What is the molecular geometry of dichloromethane?
As the hybridization is sp3, the molecular geometry of Dichloromethane becomes tetrahedral. The shape of the compound is a trigonal pyramidal.
Why doesn't tetrachloromethane have a dipole moment?
Because tetrachloromethane has four polar bonds, while dichloromethane (DCM) only has two. Try drawing structures of DCM with one of the chlorine atoms exchanged with one of the hydrogen atoms. You’ll find that the direction of the dipole moment changes, but it’s always there.
What is dichloromethane (DCM)?
Methylene chloride, also known as Dichloromethane (DCM), is an organic chemical compound. CH2Cl2 is the chemical formula for DCM. It is a colorless and volatile liquid with a sweet smell. The compound is naturally derived from the volcanoes, wetlands and other oceanic sources. It has many uses, but majorly it is used in the food industry.
Is diclo the same as dichloromethane?
For the anti-inflammatory drug trade named Diclo, see Diclofenac. Dichloromethane (DCM or methylene chloride) is an organochloride compound with the formula C H 2 Cl 2. This colorless, volatile liquid with a chloroform -like, sweet odour is widely used as a solvent.
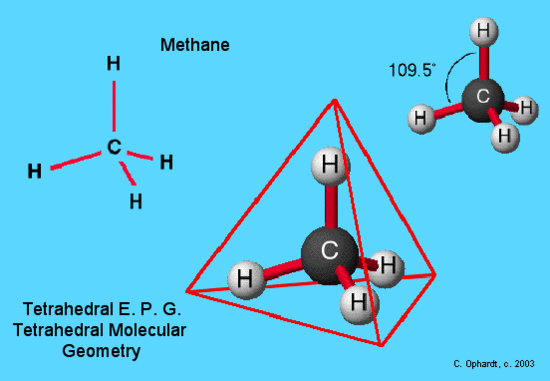
Why is dichloromethane a tetrahedral?
The CH2Cl2 molecule has a tetrahedral geometry shape because it contains two chlorine and two hydrogen atoms. There are two C-H and two C-Cl bonds at the CH2Cl2 molecular geometry. After linking the two hydrogens and two chlorine atoms in the tetrahedral form, it maintains the tetrahedral-like structure.
Is CH2Cl2 tetrahedral?
According to the above table, the geometry of CH2Cl2 is tetrahedral, corresponding to the conditions stated for AX4. The tetrahedral shape of CH2Cl2 is not perfect unlike that of CH4. This is because CH4 has all the identical hydrogen atoms around carbon, whereas CH2Cl2 has 2 H and 2 Cl.
What is dichloromethane structure?
CH2Cl2Dichloromethane / FormulaThe chemical formula of Dichloromethane is CH2Cl2. Methylene chloride is a colourless liquid which has a sweet, penetrating, ether-like smell. It is a volatile liquid chlorinated hydrocarbon. It is non-combustible but if exposed to high temperatures it may produce toxic chloride fumes.
Is CH2Cl2 tetrahedral polar or nonpolar?
So, Is CH2Cl2 polar or nonpolar? CH2Cl2 is a polar molecule due to its tetrahedral geometrical shape and difference between the electronegativity of Carbon, Hydrogen and Chlorine atoms.
What is the molecular geometry of Dichloromethane?
As the hybridization is sp3, the molecular geometry of Dichloromethane becomes tetrahedral. The shape of the compound is a trigonal pyramidal.
Is DCM polar or nonpolar?
polarDichloromethane is polar because it has different polarity bonds and its shape cannot arrange those bond dipoles to cancel out.
What are the properties of dichloromethane?
Dichloromethane appears as a colorless liquid with a sweet, penetrating, ether-like odor. Noncombustible by if exposed to high temperatures may emit toxic chloride fumes. Vapors are narcotic in high concentrations.
How dichloromethane is formed?
DCM is produced by treating either chloromethane or methane with chlorine gas at 400–500 °C. At these temperatures, both methane and chloromethane undergo a series of reactions producing progressively more chlorinated products.
What is the molecular geometry of CO2?
linear molecular geometryBoth electron domains are bonding pairs, so CO2 has a linear molecular geometry with a bond angle of 180°.
Is ch2cl2 asymmetric or symmetrical?
Although the bond arrangement around the C atom in CH2Cl2 is symmetrical, the differing polarities of the C–H and C–Cl bonds means the effect of the polar bonds is not cancelled, so the molecule is polar.
What is the best Lewis structure for ch2cl2?
