What is a lysosome classified as?
Lysosomes are an important cell organelle found within eukaryotic animal cells.
Is lysosomes an organelle or structure?
A lysosome is a membrane-bound cell organelle that contains digestive enzymes. Lysosomes are involved with various cell processes. They break down excess or worn-out cell parts.
What is considered an organelle?
Organelles are specialized structures that perform various jobs inside cells. The term literally means “little organs.” In the same way organs, such as the heart, liver, stomach, and kidneys, serve specific functions to keep an organism alive, organelles serve specific functions to keep a cell alive.
Is a lysosome a cell?
A lysosome (/ˈlaɪsəˌsoʊm/) is a membrane-bound organelle found in many animal cells. They are spherical vesicles that contain hydrolytic enzymes that can break down many kinds of biomolecules. A lysosome has a specific composition, of both its membrane proteins, and its lumenal proteins.
What organelle produces lysosomes?
the golgi apparatusLysosomes are spherical, membrane bound organelles that are generated by the golgi apparatus. They contain hydrolytic enzymes, and so function as part of the recycling system of the cell.
What is the role of lysosomes?
Lysosomes are membrane-bound organelles found in every eukaryotic cell. They are widely known as terminal catabolic stations that rid cells of waste products and scavenge metabolic building blocks that sustain essential biosynthetic reactions during starvation.
What are the 8 types of organelles?
Contents1 Nucleus.2 Mitochondria.3 Ribosomes.4 Endoplasmic Reticulum. 4.1 Smooth ER. 4.2 Rough ER.5 Golgi Complex.6 Vacuole.7 Peroxisomes.8 Lysosomes.
Which of the following is not an organelle?
Final answer: Microsome is not a cell organelle.
Which of the following is not considered an organelle?
In this sense, ribosomes and nucleosomes are not regarded as organelles because they are not bounded by membranes. In the same way, lysosomes and vacuoles, would not qualify as organelle because they are single-membrane bounded cytoplasmic structures.
What is lysosome made of?
Lysosomes are composed of lipids and proteins, with a single membrane covering the internal enzymes to prevent the lysosome from digesting the cell itself.
Are lysosomes in all cells?
Lysosomes are found in all animal cells, but are most numerous in disease-fighting cells, such as white blood cells. This is because white blood cells must digest more material than most other types of cells in their quest to battle bacteria, viruses, and other foreign intruders.
Is the lysosome a plant or animal cell?
animal cellsCentrosomes and lysosomes are found in animal cells, but do not exist within plant cells. The lysosomes are the animal cell's “garbage disposal”, while in plant cells the same function takes place in vacuoles.
How is the structure of a lysosome related to its function?
The general structure of a lysosome consists of a collection of enzymes surrounded by a single-layer membrane. The membrane is a crucial aspect of its structure because without it the enzymes within the lysosome that are used to breakdown foreign substances would leak out and digest the entire cell, causing it to die.
Is a cytoplasm a structure or function?
The cytoplasm is an integral part of both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and functions to house and maintain an optimal environment for the cellular organelles. Organelles of cytoplasm carry out complex metabolic reactions which include protein synthesis and energy production.
What is the structure of vacuoles?
Vacuoles have a simple structure: they are surrounded by a thin membrane and filled with fluid and any molecules they take in. They look similar to vesicles, another organelle, because both are membrane-bound sacs, but vacuoles are significantly larger than vesicles and are formed when multiple vesicles fuse together.
How does the lysosomes structure affect its function?
Structurally, lysosomes are like a floating garbage bag that contains enzymes capable of digesting molecules. Their external membrane is like a gateway that allows molecules inside of the lysosome without allowing the digestive enzymes to escape into the cell.
Define Lysosome.
Lysosomes are defined as sphere-shaped vesicles or sacs filled with hydrolytic enzymes that have the ability to break down almost all types of biom...
Who discovered Lysosomes?
Lysosomes were discovered by a Belgian biologist, Christian de Duve, and was awarded a Nobel Prize in Medicine or Physiology in the year 1974. He i...
What type of cells possesses lysosomes?
Only eukaryotic animal cells contain lysosomes. Prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria do not contain lysosomes or any of the other membrane-bound org...
Do plants cells have lysosomes?
Plants do not possess lysosomes; however, the role of lysosomes are undertaken by the vacuoles. Findings even suggest that vacuoles contain hydrol...
What is a lumen in a lysosome?
Lumen is the area within the membrane-bound exterior of the lysosome. It contains cellular debris suspended in hydrolytic enzymes. It is also acidi...
