Is cellular respiration an example of a physical or chemical change?
Is cellular respiration an example of a physical change or an chemical change? - Answers Is cellular respiration an example of a physical change or an chemical change? Respiration is the result of a chemical change. Q: Is cellular respiration an example of a physical change or an chemical change?
What is cellular respiration in the human body?
Cellular respiration includes the reactions in the cells of your body when they convert the food you eat into a molecule of energy in a form your cells can use. This energy is called adenosine triphosphate, or ATP.
What is respiration in biochemical means?
In biochemical means, the respiration is defined as cellular respiration. In the cellular respiration, the glucose is broken down into carbon dioxide and water in the presence of oxygen. The resulted energy is stored in ATP where it is used in metabolism.
How does cellular respiration relate to exercise intensity?
Cellular respiration includes the reactions in the cells of your body when they convert the food you eat into a molecule of energy in a form your cells can use. This energy is called adenosine triphosphate, or ATP. There is a direct correlation between cellular respiration and exercise intensity.

Is cellular respiration physical?
In simple terms, cellular respiration is the release of energy and breakdown of molecules. 9. The reaction in cellular respiration that creates new substances is a physical process.
What type of change is cellular respiration?
The reactions of cellular respiration are catabolic reactions. In catabolic reactions, bonds are broken in larger molecules and energy is released. In cellular respiration, bonds are broken in glucose, and this releases the chemical energy that was stored in the glucose bonds. Some of this energy is converted to heat.
Is cellular respiration chemical energy?
Cellular respiration may be described as a set of metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert chemical energy from nutrients into adenosine triphosphate (ATP), and then release waste products.
Is respiration a chemical process?
Respiration is the chemical process by which organic compounds release energy. The compounds change into different ones by exergonic reactions. The hydrolysis of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and phosphoric acid (Pi) releases energy (it is an exergonic reaction).
Is photosynthesis a chemical change?
Photosynthesis is a process that is mainly used by plants to convert light energy into chemical energy. It is a chemical process that occurs in plants. In this process, plants convert water and carbon dioxide into sugars and oxygen.
What is true about cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration can occur both aerobically (using oxygen), or anaerobically (without oxygen). During aerobic cellular respiration, glucose reacts with oxygen, forming ATP that can be used by the cell. Carbon dioxide and water are created as byproducts.
Which of the following is not true about cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration is not dependent on light.
What type of reaction is respiration?
Respiration is an exothermic process. During respiration, glucose molecules are converted into a number of other molecules which in the end give CO2 and H2O. It is exothermic because the C=O. and O-H bonds in the products are so much more stable than the bonds in the reactants.
What causes cellular respiration?
The starting reactants of cellular respiration include glucose, ATP, and NAD+; and the final products include ATP and H2O. The rate-determining enzymes for cellular respiration include phosphofructokinase-1, pyruvate dehydrogenase, and isocitrate dehydrogenase.
Is respiration a chemical or physical change?
chemical changeRespiration is a chemical change because: Q. What is respiration?
Why respiration is a physical change?
Respiration is a chemical change as new substances like carbon dioxide and water are formed. Also there is change in the mass as glucose is oxidised by oxygen and heat is released. This change is permanent. All these factors conclude that respiration is a chemical change.
Why breathing is a physical change?
Breathing is a physical change because during breathing we only inhale and exhale the gases oxygen and carbon dioxide. There is no chemical change during the process of breathing.
Is cellular respiration endothermic or exothermic?
exothermic processRespiration releases energy - it is an exothermic process.
Is cellular respiration Endergonic or Exergonic?
Cellular respiration is an exergonic (energy-releasing) process.
Is cellular respiration anabolic or catabolic?
catabolic processCellular respiration is a catabolic process during which glucose is broken down to release usable energy for a cell. As in all catabolic processes, cellular respiration releases energy which can then be harnessed and used by other reactions in the cell.
What is cellular respiration examples?
An example of cellular respiration in plants is the use of photoautotrophic processes to obtain the glucose needed for cellular respiration. This means that plants can use the light energy they acquire from the sun to yield glucose and oxygen.
