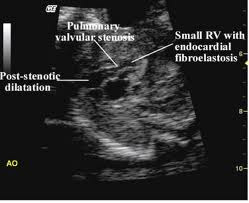
What is endocardial fibroelastosis EFE?
Endocardial fibroelastosis (EFE) is a rare cardiac condition which is classically described in the pediatric population (typically first two years). It is one of the causes for infants to present with unexplained heart failure. Pathology.
Is endocardial fibroelastosis a congenital anomaly?
Endocardial fibroelastosis is a reaction of the endocardium to hypoxia and often associated with heart disease, which results in dilated cardiac chambers. It is unclear whether this is a true congenital anomaly or a response to left atrial dilation. Valvular Hematomas.
What is the prevalence of endocardial fibroelastosis?
Endocardial fibroelastosis is a rare disorder that affects males and females in equal numbers. Fewer than 1 percent of infants and children with congenital heart disease are diagnosed with this disorder. A 1964 study suggested an incidence of 1 in 5,000 live births.
What is endocardial fibroelastosis (endocardial hypertrophy)?
Valves connect the atria (left and right) to their respective ventricles. The symptoms of endocardial fibroelastosis are related to the overgrowth of fibrous tissues causing abnormal enlargement of the heart (cardiac hypertrophy), especially the left ventricle. Impaired heart and lung function eventually lead to congestive heart failure.

What does Fibroelastosis mean?
Medical Definition of fibroelastosis : a condition of the body or one of its organs (as the left ventricle of the heart) characterized by proliferation of fibroelastic tissue — see endocardial fibroelastosis.
What is endomyocardial Fibroelastosis?
Endocardial fibroelastosis (EFE) refers to a pronounced, diffuse thickening of the ventricular endocardium and presents as unexplained heart failure in infants and children. The term endocardial fibroelastosis was introduced by Weinberg and Himmelfarb in 1943.
Is endocardial fibroelastosis genetic?
It is often associated with congenital heart anomalies (HEART DEFECTS CONGENITAL;) INFECTION; or gene mutation. Defects in the tafazzin protein, encoded by TAZ gene, result in a form of autosomal dominant familial endocardial fibroelastosis.
What are the causes of endocardial disease?
This lining is called the endocardium. Endocarditis is usually caused by an infection. Bacteria, fungi or other germs get into the bloodstream and attach to damaged areas in the heart. Things that make you more likely to get endocarditis are artificial heart valves, damaged heart valves or other heart defects.
What does endomyocardial mean?
Medical Definition of endomyocardial : of, relating to, or affecting the endocardium and the myocardium an endomyocardial biopsy.
What is endomyocardial disease?
INTRODUCTION. Endomyocardial fibrosis (EMF) is a disease of rural poverty that is characterized by fibrosis of the apical endocardium of the right ventricle (RV), left ventricle (LV), or both.
How does amyloidosis cause heart failure?
Cardiac amyloidosis is a heart condition where misshapen proteins get stuck in and around different parts of your heart. As these proteins build up, your heart struggles to pump blood so it tries to pump harder. Ultimately, the extra effort weakens and damages your heart, causing it to fail.
Is Arvc rare?
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia / cardiomyopathy (ARVD/C) is a rare familial disorder that may cause ventricular tachycardia and sudden cardiac death in young, apparently healthy individuals. The clinical hallmark of the disease is ventricular arrhythmias, arising predominantly from the right ventricle.
How common is Barth Syndrome?
Children with Barth syndrome can develop serious heart problems including congestive heart failure, heart muscle weakness (cardiomyopathy), and serious arrhythmias. They can also have infection or sepsis. Barth syndrome affects about 1 in every 300,000 to 400,000 babies born worldwide.
What are 4 types of heart diseases?
4 of the main types are described on this page.Coronary heart disease. Coronary heart disease occurs when the flow of oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle is blocked or reduced. ... Strokes and TIAs. ... Peripheral arterial disease. ... Aortic disease.
What are the 5 most common heart problems?
A List of Cardiovascular Diseases: The 5 Most CommonHeart Attack. A heart attack, or myocardial infarction, usually tops the list of cardiovascular diseases in the United States — statistically and anecdotally. ... Stroke. ... Heart Failure. ... Arrhythmia. ... Heart Valve Complications.
What are the symptoms of blockage in your heart?
