Common Causes
Tachycardia that puts you in danger doesn’t go away on its own. You’ll need to live a healthier lifestyle and take medicines to control it. You may also need to have a procedure, such as an ablation, to help you manage it. Outlook for tachycardia. Although medications can’t cure tachycardia, they can help you control it.
Related Conditions
While this condition isn’t fatal in itself, it can lead to potentially life-threatening complications. Two of the most common complications of AFib are stroke and heart failure, both of which can be fatal if not managed quickly and effectively.
Can atrial tachycardia go away?
These can include the following:
- heavy exercise
- stress, fear, anxiety, or panic attacks
- low blood sugar or low blood pressure
- fevers, anemia, and dehydration
- pregnancy or menstruation
- too much alcohol, caffeine, or nicotine
- illegal drugs like ecstasy, methamphetamines, or cocaine
Can atrial tachycardia be fatal?
Tachycardia. Tachycardia is the term for a heart rate that’s faster than normal ― more than 100 beats per minute. Tachycardia can start in your upper or lower chambers of your heart and can range from mild to life-threatening. Treatments include medicines and procedures such as ablation and implantable cardiac defibrillator (ICD) placement.
Why is my heart beating fast for no reason?
How dangerous is tachycardia?
Can you live with atrial tachycardia?
Atrial tachycardia is a type of SVT or supraventricular tachycardia. These happen in your atria, which are the upper chambers of your heart. This condition has several possible causes, but usually isn't dangerous. It's often curable or manageable with medication.
What is the best treatment for atrial tachycardia?
The primary treatment during an episode of atrial tachycardia is considered to be rate control using atrioventricular (AV) nodal blocking agents (eg, beta-blockers or calcium channel blockers).
What is the most common cause of atrial tachycardia?
Atrial tachycardia occurs most commonly in elderly patients and those with other types of heart disease, though it occasionally appears in children, younger people and those with healthy hearts. Causes include: A "stretched" atrium resulting from high blood pressure (hypertension) or from cardiomyopathy.
How long does atrial tachycardia last?
The symptoms usually last an average of 10 to 15 minutes. You may feel a rapid heartbeat, or palpitations, for just a few seconds or for several hours, though that's rare. They may appear several times a day or only once a year. They usually come up suddenly and go away just as fast.
Can I exercise with atrial tachycardia?
Once cleared by the physician, it would then be okay to exercise as long as the individual does not have symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath or dizziness while exercising." If any of these symptoms occur, stop the activity and seek medical attention if they do not resolve with rest.
Does tachycardia damage the heart?
Tachycardia may not cause any symptoms or complications. But if left untreated, some forms of tachycardia can lead to serious health problems, including heart failure, stroke or sudden cardiac death.
What medications can cause atrial tachycardia?
Certain medications have been known to trigger the pounding heart rhythm of SVT. These include: Digoxin(Digitek, Digox, Lanoxin), for treating heart failure. Theophylline(Elixophyllin, Norphyl, Phyllcontin), for treating asthma and other lung problems....Medications and StimulantsEphedrine.Pseudoephedrine.Phenylephrine.
Can stress cause atrial tachycardia?
Any of the following can increase your risk for atrial tachycardia: A heart condition, hypertension, or fatigue. Anxiety, stress, or pain. Large amounts of caffeine from coffee, tea, and energy drinks.
Is atrial tachycardia a disability?
If your resting heart rate is faster than 100 beats per minute, you have a condition known as tachycardia (tak-ih-KAHR-dee-uh). If you've had a test like an EKG, MRI, or exercise stress test that reveals you have severe limitations, you may be able to qualify for disability automatically.
Can a pacemaker cure atrial tachycardia?
Pacemaker. This small device may be needed if other treatments for atrial tachycardia don't work. It's surgically implanted under the skin in the chest area. When the pacemaker detects an irregular heartbeat, it sends an electrical pulse that helps correct the heart's rhythm.
At what heart rate should you go to the hospital?
Go to your local emergency room or call 911 if you have: New, unexplained, and severe chest pain that comes with shortness of breath, sweating, nausea, or weakness. Fast heart rate (more than 120-150 beats per minute, or a rate noted by your doctor) -- especially if you are short of breath.
