The respiratory tract is divided into upper and lower regions at the epiglottis. Air enters the upper respiratory tract through the nasal cavity and mouth, which both lead to the pharynx . The lower respiratory tract extends from the larynx into the trachea before branching into the bronchi , which divide further to form the bronchioles , which terminate in alveoli , where gas exchange occurs.
What is epiglottitis and what causes it?
Epiglottitis is a life-threatening infection that causes profound swelling of the upper airways which can lead to asphyxia and respiratory arrest. [1] Go to: Etiology The cause of epiglottitis is more commonly infectious rather than noninfectious. It can be bacterial, viral, or fungal in origin.
How common is epiglottitis in the ER?
Epiglottitis is a relatively common fear in the emergency department, but actually rather rare.
What is the difference between the epiglottis in adults and children?
In a young child, the epiglottis is located more superiorly and anteriorly than in an adult. There is also a more oblique angle with the trachea. The narrowest portion of the infant and pediatric airway is the subglottis, while in adults it is the glottis.
What is the pathophysiology of epiglottitis with influenzae?
H. influenzae, and other, infections of the epiglottis can lead to marked edema and swelling 0f the epiglottis and supraglottis of patients of any age. This edema can rapidly spread to adjacent structures leading to the rapid development of airway obstruction symptoms.
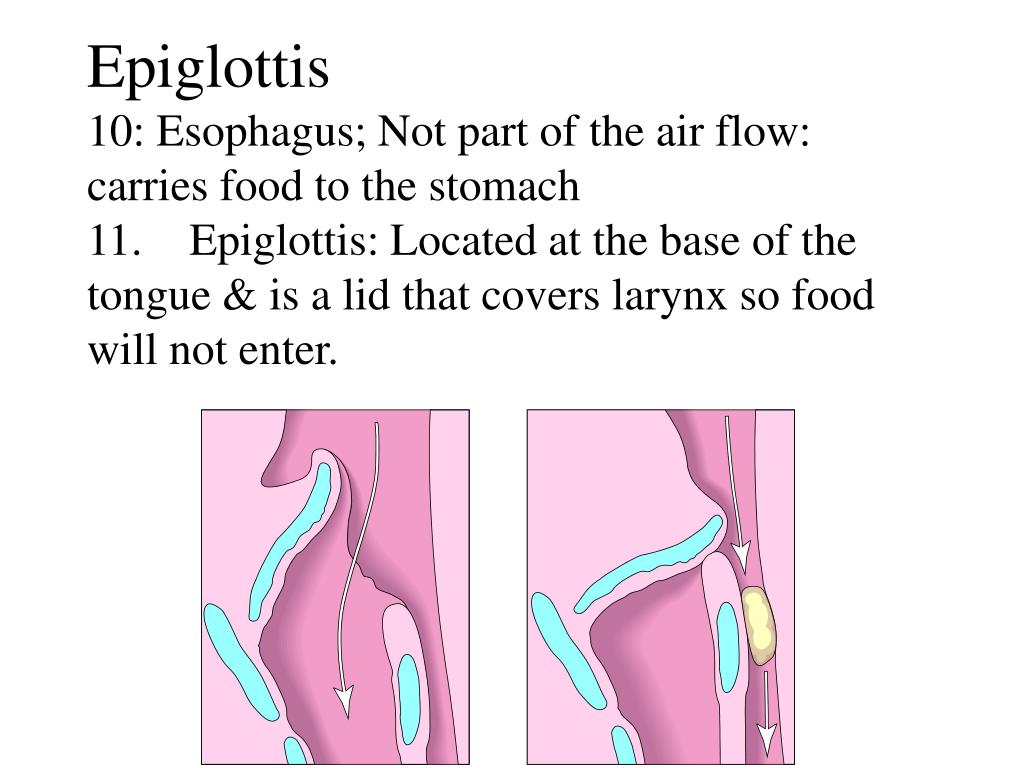
Is epiglottis part of upper airway?
It is situated directly above the trachea and makes up the lowest part of the upper respiratory tract. It is important to know that the larynx is made up of the thyroid cartilage and the cricoid cartilage. There is also a structure known as the epiglottis that covers the top of the larynx.
