Comparison Table Between Bond Yield and Yield to Maturity
| Parameters of Comparison | Bond Yield | Yield to Maturity |
| Denotation | Bond Yield, or commonly known as yield, ... | Yield to maturity comes into effect when ... |
| Relation with Coupon amount | It is directly proportional to the coupo ... | It is indirectly proportional to the cou ... |
| Relation with Price | Bond Yield is inversely proportional to ... | Yield to maturity is the predicted retur ... |
| Formula | Bond Yield is calculated as (Coupon rate ... | Yield to maturity is calculated by the f ... |
How do you calculate bond maturity?
Yield to Maturity Calculator Inputs
- Current Bond Trading Price ($) - The price the bond trades at today.
- Bond Face Value/Par Value ($) - The face value of the bond, also known as the par value of the bond.
- Years to Maturity - The numbers of years until bond maturity.
What is the formula to calculate the yield to maturity?
where:
- cf - Cash flows, i.e., coupons or the principal;
- r - YTM; and
- n - Years to maturity.
How do you calculate the yield of a bond?
What is the Bond Yield Formula?
- Example of Bond Yield Formula (With Excel Template) Let’s take an example to understand the calculation of the Bond Yield in a better manner. ...
- Explanation. ...
- Relevance and Use of Bond Yield Formula. ...
- Bond Yield Formula Calculator
- Recommended Articles. ...
What is the Bond"s promised yield to maturity?
Yield To Maturity Par Value. - The is the original value that a bond is issued at and is predetermined by the company or organization issuing the bond. Maturity. - This is the date that a bond matures or in other words, is redeemed. ... Market Value. - While a bond is issued and until maturity, it will have a market value. ... Coupon Rate. ...

Is maturity the same as yield?
The yield to maturity (YTM) is an estimated rate of return. It assumes that the buyer of the bond will hold it until its maturity date, and will reinvest each interest payment at the same interest rate. Thus, yield to maturity includes the coupon rate within its calculation. YTM is also known as the redemption yield.
What is a bond yield?
A bond's yield is the return to an investor from the bond's coupon (interest) payments. It can be calculated as a simple coupon yield, which ignores the time value of money, any changes in the bond's price, or using a more complex method like yield to maturity.
Is yield and bond the same?
A bond's coupon rate is the rate of interest it pays annually, while its yield is the rate of return it generates. A bond's coupon rate is expressed as a percentage of its par value.
What is yield to maturity also called?
Expressed simply, the yield to maturity (YTM) of a bond is the annualized return that a bond investor would receive from holding the bond until maturity. It is also referred to as the redemption yield or the book yield.
How do you calculate yield to maturity on a bond?
Yield to Maturity = [Annual Interest + {(FV-Price)/Maturity}] / [(FV+Price)/2]Annual Interest = Annual Interest Payout by the Bond.FV = Face Value of the Bond.Price = Current Market Price of the Bond.Maturity = Time to Maturity i.e. number of years till Maturity of the Bond.
How do you calculate bond yield?
Yield is a figure that shows the return you get on a bond. The simplest version of yield is calculated by the following formula: yield = coupon amount/price. When the price changes, so does the yield.
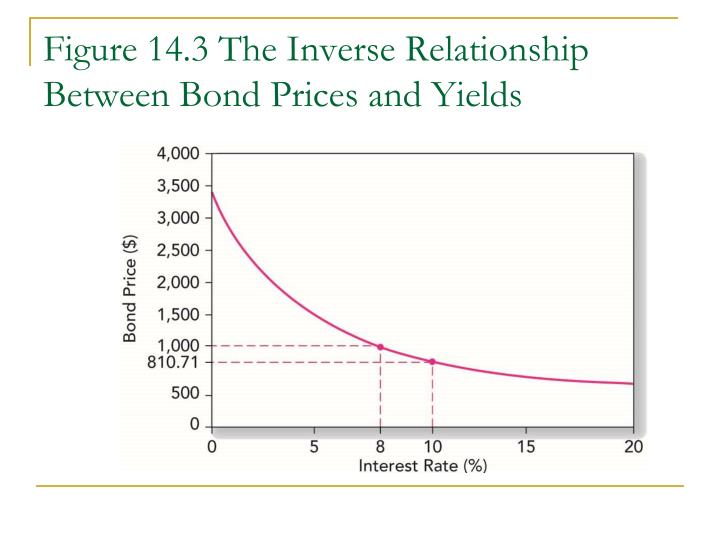
How are the price and the yield to maturity YTM of a bond related?
The yield-to-maturity is the implied market discount rate given the price of the bond. A bond's price moves inversely with its YTM. An increase in YTM decreases the price and a decrease in YTM increases the price of a bond. The relationship between a bond's price and its YTM is convex.
What is a corporate bond's yield to maturity YTM?
What is a corporate bond's yield to maturity (YTM)? YTM is the expected return for an investor who buys the bond today and holds it to maturity. YTM is the prevailing market interest rate for bonds with similar features.
