The condenser microphone is a similar construct initially. There’s still a diaphragm that the sound waves hit and move, but it’s metal instead of plastic, and instead of magnets, these microphones use a small amount of electricity to suspend the diaphragm.
What is the function of iris diaphragm and condenser?
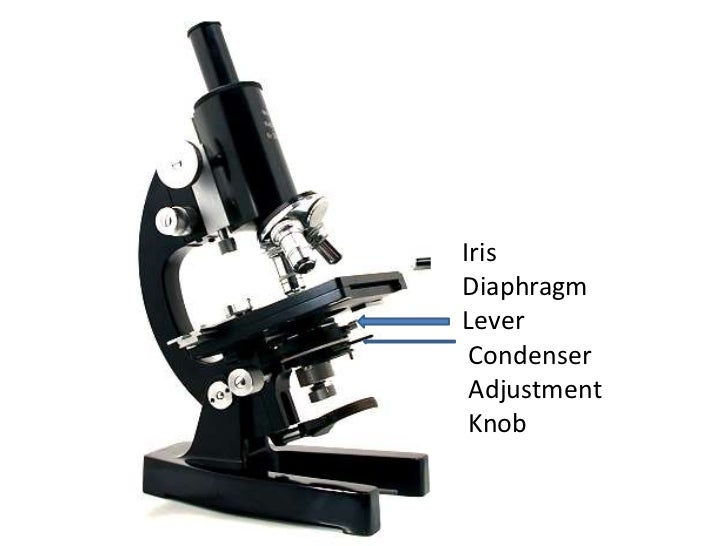
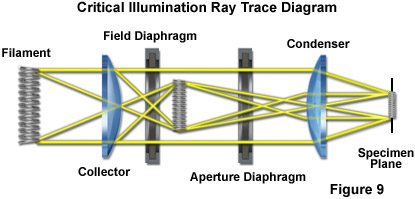
The condenser concentrates and controls the light that passes through the specimen prior to entering the objective. It has two controls, one which moves the Abbe condenser closer to or further from the stage, and another, the iris diaphragm, which controls the diameter of the beam of light. What is the purpose of iris diaphragm?
What is the purpose of a condenser in a microscope?
Many modern course microscopes are equipped with a condenser and an associated condenser diaphragm. The purpose of the condenser is to concentrate the light onto the specimen, its diaphragm regulates resolution, contrast and depth of field.
What is the difference between a large and small diaphragm condenser microphone?
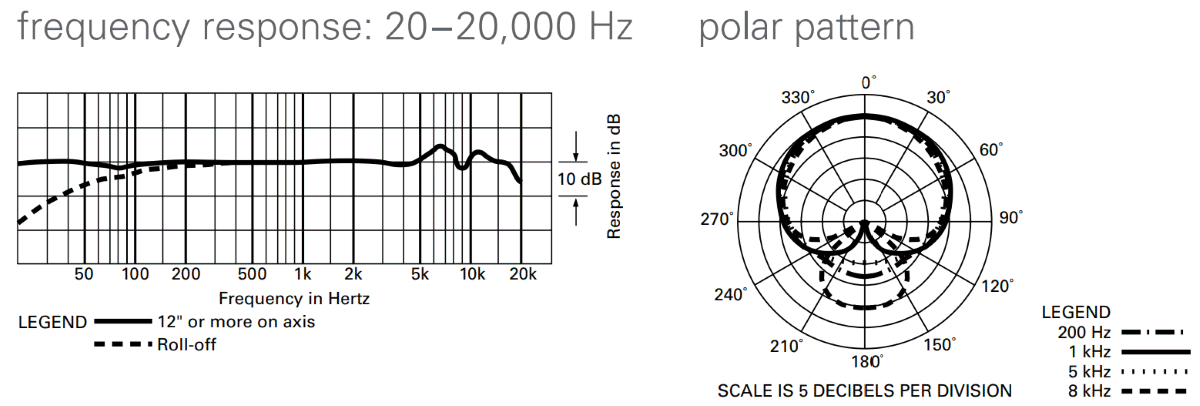
There are both large and small diaphragm condenser microphones that have specific recording advantages. Large diaphragm condenser microphones are particularly effective at picking up low-end frequencies with high sensitivity. Small diaphragm condenser microphones are very good with high frequencies.
Where is the aperture diaphragm located on a microscope?
The aperture diaphragm (also called an iris diaphragm) controls contrast, and is found in the condenser, which sits right below the stage in line with the microscope objectives. The condenser may be movable, both in the horizontal and vertical directions. Why is the diaphragm important in a microscope?
Is a condenser a diaphragm?
The condenser has an iris diaphragm that controls the angle of the beam of light focused onto the specimen. The iris diaphram is an adjustable shutter which allows you to adjust the amount of light passing through the condenser.
Is the diaphragm below the condenser?