What medications can cause atrial tachycardia?
Certain medications have been known to trigger the pounding heart rhythm of SVT. These include: Digoxin(Digitek, Digox, Lanoxin), for treating heart failure. Theophylline(Elixophyllin, Norphyl, Phyllcontin), for treating asthma and other lung problems....Medications and StimulantsEphedrine.Pseudoephedrine.Phenylephrine.
Can a pacemaker cure atrial tachycardia?
Pacemaker. This small device may be needed if other treatments for atrial tachycardia don't work. It's surgically implanted under the skin in the chest area. When the pacemaker detects an irregular heartbeat, it sends an electrical pulse that helps correct the heart's rhythm.
How successful is ablation for atrial tachycardia?
The overall success rates were 81% for atrial tachycardia, 92% for accessory pathways or flutter, and 99% for AVNRT or atrioventricular node ablation.
Can a pacemaker stop tachycardia?
Pacemakers are, in general, programmed to respond to magnet application by switching to asynchronous pacing mode, meaning that the pacemaker will only pace at a set rate and will not track atrial activity. This will terminate the tachycardia by removing the antegrade limb of the reentrant circuit.
What happens during atrial tachycardia?
During atrial tachycardia, an electrical impulse outside the sinus node fires repeatedly, often due to a short circuit — a circular electrical pathway. Electricity circles the atria again and again, causing the upper chambers to contract more than 100 times per minute. (A normal heart rate is between 60 and 100 beats per minute.) The rapid heart contractions prevent the chambers from filling completely between beats.
How is atrial tachycardia diagnosed?
Atrial tachycardia can sometimes be diagnosed in your physician's office with an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG). But when atrial tachycardia is an occasional event, an office ECG may be normal. If this is the case, your doctor may give you an ECG monitor to wear at home that will record your heart rhythm over time. These include:
How to cure arrhythmias?
Fine wires inside the catheter can help pinpoint the origin of the errant electrical signal. Electrophysiology testing is generally combined with catheter ablation — a procedure that aims to cure the arrhythmia by cauterizing its source.
What is the name of the heart rhythm that causes the heart to beat so fast?
Atrial Tachycardia. Atrial tachycardia (AT) is a type of abnormal heart rhythm, or arrhythmia. It occurs when the electrical signal that controls the heartbeat starts from an unusual location in the upper chambers (atria) and rapidly repeats, causing the atria to beat too quickly.
What is a stretched atrium?
A "stretched" atrium resulting from high blood pressure ( hypertension) or from cardiomyopathy. A previous heart attack. Excessive use of alcohol, cocaine and other stimulants. An "irritable focus," when cells outside the sinus node start generating an electrical impulse automatically on their own. Sometimes, atrial tachycardia is idiopathic, ...
Why do elderly people have tachycardia?
Causes include: A "stretched" atrium resulting from high blood pressure ( hypertension) or from cardiomyopathy. A previous heart attack.
Can atrial tachycardia be reversible?
Incessant (prolonged) atrial tachycardia may lead to cardiomyopathy (a weakening of the heart muscle) and heart failure. This type of cardiomyopathy is often reversible if the atrial tachycardia can be controlled.
How to treat ventricular tachycardia?
A person with ventricular tachycardia may be prescribed antiarrhythmic medication or treated with a procedure called cardiac ablation. This involves sending a catheter through the groin that’s inserted into the heart to scar or destroy heart tissue in a very specific, or localized, area of the muscle that’s thought to be associated with the heart rhythm problem. That’s commonly done using radiofrequency, which generates heat at the tip of the catheter to burn the tissue; but other techniques like cryoenergy catheter ablation, which involves freezing the targeted heart tissue, can also be used. Risks include bleeding and infection, and damage to heart tissue that can actually cause an arrhythmia, as well as clots at the site of the ablation.
What to tell a doctor about tachycardia?
When seeing a doctor about tachycardia, it's important to discuss any accompanying symptoms you may have had, as well as to let the doctor know about any medications you're currently taking. That's because some drugs, ranging from antidepressants to asthma medications to antibiotics like azithromycin, can speed up a person's heart rate.
