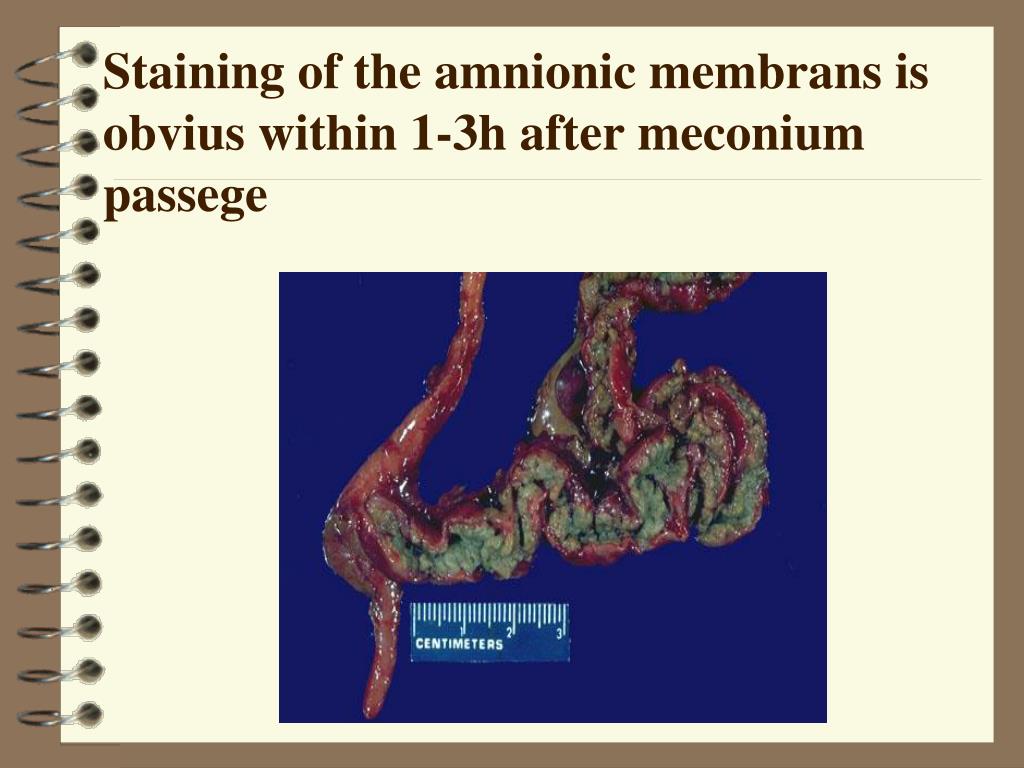
Explore
Too much amniotic fluid can cause the mother's uterus to become overdistended and may lead to preterm labor or premature rupture of membranes (the amniotic sac). Hydramnios is also associated with birth defects in the fetus. When the amniotic sac ruptures, large amounts of fluid leaving the uterus may increase the risk of placental abruption ...
What are the risks of too much amniotic fluid?
How often does your body replace amniotic fluid? The amount of amniotic fluid increases until about 36 weeks of pregnancy. At that time, it makes up about 1 quart. After that, the amount of amniotic fluid usually begins to decrease. Sometimes you can have too little or too much amniotic fluid.
How often does amniotic fluid replenish?
You are leaking amniotic fluid if:
- The fluid is odourless
- It has a clear, watery colour, possibly tinged white-pink.
- It continues to leak and is out of your control, even if you bring your pelvic floor muscles into action
- The leak is steady, and you need to change your sanitary pad often You won’t have any doubt about whether to use a panty liner or a pad
What are the signs of leaking amniotic fluid?
Other treatments that may be used include:
- Amnio-infusion during labor through an intrauterine catheter. ...
- Injection of fluid prior to delivery through amniocentesis. ...
- Maternal re-hydration with oral fluids or IV fluids has shown to help increase amniotic fluid levels.
How to increase amniotic fluid in second trimester?
