Is Alternaria alternata dangerous? A. alternata is one of the most important and best-studied aeroallergen. Continued exposure to A. alternata may cause an allergy, later inducing asthma, allergic rhinitis, and sometimes even life-threatening asthmatic seizures associated with increased airborne concentrations of Alternaria . spores [11, 12].
Does exposure to Alternaria alternata cause asthma?
Not only the presence of asthma but also persistence and severity of asthma have been strongly associated with sensitization and exposure to A alternata. Although exposure to Alternaria is an important risk factor for asthma, few studies have assessed exposure to this fungus in indoor environments.
What is Alternaria mold and why is it dangerous?
Alternaria is also a common species that appears as a result of water damage to a home or buildings an allergenic mold, alternaria causes asthma-like symptoms including in the upper respiratory tract, nose and mouth. Because is spreads quickly, it’s important to remediate alternaria mold immediately before it overtakes a home.
What are the health effects of Alternaria?
Alternaria has been known to cause certain health problems in individuals who are exposed to the mold in their personal indoor environment, and these health effects can vary depending on the amount of mold in the environment, the duration of exposure, and the ventilation and air flow within this indoor space.
What is Alternaria alternata?
Alternaria alternata. Alternaria alternata is a fungus which has been recorded causing leaf spot and other diseases on over 380 host species of plant. It is an opportunistic pathogen on numerous hosts causing leaf spots, rots and blights on many plant parts.

How do I get rid of Alternaria at home?
Alternaria is commonly found on carpets, clothing, basements, windows, and doors. Most harmful indoor mold growth starts with dust, dander, and moisture. This means regularly dusting and vacuuming with a HEPA filter vacuum to eliminate dust and dirt.
Is Alternaria dangerous to humans?
Alternaria, a phytotoxins have toxic effect in humans and animals.
What is Alternaria alternata in humans?
Alternaria is an ubiquitous fungus that is considered to be a nonpathogenic contaminant of the clinical specimen unless isolated by repeated culture and correlated with clinical findings. However, it is a rare cause of human infection, especially in immunocompromised patients but even more rarely in healthy hosts [1].
What disease does Alternaria alternata cause?
Alternaria mycotoxins such as alternariol are contaminants of cereals, fruit, and fermented foods (3). A. alternata can cause human infections such as cutaneous and subcutaneous infections, oculomycosis, sinusitis, onychomycosis, and invasive diseases (36).
Where is Alternaria alternata found in home?
Alternaria alternata is mainly an outdoor fungus that typically grows on vegetation. However, the species can also be found indoors, where it prefers humid locations such as bathrooms and often produces large brown spores that are a well-known cause of allergy and asthma.
How do I get rid of Alternaria alternata?
Treatment for Alternaria requires fungicide to be sprayed directly on infected plants, as well as improvements in sanitation and crop rotation to prevent future outbreaks. Organic gardeners are limited to sprays of captan or copper fungicides, making control much more challenging.
What is the main symptom of Alternaria?
Leaf symptoms include round, brown spots with concentric rings. Spots often have a yellow halo, and can crack through the middle. Spots often occur first on older leaves. As the disease spreads, leaves can develop enough spots that they begin to meld together to create large necrotic areas on leaves.
Is Alternaria black mold?
Black mold is a late-season and post-harvest disease of tomatoes caused by the fungus Alternaria alternata.
When is Alternaria mold season?
Outdoor molds include Alternaria, whose spore count peaks in late summer or early fall, and Cladosporium, whose spore count peaks during the summer months. People who are allergic to mold should minimize exposure to airborne molds by avoiding wooded areas or activities like raking damp leaves.
Is Alternaria Alternata pathogenic?
These toxins are produced by Alternaria alternata f. sp. lycopersici, a pathogen causing stem canker in tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) which exhibits high degree of host specificity and plays a major role in pathogenesis by causing leaf necrosis (Prasad and Upadhyay, 2010).
What are Alternaria toxins?
Alternaria toxins are secondary metabolites produced by fungi that can contaminate cereals, oilseeds, fruits and vegetables.
What is habitat of Alternaria?
Habitat/Ecology. Alternaria spp. are cosmopolitan dematiaceous fungi commonly isolated from plants, soil, food and indoor air environment. Alternaria species are known as major plant pathogens {1635; 725} and saprophytes on many substrates {816; 1056; 3729; 725}.
