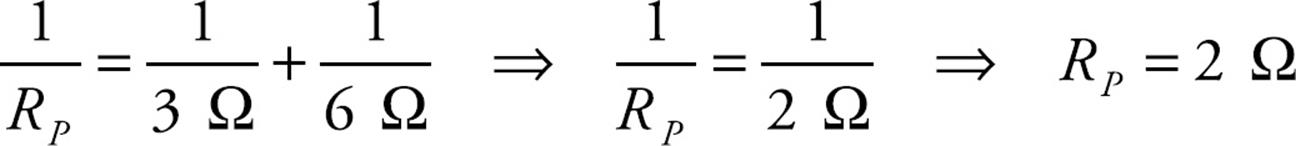
Do resistors in parallel have same voltage?
The current through a resistor is determined by its resistance and the voltage across it. Resistors in parallel have the same voltage across them. In this case, the current through each resistor will be the same value if their resistances are the same value.
What is the formula for current in a parallel circuit?
What is the formula for finding total current in a parallel circuit when branch currents are known? i^t= i^1 + i^2 + ^n Adding parallel loads to a circuit will increase total circuit resistance and increase the total circuit current.
How do you calculate the resistance of a parallel circuit?
Method 3 Method 3 of 4: Combination Circuit
- Break down your circuit into series sections and parallel sections. ...
- Find the resistance of each parallel section. The example circuit has two branches with resistance R 1 = 5 Ω and R 2 = 3 Ω.
- Simplify your diagram. ...
- Add up resistances in series. ...
- Use Ohm's Law to find unknown values. ...
How to combine resistors in parallel?
Thus the parallel connection can be characterized by :
- The same voltage exists across all the resistors connected in parallel .
- The reciprocal of resultant or total resistance is the sum of reciprocals of all resistors in parallel .
- Parallel resistors divide the total current in an inverse proportion to their magnitude.
When are resistors in parallel?
What is the voltage relationship between parallel resistors?
What is the effect of parallel resistors?
How do resistors in series work?
Why do resistors in parallel have the same voltage drop?
Why is the voltage between two resistors not the same?
How is the current of a branch determined?
See 2 more

Do resistors in parallel have constant current?
In the case of a parallel configuration, each resistor has the same potential drop across it, and the currents through each resistor may be different, depending on the resistor.
Is current the same in parallel resistors?
Resistors in Parallel Summary The voltage across each resistor within a parallel combination is exactly the same but the currents flowing through them are not the same as this is determined by their resistance value and Ohms Law.
Is current constant in series or parallel?
#current is constant for a series resistors since according to Kirchoff's current rule ,current entering a branch should leave the branch ,therefore current through each resistors in series is constant # Now the voltage across parallel resistors are same because the potential difference between any two points remains ...
Is current constant across resistors?
The current does not vary as it passes through each individual resistor.
Is current the same in series or parallel?
The current in the series circuit is the same throughout the circuit. On the other hand, parallel circuits refer to a circuit with more than one path through which current flows. In the parallel circuit, all the components have various branches for current flow; thus, the current is not the same throughout the circuit.
Why does current decrease in a parallel circuit?
In a parallel circuit, the net resistance decreases as more components are added, because there are more paths for the current to pass through. The two resistors have the same potential difference across them. The current through them will be different if they have different resistances.
Is current the same in parallel?
A parallel circuit has two or more paths for current to flow through. Voltage is the same across each component of the parallel circuit. The sum of the currents through each path is equal to the total current that flows from the source.
What remains constant in a parallel circuit?
Voltage remains constant in a parallel circuit combination.
Why is current constant in a series?
Since there is only one path for electron flow in a series circuit, the current is the same magnitude at any point in the circuit. The total current in a series circuit is the same as the current through any resistance of the circuit.
Is current constant in series circuit?
In a series circuit, current is constant. Current will remain constant in a series circuit because of the principle of conservation of charge, which assures that charges will not be created or destroyed.
What happens to current in a parallel circuit?
The current in a parallel circuit splits into different branches then combines again before it goes back into the supply. When the current splits, the current in each branch after the split adds up to the same as the current just before the split.
Is current the same in series?
Series Circuits: Current is the same in each device since there is only a single pathway for the charge to flow. Resistance in the circuit is the sum of all the individual resistances of each device.
Is the current through resistors in series the same?
When resistors are connected in series, the current through each resistor is the same. In other words, the current is the same at all points in a series circuit.
What is the current in parallel circuit?
Total current in a parallel circuit is the sum of the individual branch currents. This relationship in a parallel circuit is expressed as: IT = I1 + I2 + I3… Whenever more resistances are connected in parallel, they have the effect of reducing the overall circuit resistance.
Is current the same in a series?
Series Circuits: Current is the same in each device since there is only a single pathway for the charge to flow. Resistance in the circuit is the sum of all the individual resistances of each device. As the number of resistors increases, the total current decreases.
Is current the same throughout a series circuit?
The same current flows through each part of a series circuit." In a series circuit, the amperage at any point in the circuit is the same. This will help in calculating circuit values using Ohm's Law.
Which resistors are connected in parallel?
In the following resistors in parallel circuit the resistors R1, R2 and R3 are all connected together in parallel between the two points A and B as shown.
What is a parallel resistor?
Resistors in Parallel. Unlike the previous series resistor circuit, in a parallel resistor network the circuit current can take more than one path as there are multiple paths for the current. Then parallel circuits are classed as current dividers. Since there are multiple paths for the supply current to flow through, ...
