so deep that its floor was below the water table, letting groundwater seep in to form a lake.
Where are the calderas on other planets?
Calderas on Other Planets. Calderas on Other Planets: Complex caldera at the summit of Olympus Mons Volcano - a shield volcano that is the tallest feature on Mars. This caldera is very similar to the caldera complex at the summit of Earth's largest shield volcano - Mauna Loa Volcano on the island of Hawaii.
What is the cause of caldera eruptions?
Further information: Explosive eruption. Explosive caldera eruptions are produced by a magma chamber whose magma is rich in silica. Silica-rich magma has a high viscosity, and therefore does not flow easily like basalt. The magma typically also contains a large amount of dissolved gases, up to 7 wt% for the most silica-rich magmas.
How many calderas have collapsed?
Only seven caldera-forming collapses are known to have occurred since 1900, most recently at Bárðarbunga volcano, Iceland in 2014.
How do calderas form?
A caldera is a large cauldron -like hollow that forms shortly after the emptying of a magma chamber in a volcanic eruption. When large volumes of magma are erupted over a short time, structural support for the rock above the magma chamber is lost. The ground surface then collapses downward into the emptied or partially emptied magma chamber, leaving a massive depression at the surface (from one to dozens of kilometers in diameter). Although sometimes described as a crater, the feature is actually a type of sinkhole, as it is formed through subsidence and collapse rather than an explosion or impact. Only seven caldera-forming collapses are known to have occurred since 1900, most recently at Bárðarbunga volcano, Iceland in 2014.
How many years ago did the La Garita Caldera erupt?
Eruptions forming even larger calderas are known, such as the La Garita Caldera in the San Juan Mountains of Colorado, where the 5,000 cubic kilometres (1,200 cu mi) Fish Canyon Tuff was blasted out in eruptions about 27.8 million years ago.
What happens if magma is injected into the collapsed magma chamber?
If magma continues to be injected into the collapsed magma chamber, the center of the caldera may be uplifted in the form of a resurgent dome such as is seen at the Valles Caldera, Lake Toba, the San Juan volcanic field, Cerro Galán, Yellowstone, and many other calderas.
How does a caldera affect the environment?
Because a silicic caldera may erupt hundreds or even thousands of cubic kilometers of material in a single event, it can cause catastrophic environmental effects. Even small caldera-forming eruptions, such as Krakatoa in 1883 or Mount Pinatubo in 1991, may result in significant local destruction and a noticeable drop in temperature around the world. Large calderas may have even greater effects. The ecological effects of the eruption of a large caldera can be seen in the record of the Lake Toba eruption in Indonesia .
What are the ecological effects of a large caldera?
Large calderas may have even greater effects. The ecological effects of the eruption of a large caldera can be seen in the record of the Lake Toba eruption in Indonesia . At some points in geological time, rhyolitic calderas have appeared in distinct clusters.
How often do volcanoes erupt in Alaska?
How often do Alaskan volcanoes erupt? Alaskan volcanoes have produced one or two eruptions per year since 1900. At least 20 catastrophic caldera -forming eruptions have occurred in the past 10,000 years; the awesome eruption of 1912 at Novarupta in what is now Katmai National Park and Preserve is the most recent.
Where did the largest eruption of the 20th century occur?
The world's largest eruption of the 20th century occurred in 1912 at Novarupta on the Alaska Peninsula. An estimated 15 cubic kilometers of magma was explosively erupted during 60 hours beginning on June 6th.
What was the most significant volcanic activity in 2016?
The most notable volcanic activity consisted of eruptions at Pavlof and Bogoslof volcanoes.
How long has the Alaska Volcano Observatory been monitoring?
Twenty-five years of monitoring and studying Alaska's volcanoes by the Alaska Volcano Observatory have improved global understanding of how volcanoes work and how to live safely with volcanic eruptions. Timely warnings from AVO throughout its 25-year history have helped reduce the impact of erupting volcanoes, protecting lives, property, and economic well-being.
What volcano erupted in 1980?
The May 18, 1980 eruption of Mount St. Helens (Washington) was the most destructive in the history of the United States. Novarupta (Katmai) Volcano in Alaska erupted considerably more material in 1912, but owing to the isolation and sparse population of the region, there were no human deaths and little property damage.
What year was the Novarupta eruption?
The explosive outburst at Novarupta (Alaska) in June 1912 was the 20th century's most voluminous volcanic eruption. Marking its centennial, we illustrate and document the complex eruptive sequence, which was long misattributed to nearby Mount Katmai, and how its deposits have provided key insights about volcanic and magmatic processes. It was one...
What are the warnings of volcanoes?
Most volcanoes provide warnings before an eruption. Magmatic eruptions involve the rise of magma toward the surface, which normally generates detectable earthquakes. It can also deform the ground surface and cause anomalous heat flow or changes in the temperature and chemistry of the groundwater and spring waters. Steam-blast eruptions, however,...
How often do volcanoes erupt?
Some small volcanoes only erupt once in their lives, while other volcanoes erupt multiple times.
When do we notice volcanoes?
Many of us only notice volcanoes when they are about to explode or disrupt our travel plans, but these spectacular forces of nature can have a significant impact on people living in the local area.
What is a volcano?
A volcano is like a chimney that allows hot liquid rock, called magma, to flow from a layer within the Earth and erupt onto the surface. The magma can come from as far down as 200 kilometres in the mantle and once it erupts — at a piping hot 700 to 1,200 degrees Celsius — it is called lava.
Where are volcanoes found?
Volcanoes are found all over the world but the most common location for active volcanoes is at the boundaries of tectonic plates where plates are converging.
What happens when a volcano erupts?
Flowing hot lava can incinerate, bury and bulldoze things in its path but at least is usually moving slowly enough for humans to get out of its way.
What are some examples of strato volcanoes?
Examples of strato volcanoes include Agung in Bali, Yasur in Vanuatu, Etna in Italy and Fuji in Japan.
What is the gas bubble in a volcano?
Bubbles of gas build up in the magma — which has a high silica content — and explode creating volcanic ash, consisting of tiny gritty sharp fragments of glassy snap-frozen magma and rock from the sides of the volcano vent.