What is the main symptom of Alternaria?
Leaf symptoms include round, brown spots with concentric rings. Spots often have a yellow halo, and can crack through the middle. Spots often occur first on older leaves. As the disease spreads, leaves can develop enough spots that they begin to meld together to create large necrotic areas on leaves.
How do you detect Alternaria?
Identification: The initial symptoms of Alternaria leaf spot are small black dots surrounded by chlorotic haloes. As the disease progresses, lesions expand into characteristic, dark brown to black circular leaf spots with target-like concentric rings.
Does Alternaria mold smell?
Sometimes it can be detected by scent, but oftentimes it is odorless. Some of the most common types of mold found in homes include alternaria, aspergillus, and stachybotrys. Alternaria is an allergenic mold with a velvety texture.
What causes Alternaria?
Under the right environmental conditions, the fungus can thrive and cause severe infection. Alternaria brassicicola produces spores after exposure to high relative humidity (~87%) and temperatures between 68-86 °F. The spores are then released during warm dry periods shortly after a rain.
What is Alternaria alternata?
(1832) Alternaria alternata is a fungus which has been recorded causing leaf spot and other diseases on over 380 host species of plant. It is an opportunistic pathogen on numerous hosts causing leaf spots, rots and blights on many plant parts.
What is the disease caused by Alternaria alternata?
For the fungal disease caused by Alternaria alternata, see Alternaria leaf spot. Alternaria alternata is a fungus which has been recorded causing leaf spot and other diseases on over 380 host species of plant. It is an opportunistic pathogen on numerous hosts causing leaf spots, rots and blights on many plant parts.
How does Alternaria alternata spread?
It is often found in areas with humid climates, or where there has been significant rainfall. The fungus lives in seeds and seedlings, and is also spread by spores. This disease flourishes in dead plants that have been left in gardens over winter. Additionally, when dead infected debris is added to compost pile it can spread to other vegetables throughout the garden.
How to prevent AAL?
Cultural practices for preventing this disease include planting tomatoes in a row north to south, monitoring plants heavily April through June, and using a drip irrigation system to keep as much plant tissue dry and free of favorable environments for this pathogen.
Can AAL be eradicated?
A fungicide may be used to save the plants once they are infected; however, the disease cannot be completely eradicated.
What are the pathotypes of Alternaria alternata?
5-15C ), the AAL toxin causing stem canker on tomato, the AF toxin on strawberry, the AM toxin on apple, the ACT toxin on tangerine, the ACL toxin on rough lemon, and the HS toxin on sugar cane.
Why is alternaria more common in fruits and vegetables?
Postharvest occurrence of Alternaria in fruits and vegetables is more common because the moisture content of these products remains high after harvest. Alternaria infection of fruits and vegetables has been observed in apples, oranges, tomatoes, and bell peppers.
What are the mycotoxins produced by Alternaria alternata?
species are capable of producing dibenzo-α-pyrone types of mycotoxins (alternariol, alternariol monomethyl ether (AME), altenuene, isoaltenuene and altenuisol), tetramic acid metabolites, tenuazonic acid (TzA) and related compounds, ...
What fruits and vegetables have Alternaria mycotoxins?
The production of Alternaria mycotoxins has been recorded in a variety of naturally infected fruits and vegetables, such as tomatoes, apples, grapes, blueberries, oranges, lemons, mandarins, and olives ( Barkai-Golan, 2008c ).
Why is alternata used instead of tenuis?
The epithet alternata should be used instead of tenuis, because the last name is invalid. Colonies filamentous, grey, dark brown or black, growing fast in potato dextrose agar (PDA) or malt extract agar (MEA). Conidiophores single or in small groups, straight or curved, sometime geniculate, 3–6 nm × 20–50 nm, with scars.
Is Alternaria toxic to mice?
These compounds are toxic to Bacillus mycoides and HeLa cells. The toxins, however, are only weakly toxic to mice and do not appear to be toxic to rats or chicks when administered as single purified compounds.
Is Alternaria alternata a pathogen?
