What are some fungi like protists?
Examples of Fungus-like Protists
- Slime Molds. Slime molds are often found on rotting logs, where they feed on decaying organic matter. ...
- Water Molds. Water molds usually live on the surface of water, or in damp soil and, like slime molds, feed on decaying organic matter.
- Plant-like Protists. ...
What is the difference between fungi and protists?
Nutrient Sources & Nutrient Acquisition Strategies
- Fungi Nutrient Acquisition. Fungi use mycelium, their collection of hyphae, to acquire and transport nutrients across the plasma membrane of their cells [2].
- Protist Nutrient Acquisition. ...
- Reproductive Differences. ...
- Aesexual Reproductive Differences. ...
- Sexual Reproductive Differences. ...
- Fungal Sexual Reproduction. ...
- Protist Sexual Reproduction. ...
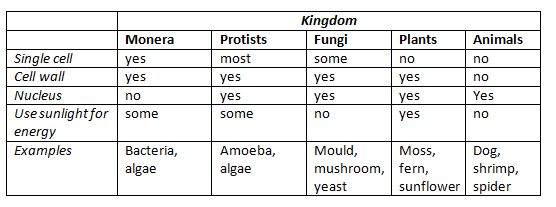
- Summarizing Table. ...
What are the four types of plant like protists?
Types of Protists
- Different Types of Protists. As mentioned above, the three broad types of protists are those that are plant-like, those that are animal-like and those that are fungus like.
- Archaeplastida. Archaeplastida consists of eukaryotic life forms that have chloroplasts which are enclosed by two membranes.
- Chromalveolata. ...
- Excavata. ...
- Rhizaria. ...
- Unikont. ...
What are four examples of plantlike protists?
What are four examples of plant like protists? Plant-like protists include algae, kelp, and seaweed. What are the major types of protists? Protists are typically divided into three categories, including animal-like protists, plant-like protists, and fungus-like protists. Protists vary in how they move, which can range from cilia, flagella, and ...
Is fungi a protist or bacteria?
Bacteria and archaea are prokaryotes, while all other living organisms — protists, plants, animals and fungi — are eukaryotes, according to the educational website tutors.com (opens in new tab). Many diverse organisms including algae, amoebas, ciliates (such as paramecium) fit the general moniker of protist.
Are fungi and Protista the same?
Fungi and Protists are lower-level entities that are categorised into the Kingdom Fungi and Kingdom Protista, respectively. Mostly, Protista are unicellular entities and fungi are multicellular. Protists have plant-like, animal-like and fungus-like species.
Are fungi and plants protists?
Many are single-celled organisms. Protists consist of animal-like, plant-like, and fungus-like species. Protists evolved into the other three types of eukaryotes, including fungi. Other than that, these two types of eukaryotes are very different.
Which organism is a fungus protist?
their lives as one-celled organisms and part of their lives as many-celled organisms. Although many are called molds, they are not the same as the molds you will read about in the next section of this chapter. Slime molds, water molds, and downy mildews are examples of funguslike protists.
Why are protists not fungi?
The main difference between protists and fungi is that protists are mainly unicellular organisms whereas fungi are mainly multicellular organisms.
What kingdom is fungi in?
Fungi are eukaryotic organisms that include microorganisms such as yeasts, moulds and mushrooms. These organisms are classified under kingdom fungi. The organisms found in Kingdom fungi contain a cell wall and are omnipresent. They are classified as heterotrophs among the living organisms.
What are the 4 protists?
Animal-like protists are also known as Protozoa. Some are also parasites. The Protozoa is often divided into 4 phyla : Amoebalike protists, flagellates, ciliates, and spore-forming protists.
What are fungus-like protists?
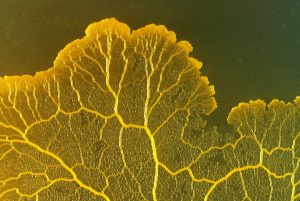
Fungus-like protists are molds. Molds are absorptive feeders, found on decaying organic matter. They resemble fungi and reproduce with spores as fungi do. Examples of fungus-like protists include slime molds and water molds.
