
Why do competitive markets move toward equilibrium?
A competitive market is efficient because equilibrium is achieved where the demand price and supply are price equal. Competition on the supply side forces sellers to sell the good at the minimum supply price that they are willing and able to accept.
How to calculate competitive equilibrium?
Apr 09, 2020 · A competitive market is efficient because equilibrium is achieved where the demand price and supply are price equal. Competition on the supply side forces sellers to sell the good at the minimum supply price that they are willing and …
How important is equilibrium in the market?
Apr 04, 2020 · In an exchange economy, a competitive equilibrium is Pareto efficient. In a competitive equilibrium price is equal to short run marginal cost, so no firm can sell an extra unit at a price that covers its short run marginal cost. Which market structure has lowest prices?
How do markets reach equilibrium?
The below mentioned article provides quick notes on efficiency of a competitive market. We have seen that price controls create a deadweight loss when the government wants that a price would be below the market-clearing price, economic efficiency is reduced. It does not mean that such a policy is bad; it may achieve objectives that policy-makers and the public think are important.
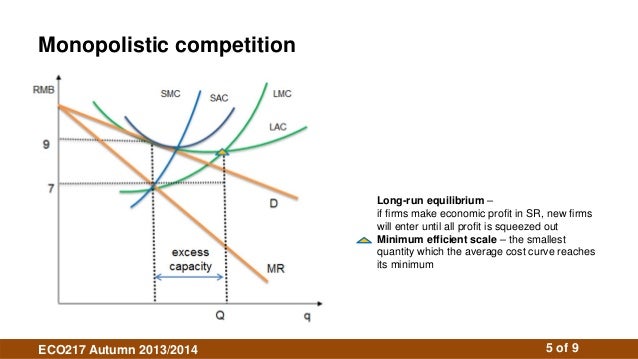
How is a competitive equilibrium efficient?
Competitive equilibrium is achieved when profit-maximizing producers and utility-maximizing consumers settle on a price that suits all parties. At this equilibrium price, the quantity supplied by producers is equal to the quantity demanded by consumers.
Is a competitive equilibrium an efficient equilibrium?
In an exchange economy, a competitive equilibrium is Pareto efficient. Now consider an economy in which goods are produced by firms. In a competitive equilibrium price is equal to short run marginal cost, so no firm can sell an extra unit at a price that covers its short run marginal cost.
Is market equilibrium the most efficient?
Equilibrium quantity is when supply equals demand for a product. The supply and demand curves have opposite trajectories and eventually intersect, creating economic equilibrium and equilibrium quantity. Hypothetically, this is the most efficient state the market can reach and the state to which it naturally gravitates.
Why are competitive markets efficient at equilibrium?
When perfectly competitive firms maximize their profits by producing the quantity where P = MC, they also assure that the benefits to consumers of what they are buying, as measured by the price they are willing to pay, is equal to the costs to society of producing the marginal units, as measured by the marginal costs ...
Is the competitive equilibrium always Pareto efficient?
Any outcome in which the buyers and sellers who trade are the same as the ones who trade in a competitive equilibrium is Pareto efficient, regardless of the prices at which the transactions take place.
When a competitive market is in equilibrium What is the economically efficient level of output?
When a competitive market is in equilibrium, what is the economically efficient level of output? The output where marginal cost is exactly equal to marginal benefit. You just studied 18 terms!Dec 2, 2021
Why is the equilibrium price most efficient?
This is efficient because there is neither an excess of supply and wasted output, nor a shortage – the market clears efficiently. This is a central feature of the price mechanism, and one of its significant benefits.Jan 13, 2020
Why competitive markets allocate resources efficiently?
Markets use prices as signals to allocate resources to their highest valued uses. Consumers will pay higher prices for goods and services that they value more highly. Producers will devote more resources to the production of goods and services that have higher prices, other things being equal.
What is the difference between equilibrium and efficiency?
