What foods contain adenine?
Mar 16, 2020 · Adenine is one of the two purine nucleobases (the other being guanine) used in forming nucleotides of the nucleic acids. In DNA, adenine binds to thymine via two hydrogen bonds to assist in stabilizing the nucleic acid structures. In RNA, which is used for protein synthesis, adenine binds to uracil. Click to see full answer.
Why there is uracil instead of thymine in RNA?
Adenine | C5H5N5 | CID 190 - structure, chemical names, physical and chemical properties, classification, patents, literature, biological activities, safety/hazards ...
What does adenine pair with during DNA replication?
Crystal Structure of an Adenine Bulge in the RNA Chain of a DNA.RNA Hybrid, d(CTCCTCTTC).r(gaagagagag) Crystal structure of a DNA.RNA hybrid, d(CTCCTCTTC).r(gaagagagag), with an adenine bulge in the polypurine RNA strand was determined at 2.3 A resolution. The structure was solved by the molecular replacement method …
What bonds to adenine in DNA?
It is water-soluble. Purines (adenine and guanine) are found both in DNA and RNA. Complete answer: Nucleic acids are composed of 3 components namely nitrogenous bases, pentose (5 carbon) sugars and one or more phosphate groups. Purines and pyrimidines are the two main kinds of nitrogenous bases that make up nucleic acids.

Is adenine found in RNA?
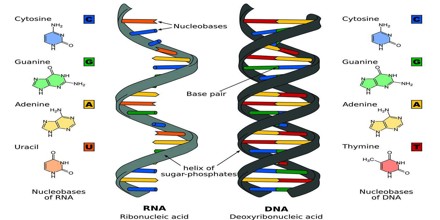
RNA consists of four nitrogenous bases: adenine, cytosine, uracil, and guanine.
Is there adenine in DNA?
DNA is made up of four building blocks called nucleotides: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C).
Is cytosine DNA or RNA?
Cytosine is one of the four building blocks of DNA and RNA. So it's one of the four nucleotides that's present both in DNA, RNA, and each cytosine makes up part of the code.
Is deoxyribose in DNA or RNA?
DNA contains deoxyribose as the sugar component and RNA contains the sugar ribose.
What is the name of the chemical base in DNA?
Adenine. Adenine. =. Adenine (A) is one of four chemical bases in DNA, with the other three being cytosine (C), guanine (G), and thymine (T).
What is the name of the molecule that is used to power chemical reactions?
The sequence of four DNA bases encodes the cell's genetic instructions. A form of adenine called adenosine triphosphate (ATP) serves as an energy storage molecule and is used to power many chemical reactions within the cell.
Is adenine a molecule?
Adenine is also used elsewhere in the cell, not just in D NA and RNA , but it's part of the molecule adenosine triphosphate, which is the energy source for the cell.
What is the adenine molecule in RNA?
In RNA, which is used for protein synthesis, adenine binds to uracil . Adenine forms adenosine, a nucleoside, when attached to ribose, and deoxyadenosine when attached to deoxyribose. It forms adenosine triphosphate (ATP), a nucleoside triphosphate, when three phosphate groups are added to adenosine.
What is the name of the nucleobase that is adenine?
Adenine / ˈædɪnɪn / ( A, Ade) is a nucleobase (a purine derivative). It is one of the four nucleobases in the nucleic acid of DNA that are represented by the letters G–C–A–T. The three others are guanine, cytosine and thymine.
What is the name of the nucleotide that binds to thymine?
Adenine is one of the two purine nucleobases (the other being guanine) used in forming nucleotides of the nucleic acids. In DNA, adenine binds to thymine via two hydrogen bonds to assist in stabilizing the nucleic acid structures. In RNA, which is used for protein synthesis, adenine binds to uracil .
What molecules pass through charcoal?
The water and formamide molecules, being small molecules, will pass through the charcoal and into the waste flask; the large adenine molecules, however, will attach or “adsorb” to the charcoal due to the van der waals forces that interact between the adenine and the carbon in the charcoal.
Why does adenine lose solubility?
The solution containing water, ammonia, and adenine is then left to air dry, with the adenine losing solubility due to the loss of ammonia gas that previously made the solution basic and capable of dissolving adenine, thus causing it to crystalize into a pure white powder that can be stored.