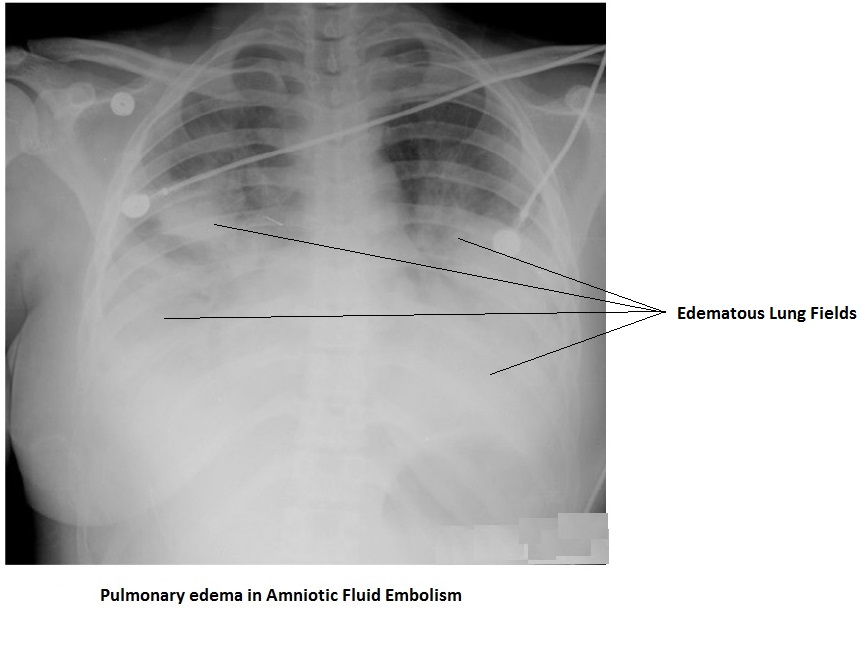
How fast does amniotic fluid embolism happen?
Amniotic fluid embolism is thought to occur in labor or within 30 minutes of delivery. There are several signs and phases of amniotic fluid embolism.
Who is most likely to have amniotic fluid embolism?
Amniotic fluid embolism is a rare obstetric emergency, estimated to occur in 2 to 6/100,000 pregnancies. It usually occurs during late pregnancy but may occur during termination of a 1st- or 2nd-trimester pregnancy.
Can amniotic fluid embolism be prevented?
AFE is a negative reaction that occurs when amniotic fluid enters your circulatory system. It can't be prevented, and the reason why this reaction occurs is unknown.
How many people survive amniotic fluid embolism?
Treatment is mainly supportive, but exchange transfusion, extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, and uterine artery embolization have been tried from time to time. The maternal prognosis after amniotic fluid embolism is very poor though infant survival rate is around 70%.
How common is an amniotic embolism?
It's estimated that there are between one and 12 cases of amniotic fluid embolism for every 100,000 deliveries. Because amniotic fluid embolisms are rare, it's difficult to identify risk factors.
What is an AFE Survivor?
AFE is a life-threatening and unexpected birth complication that can affect both mother and baby. It is characterized by acute and rapid collapse of the mother and/or baby because of an allergic reaction to amniotic fluid entering the maternal circulatory system.
Can you have another baby after amniotic fluid embolism?
Conclusion: This case of a 29-year-old woman with successful subsequent pregnancy after amniotic fluid embolism and a limited number of case reports in the literature suggest that AFE is a sporadic event.
How do you control amniotic fluid embolism?
Amniotic fluid embolism requires rapid treatment to address low blood oxygen and low blood pressure. Emergency treatments might include: Catheter placement. A thin, hollow tube placed into one of your arteries (arterial catheter) might be used to monitor your blood pressure.
Is amniotic fluid embolism more common with C-section?
The incidence of amniotic fluid embolism was higher with cesarean section, 5,000 of 22,937,000 (22/100,000) than with vaginal delivery, 7,000 of 89,775,000 (8/100,000) (relative risk 2.80, 95% CI 2.70-2.90) (p < 0.0001).
Can amniotic fluid embolism happen during C-section?
What are the Causes of Amniotic Fluid Embolism? AFE is more common in vaginal delivery but can occur during a C-section as well. It can also happen shortly after birth while the placenta is still inside the mother's body.
How can you tell the difference between amniotic fluid embolism and pulmonary embolism?
Symptoms of pulmonary embolism include tachycardia, tachypnea, and shortness of breath, all of which are common complaints in pregnancy. Heightened awareness leads to rapid diagnosis and institution of therapy. Amniotic fluid embolism is associated with maternal collapse.
When does amniotic fluid embolism occur?
Overview. Amniotic fluid embolism is a rare but serious condition that occurs when amniotic fluid — the fluid that surrounds a baby in the uterus during pregnancy — or fetal material, such as fetal cells, enters the mother's bloodstream. Amniotic fluid embolism is most likely to occur during delivery or in the immediate postpartum period.
What causes amniotic fluid embolism?