Why are Lysosomes known as Suicidal Bags?
The main function of lysosomes is to breakdown and recycle cellular debris, discarded cellular contents and foreign pathogens, however, the digesti...
Where are the enzymes needed by lysosomes made?
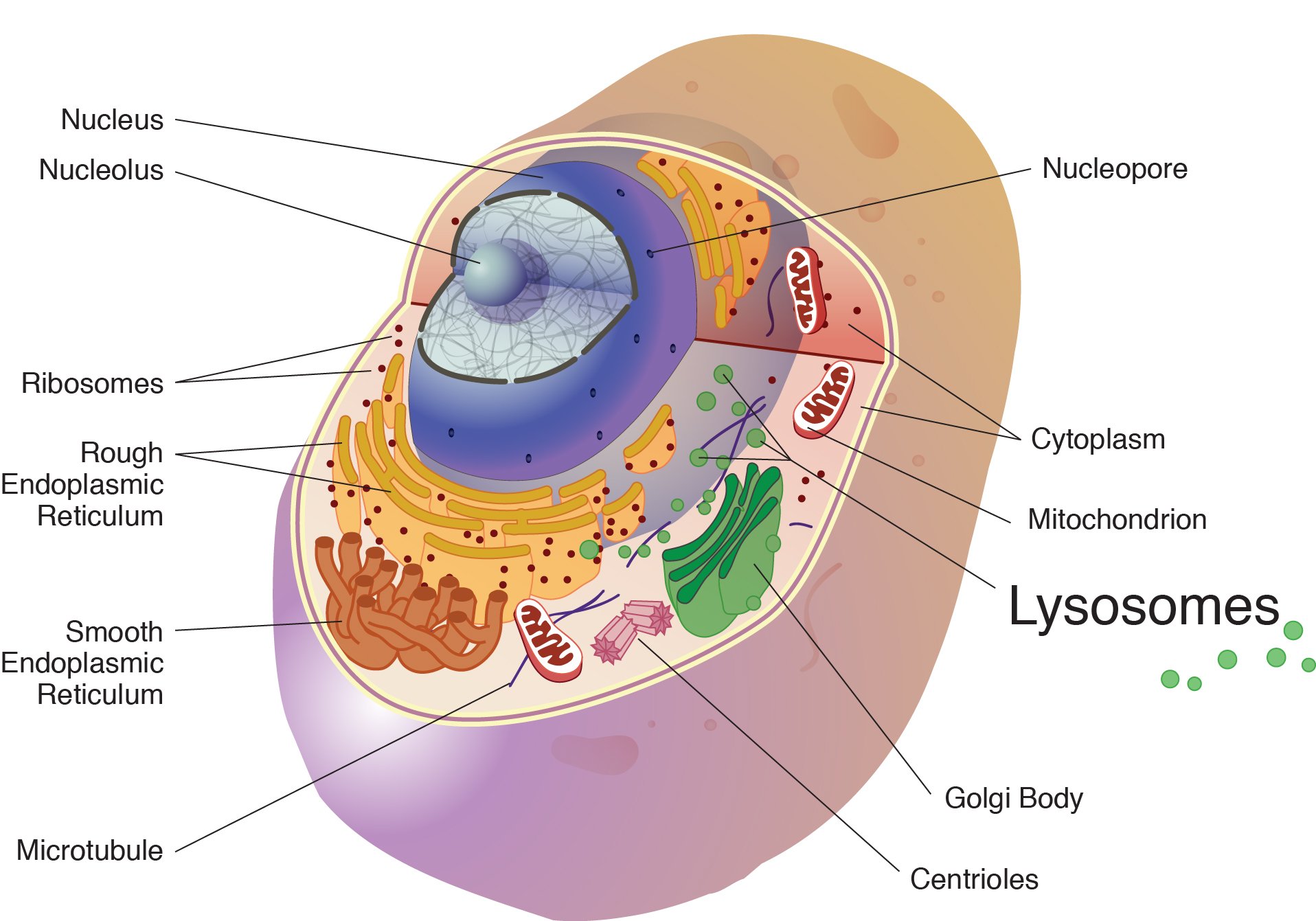
The enzymes are synthesized in the rough endoplasmic reticulum and once synthesized; the enzymes are brought in from the Golgi apparatus in tiny ve...
What are lysosomal storage diseases?
Any mutations that occur in the nuclear genes may result in over 30 diverse human genetic ailments. These ailments are collectively called lysosoma...
Why Are Lysosomes Acidic?