What is 10 year bond yield?
The 10-year Treasury yield is the yield that the government pays investors that purchase the specific security. Purchase of the 10-year note is essentially a loan made to the U.S. government.
Is YTM ear or APR?
The YTM is often given in terms of Annual Percentage Rate (A.P.R.), but more often market convention is followed.
What is a good bond yield?
When bond yields are below 3% (as they've been since 2018), bonds lose their luster as a desirable place to park your money. Paulsen examined average annualized real monthly stock and bond returns between 1926 and 2021 when the 10-year Treasury yielded more and less than 3%.
What does it mean when bond yields are low?
Lower Bond Yields Mean Higher Stock Prices Bonds and stocks tend to move together right after a recession, when inflationary pressures and interest rates are low. Central banks are committed to low-interest rates to stimulate the economy during recessions.
What does it mean when bond yields go up?
A Common Yield Curve Shows Yields Rising with Maturity Investors who tie up their money for longer periods tend to expect a higher payoff as they fear large capital losses on long-term debt, so bonds with longer maturity often have higher yields.
Why are bond yields important?
The longer the Treasury bond's time to maturity, the higher the rates (or yields) because investors demand to get paid more the longer their money is tied up. Typically, short-term debt pays lower yields than long-term debt, which is called a normal yield curve.
What is bond yield?
These interest payments constitute a bond's yield. A bond's current yield is an investment's annual income, including both interest payments and dividends payments, which are then divided by the current price of the security.
How to calculate current yield on a bond?
Current Yield of Bonds. The current yield of a bond is calculated by dividing the annual coupon payment by the bond's current market value. Because this formula is based on the purchase price rather than the par value of a bond, it more accurately reflects the profitability of a bond, relative to other bonds on the market.
What is the coupon rate on a bond?
For example, a bond with a $1,000 par value and a 7% coupon rate pays $70 in interest annually.
What is the YTM formula?
The YTM formula is a more complicated calculation that renders the total amount of return generated by a bond based on its par value, purchase price, duration, coupon rate, and the power of compound interest .
What is yield to maturity?
Yield to maturity (YTM) is the total rate of return that will have been earned by a bond when it makes all interest payments and repays the original principal. YTM is essentially a bond's internal rate of return (IRR) if held to maturity. Calculating the yield to maturity can be a complicated process, and it assumes all coupon, or interest, ...
What is the IRR of a bond?
In other words, it is the internal rate of return (IRR) of an investment in a bond if the investor holds the bond until maturity, with all payments made as scheduled and reinvested at the same rate. Yield to maturity is also referred to as "book yield" or "redemption yield.".
What is the difference between YTM and coupon rate?
The main difference between the YTM of a bond and its coupon rate is that the coupon rate is fixed whereas the YTM fluctuates over time. The coupon rate is contractually fixed, whereas the YTM changes based on the price paid for the bond as well as the interest rates available elsewhere in the marketplace.
Does YTM account for purchasing or selling costs?
YTM calculations also do not account for purchasing or selling costs. YTM also makes assumptions about the future that cannot be known in advance. An investor may not be able to reinvest all coupons, the bond may not be held to maturity, and the bond issuer may default on the bond.
What is the maturity date of a bond?
Bond Maturity Date. The bond issuer also agrees to repay you the original sum loaned at the bond’s maturity date. This is the date on which the principal amount of a bond – also known as the “par value” – is to be paid in full. A bond’s maturity usually is set when it is issued. Bonds often are referred to as being short-, medium- or long-term.
How long does it take for a bond to mature?
Bonds often are referred to as being short-, medium- or long-term. Generally, a bond that matures in one to three years is referred to as a short-term bond.
What is callable bond?
Callable bonds are common: they allow the issuer to retire a bond before it matures. Call provisions are outlined in the bond’s prospectus (or offering statement or circular) and the indenture – both are documents that explain a bond’s terms and conditions.
What happens if you sell a bond before it matures?
If you sell a bond before it matures or buy a bond in the secondary market, you most likely will catch the bond between coupon payment dates. If you’re selling, you’re entitled to the price of the bond plus the accrued interest that the bond has earned up to the sale date.
How are price and yield related?
Note: Price and yield are inversely related. As the price of a bond goes up , its yield goes down, and vice versa. If you buy a new bond at par and hold it to maturity, your current yield when the bond matures will be the same as the coupon yield.
What is a zero coupon bond?
The buyer compensates you for this portion of the coupon interest, which generally is handled by adding the amount to the contract price of the bond. Bonds that don’t make regular interest payments are called zero-coupon bonds – zeros, for short. As the name suggests, these are bonds that pay no coupon or interest.
How long does a medium term bond last?
Medium or intermediate-term bonds generally are those that mature in four to 10 years, and long-term bonds are those with maturities greater than 10 years. Whatever the duration of a bond, the borrower fulfills its debt obligation when the bond reaches its maturity date, and the final interest payment and the original sum you loaned (the principal) ...
