
Full Answer
What is the thickness of a timber wall?
In the UK the most common timber for internal timber stud walls is a 3x2. That means the wall will be the thickness of the timber plus the sheeting on either side. Usually 12mm plasterboard - so a total thickness of around 100mm.
What is a lightweight timber wall frame?
Used in both detached and multi-residential buildings, lightweight timber construction offers flexibility and a wide range of cost effective design options. Timber wall frames are typically either 90 or 70mm deep with 35 or 45mm thick studs (depending on load and spacing) spaced at 450 or 600mm centres.
How thick is a standard wall in a house?
Standard Interior Wall Thickness If the walls of your home are made from standard construction, i.e., a wooden frame and drywall, then the width of the walls will be predetermined by the construction method. In standard homes, interior walls are framed with 2-by-4 timber, which will have a width of three and a half inches.
How thick should plasterboard be on a wall?
Usually 12mm plasterboard - so a total thickness of around 100mm. External timber framed walls are generally framed in 6x2 though more and more I’m getting ones done in 8x2 to enable more insulation to be included. Total thickness will depend on the finish cladding on the outside.
How thick are the walls on a timber frame?
70mm thick timber walls 70mm thick walls are required for timber buildings that will be used all year round. If you're planning to spend time in a timber garden building regardless of the weather, 70mm timber is ideal – it's dense enough to keep in the heat even when it's snowing, sleeting or hailing outside.
How thick is a wooden exterior wall?
However, the standard thickness of ICF exterior walls is 12 inches, reducing room sizes and minimizing the home's square footage. To maintain the original square footage of a building plan, you must increase the overall dimensions of the house, which also impacts the design of the roof and foundation.
What is the thickness a framed wall?
Most interior walls are constructed with 2-by-4 framing, and each 2-by-4 has a nominal width of 3 1/2 inches. Drywall typically covers both sides, and it's usually 1/2 inch thick, which makes the wall 4 1/2 inches thick. Door jambs are typically milled to this width so the edges of the jabs come flush with the walls.
How thick are wood wall studs?
Wooden walls studs are more common and less expensive than steel studs. They generally come in two dimensions: 1-1/2 in. x 3-1/2 in. (called two-by-fours), or 1-1/2 in.
How thick should outside walls be?
External walls are generally 10 to 12 inches wide. Homes that are built with rammed earth or heavy exterior masonry will have thicker walls. There is no limit to how thick an exterior wall can be.
How thick are external house walls?
A solid brick wall is usually about 22 cm thick, a cavity wall between 27 cm and 30 cm thick, and a solid stone wall could be as much as 50 cm.
What thickness should walls be?
A 4.5-inch thick brick wall is provided for partition walls only and should not be more than 7 feet in height. Therefore I recommend that all the walls should be at least 9 inch thick. 4.5-inch thick walls are not structurally safe if they are beyond 7 feet in height or carry some imposed load.
How thick is a wall in MM?
Typically, the wall thickness will be in the range 0.5 mm to 4 mm. In specific cases, wall thicknesses that are either smaller or bigger also occur.
How thick is a 2x4 wall?
about 4½ inchesTypical interior walls are framed with 2x4s. This makes walls about 4½ inches thick (3½ inches of wood covered on both sides by ½-inch-thick drywall).
How thick should a stud wall be?
5 inchesHow thick is a stud wall? Timber stud walls are usually just over 5 inches in thickness. This includes the combined thickness of your studs (either 70 or 100mm), two plasterboard sheets (each 12.5mm in thickness) and the skim plaster finishes.
How thick is a standard stud?
Studs are vertical boards -- they are generally 2 x 4's, although they actually measure 1 1/2 inches thick and 3 1/2 wide -- and are installed at intervals inside a wall to strengthen it and support the wallboard, paneling or plaster.
How thick is a load-bearing wall?
The minimum thickness of interior load-bearing walls shall be 8 inches (203 mm). The unsupported height of any wall constructed of adobe units shall not exceed 10 times the thickness of such wall.
What is the thickness of wood siding?
They are historically around 3/4″ thick and come in varying widths. Some of the most popular are 6″ and 8″ widths.
How thick is a 2x6 exterior wall?
2x6 width: 5 ½ inches. Wall surface thickness on each side: ½ inches.
How thick is a 2x4 wall?
about 4½ inchesTypical interior walls are framed with 2x4s. This makes walls about 4½ inches thick (3½ inches of wood covered on both sides by ½-inch-thick drywall).