0:000:55How to Draw the Lewis Structure for CH2Cl2 (Dichloromethane)YouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipWe have a total of 20 valence electrons for ch2cl2 carbon is less electronegative than chlorine soMoreWe have a total of 20 valence electrons for ch2cl2 carbon is less electronegative than chlorine so it'll go on the inside and hydrogen's always go on the outside put our hydrogen's here.
How do you determine the polarity of ch2cl2?
0:081:47Is CH2Cl2 Polar or Nonpolar? (Dichloromethane) - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAnd to understand its polarity we will first look at its lewis structure followed by its shape. SoMoreAnd to understand its polarity we will first look at its lewis structure followed by its shape. So if you look at the lewis structure both the hydrogen atoms are on the downside.
Is CH2Cl2 asymmetric or symmetrical?
Although the bond arrangement around the C atom in CH2Cl2 is symmetrical, the differing polarities of the C–H and C–Cl bonds means the effect of the polar bonds is not cancelled, so the molecule is polar.
How is CCl2H2 polar?
Is CCl2H2 polar or nonpolar? Yes, CCl2H2 is a polar compound. Since Cl is more electronegative than H, the electrons would be tugged more. Unlike carbon tetrachloride, the net dipole moment will not cancel out in this situation.
What are the bond angles in CH2Cl2?
The bond angle of CH2Cl According to the VSEPR theory, for a regular tetrahedral structure, the bonded atoms around the central atom will spread at an angle of approx 109.5° to minimize the repulsion and attains stability.
What is the molecular geometry of dichloromethane?
Molecular Geometry of Dichloromethane. It is comparatively easy to understand the molecular geometry of a compound after knowing its Lewis structure and hybridization. The arrangement of the molecules in this compound is such that the Carbon atom is in the central atom, one Hydrogen atom is on the upper topmost position and the other one is on ...
What is the hybridization of carbon in CH2Cl2?
An electron from the 22 orbital and three other electrons from 2p orbitals participate in forming bonds. Thus the hybridization of Carbon atom in CH2Cl2 is sp3.
How many valence electrons does carbon have?
Carbon has four valence electrons, Hydrogen has one valence electrons and like all halogens, Chlorine has seven valence electrons. There are twenty valence electrons in the compound, and four bonds are formed. Central carbon atom forms two bonds with both Hydrogen and Chlorine atoms.
What are the valence electrons?
Valence electrons are the sum total of the electrons every molecule has in their outer shell in a compound. These electrons include the ones that participate in bond formation as well as the ones that don’t participate in forming bonds. The electrons that are involved in bond formation are called bonding pairs of electrons.
Is dichloromethane volatile?
Hazards of using Dichloromethane. As the compound is highly volatile in nature, it can cause acute inhalation hazards. Prolonged exposure to DCM can cause dizziness, fatigue, headache and much more as a result of acute absorption of the gas.
Is DCM a carcinogen?
DCM is metabolized as Carbon monoxide in the body that can lead to Carbon Monoxide Poisoning in the body . It has also been linked to various types of cancer and thus is a carcinogenic compound .
Is chloromethane tetrahedral?
As the hybridization is sp3, the molecular geometry of Dich loromethane becomes tetrahedral. The shape of the compound is a trigonal pyramidal.
Where does CH2Cl2 come from?
It is naturally obtained from volcanoes and macro algaes. Although not miscible with water but used as a solvent for many organic reactions.
What is CH2Cl2 used for?
CH2Cl2 is used to clean medical equipment without causing corrosion or heating damage. CH2Cl2 is used as a diluter of ink. Dichloromethane is used to degrease metal surfaces, airplane components, railway tracks, and equipment. Used in automotive products as a gasket removal and for prepping metal parts for new gaskets.
How is methyl chloride produced?
Methyl Chloride is majorly produced by the emission through industries. It is produced by treating methane with chlorine at a high temperature of 400–500 °C. Below are the chemical reactions that take place in the production of CH2Cl2. CH4 + Cl2 —–heat——–> CH3Cl + HCl. CH3Cl + Cl2 ———heat——> CH2Cl2 + HCl.
What determines the polarity of a complex molecule?
The polarity or non-polarity of a complex molecule depends upon the overall center of overlapping positive and negative charges. If a molecule is completely symmetric, then the dipole moment on each molecule will cancel out and make the molecule nonpolar.
How many valence electrons does carbon have?