Why is yield to maturity calculated?
Because coupon payments are not the only source of bond profits, the yield to maturity calculation incorporates the potential gains or losses generated by variations in market price. If an investor purchases a bond for its par value, the yield to maturity is equal to the coupon rate. If the investor purchases the bond at a discount, ...
When a bond's yield to maturity equals its coupon rate, what is the difference?
When a Bond's Yield to Maturity Equals Its Coupon Rate. If a bond is purchased at par, its yield to maturity is thus equal to its coupon rate, because the initial investment is offset entirely by repayment of the bond at maturity, leaving only the fixed coupon payments as profit. If a bond is purchased at a discount, ...
What is the maturity date of a bond?
A bond's maturity date is simply the date on which the bondholder receives repayment for his investment. At maturity, the issuing entity must pay the bondholder the par value of the bond, regardless of its current market value.
What is the coupon rate of a bond?
The coupon rate of a bond is its interest rate , or the amount of money it pays the bondholder each year, expressed as a percentage of its par value. A bond with a $1,000 par value and coupon rate of 5% pays $50 in interest each year until maturity.
What are the factors that affect the price of a bond?
These factors include the bond's coupon rate, maturity date, prevailing interest rates and the availability of more lucrative bonds.
What happens to bonds when interest rates go up?
As interest rates go up, the price of pre-existing bonds goes down. As rates decline, current bonds with higher rates become more valuable. For example, if a company issues a $1,000 bond with a 4% interest rate, but the government subsequently raises the minimum interest rate to 5%, then any new bonds being issued have higher coupon payments ...
What is the par value of a bond?
Most bonds have par values of $100 or $1,000. The par value of a bond does not dictate its market price, however. Instead, the market or selling price of a bond is influenced by a number ...
What is yield to maturity?
Yield to maturity is a measure of what a bond investment will earn over its life. Expressed as a percentage, yield to maturity sheds light on the annual real rate of return offered by bonds with specific interest rates compared with other bonds on the market.
How do bond interest rates work?
Companies and government entities set different bond interest rates at different times. Bond interest rates are set by the market, by a consensus of buyers and sellers. Because of this, bond investors need to analyze the long-term value of bond investments based on their total payout and their value in relation ...
Why are bonds good for investing?
Bonds provide long- and short-term investment opportunities for investors who favor relatively safe holdings with reasonable returns. Bond investors analyze bond prices and interest rates to determine the best times to buy and sell.
What is required rate of return?
Required Rate of Return. The required rate of return on a bond is the interest rate that a bond issuer must offer in order to get investors interested. Required returns are predominantly set by market forces and determined by the price at which issuers and investors agree.
What is the yield to maturity of a bond?
If an investor purchases a bond at par or face value, the yield to maturity is equal to its coupon rate. If the investor purchases the bond at a discount, its yield to maturity will be higher than its coupon rate. A bond purchased at a premium will have a yield to maturity that is lower than its coupon rate. YTM represents the average return of the ...
What happens to the coupon rate when a bond is issued?
At face value, when the bond is first issued, the coupon rate and the yield are usually exactly the same. However, as interest rates rise or fall, the coupon rate offered by the government or corporation may be higher or lower.
What is YTM in bond?
Investors of any age may add some bonds to a portfolio to lower its overall risk profile. The yield to maturity (YTM) is the percentage rate of return for a bond assuming that the investor holds the asset until its maturity date. It is the sum of all of its remaining coupon payments. A bond's yield to maturity rises or falls depending on its market ...
What do you look for when buying bonds?
When investors consider buying bonds they need to look at two vital pieces of information: the yield to maturity (YTM) and the coupon rate. Investment-quality bonds are low-risk investments that generally offer a rate of return slightly higher than a standard savings account.
What is the coupon rate of a bond?
The coupon rate is the annual amount of interest that the owner of the bond will receive. To complicate things the coupon rate may also be referred to as the yield from the bond.

What’s The Difference Between Current Yield and Yield to Maturity?
- Bondsare bought and sold in the market at par, a discount to par, or a premium to par. Par is the principal of the bond, or the face value, such as $100 or $1,000 per bond. Bond prices are quoted as a percent of par. A price below 100% is considered a discount, and a price above 100% is considered a premium. Interest payments to the investor are based on the “coupon rate” and pa…
Example of Current Yield vs. Yield to Maturity
- Let’s look at two hypothetical $1,000 bonds with different coupon rates, maturities, and market prices. With these two examples, you can see the role a bond’s current market price plays in its yields. The ABC 7% bond is selling at a premium to the $1,000 face value, likely because the coupon rate of 7% is much higher than current interest rates. So the current yield is lower than th…
The Bottom Line
- For bond investors, yield is the interest and capital gains earnings. Current yield and yield to maturity are two common metrics bond investors use to compare bonds. Yield to maturity is more widely used, and is a more comprehensive metric than current yield. Investors can find both types of yields in bond quotes provided by financial services webs...