A completely blocked coronary artery will cause a heart attack. The classic signs and symptoms of a heart attack include crushing chest pain or pressure, shoulder or arm pain, shortness of breath, and sweating. Women may have less typical symptoms, such as neck or jaw pain, nausea and fatigue.
How does amyloidosis cause heart failure?
Cardiac amyloidosis is a heart condition where misshapen proteins get stuck in and around different parts of your heart. As these proteins build up, your heart struggles to pump blood so it tries to pump harder. Ultimately, the extra effort weakens and damages your heart, causing it to fail.
What is left ventricular non compaction cardiomyopathy?
Left ventricular non-compaction (LVNC) is a very rare congenital cardiomyopathy. It is a disease of endomyocardial trabeculations that increase in number and prominence. This cardiomyopathy carries a high risk of malignant arrhythmias, thromboembolic phenomenon and left ventricular dysfunction.
What is left ventricular non compaction?
Left ventricular noncompaction is a heart (cardiac) muscle disorder that occurs when the lower left chamber of the heart (left ventricle), which helps the heart pump blood, does not develop correctly. Instead of the muscle being smooth and firm, the cardiac muscle in the left ventricle is thick and appears spongy.
What is Loeffler endocarditis?
Loeffler endocarditis is a rare restrictive cardiomyopathy caused by abnormal endomyocardial infiltration of eosinophils, with subsequent tissue damage from degranulation, eventually leading to fibrosis. Although an uncommon entity, it is still a disease with significant morbidity and mortality.
What are the symptoms of endocardial fibroelastosis?
The most common symptoms of endocardial fibroelastosis include difficulty breathing (dyspnea), breathlessness, grunting sounds during breathing, coughing, irritability, weakness, and/or a pale facial appearance (pallo r). Other symptoms may include fatigue, failure to thrive, increased sweating, an abnormal blue skin coloration on the feet and hands (peripheral cyanosis), and/or wheezing.
How long does it take for endocardial fibroelastosis to show?
Signs & Symptoms. The symptoms of endocardial fibroelastosis begin rapidly, generally between the ages of 4 and 12 months. Symptoms are due to the overgrowth of fibrous tissue and thickening of the lining of the hearts’ chambers (i.e., endocardium and subendocardium), especially the left ventricle. In some very rare cases ...
What is the name of the disease where blood flows backwards?
Excessive backward flow of blood from the left ventricle, through the mitral valve and into the left atrium (mitral regurgitation) is also a common finding in children with this disorder. Symptoms of mitral regurgitation may include heart palpitation and intolerance to exercise.
Can endocardial fibroelastosis cause congestive heart failure?
Impaired heart and lung function eventually lead to congestive heart failure. Endocardial fibroelastosis may occur for no apparent reason (sporadic) or may be inherited as an X-linked (EFE2) or autosomal recessive (EFE1) genetic trait.
Can a male survive endocardial fibroelastosis?
Males with an abnormal gene are more severely affected than females, and many of these males do not survive. Other cases of endocardial fibroelastosis are thought to occur in association with other metabolic defects, such as Barth syndrome or carnitine deficiency syndromes.
Can endocardial fibroelastosis be inherited?
Impaired heart and lung function eventually lead to congestive heart failure. Endocardial fibroelastosis may occur for no apparent reason (sporadic) or may be inherited as an X-linked (EFE2) or autosomal recessive (EFE1) genetic trait.
When was endocardial fibroelastosis first discovered?
The term "endocardial fibroelastosis" was introduced by Weinberg and Himmelfarb in 1943 . In their pathology laboratory they noted that usually the endocardium was pearly white or opaque instead of normally thin and transparent and microscopically showed a systematic layering of collagenous and elastic fibers.
What is the name of the disease that affects both the heart muscle and the endocardium?
This was thought to be a disease affecting both the heart muscle and the endocardium and it was given various names such as: idiopathic hypertrophy of the heart, endocardial sclerosis, cardiac enlargement of unknown cause, etc.
What is EFE in medical terms?
Specialty. Cardiology. Endocardial fibroelastosis ( EFE) is a rare heart disorder usually occurring in children two years old and younger. It may also be considered a reaction to stress, not necessarily a specific disease. It should not be confused with endomyocardial fibrosis .
What is the last resort for heart failure?
The cause should be identified and, where possible, the treatment should be directed to that cause. A last resort form of treatment is heart transplant.
Is EFE a viral infection?