How long does it take for formamide to form adenine?
This method heats up formamide under 120 degree Celsius conditions within a sealed flask for 5 hours to form adenine. The reaction is heavily increased in quantity by using a phosphorus oxychloride (phosphoryl chloride) or phosphorus pentachloride as an acid catalyst and sunlight or ultraviolet conditions.
What are the building blocks of DNA and RNA?
On August 8, 2011, a report, based on NASA studies with meteorites found on Earth, was published suggesting building blocks of DNA and RNA (adenine, guanine and related organic molecules) may have been formed extraterrestrially in outer space.
What is the parent compound of adenine?
Adenine is the precursor for adenosine and deoxyadenosine nucleosides. Adenine is the parent compound of the 6-aminopurines, composed of a purine having an amino group at C-6.
What is the purpose of adenine?
Adenine is one of four nitrogenous bases utilized in the synthesis of nucleic acids. A modified form of adenosine monophosphate ( cyclic AMP) is an imporant secondary messenger in the propagation of many hormonal stimuli. Adenine is an integral part of the structure of many coenzymes.
What is adenine used for?
Adenine is one of four nitrogenous bases utilized in the synthesis of nucleic acids. A modified form of adenosine monophosphate ( cyclic AMP) is an imporant secondary messenger in the propagation of many hormonal stimuli. Adenine is an integral part of the structure of many coenzymes. Adenosine (adenine with a ribose group) causes transient heart block in the AV node of the heart. In individuals suspected of suffering from a supraventricular tachycardia (SVT), adenosine is used to help identify the rhythm. Certain SVTs can be successfully terminated with adenosine.
What is the name of the nucleoside that forms when ribose is attached to aden
Adenine forms adenosine, a nucleoside, when attached to ribose, and deoxyadenosine when attached to deoxyribose, and it forms adenosine triphosphate ( ATP ), which drives many cellular metabolic processes by transferring chemical energy between reactions.
What is the role of adenine in the heart?
Adenine is an integral part of the structure of many coenzymes. Adenosine (adenine with a ribose group) causes transient heart block in the AV node of the heart. In individuals suspected of suffering from a supraventricular tachycardia (SVT), adenosine is used to help identify the rhythm.
What is the name of the compound that is attached to the carbon at position 6?
Adenine. More... Adenine is a purine nucleobase with an amine group attached to the carbon at position 6. Adenine is the precursor for adenosine and deoxyadenosine nucleosides. Adenine is the parent compound of the 6-aminopurines, composed of a purine having an amino group at C-6.
Is a Daphnia magna a human metabolite?
It has a role as a human metabolite, a Daphnia magna metabolite, a Saccharomyces cerevisiae metabolite, an Escherichia coli metabolite and a mouse metabolite. It is a purine nucleobase and a member of 6-aminopurines. It derives from a hydride of a 9H-purine. A purine base and a fundamental unit of adenine nucleotides.
What are the bases of DNA?
Bases. The nitrogen bases in DNA are the basic units of genetic code, and their correct ordering and pairing is essential to biological function . The four bases that make up this code are adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G) and cytosine (C).
Where is DNA stored in eukaryotic cells?
Location. Eukaryotic cells, including all animal and plant cells, house the great majority of their DNA in the nucleus, where it exists in a tightly compressed form, called a chromosome 5. This squeezed format means the DNA can be easily stored and transferred.
What is the sugar in DNA called?
Both DNA and RNA are built with a sugar backbone, but whereas the sugar in DNA is called deoxyribose (left in image), the sugar in RNA is called simply ribose (right in image).
What is the process of bringing amino acids to the protein factories?
Transfer RNA ( tRNA) is responsible for bringing amino acids, basic protein building blocks, to these protein factories, in response to the coded instructions introduced by the mRNA. This protein-building process is called translation.
What is the purpose of DNA?
DNA encodes all genetic information, and is the blueprint from which all biological life is created. And that’s only in the short-term. In the long-term, DNA is a storage device, a biological flash drive that allows the blueprint of life to be passed between generations 2. RNA functions as the reader that decodes this flash drive.
How many strands does DNA have?
DNA consists of two strands, arranged in a double helix. These strands are made up of subunits called nucleotides. Each nucleotide contains a phosphate, a 5-carbon sugar molecule and a nitrogenous base. RNA only has one strand, but like DNA, is made up of nucleotides. RNA strands are shorter than DNA strands.