How are fungi similar to protists?
What are fungus-like protists? They are protists that absorb their food from dead organic matter. They are grouped into 2 groups, slime molds and water molds. Most fungus-like protists use psuepods, (“false feet”) to move around.
What is not a protist?
Answer and Explanation: Bacteria do not belong to kingdom Protista. Although bacteria are unicellular, as are most protists, they are very different organisms. Bacteria...
Which do not belong to Protista?
So, the correct option is 'Methanogens'.
What are the 3 groups of protists?
For classification, the protists are divided into three groups:Animal-like protists, which are heterotrophs and have the ability to move.Plant-like protists, which are autotrophs that photosynthesize.Fungi-like protists, which are heterotrophs, and they have cells with cell walls and reproduce by forming spores.
What is the second group of fungus-like protists?
This is one of the slime molds where thousands of single cells can fuse together into one giant cell with thousands of nuclei! The second group of fungus-like protists is the water molds. The water molds are filamentous protists, which means their cells form long, strand-like structures.
Why do we call organisms protists?
Because we still like to group organisms together based on their lifestyle, calling organisms protists still comes in handy, however. The protists typically live in water or moist soil as single cells that must fend for themselves to find nutrition.
What is a slime mold?
So within the fungus-like protists, the slime molds are characterized by the ability of single cells to swarm together into groups and the ability to form spores during environmental stress. Physarum polycephalum is an example of a slime mold.
Why do slime molds form spores?
The slime molds form spores to survive environmental stress, and individual cells can aggregate to form slimes. The water molds live in wet environments and form long filament-type cells and spores much like a fungus. To unlock this lesson you must be a Study.com Member. Create your account.
How do fungi get energy?
Finally, the fungus-like protists get their energy and nutrition like a fungus does, by releasing a digestive enzyme into the environment to break down large organic molecules into pieces small enough to absorb. There are two branches within the fungus-like protists that we will discuss here.
How do plant-like protists obtain energy?
Plant-like protists obtain their energy through photosynthesis ; they are more commonly called algae. But when it comes to food, the fungus-like protists act like fungi! They release enzymes into the environment to chop up organic food molecules into pieces small enough to absorb into the cell.
What is water mold?
The water molds are filamentous protists, which means their cells form long, strand-like structures. These filaments appear similar to the growth of certain fungi, and they can also form spores like fungi. So, again, that explains the mold part of the name. Now, the water part of the name is a bit misleading.
Answer
Slime molds would be a fungus-like protist. They usually use psuedopods to move around.
New questions in Biology
If one plant cell sends a signal to another plant cell by passing a small molecule to that cell through the plasmodesmata, this would be referred to a …
What is a protist?
The term protist typically is used in reference to a eukaryote that is not a true animal,... Encyclopedia / Fungi, Protists & Viruses. Agaricales. Agaricales, order of fungi in the class Agaricomycetes (phylum Basidiomycota, kingdom Fungi).
What are some organisms that are not part of the kingdom of fungi?
There are also many funguslike organisms, including slime molds and oomycetes (water molds), that do not belong to kingdom Fungi but are often called... Ebolavirus, genus of viruses in the family Filoviridae, certain members of which are particularly fatal in humans and nonhuman primates.
What is a small polygonal virus?
They are small polygonal viruses containing... Encyclopedia / Fungi, Protists & Viruses. Hantavirus. Hantavirus, any member of a genus of viruses (Hantavirus) of the family Bunyaviridae that cause acute respiratory illnesses in humans.
What is the name of the fungus that has a fruiting body?
Mushroom. Mushroom, the conspicuous umbrella-shaped fruiting body (sporophore) of certain fungi, typically of the order Agaricales in the phylum Basidiomycota but also of some other groups. Popularly, the term mushroom is used to identify the edible sporophores; the term toadstool is often reserved for...