Evidence that viral infection may play a role as a cause or trigger of EFE was greatly reinforced by the study directed by Towbin in the virus laboratory of Texas Children's Hospital . They applied the methods of today's genetics to old preserved specimens from autopsies of patients with EFE done well before mumps immunization began and found mumps genome in the tissues of over 80% of these patients. It seems undeniable that transplacental mumps infection had been in the past the major cause of EFE, and that immunization was indeed the cause of EFE having become rare.
Is EFE a rare disease?
Thus, the past half-century has seen EFE evolve from a mysterious but frequently observed disease to a rare but much better understood reaction to many diseases and other stresses.
Is EFE a genetic disorder?
These include infections, cardiomyopathies, immunologic diseases, congenital malformations, even electrocution by lightning strike. EFE has two distinct genetic forms, each having a different mode of inheritance. An X-linked recessive form, and an autosomal recessive form have both been observed.
When does endocardial fibroelastosis occur?
Endocardial fibroelastosis usually presents in infancy, and the clinical features are typically indistinguishable from those seen in dilated cardiomyopathy.518In many cases, patients progress to end-stage cardiac failure and death.519–521Survival of three-quarters at 4 years has been reported.518The management is symptomatic, and follows that of dilated cardiomyopathy, including diuretics, vasodilators and digoxin.
What is the cause of fibroelastosis in cats?
Affected animals had prominent, white, thickened endocardium, especially of the left ventricle, because of the proliferation of fibroelastic tissue (see Fig. 10-45). Endocardial fibroelastosis is a reaction of the endocardium to hypoxia and often associated with heart disease, which results in dilated cardiac chambers. It is unclear whether this is a true congenital anomaly or a response to left atrial dilation.
What is the term for a reaction of the endocardium to hypoxia and often associated with heart disease?
Endocardial fibroelastosis is a reaction of the endocardium to hypoxia and often associated with heart disease, which results in dilated cardiac chambers.
What is Barth syndrome?
Barth syndrome is a rare complex disorder characterized by cardiomyopathy (dilated or hypertrophic, associated with left ventricular non-compaction or endocardial fibroelastosis), skeletal muscle weakness, growth delay, and low neutrophil granulo cyte counts. Neutropenia can be constant, intermittent, or cyclic. The diagnosis can be confirmed by analysis of 3-methylglutaconic aciduria.84 Barth syndrome is caused by mutations in the ubiquitously expressed gene TAZ, which encodes tafazzin, a mitochondrial acyltransferase involved in cardiolipin metabolism. 85 Tafazzin-deficient cells show reduced mature cardiolipin levels and increased levels of monolysocardiolipin. The pathophysiology of neutropenia is not fully understood; increased clearance of neutrophils by tissue macrophages has been proposed as one potential mechanism. 86 A recent survey reported a 5-year survival rate of 70% for patients born after 2002. 87 Cardiomyopathy and infections are life-threatening complications. Early diagnosis and rapid interdisciplinary interventions are needed to further improve survival and quality of life.

Overview
Endocardial fibroelastosis (EFE) is a rare heart disorder usually occurring in children two years old and younger. It may also be considered a reaction to stress, not necessarily a specific disease.
It should not be confused with endomyocardial fibrosis.
Signs and symptoms
EFE is characterized by a thickening of the innermost lining of the heart chambers (the endocardium) due to an increase in the amount of supporting connective tissue and elastic fibres. It is an uncommon cause of unexplained heart failure in infants and children, and is one component of HEC syndrome. Fibroelastosis is strongly seen as a primary cause of restrictive cardiomyopathy in children, along with cardiac amyloidosis, which is more commonly seen in pro…
Cause
A review cites references to 31 different diseases and other stresses associated with the EFE reaction. These include infections, cardiomyopathies, immunologic diseases, congenital malformations, even electrocution by lightning strike. EFE has two distinct genetic forms, each having a different mode of inheritance. An X-linked recessive form, and an autosomal recessive form have both been observed.
Treatment
The cause should be identified and, where possible, the treatment should be directed to that cause. A last resort form of treatment is heart transplant.
History
An infant with dilated, failing heart was no rarity on the pediatric wards of hospitals in the mid-twentieth century. On autopsy, most of these patients' hearts showed the thickened endocardial layer noted above. This was thought to be a disease affecting both the heart muscle and the endocardium and it was given various names such as: idiopathic hypertrophy of the heart, endocardial sclerosis, cardiac enlargement of unknown cause, etc. Some of these hearts also h…
See also
• Papillary fibroelastoma