What is the average size of human hair in nanometers?
The width of a human hair is approximately 75,000 nm. Objects that small require scanning electron microscopy to be seen. A sheet of toilet paper, which is so precious these days, is about 100,000 nanometers thick.
How many microns thick is a human hair?
Denny & Gayle Rossbach. Palmdale, CA. “Diameter of a human hair inches: 0.001; centimeters: 0.00254” 25.4 µm. Likewise, How thick is a human hair in microns? approximately 70 microns. Also, Does thick hair mean more hair? As it turns out, just because your ponytail is extra full, it doesn’t automatically mean your hair is thick.
How long is your hair to the nearest nanometer?
It helps to put these numbers into perspective. A human hair is around 75 microns (abbreviated 75μm) or 75,000nm (nanometers) in diameter. The relationship between a nanometer and that hair is similar to the relationship between one mile and an inch - one mile is 63,360 inches.
How many toes does a normal human have?
There are five toes present on each human foot. Each toe consists of three phalanx bones, the proximal, middle and distal, with the exception of the big toe (Latin: Hallux). The hallux only contains two phalanx bones, the proximal and distal. 8 clever moves when you have $1,000 in the bank.
See more
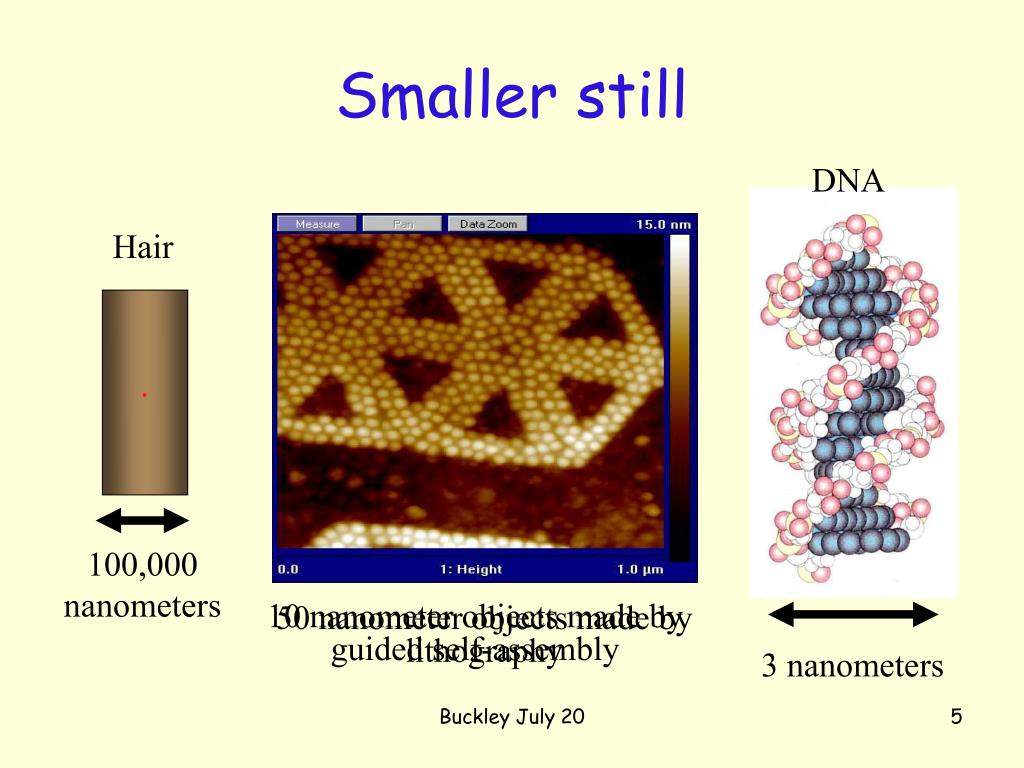
What objects are 10 nanometers?
Most proteins are about 10 nanometers wide, and a typical virus is about 100 nanometers wide. A bacterium is about 1000 nanometers. Human cells, such as red blood cells, are about 10,000 nanometers across.
How wide is 1 nanometer?
A nanometer is one billionth of a meter, 0.000000001 or 10-9 meters. The word nano comes from the Greek word for “dwarf.” The term nanoscale is used to refer to objects with dimensions on the order of 1-100 nanometers (nm).