How many families are there in the agaric family?
One of the most diverse orders of the phylum Basidiomycota, Agaricales contains about 30 families, about 350 genera, and some 10,000 species. Traditionally, agarics were classified based on the presence of... Encyclopedia / Fungi, Protists & Viruses. Bacteriophage.
What are the major groups of microorganisms?
The major groups of microorganisms—namely bacteria, archaea, fungi (yeasts and molds), algae, protozoa, and viruses —are summarized below. Links to the more detailed articles on each of the major groups are provided.
What is the name of the virus that causes warts?
Encyclopedia / Fungi, Protists & Viruses. Human papillomavirus. Human papillomavirus (HPV), any of a subgroup of viruses belonging to the family Papovaviridae that infect humans, causing warts (papillomas) and other benign tumours as well as cancers of the genital tract, especially of the uterine cervix in women.
How do fungi and other protists get food?
Many plant-like protists, such as algae, use photosynthesis to obtain their energy from sunlight. Slime molds (seen below), for example, are fungus-like protists that degrade decomposing materials. Food must be “eaten” or ingested by the animal-like protists. Some animal-like protists feed using their “tails.”
What are the differences between protists and fungi?
Eukaryotic creatures include both protists and fungi. Many of the creatures are single-celled. Animal-like, plant-like, and fungus-like species make up the protists. The other three kinds of eukaryotes, including fungi, developed from protists. Aside from that, these two kinds of eukaryotes are very unlike.
What are the benefits of protists?
Slime molds are beneficial to ecosystems because they decompose and provide essential nutrients to the environment. Because protists provide humans with oxygen, are key players in food chains, and recycle important nutrients for other living forms to utilize, you might argue that life on Earth is dependent on them.
Fungi reproduce in a variety of ways
Fungi reproduce in an asexual manner via fragmentation, budding, or spore production. Hyphae fragments may form new colonies. When a fungal mycelium splits into fragments, each component grows into its own mycelium, this is known as mycelial fragmentation. Asexual spores come in a variety of forms.
Molds are fungi, right?
Mold (US) or mold (UK / NZ / AU / ZA / IN / CA / IE) is a fungus that develops as multicellular filaments known as hyphae. Yeasts, on the other hand, are fungi that can develop as a single-celled organism. A mycelium is a network of tubular branching hyphae that is considered a single organism.
What is the best way to categorize protists?
Animal-like, plant-like, and fungus-like protists may all be divided into three groups. The mode of reproduction, technique of feeding, and motility of an organism are used to classify it into one of three groups.
Is mold a kind of protist?
Slime molds are eukaryotic microorganisms that do not belong to the animal, plant, fungus, or bacterium kingdoms. Slime molds are a kind of protist that forms colonies and feeds on bacteria, fungal spores, and other microorganisms.
What are fungi like protists?
Fungus-like Protists. Fungus-like protists are known as molds. Like true fungi, they are heterotrophic feeders and absorb nutrients from decaying organic matter in their environment. They also reproduce using spores. However, they differ from true fungi in that their cell walls contain cellulose, rather than chitin.
What are animal-like protists called?
Animal-like Protists. Animal-like protists are called protozoa (meaning ‘first animal’). All protozoans are unicellular and heterotrophic, meaning they seek out food in their surrounding environments. Some animal-like protists prey on other, smaller microorganisms, which they engulf and digest in a process known as phagocytosis .
What is the name of the algae that glows in the ocean?
Fire algae include a group of unicellular organisms called the dinoflagellates. Some dinoflagellates are bioluminescent and can light up the surface of the ocean with an eerie, night-time glow. When present in large numbers, dinoflagellates can also cause a phenomenon known as ‘red tide.’
What do protists eat?
Some protists are heterotrophs, and feed on other microscopic organisms and carbon-rich materials they find in their surrounding environment; others are photosynthetic and make their own food using chloroplasts. Protists may be classified as animal-like, fungus-like, or plant -like.