What does it mean when your heart beats fast?
Based on the word’s Latin roots, tachycardia essentially means fast or swift heart. From a medical perspective, this refers to a heart rate that’s faster than normal. Although what’s abnormally fast, or considered too fast varies somewhat – namely by a person’s age. In adults, this generally refers to a heart rate that exceeds 100 beats per minute.
Why does sinus tachycardia occur?
Sinus tachycardia can also occur in association with stressful situations, dehydration and if someone is fighting an ongoing infection. “These are physiological responses to increased demands of blood flow to the vital organs,” Barrett says. [.
Where does supraventricular tachycardia originate?
That’s the case for what’s called supraventricular tachycardia, which originates in the upper chambers of the heart, and ventricular tachycardia – a fast, abnormal heart rate that starts in the ventricles, or lower chambers of the heart. The latter is linked with an array of underlying heart problems – and it can be deadly.
What is the procedure called for AFIB?
Afib, for example, can be addressed in a variety of ways, including medication like blood thinners to prevent clots and drugs to control the heart rate; a nonsurgical procedure called electrical cardioversion, where a patient receives a shock under mild anesthesia to normalize heart rhythm; or a pacemaker put in to regulate one’s heartbeat.
How long does a heart monitor record heart rate?
These devices, which have gotten increasingly smaller and more streamlined, record heart rate and rhythm on a continuous basis for 24 hours, a few days or even a month.
What is paroxysmal tachycardia?
Paroxysmal atrial tachycardia is a type of arrhythmia, or irregular heartbeat. Paroxysmal means that the episode of arrhythmia begins and ends abruptly. Atrial means that arrhythmia starts in the upper chambers of the heart (atria). Tachycardia means that the heart is beating abnormally fast.
What does it mean when your heart beats so fast?
Tachycardia means that the heart is beating abnormally fast. Paroxysmal atrial tachycardia (PAT) is also known as paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT). Other types of tachycardia that start in the atria include: atrial fibrillation. atrial flutter.
What causes a high heart rate?
atrial fibrillation. atrial flutter. Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. PAT can cause an adult’s heart rate to increase from between 60 and 100 beats per minute (bpm) to between 130 and 230 bpm. Infants and children normally have higher heart rates than adults — between 100 and 130 bpm.
How does the heart rate affect the pacemaker?
This affects the electrical signals transmitted from the sinoatrial node, which is your heart’s natural pacemaker. Your heart rate will speed up. This prevents your heart from having enough time to fill with blood before pumping blood out to the rest of the body .
Can mitral valve disease cause a high risk of PAT?
Children who have congenital heart disease are at a high risk for PAT.
Is pat a life threatening condition?
PAT is the most common form of tachycardia in infants and children. In most cases this condition isn’t life-threatening, but it can be uncomfortable. In rare cases, some people with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome may develop a rapid heart rate that is life-threatening.
Treatment of V-fib
If someone is having a cardiac arrest, a person should respond quickly and follow these steps:
Causes of ventricular tachycardia
There are a number of factors that can cause ventricular tachycardia. These include:
Treatment of ventricular tachycardia
According to the AHA, the cause of a person’s ventricular tachycardia will help a medical professional decide on the right treatment.
Treatment for HAVB
A person will need to have an EKG in the hospital, which shows the electrical rhythm of the heart and can help doctors diagnose HAVB.
Causes of sick sinus syndrome
The genetic or environmental factors that can cause sick sinus syndrome include:
Treatment for sick sinus syndrome
Doctors usually treat sick sinus syndrome by changing medicines if they could be contributing to the condition or inserting a pacemaker to control a person’s heartbeat.
Can other arrhythmias be dangerous?
There are other arrhythmias that can have dangerous complications. These include:
What is tachycardia?
Untreated supraventricular tachycardia may cause life-threatening complications.
What are the types of supraventricular tachycardia?
