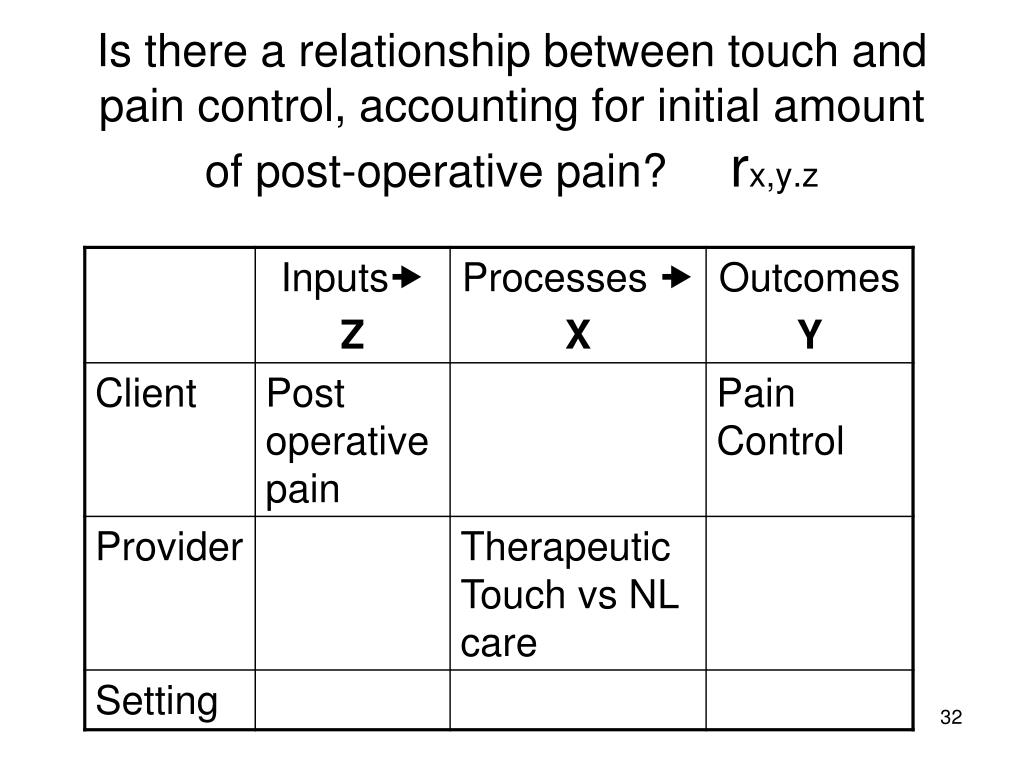
Most physical measures, such as height, weight, systolic
Systole
Systole /ˈsɪstəliː/ is the part of the cardiac cycle when the ventricles contract. The term "systole" originates from New Latin, from Ancient Greek συστολή (sustolē), from συστέλλειν (sustellein, "to contract"), from σύν (syn, "together") + στέλλειν (stellein, "send").
What are nominal ordinal interval and ratio scales?
What are Nominal, Ordinal, Interval and Ratio Scales? Nominal, Ordinal, Interval, and Ratio are defined as the four fundamental levels of measurement scales that are used to capture data in the form of surveys and questionnaires, each being a multiple choice question.
Is systolic blood pressure an interval or ratio scale?
Ratio. All pressure readings are on the ratio scale. There is a starting point, atmospheric pressure. If there blood pressure increases by 10%, there is 10% more force being exerted. I note a related one - temperature is a tricky one.
What is 1st level of measurement nominal scale?
Nominal Scale: 1 st Level of Measurement Nominal Scale, also called the categorical variable scale, is defined as a scale used for labeling variables into distinct classifications and doesn’t involve a quantitative value or order. This scale is the simplest of the four variable measurement scales.
What is an ordinal scale?
An ordinal scale is one where the order matters but not the difference between values. Examples of ordinal variables include:
What is a nominal scale?
How is nominal scale data collected?
What is the nicest thing about interval scale data?
What is the next type of measurement scale that we can use to label variables?
What is the last type of measurement scale?
What are some examples of variables that can be measured on a ratio scale?
Can a ratio be negative?
See 4 more
About this website

Is blood pressure a ratio variable?
Some examples of ratio variables are length measures in the english or metric systems, time measures in seconds, minutes, hours, etc., blood pressure measured in millmeters of mercury, age, and common measures of mass, weight, and volume (see Figure 1.1).
Is blood pressure nominal data?
Blood pressure is an example of continuous data. Blood pressure can be measured to as many decimals as the measuring instrument allows.
Is blood type nominal or ordinal or interval or ratio?
nominal variablesYou can code nominal variables with numbers if you want, but the order is arbitrary and any calculations, such as computing a mean, median, or standard deviation, would be meaningless. Examples of nominal variables include: genotype, blood type, zip code, gender, race, eye color, political party.
