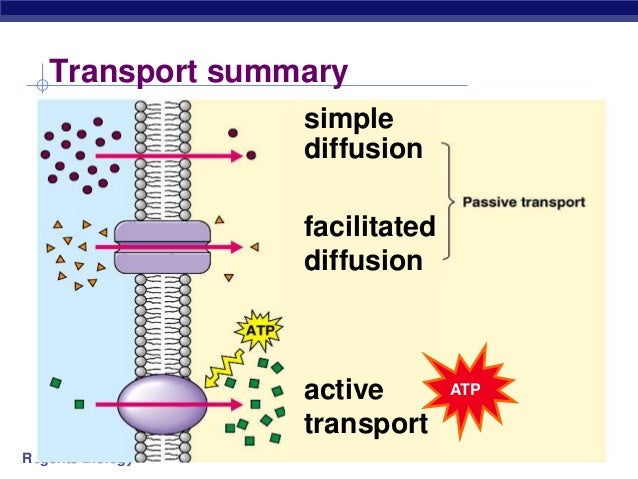
An example of diffusion is oxygen moving from the airways to the lungs – there is very little oxygen in the lungs but lots in the air. Active transport is the movement of particles from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration. This process requires energy (ATP
Adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine triphosphate is a complex organic chemical that provides energy to drive many processes in living cells, e.g. muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, and chemical synthesis. Found in all forms of life, ATP is often referred to as the "molecular unit of currency" of i…
What are the similarities of diffusion and active transport?
Facilitated diffusion and active transport both utilize proteins to transport substances across membranes. 1. Active transport requires an input of energy, usually ATP, while facilitated transport does not.
Which of the active transport types employs diffusion?
Which of the active transport types employs diffusion? Symport Uniport Antiport Uniport and Antiport All types of active transport make use of some form of diffusion.
Is diffusion passive or active transport?
Diffusion is a passive process, whereas active transport requires the metabolic energy for the molecule’s transportation across the cell membrane. The primary difference between both the terms is their energy requirements for the molecule’s transportation across the cell membrane.
Does active transport rely on the process of diffusion?
Facilitated diffusion does not require cellular energy to transport molecules. However, active transport uses ATP or electrochemical potential to transport molecules. Therefore, the main difference between facilitated diffusion and active transport is the use of energy for the transportation by each method.
Is a diffusion active transport?
Diffusion is a passive process, but active transport requires metabolic energy or an electrochemical gradient for the transportation of molecules across the membrane. Simple diffusion occurs directly through the cell membrane.
Is diffusion an example of passive or active transport?
passive transportOsmosis, diffusion and facilitated diffusion are some of the examples of passive transport.
Which is an example of active transport?
Examples of active transport include the transportation of sodium out of the cell and potassium into the cell by the sodium-potassium pump. Active transport often takes place in the internal lining of the small intestine.
Is diffusion a passive transport?
1: Passive Transport: Diffusion is a type of passive transport. Diffusion through a permeable membrane moves a substance from an area of high concentration (extracellular fluid, in this case) down its concentration gradient (into the cytoplasm).
What are 4 types of active transport?
CONTENTSAntiport Pumps.Symport Pumps.Endocytosis.Exocytosis.
Why is diffusion a passive transport?
Passive transport does not require the cell to expend any energy and involves a substance diffusing down its concentration gradient across a membrane.
What are the 3 active transports?
It is usually powered by ATP. Examples of active transport include the Sodium-Potassium Pump (primary transport), the Na+/glucose symporter (secondary transport), and endocytosis and exocytosis (bulk transport).
What are active transport 5 examples?
Examples of Active Transport in Animals and Humans Sodium-potassium pump (exchange of sodium and potassium ions across cell walls) Amino acids moving along the human intestinal tract. Calcium ions moving from cardiac muscle cells. Glucose moving in or out of a cell.
What are the 2 types of active transport?
Two types of active transport are membrane pumps (such as the sodium-potassium pump) and vesicle transport.
Is diffusion active or passive quizlet?
Is diffusion a kind of passive or active transport? Diffusion is passive transport because it does not use the cell's energy.
Is facilitated diffusion and active transport?
Facilitated diffusion (also known as facilitated transport or passive-mediated transport) is the process of spontaneous passive transport (as opposed to active transport) of molecules or ions across a biological membrane via specific transmembrane integral proteins.
Is diffusion active or passive quizlet?
Is diffusion a kind of passive or active transport? Diffusion is passive transport because it does not use the cell's energy.
Are active transport and passive diffusion the same?
There are two major ways that molecules can be moved across a membrane, and the distinction has to do with whether or not cell energy is used. Passive mechanisms like diffusion use no energy, while active transport requires energy to get done.
What is passive transport example?
Summary. Passive transport does not require energy input. An example of passive transport is diffusion, the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. Carrier proteins and channel proteins are involved in facilitated diffusion.
What is active transport and how does it work?