Alternaria alternata. Alternaria alternata is generally considered as a weak and opportunistic pathogen that follows different routes for penetrating plant tissue, like wounds (Pearson and Hall, 1975), natural openings such as lenticels, stem ends, and pedicels (Prusky, 1996), and by direct breaching of the host cuticle (Mersha et al., 2012), ...
When was Alternaria first discovered?
Mold-induced respiratory allergies and research on Alternaria both have a lengthy history: the first was described as early as 1698 and the second dates back to 1817. However, the two were only linked in 1930 when Alternaria spores were found to cause allergic asthma.
How many allergens are in A. alternata?
To date, 16 allergens of A. alternata have been isolated, many of which are enzymes: Alt a 4 (disulfide isomerase), Alt a 6 (enolase), Alt a 8 (mannitol dehydrogenase), Alt a 10 (alcohol dehydrogenase), Alt a 13 (glutathione-S-transferase), and Alt a MnSOD (Mn superoxide dismutase).
Is Alternaria alternata a fungus?
Alternaria alternata is mainly an outdoor fungus whose spores disseminate in warm, dry air, so in temperate climates, their count peaks in the summers. Alternaria may also be found in damp, insufficiently ventilated houses, where its allergenic properties cocreate the sick building syndrome. Mold-in …. Alternaria alternata is mainly an outdoor ...
What is Alternaria alternata capable of producing?
Alternaria alternata is capable of producing secondary metabolites such as phytotoxins and mycotoxins which cause spoilage in plants.
What is Alternaria spp?
Alternaria spp. Alternaria spp are a group of Ascomycete fungi that are known for their saprophytic nature in decomposing soil and plants. They are ubiquitous, found in soil, air, and plants. They have a clinical impact as well as, it is a plant pathogen. There are over 299 species of Alternaria spp with the most commonly known species including: ...
Where do Alternaria live?
Alternaria species are saprophytic meaning that they thrive in decomposing materials and environments. They are also commonly found in organic materials and water or moisture areas. Some are endophytic, therefore they live in various plant parts such as seeds, and fruits. Alternaria alternata specifically lives in the soil as a saprophyte ...
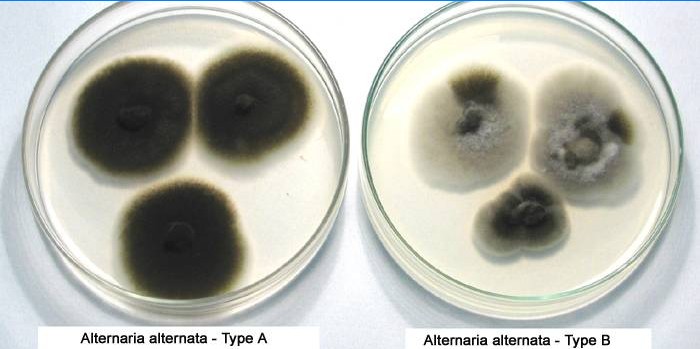
What temperature did Alternaria grow?
All the Alternaria isolated were grown on PDA culture media and incubated at 28 °C for 12 h light/dark photoperiod. The pictures of the colonies were taken on the 6 th day after the incubation of the pathogen. Image Source: Scientific Reports (Mukesh Meena et al.)
What is the color of alternata?
In culture, Alternaria alternata grows as long chains with dark brown conidiophores.
Which antibiotic is most effective for a bacterial infection caused by Alternaria species?
Amphotericin B and flucytosine are very effective in treating all infections caused by Alternaria species.
Does Alternaria alternata cause opportunistic infections?
Alternaria alternata has been associated with causing cutaneous and subcutaneous infections, in individuals with an immunocompromised system, therefore it causes opportunistic infections
How does Alternaria affect humans?
The impact that environmental factors can play on human health can be drastic in many cases, as there are many people who suffer from conditions like allergies and asthma that are triggered largely by those environmental allergens and/or triggers that seamlessly float within the air.
Where can Alternaria be found?
However, when this mold produces its spores into the environment they can circulate feverishly throughout the airspace and are often found growing in showers, basements, and in attics.
Why does Alternaria float in the air?
When Alternaria floats in the air this allows for homes and other indoor environments to become susceptible to an invasion from this mold in the environment, ...
When is Alternaria season?
The Alternaria allergy season usually falls between spring through the summer months and this is typically when those individuals who suffer from allergies and/or asthma will begin to experience symptoms from Alternaria.