What plywood is used for exterior walls?
Exterior plywood is weather (and water) resistant, so it's strong enough to be used outside and also in areas that are exposed to water and humidity, like a garage. This type of plywood, often made from Douglas fir, is made stronger by adhering its layers with a waterproof glue.
What is a timber frame home?
Besides adding an eye-catching, classic appearance to your home, timber frame construction offers homeowners extended design opportunities. Compared to other building methods, timber-framed homes are often open-concept and spacious, enabling you to design your home's interior as much as you wish. Yellowstone Timber Frame can fully customize your dream floor plan to make your dreams come true!
How long does it take to build a timber frame?
Fabrication of a timber frame structure usually takes between two to three months depending on the wood species, beam sizes, and the project’s overall scale. It’s also important to note that installation will likely take two to six weeks including installation of Structural Insulated Panels (SIPS) on your home.
How long do timber frames last?
Timber framing is renowned for being one of the most durable building methods available, as timber frame homes can last up to three times longer than conventional houses (over 100 years!).
What are the two main categories of timber homes?
Builders and buyers alike will find that the majority of timber homes fall into one of these two major categories: timber frame and post-and-beam. While both of these methods are capable of crafting beautiful and reliable houses, some key differences separate the two — primarily concerning how each process fastens its joinery system together.
What is the difference between a timber frame and a post and beam?
For instance, post-and-beam homes will utilize metal fasteners to hold the frame’s components together. In contrast, timber frame homes will primarily employ wooden pegs to achieve this. As such, each method will result in a unique look that can very well change the entire appearance of your home’s interior.
How does a frame construction work?
The process occurs by raising and connecting bents one at a time with horizontal beams. Once the frame has been fully raised and tested to be secure and structurally sound, construction will be marked as complete with a symbolic final nail into the frame’s highest point.
What is the most popular wood framing?
The most popular wood types are red and white oak, white pine, Douglas fir, cypress and cedar.
How thick should a house be for a 70 foot wall?
For properties that measure up to 70 feet in height, it is recommended that the exterior walls be no thicker than twelve inches. For every additional 70 feet of height added onto the property, the wall thickness can be increased by an extra four inches to support the additional weight of the structure. However, there are no set rules on how thick ...
How wide is a wall?
In standard homes, interior walls are framed with 2-by-4 timber, which will have a width of three and a half inches.
How thick is a door jamb?
This is the standard width for walls in wooden construction residential properties, and as a result, standard interior door jambs are produced at a width of four and a half inches so that they fit flush with the walls.
How thick is a cavity wall?
This makes the total thickness of brick-built cavity walls around 9 and a quarter inches thick, but on top of this, the interior of the room will be plastered or fitted with drywall which will add up to an additional half inch. These types of walls are known for being very energy-efficient, as well as preventing moisture from entering the property.
How thick is cement board for a bathroom?
Greenboard is generally ⅝ inches thick, which again will increase the thickness of a wall in a bathroom. However cement board can be purchased in a variety of thicknesses, including a quarter-inch, half an inch, ⅜ of an inch, and ⅝ of an inch.
Why is there no standard measurement for exterior walls?
When it comes to the width of exterior walls, there is no standard measurement because the total width will be determined by the siding on the property. In some instances, you might be interested in intentionally adding width to your home by choosing a chunky or thick type of siding. Extra thick exterior walls can offer numerous benefits, such as creating additional room for insulation and soundproofing. If you live in a cold climate, then extra-thick external walls can help to keep your home warm by offering better insulation.
What is a cavity wall?
Cavity walls are built as the external walls on modern brick-built homes. These are especially common in the United Kingdom and other areas of Europe. The wall is made up of three ‘layers.’. The inner layer closest to the interior of the property will be the width of a brick, which is 3 and ⅝ inches as standard.
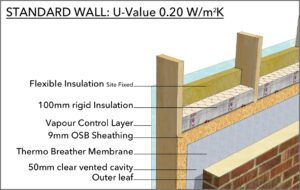
What is the requirement for fire resistance in a timber frame wall?
A half hour fire resistance in domestic external walls is required by the Building Regulations. Timber frame walls filled with mineral wool insulation are ideal for meeting this requirement. In most timber frame constructions, cavity barriers must be used to divide up the external cavity in order to reduce the risk of fire spread.
Why do you need a vapour control layer?