Carbon contains 4 valence electrons and hydrogen has 1 electron and chlorine has 7 valence electrons. So,there are total 20 valence electrons 4*1+1*2+7*2=20. Both carbon atoms at the center form two bonds with 2 hydrogen and two bonds with 2 chlorine atoms.
Does chlorine attract electrons?
Chlorine has an ability to attract electrons, makes one side of dichloromethane partially positive, and the other side negative. The polarity of bonds is determined by comparing the electronegativity of the bonding atoms. In the case of dichloromethane electronegativity of all the bonding atoms are as follows.
Is a diatomic molecule nonpolar?
All the inert gases and homonuclear di atomic molecules are nonpolar. To identify the polarity and non-polarity of the compounds it is advisable to revise basic chemistry terminology like electronegativity, dipole moment, geometry, and shape of the molecule that will give more clarity.
Where does dichloromethane come from?
Occurrence. Natural sources of dichloromethane include oceanic sources, macroalgae, wetlands, and volcanoes. However, the majority of dichloromethane in the environment is the result of industrial emissions.
What is the name of the compound with the formula C H 2 Cl 2?
Dichloromethane ( DCM or methylene chloride) is an organochloride compound with the formula C H 2 Cl 2. This colorless, volatile liquid with a chloroform -like, sweet odour is widely used as a solvent. Although it is not miscible with water, it is polar, and miscible with many organic solvents.
How many bathtub refinishers died from DCM?
In February 2013, the U.S. Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) and the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health warned that at least 14 bathtub refinishers have died since 2000 from DCM exposure.
What are the consequences of DCM?
More severe consequences can include suffocation, loss of consciousness, coma, and death. DCM is also metabolized by the body to carbon monoxide potentially leading to carbon monoxide poisoning. Acute exposure by inhalation has resulted in optic neuropathy and hepatitis.
How is DCM produced?
DCM is produced by treating either chloromethane or methane with chlorine gas at 400–500 °C. At these temperatures, both methane and chloromethane undergo a series of reactions producing progressively more chlorinated products. In this way, an estimated 400,000 tons were produced in the US, Europe, and Japan in 1993.
What is DCM used for?
DCM is used in the material testing field of civil engineering ; specifically it is used during the testing of bituminous materials as a solvent to separate the binder from the aggregate of an asphalt or macadam to allow the testing of the materials.
How many tons of chloroform were produced in 1993?
In this way, an estimated 400,000 tons were produced in the US, Europe, and Japan in 1993. The output of these processes is a mixture of chloromethane, dichloromethane, chloroform, and carbon tetrachloride as well as hydrogen chloride as a byproduct. These compounds are separated by distillation .
Dichloromethane (CH2CL2): Polar or Nonpolar?
Dichloromethane CH2L2 is a polar compound because of its tetrahedral structure. The molecules are arranged wherein the Carbon atom is in the middle, one Hydrogen atom is at the top, and the other is on the left side of the central atom.
Its Molecular Structure
In determining if chemical reactions can affect the structure of a compound, we look at the Lewis Structure [1]. This representation helps us understand the compound’s structure along with eight electrons for it to be stable or inert.
How to Determine CH2CL2 Molecular Polarity
Polar molecules are molecules where atoms share an unequal proportion of bonded electrons. A higher electronegativity atom pulls the electron pair to its side, gaining a partial negative charge, whereas the other atom acquires a partial positive charge. The electronegativity of an element rises from left to right, according to the periodic table.
So, Is CH2CL2 Polar or Nonpolar?
The intensity of polarity varies differently in other atoms. In CH2Cl2, it is considered a polar molecule because of its tetrahedral structure and the difference in their electronegativity. Its physical properties are as follows: it has a molecular weight of 84.93 g/mol. It has a density of 1.3226g/cm3 and a boiling point of 39.60° Celsius.
CH2Cl2 Lewis structure
The lewis structure is critical for understanding the properties and structure of every chemical compound, including organic compounds. Initially, the Lewis structure implemented inorganic compounds to fulfills the octet rule. But later, the same used in the organic molecules also.
CH2Cl2 Lewis structure calculation
The bonds are represented by line in drawing or dots, and the valence electrons are represented by dots in the Lewis structure. Carbon and hydrogen atoms are less electronegative than chlorine atoms in CH2Cl2. Calculate the cumulative number of valence electrons in Dichloromethane to better explain the Lewis structure.
