- Payment. In an ordinary annuity, the payment you make is for the period preceding its date, whereas, in the payment in an annuity, due is for the period following its ...
- Present Value. We make the payment earlier in the annuity due, so its present value is usually higher than an ordinary annuity.
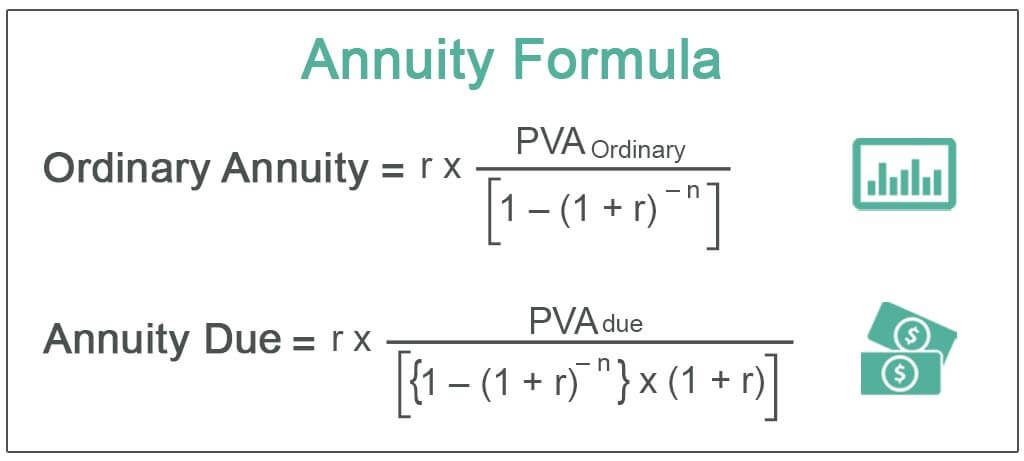
- Formula. ...
- Examples. ...
- Amount. ...
- Appropriate. ...
What is the difference between an annuity due vs. an ordinary annuity?
The points given below are noteworthy, so far as the difference between ordinary annuity and annuity due is concerned: Ordinary annuity refers to the sequence of steady cash flow, whose payment is to be made or received at the end of each period. Each cash inflow or outflow of an ordinary annuity is related to the period preceding its date.
How do you calculate annuity due?
- Pmt: Payment Made Per Period
- r: Discount Rate
- n: No of Periods
- PVA: Present Value of Annuity Due
What is an annuity and how does it work?
- CDs are typically purchased from banks or credit unions. Fixed annuities are purchased from an insurance company.
- Interest earned on a fixed annuity is tax deferred while CD interest is taxed as ordinary income for the year it’s earned.
- CDs impose high penalties if you withdraw money before the maturity date. ...
How do you calculate annuity due in Excel?
- PVA Due = Present value of an annuity due
- r = Effective interest rate
- n = number of periods
What is an annuity due?
How does annuity due work?
What is an ordinary annuity?
What is the formula for present value of an annuity?
What does the present value of an annuity tell us?
Why do annuities have to be paid at the beginning of the month?
What is an immediate annuity?
See more
About this website

What is difference between annuity and annuity due?
Key Takeaways. Annuity due is an annuity whose payment is due immediately at the beginning of each period. Annuity due can be contrasted with an ordinary annuity where payments are made at the end of each period. A common example of an annuity due payment is rent paid at the beginning of each month.
Which is higher annuity or annuity due?
Since payments are made sooner with an annuity due than with an ordinary annuity, an annuity due typically has a higher present value than an ordinary annuity. When interest rates go up, the value of an ordinary annuity goes down. On the other hand, when interest rates fall, the value of an ordinary annuity goes up.
What is annuity due formula?
The formula for calculating the future value of an annuity due (where a series of equal payments are made at the beginning of each of multiple consecutive periods) is: P = (PMT [((1 + r)n - 1) / r])(1 + r) Where: P = The future value of the annuity stream to be paid in the future.
What do you mean by annuity?
An annuity is a fixed amount of money that you will get each year for the rest of your life. An annuity is a contract between you and an insurance company that requires the insurer to make payments to you, either immediately or in the future.
What is an example of annuity?
Examples of annuities are regular deposits to a savings account, monthly home mortgage payments, monthly insurance payments and pension payments. Annuities can be classified by the frequency of payment dates.
What is PMT in annuity?
PMT = the period cash payment. r = the interest rate per period. n = the total number of periods.
How do we calculate annuity?
Annuity = r * PVA Ordinary / [1 – (1 + r)-n]PVA Ordinary = Present value of an ordinary annuity.r = Effective interest rate.n = Number of periods.
How are annuities calculated?
The formula for determining the present value of an annuity is PV = dollar amount of an individual annuity payment multiplied by P = PMT * [1 – [ (1 / 1+r)^n] / r] where: P = Present value of your annuity stream. PMT = Dollar amount of each payment. r = Discount or interest rate.
What is annuity table?