0:1311:47Efficiency and Equilibrium in Competitive Markets - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipIn a market for a good efficiency exists when the marginal benefit to consumers of consuming theMoreIn a market for a good efficiency exists when the marginal benefit to consumers of consuming the product is equal to the marginal cost to producers to make the product.
How does competition increase efficiency?
First, within firms, competition acts as a disciplining device, placing pressure on the managers of firms to become more efficient. Secondly, competition ensures that more productive firms increase their market share at the expense of the less productive.Jul 9, 2015
What is the relationship between competitiveness and efficiency?
Compared to the maximum capacity of the generator, none of them are efficient. While if we neglect the maximum capacity, it's clear that company A is more efficient than company B. Competitiveness is directly and proportionately related to productivity and the latter shares the same relationship with efficiency.
Why does competitive equilibrium maximize social surplus?
Once the price rises above the market equilibrium price, then total surplus either starts to decline or no longer increases. Hence, total surplus is maximized at the market equilibrium price. This is why competitive, free markets allocate resources most efficiently.
What is the relationship between the PED coefficient and the responsiveness of consumers to price changes?
The relationship between the PED coefficient and the responsiveness of consumers to price changes is a direct one . When the PED coefficient increases, the responsiveness of the consumer to price changes will also increase, resulting in a relatively high price elasticity.
What is the invisible hand of the competitive market?
1. “The invisible hand of the competitive market results in a more efficient allocation of resources than prices set by a government can ever hope to achieve.” Explain the economic reasoning behind this statement.#N#The free market consists of two components; consumers who wish to increase their material wealth and producers who are primarily seeking profit. This system naturally establishes an equilibrium price which is beneficial for both the producer and the consumer. At this price resources are allocated efficiently and there is neither a surplus nor a shortage.#N#However in a free market this price can allow fluctuations in demand and supply that could shift this price whereas in a command economy the price is set and therefore when the equilibrium price shifts; misallocation of resources will result and a disequilibrium between marginal cost and marginal benefit.#N#2. Why does the marginal benefit to consumers of a good decrease the greater the quantity of the good becomes available on the market? Why does the marginal cost to producers increase?#N#With increase in quantity of a good available in the market, the marginal benefit decreases because producers’ cost will increase to supply more additional units and are therefore forced to increase their prices. As the price increases quantity demanded for it will decrease as the Law of Demand states. This result in a surplus of product and therefore will again have to be altered to sell the excess (decreasing the price) until it reaches a new equilibrium.
Why does the quantity of a market move towards equilibrium over time?
Quantity in a market, if it is not at equilibrium, will move towards equilibrium over time because it is the most efficient point for all the participants in the market. At equilibrium, the quantity supplied matches the quantity demanded, minimizing excesses and shortages for firms. Log in to Reply.
What happens if the quantity of a good in a market is not at equilibrium?
If the quantity of a good in a market is not at equilibrium, over time to will return to equilibrium. This is because the price of the certain good will be either too high or too low. Therefore the invisible hand rule will move the product to its Price equilibrium over time. Log in to Reply.
How does a competitive market system work?
The competitive market system matches supply and demand in order to arrive at an equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity. The government can not possibly select the correct price (and adjust it when it changes) more efficiently than a government. 2.
Why does marginal benefit decrease with increase in quantity?
With increase in quantity of a good available in the market, the marginal benefit decreases because producers’ cost will increase to supply more additional units and are therefore forced to increase their prices . As the price increases quantity demanded for it will decrease as the Law of Demand states.
What happens if the price is too high?
In such a case, the invisible hand exerts pressure on the producers to sell their product at a cheaper price. Similarly, if the price is too low, then there is a shortage of supply of a good to the market.
What is efficiency in a market?
In the long run in a perfectly competitive market—because of the process of entry and exit—the price in the market is equal to the minimum of the long-run average cost curve. In other words, goods are being produced and sold at the lowest possible average cost. Also Know, which market structure is more ...