What are the upper and lower respiratory tract?
The upper respiratory tract (upper airway) consists of the nose, mouth, sinuses, pharynx (upper section of the throat), and larynx (voice box). The lower respiratory tract consists of the trachea (windpipe), bronchial tubes, and lungs.
Is the epiglottis part of the respiratory system?
The epiglottis is a leaf-shaped flap in the throat that prevents food and water from entering the windpipe and the lungs. It stays open during breathing, allowing air into the larynx....EpiglottisFunctionPrevent food from entering the respiratory tract.IdentifiersLatinEpiglottisMeSHD0048257 more rows
What are the organs in the lower respiratory tract?
The major passages and structures of the lower respiratory tract include the windpipe (trachea) and within the lungs, the bronchi, bronchioles, and alveoli.
Which is not part of the upper respiratory tract?
So, the correct answer is 'Trachea'
What are the 3 parts of the upper respiratory tract?
The upper respiratory system, or upper respiratory tract, consists of the nose and nasal cavity, the pharynx, and the larynx.
What system is the epiglottis part of?
The epiglottis is a leaf-shaped cartilaginous structure that is part of the laryngeal skeleton.
What is the role of epiglottis in respiration?
The epiglottis is usually upright at rest allowing air to pass into the larynx and lungs. When a person swallows the epiglottis folds backward to cover the entrance of the larynx so food and liquid do not enter the windpipe and lungs.
What is difference between epiglottis and pharynx?
The glottis opens into the windpipe and is responsible for the production of sound. While the epiglottis is a cartilaginous flap on top of the glottis that prevents the food from entering the larynx....Also Read:Human Digestive SystemDifference Between Pharynx and LarynxRole of Alimentary CanalMechanism of Breathing
Which of the following organ is not part of the lower respiratory system?
Which of the following organs is not part of the lower respiratory system? upper respiratory tract.
Which of the given organ is not a part of the lower respiratory system?
Explanation: The alveoli is the site where the exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide takes place between blood and alveoli during the process of breathing in and breathing out.
What is upper respiratory tract?
Overview. The major passages and structures of the upper respiratory tract include the nose or nostrils, nasal cavity, mouth, throat (pharynx), and voice box (larynx). The respiratory system is lined with a mucous membrane that secretes mucus.
Where are the upper and lower respiratory tract located?
The upper respiratory tract consists of the nose, the nasal cavity and the pharynx. The lower tract consists of the larynx, the trachea , the bronchi and the lungs. The trachea, which begins at the edge of the larynx, divides into two bronchi and continues into the lungs.
What are the types of respiratory tract?
The respiratory tract is divided into two main parts: the upper respiratory tract, consisting of the nose, nasal cavity and the pharynx; and the lower respiratory tract, consisting of the larynx, trachea, bronchi and the lungs.
What is the most common upper respiratory tract infection?
The most common virus is rhinovirus. Other viruses include the influenza virus, adenovirus, enterovirus, and respiratory syncytial virus. Bacteria may cause roughly 15% of sudden onset pharyngitis presentations.
How to prevent epiglottitis?
To prevent epiglottitis, vaccination should be encouraged. Children should be immunized according to the schedule prescribed by the WHO.
What is the cause of death for epiglottitis?
The cause of death is usually due to sudden upper airway obstruction and difficulty intubating the patient, with extensive swelling of the laryngeal structures. Thus, every patient admitted with a diagnosis of acute epiglottitis must be seen by an ear, nose, and throat surgeon or anesthesiologist, and a tracheostomy tray must be made available at the bedside. Globally, a mortality rate of 3% to 7% has been reported in patients with unstable airways.
What is the difference between an adult and a child's airway?