The acidic nature of the fluid inside the lysosome serves two purposes.
What happens if a lysosome leaks?
Should the lysosome rupture or leak, the acidic fluid is rapidly neutralized, and the lysosomal enzymes and other digesting chemicals will no longer be effective and will not attack healthy cell structures. Maintaining the acidic pH inside the lysosome is therefore critical for its function and for cell protection.
What is the structure of lysosomes?
The Structure of Lysosomes. Lysosomes are round membrane-bound organelles with a single outer lysosomal membrane. The membrane is impervious to the acidic contents of the lysosome. This protects the rest of the cell from the digestive enzymes inside the membrane.
How does the lysosome maintain pH?
The lysosome accomplishes this by using chemical reactions with proton pumps on its surface and inside the membrane to transfer hydrogen ions or protons across the membrane and into the interior.
How do lysosomes help with disease?
When foreign pathogens such as bacteria enter a cell, the lysosomes can help neutralize them by digesting them. In this way they help with an organism's immune response.
What is a lysosome?
Lysosomes are like small cell stomachs: they digest waste and superfluous cell fragments.
What breaks down large structures and molecules into simple components?
The digestive enzymes of their acidic interior break down large structures and molecules into simple components, and they then return the products to the cell for further use or disposal.
How do lysosomes form?
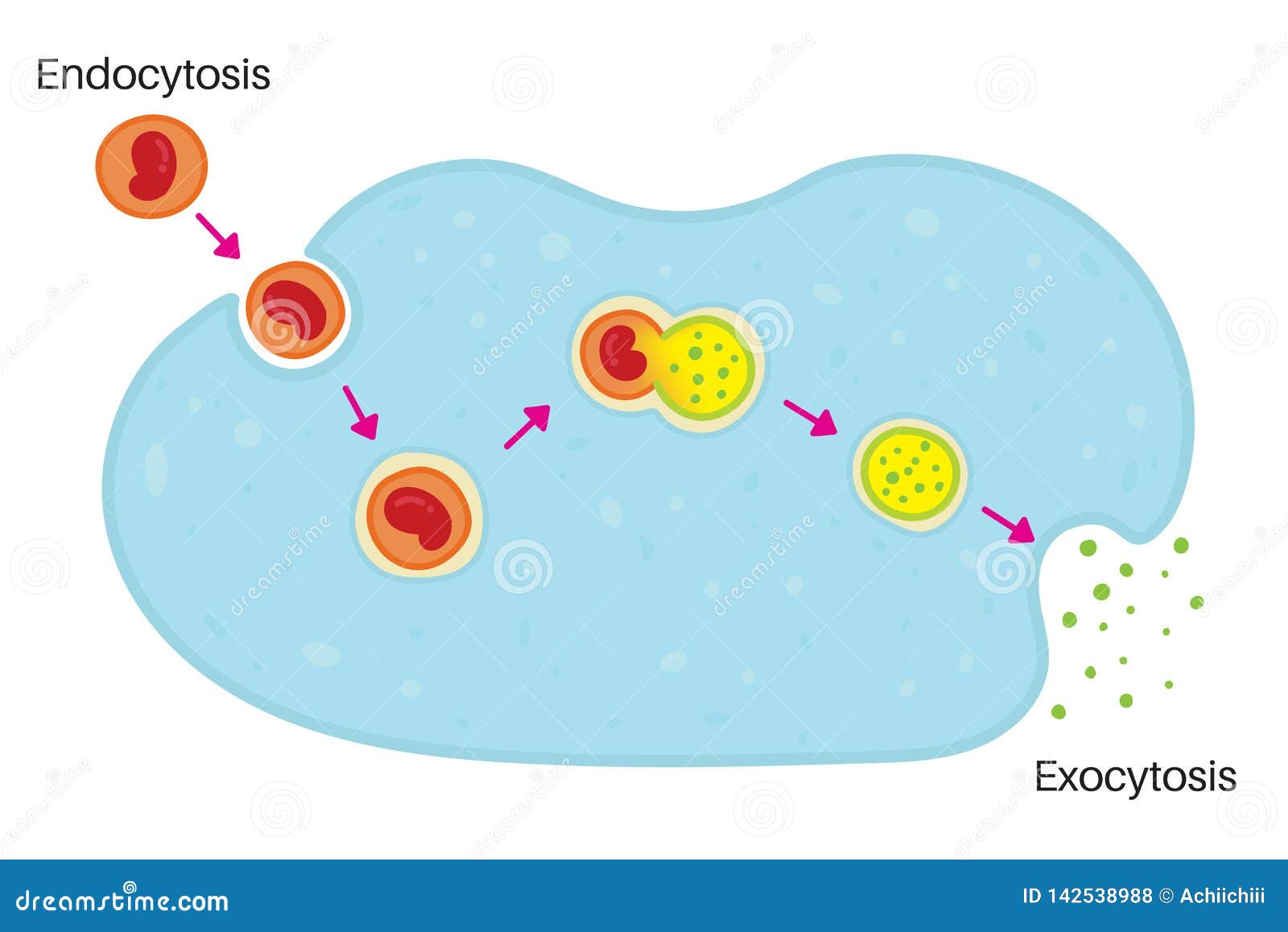
Lysosomes form by budding off from the membrane of the trans-Golgi network. Macromolecules (i.e., food particles) are absorbed into the cell in vesicles formed by endocytosis. The vesicles fuse with lysosomes, which then break down the macromolecules using hydrolytic enzymes. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. Britannica Quiz.