You will need to make this adjustment as you go up in magnification, so that you will have sufficient illumination. 3. The condenser aperture diaphragm is located below the specimen stage on the condenser lens assembly. It is an adjustable opening, which allows you to make fine adjustments in illumination.
What is the function of condenser and diaphragms?
The purpose of the condenser is to concentrate the light onto the specimen, its diaphragm regulates resolution, contrast and depth of field. Many modern course microscopes are equipped with a condenser and an associated condenser diaphragm.
What is the condenser on a microscope?
On upright microscopes, the condenser is located beneath the stage and serves to gather wavefronts from the microscope light source and concentrate them into a cone of light that illuminates the specimen with uniform intensity over the entire viewfield.
What is the difference between condenser and diaphragm in microscope?
Condenser is used to collect and focus the light from the illuminator on to the specimen. It is located under the stage often in conjunction with an iris diaphragm. Iris Diaphragm controls the amount of light reaching the specimen. It is located above the condenser and below the stage.
What is the function of condenser?
The purpose of the condenser is to receive the high-pressure gas from the compressor and convert this gas to a liquid. It does it by heat transfer, or the principle that heat will always move from a warmer to a cooler substance.
Can you use microscope without condenser?
A microscope condenser is an important microscope part because it helps to correct the light that passes through the specimen and into the microscope objective. Without a condenser, the quality of the image that you see is significantly diminished, particularly at high magnification levels.
What happens when you close the condenser diaphragm?
Opening the diaphragm too much results in glare and loss of contrast, while closing it too far results in increased diffraction and loss of resolution.
Is aperture and condenser the same?
The aperture diaphragm (also called an iris diaphragm) controls contrast, and is found in the condenser, which sits right below the stage in line with the microscope objectives. The condenser may be movable, both in the horizontal and vertical directions.
What is the purpose of the condenser in a compound microscope?
A condenser is a glass lens or lens system located within or below the stage (sub-stage) on compound microscopes. Its basic function is to gather the light coming in from the illuminator and to concentrate that light into a light cone onto the specimen.
Where is a diaphragm located?
The diaphragm, located below the lungs, is the major muscle of respiration. It is a large, dome-shaped muscle that contracts rhythmically and continually, and most of the time, involuntarily. Upon inhalation, the diaphragm contracts and flattens and the chest cavity enlarges.
What is below the diaphragm?
Your lower esophagus, stomach, intestines, liver, and kidneys are below the diaphragm, in your abdominal cavity.
Where is the condenser diaphragm on a microscope?
On upright microscopes, the condenser is located beneath the stage and serves to gather wavefronts from the microscope light source and concentrate them into a cone of light that illuminates the specimen with uniform intensity over the entire viewfield.
How do you find the diaphragm?
The diaphragm muscle is located at the bottom of your ribcage, separating your abdomen from your chest.
Which is better: a condenser or a dynamic mic?
Dynamic mics will also frequently pick up less volume if the sound source moves, while a condenser microphone is more likely to maintain a level sound that is more natural. Condenser microphones are often more expensive than their dynamic microphone cousins. Still, they’re better for recording vocals and acoustics. 5.
What is a condenser microphone?
A condenser microphone is sometimes called a capacitor microphone. It captures sound through the movements of a metallic diaphragm. This diaphragm fluctuates as it is struck by sound waves from a singer or instrument.
What is the difference between a condenser microphone and a dynamic mic?
Dynamic mics will also frequently pick up less volume if the sound source moves, while a condenser microphone is more likely to maintain a level sound that is more natural.
Why does a condenser mic need a power source?
While a dynamic mic can rely on a magnetic field that will exist regardless of whether or not it’s plugged in, a condenser mic needs some sort of electrical current to charge the backplate.
Is a condenser microphone good?
Condenser microphones make extremely accurate recordings which can be both a positive and a negative. Accuracy is important, but sometimes you get a better sound by enhancing the recording with harmonic distortion. However, a sound track can always be manipulated in post-production, so there is an obvious benefit to an accurate recording.
Why do condenser microphones have diaphragms?
Condenser microphones use a diaphragm to separate the electrical signal from the internal noise in the microphone. Because the diaphragm has to be made very thin, they are much less flexible and much heavier than a typical cardioid. In addition, they generally don’t handle very strong or far-off sounds very well, since their sensitivity may be increased by the inherent distortion that is inherent in their design. However, these microphones do produce a very crisp, consistent sound with a well-defined quality.
What is the difference between a cardioid and a condenser microphone?
However, they do produce differently shaped sounds when they do so. A cardioid microphone will tend to produce a much “wavering” sound to a condenser microphone will produce a more “tight” and crisp sound. Of course, the quality of your sound will also depend upon the quality of the source. If you’re recording over an expensive microphone, then you’ll obviously want something that produces better results.