An annuity table is a tool used to determine the present value of an annuity. An annuity table calculates the present value of an annuity using a formula that applies a discount rate to future payments. An annuity table uses the discount rate and number of period for payment to give you an appropriate factor.
What is annuity and types?
Annuities come in three main varieties—fixed, variable, and indexed—each with its own level of risk and payout potential. The income you receive from an annuity is typically taxed at regular income tax rates, not long-term capital gains rates, which are usually lower.
What is another word for annuity?
In this page you can discover 12 synonyms, antonyms, idiomatic expressions, and related words for annuity, like: income, rente, lump-sum, pension, annuitant, endowment, , mortgage, sipp, and tax-free.
What are the three types of annuities?
The main types of annuities are fixed annuities, fixed indexed annuities and variable annuities, which can each be immediate or deferred. The immediate and deferred classifications indicate when annuity payments will start.
Annuity Due - Overview, Present and Future Values
Summary . Annuity due refers to a series of equal payments made at the same interval at the beginning of each period. The first payment is received at the start of the first period and, thereafter, at the start of each subsequent period.
Annuity due definition — AccountingTools
An annuity due is a repeating payment in the same amount that is made at the beginning of each period, such as a rent payment.
Last time Example: Annuity due | asif shaikh - Academia.edu
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
When does an annuity make its payment?
Therefore, an ordinary annuity makes its payment at the end of each payment period or interval period. For example, if an annuity has monthly intervals, it will make payments at the end of each month.
What is an annuity contract?
Specifically, an annuity is a contract to guarantee a series of structured payments over time. It starts at a predetermined date and lasts for a predetermined time. It’s a payment against a larger obligation. For example, a cable bill is not, but a car payment or student loan payment is.
What is the difference between annuities and annuities?
The most notable difference in ordinary annuities and annuities due is the way they pay out. All annuities make a payment once per period, just like how bills are due during each billing cycle. The payments come at the end of the period or the beginning.
What happens to annuity payments at the end of a billing cycle?
If you make your payment at the end of a billing cycle, your payment will likely be larger than if your payment is due immediately due to interest accrual.
What is the present value of an annuity?
Present Value. The present value of an annuity is the cash value of all your future annuity payments and is based on the time value of money. The time value of money is the concept that a dollar today is worth more than a dollar at the end of the year due to inflation.
What is an ordinary annuity?
An ordinary annuity means you are paid at the end of your covered term; an annuity due pays you at the beginning of a covered term. If you have an annuity or are considering buying annuities, here’s what you need to know about an ordinary annuity vs. an annuity due.
What are some examples of annuities?
One example of an annuity due is a rent payment because it is made at the beginning of the month rather than the end. Other examples include insurance premiums and car lease payments. Key Differences: Ordinary Annuity vs. Annuity Due. There are several key differences between an ordinary annuity and an annuity due.
What Is an Ordinary Annuity?
An ordinary (or straight line) annuity has equal payments that occur at regular intervals, with the first payment made immediately.
What Is an Annuity Due?
An annuity due has unequal payments occurring at regular intervals, with the first payment occurring immediately.
Key Differences Between Ordinary Annuity and Annuity Due
Here are some key differences to take note in order to distinguish an ordinary annuity from an annuity due:
Present Value Calculation
The prevailing interest rate and inflation are two factors that greatly affect the present value of an annuity. Below are the formulas on how to compute the present value for each type of annuity:
The Bottom Line
Annuities are a series of cash flows occurring over time. Annuities have two types: ordinary annuity and annuity due.
What is an annuity due?
Annuity due is an annuity whose payment is due immediately at the beginning of each period. Annuity due can be contrasted with an ordinary annuity where payments are made at the end of each period. A common example of an annuity due payment is rent paid at the beginning of each month. An example of an ordinary annuity includes loans, ...
How does annuity due work?
How Annuity Due Works. An annuity due requires payments made at the beginning, as opposed to the end, of each annuity period. Annuity due payments received by an individual legally represent an asset. Meanwhile, the individual paying the annuity due has a legal debt liability requiring periodic payments.
What is an ordinary annuity?
In contrast, an ordinary annuity generates payments at the end of the period. As a result, the method for calculating the present and future values differ. A common example of an annuity due is rent payments made to a landlord, and a common example of an ordinary annuity includes mortgage payments made to a lender.
What is the formula for present value of an annuity?
The formula for the present value of an annuity due is: Present Value of Annuity Due. Investopedia. Let's look at an example of the present value of an annuity due.
What does the present value of an annuity tell us?
The present value of an annuity due tells us the current value of a series of expected annuity payments. In other words, it shows what the future total to be paid is worth now.
Why do annuities have to be paid at the beginning of the month?
The collector of the payment may invest an annuity due payment collected at the beginning of the month to generate interest or capital gains. This is why an annuity due is more beneficial for the recipient as they have the potential to use funds faster.
What is an immediate annuity?
An immediate annuity is an account, funded with a lump sum deposit, that generates an immediate stream of income payments. The income can be for a stated amount (e.g., $1,000/month), a stated period (e.g., 10 years), or a lifetime.