What type of measurement scale is blood pressure?
Blood pressure is measured in units of millimeters of mercury (mmHg). The readings are always given in pairs, with the upper (systolic) value first, followed by the lower (diastolic) value. diastolic blood pressure of 88 mmHg.
What type of data is blood pressure quizlet?
The blood-pressure data is quantitative data.
Is blood pressure a categorical variable?
Essentially, "categorical" is a synonym for "qualitative". Numerical variable: when the variable takes some numerical value. An example might be heart rate or blood pressure.
What type of variable is blood type?
Answer and Explanation: Blood types are divided into categories, such as O+, O-, A+, A-, etc. Blood type cannot be counted nor can it be measured. It can only be identified and categorized. Therefore, blood type is a qualitative variable.
What type of variable is hypertension?
Is blood pressure a qualitative or quantitative variable? Blood pressure is a quantitative variable, as it is measured numerically.
How do you know if data is nominal ordinal interval or ratio?
Nominal: the data can only be categorized. Ordinal: the data can be categorized and ranked. Interval: the data can be categorized and ranked, and evenly spaced. Ratio: the data can be categorized, ranked, evenly spaced and has a natural zero.
How does blood pressure measure?
For a manual blood pressure measurement, the care provider places a stethoscope over the major artery in the upper arm (brachial artery) to listen to blood flow. The cuff is inflated with a small hand pump. As the cuff inflates, it squeezes the arm. Blood flow through the artery stops for a moment.
What is blood pressure How is it measured?
A blood pressure measurement is a test that measures the force (pressure) in your arteries as your heart pumps. Blood pressure is measured as two numbers: Systolic blood pressure (the first and higher number) measures pressure inside your arteries when the heart beats.
How is blood pressure measured units?
The gauge uses a unit of measurement called millimeters of mercury (mmHg) to measure the pressure in your blood vessels. If you have high blood pressure, talk to your health care team about steps to take to control your blood pressure to lower your risk for heart disease and stroke.
Is blood pressure quantitative or categorical?
quantitative variableBlood pressure is a quantitative variable, as it is measured numerically.
Why is blood pressure a continuous variable?
2) Continuous Variables: These are sometimes called quantitative or measurement variables; they can take on any value within a range of plausible values. For example, total serum cholesterol level, height, weight and systolic blood pressure are examples of continuous variables.
How is blood pressure measured?
First, a cuff is placed around your arm and inflated with a pump until the circulation is cut off. A small valve slowly deflates the cuff, and the doctor measuring blood pressure uses a stethoscope, placed over your arm, to listen for the sound of blood pulsing through the arteries.
What are 3 examples of discrete data?
Examples of discrete data:The number of students in a class.The number of workers in a company.The number of parts damaged during transportation.Shoe sizes.Number of languages an individual speaks.The number of home runs in a baseball game.The number of test questions you answered correctly.More items...
What are levels of measurement in statistics?
When you’re collecting survey data (or, really any kind of quantitative data) for your research project, you’re going to land up with two types of...
What is nominal data?
Nominal data is a categorical data type, so it describes qualitative characteristics or groups, with no order or rank between categories. Examples...
What is ordinal data?
Ordinal data kicks things up a notch. It’s the same as nominal data in that it’s looking at categories, but unlike nominal data, there is also a me...
What is interval data?
Interval data are a numerical data type. In other words, it’s a level of measurement that involves data that’s naturally quantitative (is usually m...
What is ratio data?
Ratio-type data is the most sophisticated level of measurement. Like interval data, it is ordered/ranked and the numerical distance between points...
Why do levels of measurement matter?
The reason it’s important to understand the levels of measurement in your data – nominal, ordinal, interval and ratio – is because they directly im...
Nominal, Ordinal, Interval, and Ratio Scales - Statistics By Jim
Nominal Scales. A nominal scale simply names categories that values for the variable can fall within. Nominal = name. Analysts also refer to nominal variables as both attribute and categorical data.. Nominal scales have values that you can assign to a countable number of distinct groups based on a characteristic.
Levels of Measurement | Nominal, Ordinal, Interval and Ratio - Scribbr
Levels of Measurement | Nominal, Ordinal, Interval and Ratio. Published on July 16, 2020 by Pritha Bhandari.Revised on December 3, 2021. Levels of measurement, also called scales of measurement, tell you how precisely variables are recorded. In scientific research, a variable is anything that can take on different values across your data set (e.g., height or test scores).
What is a nominal scale?
Nominal scale: A scale used to label variables that have no quantitative values.
How is nominal scale data collected?
The most common way that nominal scale data is collected is through a survey. For example, a researcher might survey 100 people and ask each of them what type of place they live in.