A vapour control layer is essential on the ‘warm’ side of the insulation to reduce the risk of condensation forming within the timber frame. Joints should be as few as possible and sealed, with special care taken around penetrations for services.
Why do you need a vapour membrane on the outside of a sheathing board?
A vapour permeable membrane on the outside of the sheathing board is also necessary to protect the timber frame from water penetration whilst allowing water vapour to escape. As a rule of thumb, the vapour resistance of the materials on the ‘warm’ side of the insulation should have at least five times the vapour resistance ...
Why do we need cavity barriers?
In most timber frame constructions, cavity barriers must be used to divide up the external cavity in order to reduce the risk of fire spread.
What is the most environmentally friendly construction method?
Timber frame is also widely recognised as the most environmentally friendly construction method – a construction with extremely low ‘embodied energy’. This is the energy required to manufacture a building component or material, deliver it to site and install or construct it.
Why is prefabrication important?
Pre-fabrication enhances quality control due to off site manufacture, thereby reducing the risk of on-site workmanship problems
Which is better, a timber frame or a masonry wall?
Insulated external timber frame walls can provide better insulation performance than masonry walls of comparable thickness. Find out more technical details on our dedicated page today.
What is timber frame?
In simple terms, a timber frame building uses timber studs within the external structural wall to carry the loads imposed before transmitting them to the foundations. Timber frame buildings include the walls, floors and roofs, which are designed as a whole, coherent engineered structure.
What are the Advantages of Timber Frame Construction?
Responsibly sourced timber is an eco-friendly building material and there's less material wastage with this kind of build
Should I Choose an Open or Closed Panel Timber Frame System?
Open panels are manufactured ready for external joinery (doors and windows) to be placed, and are delivered to site together with flooring elements and roof trusses. Once the frame erectors have finished, work can commence both inside and outside the house.
What are the Design Restrictions in Timber Frame Construction?
From a self build point of view, provided you’re not trying to build with timber below ground, timber frame is almost always an appropriate build method. The unsuitability of timber frame is mostly to do with the scale of buildings. For example, a timber frame building over five storeys high or 18m is a big no-no.
How to keep a timber frame home comfortable?
Timber frame will offer less in the way of thermal mass so your designer will need to consider how to prevent overheating. Installing a brise soleil, shutters or retractable awning can be useful design choices to keep your timber frame home comfortable all year round.
Why are stick built timber frames so slow to build?
The problem with stick built timber frame is that because they’re built on site, mostly just following custom and practice principles rather than engineered design, the structures are inefficient and slow to build.
What is external cladding?
External cladding and cavity (brick, render, composite or timber boarding etc) to provide weather resistance.
How deep are timber frames?
Timber wall frames are typically either 90 or 70mm deep with 35 or 45mm thick studs (depending on load and spacing) spaced at 450 or 600mm centres.
What is lightweight timber?
Lightweight timber construction typically comprises framed and braced structures to which cladding is applied. Used in both detached and multi-residential buildings, lightweight timber construction offers flexibility and a wide range of cost effective design options.
How thick are top and bottom plates?
Top and bottom plates are typically 90x45mm and can be doubled (in thickness) depending on the load or the spacing of the supporting floor members. Insulation is typically placed between the structural elements (e.g. studs, plates and noggings).
What is the outside skin of a steel box?
the outside skin is going to be box profile steel sheet
What is the best insulation per £?
The best insulation per £ is rock or mineral wool. That's why it's used in lofts, where it can be as deep as you like.
Is SIPs more expensive than stick boards?
I expect SIPs will be much more costly than building your own stick/board frame. Plus it sounds like a pain getting big prefab panels into the barn.
Do you need a U value for wall insulation?
The building regulations don't specify a wall thick ness per se , but they do require a certain insulation value (U Value). Different materials have better or worse insulating properties so the eventual thickness depends on what you use. Normally you would set a target U value and then work to that. Just to throw out a very rough number, I think you ...
Do timber framed houses have a rain screen?
The traditional timber framed houses up here have a brick or block outer skin, but because the cavity has to be ventilated, the outer skin adds very little to the insulation, and is just an expensive rain screen.
Do you need more insulation than the building regs minimum?
You will find a lot of people (especially on this forum anyway) will tend to specify more insulation than the building regs minimum. In my own house, I have aimed to put my money into the building fabric and then spend less on the heating system. This can be a good tradeoff as insulation is a one-off cost, unlike running your heating.