Active transport is the energy-requiring transport of substances across a plasma membrane against the concentration gradient , i.e. from low con...
What is active transport and examples?
Active transport is the movement of substances across a plasma membrane against their concentration gradient , i.e. from low concentration to h...
What are three examples of active transport?
Examples of active transport include: Primary active transport The Sodium-Potassium Pump Secondary active transport The H+-Glucose Symporter B...
What is the difference between active transport and diffusion?
It is active transport that facilitates the transportation of large and polar molecules. The main difference between diffusion and active transport is that diffusion is a passive transport method in which molecules move across the cell membrane through a concentration gradient whereas active transport requires cellular energy in order ...
What are the two types of active transport?
Primary active transport and secondary active transport are the two types of active transport. Molecules required by the cell are specifically recognized by transmembrane proteins in the cell membrane. These transmembrane proteins are powered by ATP. The sodium/potassium pump (Na+/K+ ATPase), which maintains the resting potential ...
What is the passive movement of molecules along a concentration gradient of higher concentration to a lower concentration?
Definition. Diffusion : Diffusion is the passive movement of molecules along a concentration gradient of higher concentration to a lower concentration. Active Transport: Active transport is the movement of particles across a cellular membrane from a lower to a higher concentration by the use of metabolic energy.
What is the transport of polar ions across a biological membrane?
Facilitated diffusion is the transport of substances across a biological membrane through a concentration gradient by means of a carrier molecule. Large ions and polar molecules which are dissolved in water are transported by specific transmembrane proteins in the cell membrane. Polar ions diffuse through transmembrane channel proteins ...
What is the process of transporting molecules across the cell membrane?
Diffusion and active transport are two methods of transporting molecules across the cell membrane. Diffusion is a passive process, but active transport requires metabolic energy or an electrochemical gradient for the transportation of molecules across the membrane. Simple diffusion occurs directly through the cell membrane.
How does active transport help maintain homeostasis?
Both diffusion and active transport allow the cell to maintain homeostasis inside the cell by transporting molecules across the cell membrane. Transportation of molecules occurs with the assistance of transmembrane proteins other than simple diffusion.
What is the movement of particles across a cellular membrane from a lower to a higher concentration?
Active transport is the movement of particles across a cellular membrane from a lower to a higher concentration by the use of metabolic energy. Enzymes bound to the cellular membranes and metabolic energy in the form of ATP assist active transport . Primary active transport and secondary active transport are the two types of active transport.
What is the difference between passive diffusion and active transport?
One of the main differences between passive diffusion and active transport is the fact that passive diffusion involves the movement of substances down their concentration gradient. This simply means that substances will move from where they are highly concentrated to where they are less concentrated.
How does active transport work?
As mentioned, active transport plays an important role in moving substances against their concentration gradient. This means that it's involved in moving substances from an area in which they are less concentrated to an area in which they are highly concentrated. To do this, active transport uses energy.
Why is active transport important?
As such, active transport can be said to prevent diffusion given that it prevents molecules or ions from moving down their concentration gradient.
What is the term for the transport of macromolecules across the cell membrane?
transportation of hormones by endocrine glands out of the cells) is known as exocytosis while the intake of macromolecules across the cell membrane is known as endocytosis ( phagocytosis or pinocytosis ).
What is the effect of pumping out ions?
By actively pumping out ions (e.g. sodium ions), there is an increased concentration of these ions out of the cell.
How do ions move down the concentration gradient?
As a result of this gradient, these ions are forced to move down their concentration gradient into the cell through the protein transporters. However, because of their charge, they also bind to other substances (e.g. glucose molecules) and thus help transport them into the cell.
What is the role of ATP in active transport?
In primary active transport, direct hydrolysis of an ATP molecule results in the production of a phosphate that causes a conformational change of the transporter proteins thereby promoting the transport of given substances (e.g. ions). In this case, then, ATP is required for the protein transporters to function as required.
What are the two types of cellular transport?
There are two main types of cellular transport: active transport and passive transport. Both types of transport are necessary in every living organism.
What is the most common source of energy for active transport?
The most common source of energy for active transport is ATP, or Adenosine Tri-Phosphate. Active transport can take place anywhere in the cell, for example:
What is the term for the movement of large molecules across a membrane?
Endocytosis and Exocytosis (also known as bulk transport) — Movement of very large molecules (e.g. proteins and carbohydrates) across a membrane using vesicles.
Where do sodium ions bind to the active site of the transporter?
Three sodium ions bind to the active site of the transporter from the interior of the cell (the "intracellular space").
Which ions dissociate from the transporter?
The three sodium ions dissociate from the transporter, and two potassium ions from outside the cell bind in their place.
What is the primary active transport protein?
A famous example of primary active transport is the Sodium-Potassium (Na/ K) Pump, which is shown in the figure below.
Where is the Na+/glucose cotransporter found?
This secondary symport protein is found in cells lining the human small intestine and is the primary means of absorbing sugars from food.