What is the nicest thing about interval scale data?
The nice thing about interval scale data is that it can be analyzed in more ways than nominal or ordinal data. For example, researchers could gather data on the credit scores of residents in a certain county and calculate the following metrics:
What is the next type of measurement scale that we can use to label variables?
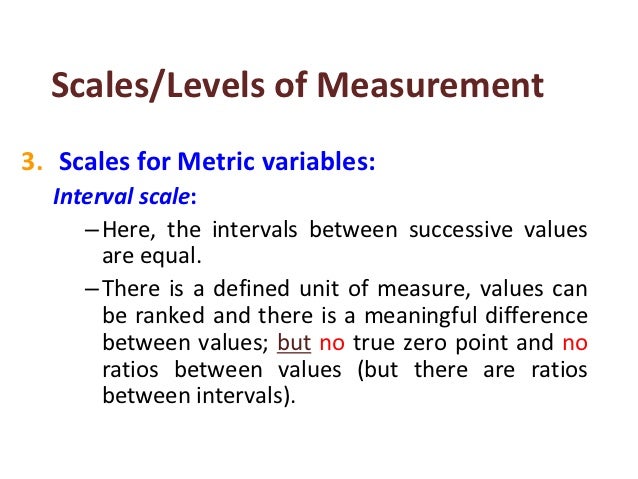
Interval. The next type of measurement scale that we can use to label variables is an interval scale . Interval scale: A scale used to label variables that have a natural order and a quantifiable difference between values, but no “true zero” value. These variables have a natural order.
What is the last type of measurement scale?
The last type of measurement scale that we can use to label variables is a ratio scale . Ratio scale: A scale used to label variables that have a natural order, a quantifiable difference between values,and a “true zero” value. Height: Can be measured in centimeters, inches, feet, etc. and cannot have a value below zero.
What are some examples of variables that can be measured on a ratio scale?
Some examples of variables that can be measured on a ratio scale include: Height: Can be measured in centimeters, inches, feet, etc. and cannot have a value below zero. Weight: Can be measured in kilograms, pounds, etc. and cannot have a value below zero.
Can a ratio be negative?
For example, length, weight, and height all have a minimum value (zero) that can’t be exceeded. It’s not possible for ratio variables to take on negative values. For this reason, the ratio between values can be calculated. For example, someone who weighs 200 lbs. can be said to weigh two times as much as someone who weights 100 lbs. Likewise someone who is 6 feet tall is 1.5 times taller than someone who is 4 feet tall.
What is nominal data?
As we’ve discussed, nominal data is a categorical data type, so it describes qualitative characteristics or groups, with no order or rank between categories. Examples of nominal data include:
What are the four levels of measurement?
If you’re new to the world of quantitative data analysis and statistics, you’ve most likely run into the four horsemen of levels of measurement: nominal, ordinal, interval and ratio. And if you’ve landed here, you’re probably a little confused or uncertain about them.
What is ratio data?
Ratio-type data is the most sophisticated level of measurement. Like interval data, it is ordered/ranked and the numerical distance between points is consistent (and can be measured). But what makes it the king of measurement is that the zero point reflects an absolute zero (unlike interval data’s arbitrary zero point). In other words, a measurement of zero means that there is nothing of that variable. Here are some examples of ratio data:
Why is it important to understand the levels of measurement in your data?
The reason it’s important to understand the levels of measurement in your data – nominal, ordinal, interval and ratio – is because they directly impact which statistical techniques you can use in your analysis. Each statistical test only works with certain types of data.
What does a zero point mean in measurement?
In other words, a measurement of zero means that there is nothing of that variable. Here are some examples of ratio data: Weight, height, or length.
Is nominal data categorical?
So, you can view nominal data as the most basic level of measurement, reflecting categories with no rank or order involved.
Can you measure the difference between options?
As you can see in these examples, all the options are still categories, but there is an ordering or ranking difference between the options. You can’t numerically measure the differences between the options ( because they are categories, after all), but you can order and/or logically rank them.
How does interval data differ from ordinal data?from scribbr.com
Interval data differs from ordinal data because the differences between adjacent scores are equal.
What are ordinal variables?from scribbr.com
In social scientific research, ordinal variables often include ratings about opinions or perceptions, or demographic factors that are categorized into levels or brackets (such as social status or income).
What is a Measurement Variable?from formpl.us
A measurement variable is an unknown attribute that measures a particular entity and can take one or more values. It is commonly used for scientific research purposes. Unlike in mathematics, measurement variables can not only take quantitative values but can also take qualitative values in statistics.