What is the most important molecule in cell biology?
December 18 2020. | by Ruairi J Mackenzie, Editor for Technology Networks. Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and Ribonucleic acid (RNA) are perhaps the most important molecules in cell biology, responsible for the storage and reading of genetic information that underpins all life. They are both linear polymers, consisting of sugars, phosphates and bases, ...
What are the bases of DNA and RNA?
DNA and RNA both use a different but overlapping set of bases: Adenine, thymine, guanine, uracil, and cytosine. Although the nucleotides of both RNA and DNA contain four different bases, a clear difference is that RNA uses uracil as a base whereas DNA uses thymine.
Where is DNA found?
DNA is found in eukaryotes, prokaryotic and cellular organelles. Viruses with DNA include adenovirus, hepatitis B, papillomavirus, bacteriophage. Viruses with RNA are ebolavirus, HIV, rotavirus, and influenza. Examples of viruses with double-stranded RNA are reoviruses, endornaviruses, and crypto viruses.
How is DNA copied?
DNA is copied via self-replication while RNA is copied by using DNA as a blueprint. DNA uses thymine as a nitrogen base while RNA uses uracil. The difference between thymine and uracil is that thymine has an extra methyl group on the fifth carbon. The adenine base in DNA pairs with thymine while the adenine base in RNA pairs with uracil.
What is the effect of UV light on DNA?
UV induces the formation of covalent linkages between consecutive bases along the nucleotide chain.
What are the targets of UV-mediated cellular damage?
DNA and proteins are the major targets of UV-mediated cellular damage due to their UV absorption characteristics and their abundance in the cells. Thymine dimers tend to predominate because thymine has a greater absorbance. pinterest-pin-it. DNA is synthesized via replication and RNA is synthesized via transcription.
What is the sugar in DNA?
1. Sugars in Nucleotides. Pentose sugar in the nucleotide of DNA is deoxyribose whereas in the nucleotide of RNA it is ribose. Both deoxyribose and ribose are five-membered ring-shaped molecules with carbon atoms and a single oxygen atom, with side groups attached to the carbons.
Why was RNA used as a genetic material?
According to this hypothesis, RNA was used to store the genetic information and catalyse the chemical reactions in primitive organisms before the evolution of DNA and proteins. But because RNA being a catalyst was reactive and hence unstable , later in evolutionary time, DNA took over the functions of RNA as the genetic material and proteins became the catalyst and structural components of a cell.
Overview
Adenine (symbol A or Ade) is a nucleobase (a purine derivative). It is one of the four nucleobases in the nucleic acid of DNA that are represented by the letters G–C–A–T. The three others are guanine, cytosine and thymine. Its derivatives have a variety of roles in biochemistry including cellular respiration, in the form of both the energy-rich adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and the cofactors nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD), flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) and Coenzyme A. It al…
Structure
Adenine forms several tautomers, compounds that can be rapidly interconverted and are often considered equivalent. However, in isolated conditions, i.e. in an inert gas matrix and in the gas phase, mainly the 9H-adenine tautomer is found.
Biosynthesis
Purine metabolism involves the formation of adenine and guanine. Both adenine and guanine are derived from the nucleotide inosine monophosphate (IMP), which in turn is synthesized from a pre-existing ribose phosphate through a complex pathway using atoms from the amino acids glycine, glutamine, and aspartic acid, as well as the coenzyme tetrahydrofolate.
Manufacturing method
Patented Aug. 20, 1968, the current recognized method of industrial-scale production of adenine is a modified form of the formamide method. This method heats up formamide under 120 degree Celsius conditions within a sealed flask for 5 hours to form adenine. The reaction is heavily increased in quantity by using a phosphorus oxychloride (phosphoryl chloride) or phosphorus pentachloride as an acid catalyst and sunlight or ultraviolet conditions. After the 5 hours have pa…
History
In older literature, adenine was sometimes called Vitamin B4. Due to it being synthesized by the body and not essential to be obtained by diet, it does not meet the definition of vitamin and is no longer part of the Vitamin B complex. However, two B vitamins, niacin and riboflavin, bind with adenine to form the essential cofactors nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) and flavin adenin…
External links
• Vitamin B4 MS Spectrum