Why are hydrolytic enzymes segregated in the lysosomes?
Potentially dangerous hydrolytic enzymes functioning in acidic conditions (pH 5) are segregated in the lysosomes to protect the other components of the cell from random destruction. Lysosome s are bound by a single phospholipid bilayer membrane. They vary in size and are formed by the…
What happens when lysosomes rupture?
All this produces an ionic milieu unsuitable to the survival of the nucleus. Loss of the cell’s capacity to synthesize protein is the ultimate…
What are the products of lysosomal digestion?
Many of the products of lysosomal digestion, such as amino acids and nucleotides, are recycled back to the cell for use in the synthesis of new cellular components. Illustration showing the fusion of a lysosome (upper left) with an autophagosome during the process of autophagy.
What is lysosomal storage disease?
Lysosomal storage diseases are genetic disorders in which a genetic mutation affects the activity of one or more of the acid hydrolases. In such diseases, the normal metabolism of specific macromolecules is blocked and the macromolecules accumulate inside the lysosomes, causing severe physiological damage or deformity.
What is Hurler syndrome?
Hurler syndrome, which involves a defect in the metabolism of mucopolysaccharides, is a lysosomal storage disease. The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica This article was most recently revised and updated by Kara Rogers, Senior Editor.
What is the function of lysosomes?
Lysosome, subcellular organelle that is found in nearly all types of eukaryotic cells (cells with a clearly defined nucleus) and that is responsible for the digestion of macromolecules, old cell parts, and microorganisms. Each lysosome is surrounded by a membrane that maintains an acidic environment within ...
What Are Lysosomes?
Lysosomes are spherical membranous sacs of enzymes. These enzymes are acidic hydrolase enzymes that can digest cellular macromolecules. The lysosome membrane helps to keep its internal compartment acidic and separates the digestive enzymes from the rest of the cell. Lysosome enzymes are made by proteins from the endoplasmic reticulum and enclosed within vesicles by the Golgi apparatus. Lysosomes are formed by budding from the Golgi complex.
How do macrophages destroy cells?
These cells destroy bacteria, dead cells, cancerous cells, and foreign matter through cell digestion. Macrophages engulf matter by phagocytosis and enclose it within a vesicle called a phagosome. Lysosomes within the macrophage fuse with the phagosome releasing their enzymes and forming what is known as a phagolysosome.
What is the process of endosomes?
Endosomes are vesicles that are formed by endocytosis as a section of the plasma membrane pinches off and is internalized by the cell. In this process, extracellular material is taken up by the cell. As endosomes mature, they become known as late endosomes.
Why is the inside of a lysosome acidic?
The inside of a lysosome is kept acidic as the enzymes within work best in an acidic environment. If a lysosome's integrity is compromised, the enzymes would not be very harmful in the cell's neutral cytosol.
Where are lysosomes made?
Lysosome enzymes are made by proteins from the endoplasmic reticulum and enclosed within vesicles by the Golgi apparatus. Lysosomes are formed by budding from the Golgi complex.
What enzymes produce hydrogen peroxide?
Peroxisome enzymes produce hydrogen peroxide as a by-product. Peroxisomes are involved in at least 50 different biochemical reactions in the body. They help to detoxify alcohol in the liver, form bile acid, and break down fats.
What is the function of lysosomes?
Lysosome Function. Lysosomes act as the "garbage disposal" of a cell. They are active in recycling the cell's organic material and in the intracellular digestion of macromolecules. Some cells, such as white blood cells, have many more lysosomes than others. These cells destroy bacteria, dead cells, cancerous cells, ...