Hybridization of Dichloromethane (CH2Cl2)
Owing to the exchange of electrons between central carbon, two hydrogen, and two chlorine atoms. The orbitals of two or more atoms converge as they form a covalent bond. This is called the hybridization of atomic orbitals to form molecular orbitals.
Preparation of Dichloromethane (CH2Cl2)
Methyl chloride or Dichloromethane is mostly emitted by industrial emissions to the environment. It’s made by heating methane to 400–500 degrees Celsius and treating it with chlorine gas.
Molecular Geometry of Dichloromethane (CH2Cl2)
Understanding a compound’s molecular geometry is relatively simple in the organic molecules as compared with inorganic molecules. In the organic chemistry, the Carbon atom is the central figure in all molecular skeletons.
Is CH2Cl2 polar or nonpolar Molecules?
There are a few key points in the subtopic of dichloromethane that we will explore below in order to assess and differentiate the polar or nonpolar existence of a CH2Cl2 molecule.
Polarity of Dichloromethane (CH2Cl2)
The polarity of any compound is determined by the number of lone pairs of electrons and the compound’s molecular geometrical symmetry.
What is Chloroform?
Chloroform is an organic compound having the chemical formula CHCl 3. It is useful as a powerful anaesthetic. The IUPAC name of this compound is trichloromethane. It is a colourless and dense liquid that has a sweet smell. Chloroform is produced on a large scale as a precursor to producing PTFE.
What is Dichloromethane?
Dichloromethane is an organic compound having the chemical formula CH 2 Cl 2. It is an organochlorine compound, and we can denote it as DCM. This compound occurs as a volatile, colourless liquid consisting of a chloroform-like sweet odour. Dichloromethane is mainly useful as a solvent.
What is the Difference Between Chloroform and Dichloromethane?
Chloroform and dichloromethane are organochlorine molecules. The key difference between chloroform and dichloromethane is that chloroform contains three chlorine atoms per molecule, whereas dichloromethane contains two chlorine atoms per molecule.
Summary – Chloroform vs Dichloromethane
In brief, chloroform and dichloromethane are organochlorine molecules. The key difference between chloroform and dichloromethane is that chloroform contains three chlorine atoms per molecule, whereas dichloromethane contains two chlorine atoms per molecule.

Overview
Dichloromethane (DCM or methylene chloride, methylene bichloride ) is an organochlorine compound with the formula CH2Cl2. This colorless, volatile liquid with a chloroform-like, sweet odour is widely used as a solvent. Although it is not miscible with water, it is polar, and miscible with many organic solvents.
Occurrence
Natural sources of dichloromethane include oceanic sources, macroalgae, wetlands, and volcanoes. However, the majority of dichloromethane in the environment is the result of industrial emissions.
Production
DCM is produced by treating either chloromethane or methane with chlorine gas at 400–500 °C. At these temperatures, both methane and chloromethane undergo a series of reactions producing progressively more chlorinated products. In this way, an estimated 400,000 tons were produced in the US, Europe, and Japan in 1993.
CH4 + Cl2 → CH3Cl + HCl CH3Cl + Cl2 → CH2Cl2 + HCl CH2Cl2 + Cl2 → CHCl3 + HCl CHCl3 + C…
Uses
DCM's volatility and ability to dissolve a wide range of organic compounds makes it a useful solvent for many chemical processes. In the food industry, it is used to decaffeinate coffee and tea as well as to prepare extracts of hops and other flavourings. Its volatility has led to its use as an aerosol spray propellant and as a blowing agent for polyurethane foams.
Toxicity
Even though DCM is the least toxic of the simple chlorohydrocarbons, it has serious health risks. Its high volatility makes it an acute inhalation hazard. It can also be absorbed through the skin. Symptoms of acute overexposure to dichloromethane via inhalation include difficulty concentrating, dizziness, fatigue, nausea, headaches, numbness, weakness, and irritation of the upper respiratory tract and eyes. More severe consequences can include suffocation, loss of cons…
Environmental effects
Dichloromethane is not classified as an ozone-depleting substance by the Montreal Protocol. The U.S. Clean Air Act does not regulate dichloromethane as an ozone depleter. Recent research shows that dichloromethane and other halogenated very short-lived substances (VSLSs), despite their short atmospheric lifetimes of less than 0.5 year, can contribute to stratospheric oz…
See also
• Chloromethane
• Trichloromethane
• Tetrachloromethane
• List of chemical compounds
• List of organic compounds
External links
• International Chemical Safety Card 0058
• NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0414". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
• National Pollutant Inventory – Dichloromethane Fact Sheet