When does Alternaria mold grow?
The Alternaria allergy season usually falls between spring through the summer months and this is typically when those individuals who suffer from allergies and/or asthma will begin to experience symptoms from Alternaria.
Can Alternaria cause mold allergies?
In addition, this fungal allergy has been described as a major allergen that is a major contributor to mold allergies.”. The Alternaria allergen can also affect those individuals with sensitive and compromised immune systems that can cause serious infections in the respiratory tract along with other potential adverse health effects.
Is Alternaria mold a contaminant?
The Alternaria alternate spores produced from this species of Alternaria mold are a well-known biological contaminant and a very common potent aeroallergen source in the environment. According to ScienceDirect, they state the following about Alternaria alternata allergy;
Is Alternaria alternata a fungus?
Alternaria alternata spores are considered a well-known biological contaminant and a very common potent aeroallergen source that is found in environmental samples. The most intense exposure to A. alternata allergens is likely to occur outdoors; however, Alternaria and other allergenic fungi can colo ….
Can Alternaria be found outdoors?
The most intense exposure to A. alternata allergens is likely to occur outdoors; however, Alternaria and other allergenic fungi can colonize in indoor environments and thereby increase the fungal aeroallergen exposure levels.
How big is alternaria?
Acute symptoms include edema and bronchi spasms, chronic cases may develop pulmonary emphysema. As with other toxigenic molds, alternaria can also alter DNA, as well as destroy the human immune system. Conidia dimensions is about 18-83 x 7-18. Large spore size 20-200 x 7-18 suggest that the spores from this fungi will be deposited in the nose, mouth, gut, and upper respiratory tract.
Is AAL toxic to birds?
It is lethally toxic to young birds, and in administration to animals produced effects such as “salivation, emesis (vomiting), anorexia (avoidance of eating), erythema (red skin flush), gastrointestinal haemorrhage, convulsions, increase in packed cell volume (an immune parameter) and many other effects” (15). AAL toxins appear to have limited toxic effects against some cultured mammalian cell lines, but are mainly of significance in invasions of plants by Alternaria phytopathogens.
Is Alternaria radicina a fungus?
Alternaria radicina, A. carotiincultae, and A. petroselini are closely related pathogens of umbelliferous crops. Relationships among these fungi were determined based on growth rate, spore morphology, cultural characteristics, toxin production, and host range. Random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) analysis of these species, other species of Alternaria, and closely related fungi was also performed. A. petroselini was readily differentiated from A. radicina and A. carotiincultae on the basis of spore morphology, production of microsclerotia, host range, and RAPD analysis.
Is Alternaria a mycotoxins?
Alternaria has a unique group of mycotoxins, including alternariols, altenuenes, altertoxins, tenuazonic acid, and AAL toxins. Alternariols and altenuenes are weakly toxic to mice and are cytotoxic (toxic to cultured human cell lines) in vitro at concentrations between 6 and 28 ug/ml (15). Altertoxins and the related compound stemphyltoxin-III, also produced by Alternaria, are mutagenic. Tenuazonic acid (Chemical name: 2H-Pyrrol-2-one, 3-acetyl-1,5-dihydro-4-hydroxy-5- (1-methylpropyl)-, (S- (R*,R*))-) appears to inhibit protein synthesis by preventing newly formed protein molecules from detaching from the ribosomes on which they formed.
Is Alternaria radicina the same as A. petroselini?
Alternaria radicina and A. carotiincultae were considerably more similar to each other than to A. petroselini, but could be differentiated on the basis of growth rate, spore morphology, colony morphology, and, to a limited extent, RAPD analysis.
Where does alternaria mold grow?
It can also live and grow under your carpets and inside walls. Mold companies often find spores growing in the shower, basement, and attic.
How to prevent alternaria mold?
While you should practice prevention all year long, it is especially important to take action during summer. Keep all entryways closed as much as you can, especially when it is hot, windy, and dry.
How does alternaria mold get into your house?
Unfortunately, if alternaria mold gets into your house, it may settle on your produce, houseplants, furniture, or clothing. It can also live and grow under your carpets and inside walls. Mold companies often find spores growing in the shower, basement, and attic. Homes containing higher than normal humidity are especially susceptible to this type of fungi growth, which may reach tens of thousands of spores per cubic foot.