How thick is a strand of hair in nm?
about 80,000 to 100,000 nanometers wideA strand of hair is about 80,000 to 100,000 nanometers wide. A sheet of paper is 100,000 nanometers thick. An ant is 5 million nanometers long. The human hand is 100 million nanometers long.
How big is a nanoparticle compared to a human hair?
One strand of human hair is about 50 to 100 micrometers thick. One nanometer is 1/1000 of a micrometer. A nanoparticle is 100 nanometers thick.
Whats smaller than a nano?
Anyway, smaller than nano? Of course… here's the full list of prefixes that define the thousandths and millionths and billionths of nano… pico (million-millionth), femto (million-billionth), atto (billion-billionth), zepto (billion-trillionth), yocto (trillion-trillionth).
What's smaller than a Picometer?
A nanometer is 1,000 times smaller than a micrometer. In other words, one micrometer (μm) is 1,000 nanometers. Is a centimeter bigger than a nanometer?...The Metric Table.MetricPowerFactorMillimeter (mm)10-30.001Micrometer (μm)10-60.000 001Nanometer (nm)10-90.000 000 001Picometer (pm)10-120.000 000 000 00113 more rows•Jul 30, 2021
What is the thickest human hair?
0.03 inchesThe thickest strand of human hair is 772 micrometres (0.03 inches) and was plucked from the beard of Muhammad Umair Khan (Pakistan), in Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan, as verified on 3 March 2021.
What is something that is 700 nm?
Red light has a wavelength of ~700 nm, and a frequency of ~4.3*1014 Hz.
How wide is a human hair in microns?
A human hair is approximately 70 microns, give or take 20 microns depending on the thickness of a given individual's hair. This is about three times the size of a trace or space on one of Benchmark Lark Technology's high-density circuits.
How wide is human hair?
between 17 and 180 micrometersHuman hair widths are generally between 17 and 180 micrometers, and the hairs from Science News fall nicely into that distribution, though they appear to be a bit thinner than average. Try it yourself!
What is the width of a human hair in MM?
about 0.016 to 0.05mmMeasured in millimeters, the average human hair is about 0.016 to 0.05mm thick. This number is affected by the various characteristics of your natural strands.
What is the diameter of a human hair?
17 μm to 181 μmThis measurement is not precise because human hair varies in diameter, ranging anywhere from 17 μm to 181 μm. One nominal value often chosen is 75 μm, but this – like other measures based upon such highly variable natural objects, including the barleycorn – is subject to a fair degree of imprecision.
Can you see a nanometer?
So small you cannot see something a nanometer in size unless you use very powerful microscopes like atomic force microscopes. A nanometer is used to measure things that are very small. Atoms and molecules, the smallest pieces of everything around us, are measured in nanometers.
How many atoms wide is a nanometer?
There are about 20 atoms along this line, so one nanometer is about the width of 2 silicon atoms, and the gate length of a 20nm NAND flash chip would be 40 atoms across.
Which is bigger 1 nm or 10 nm?
'Nano' is a prefix (goes at the beginning of a word) and refers to a measurement of 10-9 or 0.000000001. 'Scale' in this context means length. The standard measure of length in science is in meters (m). One nanometer (1 nm) is equal to 10-9 m or 0.000000001 m.
How small is 7nm?
What is 7-nanometer? When used in relation to stuff like CPUs and video cards, the term 7-nanometer refers to the size of the transistors involved. The smaller the transistor, the more you can fit onto a piece of silicon and the more powerful and complex that the components built from these transistors are able to be.
How many nanometers are there in a meter?
In the International System of Units, the prefix "nano" means one-billionth, or 10 -9; therefore one nanometer is one-billionth of a meter. It’s difficult to imagine just how small that is, so here are some examples: A sheet of paper is about 100,000 nanometers thick. A strand of human DNA is 2.5 nanometers in diameter.
How big is a gold atom?
A single gold atom is about a third of a nanometer in diameter. On a comparative scale, if the diameter of a marble was one nanometer, then diameter of the Earth would be about one meter. One nanometer is about as long as your fingernail grows in one second.
How thick is a sheet of paper?