Is perfect competition more efficient than monopoly?
Evaluate the view that perfect competition is a more efficient market structure than monopoly. Perfect competition is both allocatively efficient, because price equals marginal cost, and productive efficient, because firms produce at the lowest point on the average cost curve.
What does market failure mean?
Market failure means that prices fail to provide the proper signals to consumers and producers, so that market does not operate as we have described it. Without these two cases, an unregulated competitive market does lead to economically efficient production level.
What is externality in economics?
The first is when the actions of either consumers or producers result in costs or benefits that do not show up as part of the market price. Such benefits and costs are called externalities. For example, the cost to the society of environment pollution by a producer.
Should a competitive market be left alone?
One might think that if the only objective is to achieve economic efficiency, a competitive market should be left alone. This is not always the case. In two situations government intervention can increase the total welfare in an otherwise competitive market.
What are the two conditions of long-run equilibrium?
Long-run equilibrium in perfectly competitive markets meets two important conditions: allocative efficiency and productive efficiency. These two conditions have important implications. First, resources are allocated to their best alternative use. Second, they provide the maximum satisfaction attainable by society.
What is productive efficiency?
Productive efficiency means producing without waste, so that the choice is on the production possibility frontier. In the long run in a perfectly competitive market, because of the process of entry and exit, the price in the market is equal to the minimum of the long-run average cost curve. In other words, firms produce and sell goods at ...
Who is the president of the National Association of Wheat Growers?
Erik Younggren, president of the National Association of Wheat Growers said in the Agweek article, “I don’t think we’re going to see mile after mile of waving amber fields [of wheat] anymore.” (Until wheat prices rise, we will probably be seeing field after field of tasseled corn.)
Do firms always produce at the minimum of average cost?
For market structures such as monopoly, monopolistic competition, and oligopoly, which are more frequently observed in the real world than perfect competition, firms will not always produce at the minimum of average cost, nor will they always set price equal to marginal cost.
Is efficiency a synonym for desirable?
Remember, economists are using the concept of “efficiency” in a particular and specific sense, not as a synonym for “desirable in every way.”. For one thing, consumers’ ability to pay reflects the income distribution in a particular society.

Advantages
Benefits
Results
- If the quantity in a market is not at equilibrium over time the invisible hand of the market will naturally shift the quantity to equilibrium. For example if the quantity of a good available on the market is below the equilibrium quantity, the marginal benefit is greater than the marginal cost meaning that resources are under allocated. Society would be better off if more of the good wa…
Introduction
- The free market consists of two components; consumers who wish to increase their material wealth and producers who are primarily seeking profit. This system naturally establishes an equilibrium price which is beneficial for both the producer and the consumer. At this price resources are allocated efficiently and there is neither a surplus nor a shortage.
Issues
- 2. Why does the marginal benefit to consumers of a good decrease the greater the quantity of the good becomes available on the market? Why does the marginal cost to producers increase?
Purpose
- 3. How do competitive market forces assure resources will be efficiently allocated towards the provision of various goods and services? In other words, if the quantity in a market is not at equilibrium, why is it likely to move towards equilibrium over time?
Effects
- The invisible hand of a competitive market will naturally drive the price back to equilibrium over time. If the price is too high it will result in a surplus and if too low into a shortage. When a surplus results the invisible hand increases a producers incentive to decrease the price to sell all its access and if there is a shortage it will drive...
Example
- The invisible hand (a term coined by Adam Smith), basically controls the market. If the price of a consumer product is too high the producer will not sell enough of said product, and therefore has to lower the prices. If a good is sold at a too small price, there will be a shortage in supply of said good, and therefore the producer can (and will) sell the good for a higher price. This basic princi…
Mechanism
- A producer has to pay for the goods that he uses to create a certain consumer product. As he sells more of said consumer product, he also has to buy more of the resource that he needs to produce the good. Therefore the marginal benefit for the producer decreases.