How to convert conductance into resistance?
To convert conductance back into a resistance value we need to take the reciprocal of the conductance giving us then the total resistance, RT of the resistors in parallel. We now know that resistors that are connected between the same two points are said to be in parallel.
How to find RT of a parallel circuit?
The equivalent or total resistance, RT of a parallel combination is found through reciprocal addition and the total resistance value will always be less than the smallest individual resistor in the combination. Parallel resistor networks can be interchanged within the same combination without changing the total resistance or total circuit current. Resistors connected together in a parallel circuit will continue to operate even though one resistor may be open-circuited.
How to define parallel resistive circuit?
So we can define a parallel resistive circuit as one where the resistors are connected to the same two points (or nodes) and is identified by the fact that it has more than one current path connected to a common voltage source. Then in our parallel resistor example below the voltage across resistor R1 equals the voltage across resistor R2 which equals the voltage across R3 and which equals the supply voltage. Therefore, for a parallel resistor network this is given as:
Why are parallel resistors called current dividers?
Then parallel resistor networks can also be thought of as “current dividers” because the supply current splits or divides between the various parallel branches. So a parallel resistor circuit having N resistive networks will have N-different current paths while maintaining a common voltage across itself.
What is the equivalent resistance of a parallel network?
In other words, the equivalent resistance of a parallel network will always be less than the smallest individual resistor in the combination. Also, in the case of R1 being equal to the value of R2, that is R1 = R2, the total resistance of the network will be exactly half the value of one of the resistors, R/2.
Is Current The Same In Parallel?- Illustrate
We know the current is different in parallel circuitry. Let us take an analogy to understand this phenomenon better. A person is rushing to reach the office as he is already late. There are two choices for him; A road with lesser traffic, and another road with heavy traffic jams.
How to calculate current in a parallel circuit? Explain with a numerical example
We use Ohm’s law to determine the quantity of current in parallel circuit configuration. We shall discuss the process with an easy mathematical illustration.
Is current constant in parallel circuits?
The current flowing through every resistive component in a parallel circuit is neither the same nor constant.
Compare the current measurements in series and parallel circuits with a mathematical example
For this comparison, we shall take one parallel and one series combined circuits. Both the circuits contain three equal value resistors in respective configurations.
Why does current change in parallel circuit but not in series circuit?
Parallel circuitry contains more than one path for the current to pass whereas there is only one path for current in the series circuitry.
Calculate the equivalent resistance between A and B in the parallel network shown below
The electrical network depicted in the above image is nothing but the conjunction of a few parallel circuits. We’ll divide them and calculate the required current.
When Is Current The Same In Parallel?
There is only one case when the branch currents in parallel circuitry can be identical. Let us discuss this with a general circuit configuration.
When are resistors parallel?
Resistors are in parallel when their two terminals connect to the same nodes. In the following image, , , and are in parallel. The two distributed nodes are represented by the two horizontal lines. [Definition of a node.] Resistors in parallel share the same voltage on their terminals.
What is parallel resistor?
Parallel resistors. Resistors are in parallel if their terminals are connected to the same two nodes. The equivalent overall resistance is smaller than the smallest parallel resistor. Written by Willy McAllister.
Why is the equivalent resistor indistinguishable from the three parallel resistors?
From the "viewpoint" of the current source, the equivalent resistor is indistinguishable from the three parallel resistors, because in both circuits, is the same.
What is the overall resistance of a resistor?
For resistors in parallel, the overall resistance is the reciprocal of the sum of reciprocals of the individual resistors.
What is the current source?
Current source is driving current towards , , and . We know the value of current is some given constant, but we don't yet know the voltage or how splits up into the three resistor currents.
Is a new resistor the same as a parallel resistor?
The previous equation suggests we can define a new resistor, equivalent to the parallel resistors. The new resistor is equivalent in the sense that, for a given , the same voltage appears.
Do parallel resistors share the same voltage?
Resistors in parallel share the same voltage. The general form for three or more resistors in parallel is, For two parallel resistors it is usually easier to combine them as the product over the sum: is always smaller than the smallest parallel resistor.
When are resistors in parallel?
We say that resistors are in parallel when the terminals of one resistor are connected to the same two nodes as the terminals of another resistor.
What is the voltage relationship between parallel resistors?
Rather, it is the fundamental characteristic of parallel resistors: if resistors are connected between the same two nodes, the voltage across each resistor is the same , and the resistors are in parallel.
What is the effect of parallel resistors?
Parallel resistors have an analogous effect with current: the total current flowing into the network is divided between the parallel branches. Branches with higher resistance will have a smaller proportion of the total current, and branches with lower resistance will have a larger proportion of the total current.
How do resistors in series work?
Two resistors in series can function as a voltage divider. The total voltage applied to the network is divided between the two resistors, and the designer can use the node between the two resistors to produce a desired voltage. Parallel resistors have an analogous effect with current: the total current flowing into the network is divided between ...
Why do resistors in parallel have the same voltage drop?
Resistors in parallel have the same numerical voltage drop because they are connected between the same two nodes. If they are connected between different nodes, they are not in parallel, even if they look like they’re in parallel and have the same numerical voltage across them.
Why is the voltage between two resistors not the same?
They’re not, and here’s why: The voltage across these two resistors has the same numerical value (5 V), but it is not the same voltage, because the two resistors are connected to two separate voltage sources.
How is the current of a branch determined?
The current of each branch is determined by the resistance of the branch and the voltage across the branch. There is no fixed relationship between branch currents in a network of parallel resistors.