How do the Lysosome function?
The key function of lysosomes is digestion and removal of waste. Cellular debris or foreign particles are pulled in to the cell through the process of endocytosis. The process of endocytosis happens when the cell membrane falls in on itself (invagination), creating a vacuole or a pouch around the external contents and then bringing those contents into the cell.
Where are Lysosomal Enzymes made?
Lysosomes comprise of over 50 different enzymes. They are synthesized in the rough endoplasmic reticulum.
What causes a cell to die?
But sometimes, the digestive enzymes may end up damaging the lysosomes themselves, and this can cause the cell to die. This is termed as autolysis, where “ auto ” means “ self ” and “ lysis ” means “ the disintegration of the cell by the destruction of its cell membrane “. Hence, lysosomes are known as “Suicidal Bags” of the cell.
What is the area within the membrane called?
Lysosomes are membrane-bound organelles and the area within the membrane is called the lumen, which contains the hydrolytic enzymes and other cellular debris.
How do lysosomes work?
As stated before, lysosomes work as the waste discarding structures of the cell by processing undesirable materials and degrading them, both from the exterior of the cell and waste constituents inside the cell.
What is the process of removing waste from the cell?
On the other hand, discarded wastes and other substances originating from within the cell is digested by the process of autophagocytosis or autophagy. The process of autophagy involves disassembly or degradation of the cellular components through a natural, regulated mechanism.
How big are lysosomes?
The sizes of lysosomes vary, with the largest ones measuring in more at than 1.2 μm.
What are the properties of lysosomes?
Most of the properties of lysosomes are shared with a group of cell type-spe …. Lysosomes are membrane-bound cytoplasmic organelles involved in intracellular protein degradation. They contain an assortment of soluble acid-dependent hydrolases and a set of highly glycosylated integral membrane proteins. Most of the properties of lysosomes are shared ...
What are lysosomes?
Lysosomes are membrane-bound cytoplasmic organelles involved in intracellular protein degradation. They contain an assortment of soluble acid-dependent hydrolases and a set of highly glycosylated integral membrane proteins. Most of the properties of lysosomes are shared with a group of cell type-specific compartments referred to as ...
What does lysosome look like?
Lysosomes are present in almost all eukaryotic cells except red blood cells. Lysosomes locate in the cytoplasm. They display considerable variation in size and shape. In regular cells, lysosomes are spherical bodies about 50-70 nm in diameter. Several hundred lysosomes may be present in a single animal cell. These lysosomes are too small to be seen under a regular light microscope. Electron microscope or fluorescence microscope are required to observe and study lysosomes.
How do lysosomes maintain pH?
To maintain their acidic internal pH, lysosomes must actively concentrate H+ ions (protons). This is accomplished by a proton pump (called v-ATPase) embedded in the lysosomal membrane. The proton pump actively transports protons into the lysosome from the cytosol and requires an expenditure of energy in the form of ATP hydrolysis, since it maintains approximately a hundredfold higher H+ concentration inside the lysosome.
What is the process of lysosomes?
Lysosome formation (or biogenesis) represents an intersection between the secretory pathway, through which lysosomal proteins are processed, and the endocytic pathway, in which extracellular molecules are taken up at the cell surface. Material from outside the cell is taken up by endocytosis and packed into endocytic vesicles, which bud from the plasma membrane and then fuse with early endosomes. The early endosomes gradually mature into late endosomes, which are the precursors to lysosomes. During endosome maturation, the internal pH is lowered to about 5.5, which plays a key role in delivering lysosomal acid hydrolases from the trans-Golgi network.
How do lysosomes work?
Lysosomes act as the waste disposal system of the cell by digesting materials from both inside and outside the cell. Material from outside the cell is taken-up through endocytosis or phagocytosis, while material from the inside of the cell is digested through autophagy.
How many enzymes are in lysosomes?
Lysosomes contain about 50 different degradative enzymes that can hydrolyze proteins, DNA, RNA, polysaccharides, and lipids. The product of lysosome digestion can be recycle back for cell to build new organelles.
Why is the lysosome important?
The membrane surrounding the lysosome is vital to ensure these enzymes do not leak out into the cytoplasm and damage the cell from within. Several proteins are embedded in the lysosome’s membrane, including v-ATPase that pumps protons into the lysosome to acidify its pH value.
What are the functions of plant vacuoles?
Some vacuoles contain their own hydrolytic enzymes and perform the classic lysosomal activity , which is equivalent to autophagy. These vacuoles are therefore seen as fulfilling the role of the animal lysosome.