A sheet of paper is about 100,000 nanometers thick. A strand of human DNA is 2.5 nanometers in diameter. There are 25,400,000 nanometers in one inch. A human hair is approximately 80,000- 100,000 nanometers wide. A single gold atom is about a third of a nanometer in diameter.
How big is human hair?
A human hair is around 75 microns (abbreviated 75μm) or 7 5,000nm (nanometers) in diameter. The relationship between a nanometer and that hair is similar to the relationship between one mile and an inch - one mile is 63,360 inches.
What is a nanometer?
Nanometers are the way that Silicon Valley measures chip real estate. Technologists throw around the term: "nanometers" as if it were commonplace. But one billionth of a meter might be as abstract to many as is a trillion-dollar national deficit. What would be more useful would be a definition in terms that relate to the everyday world.
How many atoms are in a 20nm NAND chip?
There are about 20 atoms along this line, so one nanometer is about the width of 2 silicon atoms, and the gate length of a 20nm NAND flash chip would be 40 atoms across.
What is the nanometer in semiconductors?
Semiconductor manufacturers started to use the "nanometer" term around the beginning of this millennium when chip gate lengths had already been shrunk well below a micron. The gate length is the basic measure of how small a chip can be manufactured.
How big is one billionth of a meter?
It helps to put these numbers into perspective. A human hair is around 75 microns (abbreviated 75μm) or 75,000nm (nanometers) in diameter.
Why is hair important?
The purpose of hair is protective: the hairs on the body keeps a person warm, nose hairs prevent dust and dirt from entering the respiratory system, and eyebrows prevent sweat from entering the eyes. The diameter of a human hair does not have a standard value since different people have different hair structures.
What is the coarsest hair?
CAQTI Cosmetics, Inc. "Flaxen hair is the finest, from 1/1500 to 1/500 of an inch in diameter … and black hair is the coarsest, from 1/450 to 1/140 of an inch.". Hair can be found all over human body, except for the palms of hands and at the soles of feet.
How does weather affect hair?
The weather can also affect the diameter of a hair strand. As the weather gets warmer, the diameter of body hair increases. Age is another factor. Babies and young children have finer hair than adults. As a person grows up, their hair becomes thicker and stronger.
What are the occupational exposure limits for nanomaterials?
Examples of the latter are: crystalline silica, and carbon black. NOTE: NIOSH has draft recommended exposure limits (RELs) for : • 1.5 mg/m3fine TiO
How are humans exposed to nanoparticles?
Humans have always been exposed to nanoscale particles via dust storms, volcanic eruptions, and other natural processes. Human activity and technological advancement has increased the variety of nanoparticles to which we are exposed. While the body is well adapted to protect itself from exposure to tiny particles, and the vast majority cause little ill effect, some can cause appreciable harm and many have chronic effects that may take years to develop.
What is an engineer nanoparticle?
Engineered nanoparticles, that is, intentionally cr eated – in contrast with natural or incidentally formed – engineer ed nanomaterials with dim ensions of less than 100 nanometers. This definition excludes biomolecules (proteins, nucleic acids, and carbohydrates) and materials for which an occupational exposure limit (OEL), national consensus, or regulat ory standard exists. Nanoscale forms of radiological materials are also excluded from this definition.
What are the drivers of nanoparticle toxicity?
10. Drivers of nanoparticle toxicity include: 1. Intrinsic elemental (chemical) toxicity– For usually soluble materials, individual atoms may or ions may interfere with biological systems.
Why are we most concerned with unbound nanoparticles?
We are most concerned with unbound nanoparticles because they are capable of being dispersed. Routes of occupational exposure to free nanoparticles can occur by inhalation, skin absorption or inges tion, and we are most concerned about inhalation where their small size allows nanoparticles to deposit in the head airways and reach deep into the lungs. 9
Is a nanoparticle bound or unbound?
An engineered nanoparticle disper sed and fixed within a polymer matrix, incapable, as a practical matter, of becoming airborne, would be “bound”, while such a particle suspended as an aerosol or in a liquid would be “unbound”.
Is nanoparticle toxic?
The toxic potential of novel nanoparticles is not easily characterized and it is difficult to generalize. A wide range of chemistries are used in nanoparticle production, especially for research purposes, and the pot ential structures ar e almost unlimited. The photomicrographs above show various morphologies of zinc oxide, each one of which may have a different potential toxicity. 10