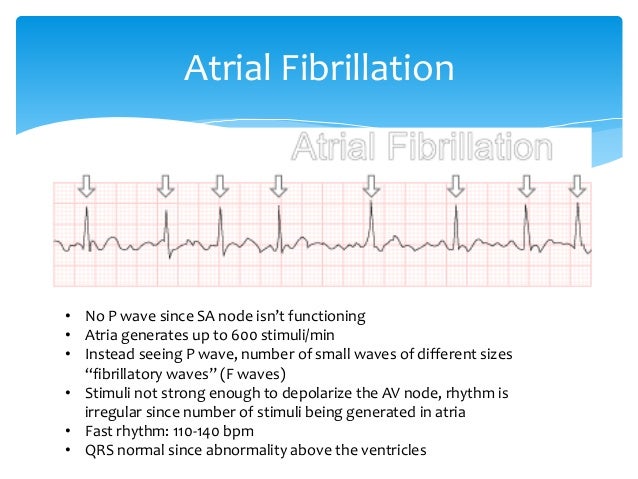
Atrial fibrillation (AF): It is the most common type of SVT. The risk of AF increases with age. It is more common in men and people with other heart conditions, diabetes, obesity, and obstructive sleep apnea. It occurs as a result of too much electrical signals coming from the atrium, causing rapid and fast heartbeat with irregular rhythm.
What is the most common symptomatic dysrhythmia seen in children?
The rapid heart rate interferes with the pumping efficiency of the heart leading to decreased ventricular filling, cardiac output, and low blood pressure. SVT is the most common symptomatic dysrhythmia seen in children. Children with congenital heart disease are at an increased risk of SVT.
Why does my heart beat irregularly?
AFib symptoms like heart racing, fluttering, and irregular heart beat may be caused by heart disease, obesity, alcohol use, thyroid disease, and other conditions. AFib medications may include blood thinners, drugs to control heart rate or convert the heart to a normal rhythm. AFib surgery is also a treatment possibility.
What causes a heart to flutter?
Atrial flutter and atrial tachycardia: They are caused by a short circuit in the right atrium, which makes the heart beat at 300 beats per minute (bpm), whereas the lower chambers beat at a lower rate. It most commonly affects the elderly and people with other heart conditions.
Is supraventricular tachycardia life threatening?
The precipitating factors for supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) include the following: In general, supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) is rarely life-threatening. Many patients are often asymptomatic.
What is the normal heart rate for a person with tachyarrhythmia?
Along with the abnormal rhythm, tachyarrhythmia causes a heart rate of more than 100 beats per minute (bpm) for an adult. A normal resting heart rate is between 60 and 100 bpm.
What is the condition where the atria sends too many signals to the ventricles?
Multi focal atrial tachycardia. Multifocal atrial tachycardia is a rare condition in which the atria send too many signals to the ventricles. It’s usually seen in people with cardiopulmonary conditions. Paroxysmal atrial tachycardia. Paroxysmal atrial tachycardia causes the atria to go in and out of atrial tachycardia.
Why does my heart beat faster than normal?
Sinus tachycardia. Sinus tachycardia occurs when the sinus node — the heart’s natural pacemaker — sends out signals that cause the heart to beat faster than normal. You may have a temporary acceleration of your heart rate due to intense exercise, caffeine, or other normal triggers. Sinus tachycardia can become a problem when it occurs without an obvious trigger, which is called inappropriate sinus tachycardia.
How do you know if you have tachyarrhythmia?
In general, the following symptoms are common to most kinds of tachyarrhythmia: heart palpitations (specifically the sensation that your heart is racing and beating much faster than normal) elevated pulse. lightheadedness.
What is the heart rate controlled by?
Your heart rate is controlled by an electrical system. It tells the heart when to pump oxygenated blood out to the body and when to relax and allow the heart to fill up with blood again. When this electrical circuit is disrupted, an arrhythmia occurs.
How to do external cardioversion?
In this procedure, two patches are placed on your chest. These are attached to a defibrillator that delivers an electrical shock to reset your heart rhythm. This is done under general anesthesia.
How long can you keep a cardiac event monitor?
Cardiac event monitor. This is a small device you can clip to a belt or keep in a pocket for about 2 to 4 weeks. When you feel a tachyarrhythmia, you place the monitor against your chest to capture a brief ECG reading. Many devices will also autocapture the arrhythmia, even if you don’t push the button.