What is cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration is a metabolic pathway that uses glucose to produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP), an organic compound the body can use for ene...
What is the purpose of cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration is used to generate usable ATP energy in order to support many other reactions in the body. ATP is particularly important for...
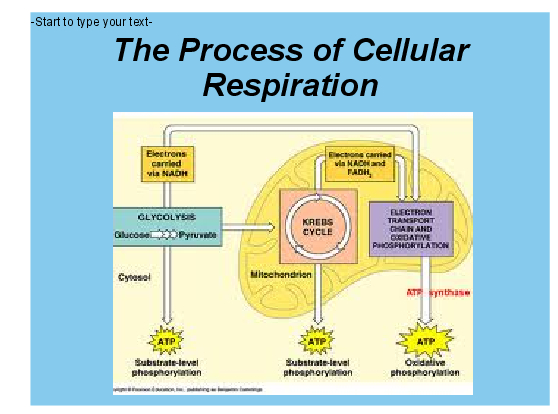
What are the main steps of cellular respiration?
There are three main steps of cellular respiration: glycolysis; the citric acid (TCA) or the Krebs cycle; and the electron transport chain, where o...
Where does cellular respiration take place?
Cellular respiration takes place in the cytoplasm and mitochondria of each cell of the body. Glycolysis occurs inside the cytoplasm, while the TCA...
What are the reactants of cellular respiration?
The reactants of cellular respiration vary at each stage, but initially, it requires an input of glucose, ATP, and NAD+. NAD+, a nicotinamide deriv...
What are the products of cellular respiration?
The final end products of cellular respiration are ATP and H2O. Glycolysis produces two pyruvate molecules, four ATPs (a net of two ATP), two NADH,...
What are the rate-determining enzymes in cellular respiration?
There are three primary rate-determining enzymes in cellular respiration. These enzymes catalyze the rate-limiting steps, which are the slowest rea...
What diseases can affect cellular respiration?
Several diseases can affect cellular respiration. Since cellular respiration is so vital to bodily functions, many of these diseases severely affec...
What are the most important facts to know about cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration is a series of chemical reactions that break down glucose to produce ATP, which may be used as energy to power many reactions...
What is the process of cellular respiration?
Cellular Respiration and Exercise. The anaerobic process relies solely on carbohydrates to make energy. The aerobic process uses carbohydrates and fats to produce energy. If most of your training consists of highly intense exercises, you must consume enough carbohydrates to fuel anaerobic respiration. Advertisement.
How does aerobic exercise help with cellular respiration?
Long duration aerobic exercise burns fat to produce energy. Incorporate a combination of intense anaerobic exercise and low-to-moderate-intensity aerobic exercise within your training week to take advantage of the benefits of both types of cellular respiration.
How long does anaerobic respiration take?
The 90-Second Barrier. Anaerobic respiration takes place at the onset of exercise for up to 90 seconds. The American Council of Exercise explains that repeated bouts of short and intense exercise, such as sprinting, power lifting or high-intensity interval training, increases the rate of anaerobic respiration.
Where does aerobic respiration take place?
Aerobic respiration takes place in an organelle or structure inside the cell called the mitochondria. Read more: Lactic Acid in Exercise Aerobic Respiration.
What is the energy that is converted into a molecule of energy called?
This energy is called adenosine triphosphate, or ATP . There is a direct correlation between cellular respiration and exercise intensity.
Does aerobic exercise increase aerobic respiration?
Performing more anaerobic exercises compared to aerobic exercises will enhance the rate of anaerobic respiration; doing more aerobic exercises will increase the rate and efficiency of aerobic respiration.
Does cellular respiration increase with exercise?
Cellular respiration increases as you exercise at higher intensities.
What is the Difference Between Respiration and Cellular Respiration?
Cellular respiration is only one part of the respiration process where glucose turns out to energy in the presence of oxygen in cellular level.
What is Respiration?
In physiology, respiration is described as the movement of oxygen molecules from outside environment to the inner cells and the movement of carbon dioxide from inner cells to the outside environment in the opposite direction. It is also known as breathing. The movement of oxygen into the cells is defined as inhalation. And the movement of carbon dioxide to the outside environment is defined as exhalation.