What is normal distribution?from formpl.us
Normal Distribution: It is also called Gaussian distribution and is used to represent real-valued random variables with unknown distribution. This can be further divided into matched and unmatched samples
What is ratio variable?from formpl.us
Ratio variable is the peak type of measurement variable in statistical analysis. It allows for the addition, interaction, multiplication, and division of variables. Also, all statistical analysis including mean, mode, median, etc. can be calculated on the ratio scale.
Which variable has an intrinsic order?from formpl.us
The ordinal variable has an intrinsic order while nominal variables do not have an order.
What is the difference between interval and ratio scale?from questionpro.com
The primary difference between interval and ratio scales is that, while interval scales are void of absolute or true zero, ratio scales have an absolute zero point. Understanding these differences is the key to getting the most appropriate research data. Another key difference in interval scale vs ratio scale is the levels of measurement that have been explained in this blog. Every statistician should thoroughly understand the difference between the two scales for data to be articulated accurately.
What is nominal scale?
Nominal scale is a naming scale, where variables are simply “named” or labeled, with no specific order. Ordinal scale has all its variables in a specific order, beyond just naming them. Interval scale offers labels, order, as well as, a specific interval between each of its variable options. Ratio scale bears all the characteristics ...
Why is interval scale important?
In statistics, interval scale is frequently used as a numerical value can not only be assigned to variables but calculation on the basis of those values can also be carried out. Even if interval scales are amazing, they do not calculate the “true zero” value which is why the next scale comes into the picture.
What is the ratio scale?
Ratio scale bears all the characteristics of an interval scale, in addition to that , it can also accommodate the value of “zero” on any of its variables. Here’s more of the four levels of measurement in research and statistics: Nominal, Ordinal, Interval, Ratio.
What is a variable in statistics?
First, let’s understand what a variable is. A quantity whose value changes across the population and can be measured is called variable. For instance, consider a sample of employed individuals.
Which scale is the most fundamental in quantitative research?
This is the fundamental of quantitative research, and nominal scale is the most fundamental research scale.
Can a question have more than one mode?
In both cases, the analysis of gathered data will happen using percentages or mode,i.e., the most common answer received for the question. It is possible for a single question to have more than one mode as it is possible for two common favorites can exist in a target population.
Can you calculate the average hourly rate of a worker?
For example, it is practically impossible to calculate the average hourly rate of a worker in the US. So, a sample audience is randomly selected such it represents the larger population appropriately. Then the average hourly rate of this sample audience is calculated. Using statistical tests, you can conclude the average hourly rate of a larger population.
Why is ratio level of measurement most appropriate?
The ratio level of measurement is most appropriate because the data can be ordered ; differences can be found and are meaningful, and there is a natural starting zero point. Determine which of the four levels of measurement (nominal, ordinal, interval, ratio) is most appropriate.
What is the average alert level of 632?
In a set of data, alert levels are represented as 0 for low, 1 for medium, and 2 for high. The average (mean) of the 632 alert levels is 0.9.
What is a parameter in statistics?
A parameter is a numerical measurement of a population, a statistic is a numerical measurement of a sample.
Why is the given value a parameter for the week?
The given value is a parameter for the week because the data collected represent a population.
Why is a value considered a parameter?
The value is a parameter because it is a numerical measurement describing some characteristic of a population.
What is a nominal scale?
Nominal scale: A scale used to label variables that have no quantitative values.
How is nominal scale data collected?
The most common way that nominal scale data is collected is through a survey. For example, a researcher might survey 100 people and ask each of them what type of place they live in.
What is the nicest thing about interval scale data?
The nice thing about interval scale data is that it can be analyzed in more ways than nominal or ordinal data. For example, researchers could gather data on the credit scores of residents in a certain county and calculate the following metrics:
What is the next type of measurement scale that we can use to label variables?
Interval. The next type of measurement scale that we can use to label variables is an interval scale . Interval scale: A scale used to label variables that have a natural order and a quantifiable difference between values, but no “true zero” value. These variables have a natural order.
What is the last type of measurement scale?
The last type of measurement scale that we can use to label variables is a ratio scale . Ratio scale: A scale used to label variables that have a natural order, a quantifiable difference between values,and a “true zero” value. Height: Can be measured in centimeters, inches, feet, etc. and cannot have a value below zero.
What are some examples of variables that can be measured on a ratio scale?
Some examples of variables that can be measured on a ratio scale include: Height: Can be measured in centimeters, inches, feet, etc. and cannot have a value below zero. Weight: Can be measured in kilograms, pounds, etc. and cannot have a value below zero.
Can a ratio be negative?
For example, length, weight, and height all have a minimum value (zero) that can’t be exceeded. It’s not possible for ratio variables to take on negative values. For this reason, the ratio between values can be calculated. For example, someone who weighs 200 lbs. can be said to weigh two times as much as someone who weights 100 lbs. Likewise someone who is 6 feet tall is 1.5 times taller than someone who is 4 feet tall.