What is the most abundant group of algae?
Green algae are the most abundant group of algae. They contain chloroplasts and cell walls and are thought to be the evolutionary ancestors of land plants. Green algae may be unicellular or multicellular.
What is the cell wall composition of yellow green algae?
Yellow-green Algae. Yellow-green algae are photosynthetic organisms that live predominantly in freshwater environments. Many have a cell wall that does not contain cellulose (as in plants and algae) or chitin (like fungi and molds). The cell wall composition of yellow-green algae is almost completely unknown.
What is brown algae?
Brown Algae. Brown algae are typically found in marine environments. They are multicellular organisms and form a variety of plant-like species. The largest known example of brown algae is the giant kelp, which often grows to over 30m in length. Giant kelp is the largest species of marine algae.

Overview
A protist is any eukaryotic organism (that is, an organism whose cells contain a cell nucleus) that is not an animal, plant, or fungus. While it is likely that protists share a common ancestor (the last eukaryotic common ancestor), the exclusion of other eukaryotes means that protists do not form a natural group, or clade. Therefore, some protists may be more closely related to animals, plants, or fun…
History
The classification of a third kingdom separate from animals and plants was first proposed by John Hogg in 1860 as the kingdom Protoctista; in 1866 Ernst Haeckel also proposed a third kingdom Protista as "the kingdom of primitive forms". Originally these also included prokaryotes, but with time these were removed to a fourth kingdom Monera.
In the popular five-kingdom scheme proposed by Robert Whittaker in 1969, Protista was defined a…
Description
Besides their relatively simple levels of organization, protists do not necessarily have much in common. When used, the term "protists" is now considered to mean a paraphyletic assemblage of similar-appearing but diverse taxa (biological groups); these taxa do not have an exclusive common ancestor beyond being composed of eukaryotes, and have different life cycles, trophic levels, modes of locomotion, and cellular structures.
Subdivisions
The term Protista was first used by Ernst Haeckel in 1866. Protists were traditionally subdivided into several groups based on similarities to the "higher" kingdoms such as:
Protozoa Protozoans are unicellular "animal-like" (heterotrophic, and sometimes parasitic) organisms that are further sub-divided based on characteristics such as motility, such as the (flagellated) Flagellata, the (ciliated) Ciliophora, the (phagocytic) amoeba, and the (spore-formin…
Classification
Among the pioneers in the study of the protists, which were almost ignored by Linnaeus except for some genera (e.g., Vorticella, Chaos, Volvox, Corallina, Conferva, Ulva, Chara, Fucus) were Leeuwenhoek, O. F. Müller, C. G. Ehrenberg and Félix Dujardin. The first groups used to classify microscopic organism were the Animalcules and the Infusoria. In 1818, the German naturalist Georg August Gol…
Metabolism
Nutrition can vary according to the type of protist. Most eukaryotic algae are autotrophic, but the pigments were lost in some groups. Other protists are heterotrophic, and may present phagotrophy, osmotrophy, saprotrophy or parasitism. Some are mixotrophic. Some protists that do not have / lost chloroplasts/mitochondria have entered into endosymbiontic relationship with other bacteria/algae to replace the missing functionality. For example, Paramecium bursaria and Paulin…
Reproduction
Some protists reproduce sexually using gametes, while others reproduce asexually by binary fission.
Some species, for example Plasmodium falciparum, have extremely complex life cycles that involve multiple forms of the organism, some of which reproduce sexually and others asexually. However, it is unclear how frequently sexual reproduction causes genetic exchange between different strains of Plasmodium in nature and most populations of parasitic protists may be clo…
Ecology
Free-living protists occupy almost any environment that contains liquid water. Many protists, such as algae, are photosynthetic and are vital primary producers in ecosystems, particularly in the ocean as part of the plankton. Protists make up a large portion of the biomass in both marine and terrestrial environments.
Other protists include pathogenic species, such as the kinetoplastid Trypanoso…