How many species of Alternaria are there?
Alternaria is a collection of nearly 300 mold species found all over the world. The club-shaped spores develop into long, chain-like structures, eventually growing into thick black, green or gray colonies. Spores spread in the air, often settling in water or soil.
What Is Alternaria Mold?
Alternaria is a collection of nearly 300 mold species found all over the world. The club-shaped spores develop into long, chain-like structures, eventually growing into thick black, green or gray colonies. Spores spread in the air, often settling in water or soil. Alternaria molds are some of the most common causes of decomposition, and are responsible for at least 20 percent of agricultural spoilage. These molds aren’t all bad, though. Some have performed well as bio-control agents that help keep invasive plant species in check.
Can Alternaria grow on wood?
Alternaria is predominantly an outdoor family of molds, so any growth that happens in your home likely began with spores from outside. Alternaria prefers plants and wood for growth. But if it finds its way inside, it can colonize on tiles, drywall, plywood and even paint and polyurethane.
Can Alternaria cause allergies?
Alternaria can cause many health problems, mainly a variety of allergies. A 2007 study of 75 U.S. locations showed a marked increase in asthma symptoms in homes with higher Alternaria concentrations. Spores can take root on eyeballs, mucus membranes and in the respiratory tract.
Can Alternaria spores spread outside?
This will make it harder for new mold to grow and existing mold to spread. Since Alternaria spores almost always come from outside, be sure to keep doors and windows closed during spring and summer if you think you may have a mold problem.
Is Alternaria mold bad for agriculture?
Alternaria molds are some of the most common causes of decomposition, and are responsible for at least 20 percent of agricultural spoilage. These molds aren’t all bad , though. Some have performed well as bio-control agents that help keep invasive plant species in check.
Is Alternaria mold dangerous?
Learn about Alternaria mold and how to eliminate it. Indoor mold growth is never a good thing, but some molds are more dangerous than others.
Overview
Alternaria alternata is a fungus which has been recorded causing leaf spot and other diseases on over 380 host species of plant. It is an opportunistic pathogen on numerous hosts causing leaf spots, rots and blights on many plant parts.
It can also cause upper respiratory tract infections and asthma in humans with compromised immunity.
Hosts and symptoms
Alternaria alternata has many different hosts depending on its forma specialis. In this review, only Alternaria alternata f. sp. lycopersici (AAL) is going to be assessed. This pathogen infects only certain cultivars of tomato plants and is often referred to as Alternaria stem canker of tomato.
AAL's main symptom is cankers in the stem. It resides in seeds and seedlings, and is often spread by spores as they become airborne and land on plants. It can also spread throughout other plant…
Environment
In order to survive, Alternaria alternata needs a moist warm environment. It is often found in areas with humid climates, or where there has been significant rainfall. The fungus lives in seeds and seedlings, and is also spread by spores. This disease flourishes in dead plants that have been left in gardens over winter. Additionally, when dead infected debris is added to compost pile it can spread to other vegetables throughout the garden.
Disease cycle
Teleomorph of Alternaria alternata is thought to be Clathrospora diplospora: this has yet to be confirmed. As a result , this pathogen propagates itself via asexual spores called conidia. These conidia are produced in lesions on mature or dying leaves. Their production can begin in as few as ten days after the first symptoms appear, and can continue for to up to fifty days. A. alternata's conidia disperse via air currents, and their release from the lesions can be triggered by rainfall, o…
Pathogenesis
At the cellular level, toxins are produced by AAL that are essential for pathogenicity on tomato. This host specific mycotoxin is called fumonisin B1. It was identified and confirmed by research conducted on fast atom bombardment and ion spray mass spectrometry. Thus, tomatoes that are resistant to this pathogen may be resistance to this specific toxin. Resistance to the pathogen in tomato is inherited as a single gene expressing complete dominance. However, sensitivity to th…
Identification
Thought to be Clathrospora diplospora (to be confirmed).
Conidiophore
• Pale brown to olive brown
• 25–60 x 3–3.5 μm
• Straight or flexuous
External links
• Index Fungorum
• USDA ARS Fungal Database
• Japanese Fungi on Plants: Alternaria alternata
• Mycology Online: Alternaria alternata