How many ATP molecules does anaerobic respiration produce?
It generates only 2 ATP molecules. Glucose → Alcohol+ 2CO 2 + 2ATP ( Anaerobic respiration in bacteria) The anaerobic respiration can also be observed when oxygen is not present in muscle cells of humans. In humans, anaerobic respiration process is produced two lactic acid molecules and 2 ATP.
What is the name of the process where glucose is broken down into carbon dioxide and water in the presence of oxygen?
Figure 01: Respiration. In biochemical means, the respiration is defined as cellular respiration. In the cellular respiration , the glucose is broken down into carbon dioxide and water in the presence of oxygen. The resulted energy is stored in ATP where it is used in metabolism.
What is the energy produced by cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration is of two types; aerobic and anaerobic. The glucose breaks into carbon dioxide and water by using atmospheric oxygen that is gained in the physiological respiration by cells in the tissues. The energy is produced by cellular respiration, and this energy is stored in ATP molecules.
What are the two types of respiration?
Those are physiological respiration (breathing) and cellular respiration. The physiological respiration is defined as the movement of oxygen (O 2) molecules from outside environment to the cells in the inner tissues of the body and the movement of carbon dioxide (CO 2) out of the body in the opposite direction. The other phase of the respiration could be defined as a biochemical reaction which is known as cellular respiration. Cellular respiration is of two types; aerobic and anaerobic. The glucose breaks into carbon dioxide and water by using atmospheric oxygen that is gained in the physiological respiration by cells in the tissues. The energy is produced by cellular respiration , and this energy is stored in ATP molecules. The oxygen is present in this type of cellular respiration, so it is also called as aerobic cellular respiration. This energy is extremely important for catabolic (breaking reactions) and anabolic (synthesizing reactions) pathways in the metabolism. In bacteria, the cellular respiration is little bit different and takes place without oxygen. It is called as anaerobic cellular respiration. In anaerobic process, alcohol and carbon dioxide are produced instead of water. In human also the anaerobic type of cellular respiration is possible in the absence of oxygen. Two molecules of lactic acids are produced from a glucose molecule in humans’ anaerobic respiration. Aerobic cellular respiration produces more energy (38ATP) than anaerobic cellular respiration (2ATP). The key difference between respiration and cellular respiration is, respiration is the entire process which consists of two phases (physiological respiration and cellular respiration) whereas, cellular respiration is only one phase of the respiration process where glucose is converted to energy in the presence of oxygen in cellular level.
How does carbon dioxide move out of the lungs?
Inhalation is an active process. The diaphragm is contracted, and internal height of the thoracic cavity is increased. The internal pressure decreases and atmospheric oxygen moves inside the respiratory tract. The exhalation is a passive process. During the exhalation, the diaphragm relaxes and decreases the volume of the thoracic cavity. Then the internal pressure increases. Hence, carbon dioxide moves out of the respiratory tract to the outside environment. Inhalation brings oxygen to the lungs, and the gas exchange takes place between air in the alveoli and blood in the pulmonary capillaries. The carbon dioxide in return moves from blood to alveoli air and out of the respiratory tract.
Where is cellular respiration carried out?
Cellular respiration is carried out in the mitochondria of the cells. There the oxygen absorbed from the external environment is combined with carbohydrates (raw material) to release the chemical energy they contain. Water vapor and carbon dioxide are also released.
Is cellular respiration an exothermic reaction?
Then, Cellular respiration is an exothermic chemical reaction.
What is the process by which a cell creates oxygen, glucose, and energy?
c. A cell creates oxygen, glucose, and energy by a biochemical reaction.
Which organelle is able to take in glucose to produce ATP, a high-energy compound?
Mitochondria are able to take in glucose to produce ATP, a high-energy compound. During which process is glucose converted into adenosine triphosphate (ATP)?
Which organelle controls the diffusion of carbon dioxide into the cell?
Chloroplasts contain chlorophyll which controls the diffusion of carbon dioxide into the cell. b. Chloroplasts contain chlorophyll which absorbs energy from the Sun. When oxygen is present, oxidative respiration follows glycolysis, and large amounts of ATP are produced.