Causes. Amniotic fluid embolism occurs when amniotic fluid or fetal material enters the mother's bloodstream. A likely cause is a breakdown in the placental barrier, such as from trauma. When this breakdown happens, the immune system responds by releasing products that cause an inflammatory reaction, which activates abnormal clotting in ...
What are the symptoms of a fetal heart failure?
Signs and symptoms might include: Sudden failure of the heart to effectively pump blood (cardiovascular collapse) Life-threatening problems with blood clotting (disseminated intravascular coagulopathy) Fetal distress, such as a slow heart rate, or other fetal heart rate abnormalities.
What percentage of maternal deaths are due to amniotic fluid embolisms?
The numbers vary, but as many as 20 percent of maternal deaths in developed countries may be due to amniotic fluid embolisms. Infant death. Your baby is at risk of brain injury or death. Prompt evaluation and delivery of your baby improves survival. By Mayo Clinic Staff.
What are the symptoms of a bleed from the uterus?
Bleeding from the uterus, cesarean incision or intravenous (IV) sites. Altered mental status, such as anxiety or a sense of doom. Chills. Rapid heart rate or disturbances in the rhythm of the heart rate. Fetal distress, such as a slow heart rate, or other fetal heart rate abnormalities. Seizures.
Can amniotic fluid enter the bloodstream during delivery?
However, amniotic fluid embolisms are rare — and it's likely that some amniotic fluid commonly enters the mother's bloodstream during delivery without causing problems.
What is the amniotic fluid embolism?
Amniotic Fluid Embolism (Anaphylactic Syndrome of Pregnancy) A very rare condition, the exact cause of amniotic fluid embolism is unknown. This condition is a dangerous and fatal complication that can happen during labor or soon after childbirth.
Why is it so difficult to diagnose amniotic fluid embolism?
Diagnosing amniotic fluid embolism is difficult because many of the symptoms can overlap with other serious medical conditions. Your doctor will rule out other possible causes while working to diagnose amniotic fluid embolism. Amniotic fluid embolism is thought to occur in labor or within 30 minutes of delivery.
What happens when a baby floats in amniotic fluid?
When this fluid mixes with a mother’s blood, it can cause an allergic-like reaction that can be fatal. This is a medical emergency requiring expert medical care. Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center.
Can amniotic fluid embolism occur after birth?
Amniotic fluid embolism is a very rare condition that can happen during childbirth or soon after birth. It’s unknown what causes amniotic fluid embolism, but some experts think it may be related to amniotic fluid entering the mother’s blood stream (circulatory system).
Can amniotic fluid be prevented?
Unfortunately, there is no way to prevent amniotic fluid embolism. Healthcare providers are still unsure why this happens and what exactly causes this condition. One way to prepare for any kind of medical emergency is to develop a plan with your family and healthcare providers.
What is an amniotic fluid embolism?
Amniotic Fluid Embolism. Amniotic fluid embolism (AFE) is a rare but serious complication that can happen during delivery or shortly after birth. AFE only affects an estimated 1 in 40,000 deliveries but is still a leading cause of maternal death during labor. This condition occurs when the baby's amniotic fluid ...
What are the factors that increase the risk of amniotic fluid embolism?
These factors include: Advanced maternal age: Mothers who are 35 years and older are at a much higher risk of pregnancy and labor complications, including AFE.
What is the condition where fetal cells make their way into the mother's bloodstream?
This condition occurs when the baby's amniotic fluid (the fluid that surrounds the baby in the placenta), fetal cells, or hair makes its way into the mother's bloodstream. AFE can rapidly develop into a life-threatening situation that puts both the baby and mother's life at risk. Emergency medical intervention is needed to stabilize ...
When does AFE occur?
AFE occurs when the amniotic fluid or fetal material passes the placental barrier, enters the mother's bloodstream and starts moving throughout the circulatory system.
What happens if a baby is deprived of oxygen for too long?
Infant death: If the baby is deprived of oxygen for too long or is not delivered quickly enough, the baby can die during delivery. Sudden cardiac arrest: The effects of AFE can develop so rapidly that the blood clots in the lungs send the mother into cardiac arrest.
How many mothers die from AFE?
The effects of AFE can be devastating. The maternal mortality rate for this condition can be as high as 80%, with 50% of mothers dying within the first hour of symptom onset. For patients that do survive the embolism, the majority of them will experience long-term neurological deficits.
What happens if you have an AFE?
Still, there are several complications that can occur from AFE: Brain injury to mother: The blood clots in the lungs from the embolism can reduce the amount of oxygen traveling to the mother's brain, which can result in permanent brain damage.