The airway in the pediatric population is markedly different compared to that of an adult. In a young child, the epiglottis is located more superiorly and anteriorly than in an adult. There is also a more oblique angle with the trachea. The narrowest portion of the infant and pediatric airway is the subglottis, while in adults it is the glottis. Furthermore, the infant epiglottis is comprised of cartilage that is far more pliant when compared to that of an adult, whose epiglottis is more rigid (this is the natural progression of cartilage maturation, and explains why laryngomalacia is more prevalent in very young children). It is not surprising, then, that an infectious process that leads to edema and increase in weight and mass of the epiglottis is more likely to cause symptoms in a child - the pliancy of the cartilage allows a ball-valve effect, where each inspiration pulls an edematous epiglottis over the laryngeal airway, causing symptoms. In adults, whose cartilages are stiffer, an isolated epiglottic infection and the resultant increase in epiglottic mass may be resisted by the more rigid laryngeal/epiglottic cartilage; but an infection that encompasses more of the tissues of the supraglottis, leading to edema, can lead to symptoms and an unstable airway.
What is the name of the condition that causes swelling of the upper airways?
Epiglottitis is an inflammatory condition of the epiglottis and/or nearby structures including the arytenoids, aryepiglottic folds, and vallecula. Epiglottitis is a life-threatening infection that causes profound swelling of the upper airways which can lead to asphyxia and respiratory arrest. This activity reviews the cause, presentation, and pathophysiology of epiglottitis and highlights the role of the interprofessional team in its management.
Is epiglottitis a viral infection?
The cause of epiglottitis is most commonly infectious, whether bacterial, viral, or fungal in origin. In children, Haemophilus influenzae type B (HIB) is still the most common cause. However, this has decreased dramatically since the widespread availability of immunizations. Other agents such as Streptococcus pyogenes, S. pneumoniae, and S. aureushave been implicated. In immunocompromised patients, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Candida have been named. Noninfectious causes can be traumatic such as thermal, caustic, or foreign body ingestion. [2][3][4]
Is epiglottitis a disease?
While in the past epiglottitis was thought to be primarily a disease of young children, it is now much more likely practitioners will encounter epiglottitis/supraglottitis in adults as well.
Can an epiglottal culture be performed with an endotracheal tube?
A complete blood count with differential, a blood culture, and an epiglottal culture should only be obtained in patients with a secured endotracheal tube. [6]
What is epiglottitis?
It sits far back in your mouth, at the base of your tongue. Epiglottitis is when the epiglottis gets inflamed . This condition can be serious. If the epiglottis swells from inflammation, it can block your airway. You may have trouble breathing. If you think you or a loved one has epiglottitis, get medical help right away.
What is laryngitis?
Your larynx is your voice box. Laryngitis is when the larynx becomes inflamed. Usually, a virus infects the upper airways, leading to laryngitis. The main symptom of laryngitis is a voice change. You may:
What is a respiratory infection?
A respiratory tract infection affects the respiratory system, the part of your body responsible for breathing. These infections can affect your sinuses, throat, lungs or airways. There are two types of respiratory infections:
How are upper respiratory infections diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider may diagnose the infection based on a physical exam and your symptoms. They’ll look in your nose, ears and throat and listen to your chest to examine your breathing. You often don’t need other tests.
Can antibiotics treat upper respiratory infections?
Most of the time, viruses cause upper respiratory infections. Viruses don’t respond to antibiotics. You can most likely treat the symptoms at home through pain relievers, rest and drinking fluids. If you have a bacterial infection, such as strep throat, you’ll take antibiotics. Penicillin or amoxicillin are frequently prescribed for strep throat.
What is the common cold?
The common cold refers to at least 200 different viruses that cause a cold. Colds often go away on their own. Colds can:
What are common respiratory infections in children?
Respiratory infections are common in children. They happen more often when children are in daycare or school. Siblings can infect each other as well.
Which part of the pharyngeal cavity is founded by the esophagus and the epi?
passageway for air and food, portion of pharyngeal cavity which is founded by the esophagus & the epiglottis
Which part of the lungs leads from the trachea to the bronchioles?
Airways in the lungs that lead from the trachea to the bronchioles.
What is the space between the parietal and visceral pleura?
Small space between the parietal and visceral pleura; contains serous fluid that prevents friction between the lungs and pleura during respiration.
Which duct opens into the alveolar sac?
Straight ducts fed by respiratory bronchioles. The end of duct is where atrium opens into alveolar sac.
Which gland produces mucous that traps debris and assist in speeach?
maxillary produce mucous which traps debris and assist in speeach
What is exchanged between alveoli and blood?
exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between alveoli and blood