Is a collision elastic or inelastic?
This is an inelastic collision. If kinetic energy before is the same as after, then the collision is elastic. Interactions between molecules are examples of perfectly elastic collisions. In most other cases (eg snooker balls), collisions are not perfectly elastic - some kinetic energy is lost.
What happens to kinetic energy in a perfectly inelastic collision?
In a perfectly inelastic collision, i.e., a zero coefficient of restitution, the colliding particles stick together. In such a collision, kinetic energy is lost by bonding the two bodies together.
What happens when two objects collide under inelastic condition?
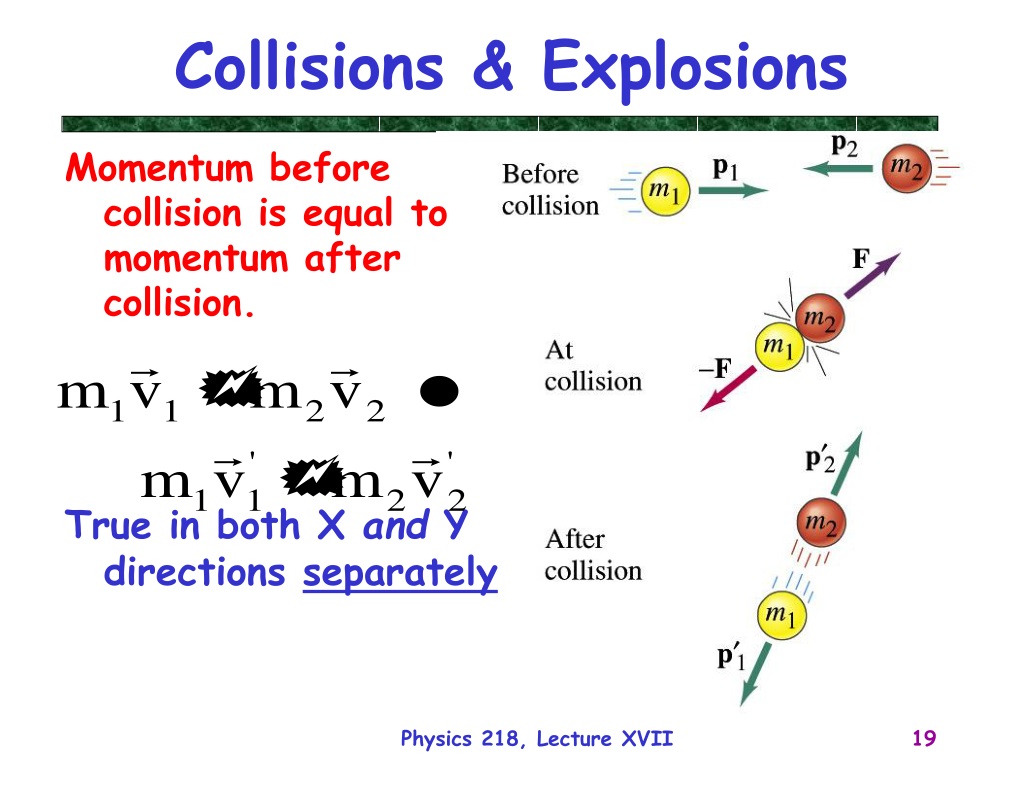
When two objects collide under inelastic condition, the final velocity with which the object moves is given by- Inelastic collision in two dimensions, conservation of momentum is applied separately along each axis.

Why is an explosion inelastic collision?
Collisions are considered inelastic when kinetic energy is not conserved, but this could be from either a loss or gain or kinetic energy. For example, in an explosion-type collision, the kinetic energy increases. It is common for people to try to conserve energy in a collision.
What is considered inelastic collision?
An inelastic collision is a collision in which there is a loss of kinetic energy. While momentum of the system is conserved in an inelastic collision, kinetic energy is not.
What are two examples of inelastic collisions?
Real World Examples Of Inelastic CollisionThe ball is dropped from a certain height and it is unable to rise to its original height.When a soft mudball is thrown against the wall, it will stick to the wall.The accident of two vehicles.A car hitting a tree.
What is an example of a perfectly inelastic collision?
Another common example of a perfectly inelastic collision is known as the "ballistic pendulum," where you suspend an object such as a wooden block from a rope to be a target.
What are 5 examples of inelastic products?
Examples of price inelastic demandPetrol – petrol has few alternatives because people with a car need to buy petrol. For many driving is a necessity. ... Salt. ... A good produced by a monopoly. ... Tap water. ... Diamonds. ... Peak rail tickets. ... Cigarettes. ... Apple iPhones, iPads.
What are examples of elastic and inelastic collisions?
Difference between Elastic and Inelastic CollisionElastic CollisionInelastic CollisionAn example of this can be swinging balls or a spacecraft flying near a planet but not getting affected by its gravity in the end.An example of an inelastic collision can be the collision of two cars.4 more rows•Jun 13, 2020
What is a good example of inelastic?
Inelastic products are usually necessities without acceptable substitutes. The most common goods with inelastic demand are utilities, prescription drugs, and tobacco products. Businesses offering such products maintain greater flexibility with prices because demand remains constant even if prices increase or decrease.
Is momentum conserved in an explosion?
Whether it is a collision or an explosion, if it occurs in an isolated system, then each object involved encounters the same impulse to cause the same momentum change. The impulse and momentum change on each object are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. Thus, the total system momentum is conserved.
Are all collisions inelastic?
Most ordinary collisions are classified as inelastic collisions because some of their kinetic energy is converted to other forms such as internal energy. Links to some examples are provided.
Which of the following is not an inelastic collision?
Therefore the answer is Option (D). A ball bearing striking another ball bearing. Note: In ball bearing striking into another ball bearing, the momentum of the balls system is conserved but kinetic energy is lost. Therefore it is not an example of perfectly inelastic collision though.
How do you know if it is elastic or inelastic collision?
You have to see if the total initial kinetic energy is the same as the total final kinetic energy. If that's the case, it's an elastic collision, and if that's not the case, it's an inelastic collision.
Which of the following in not an example of inelastic collision?
In ball bearing striking another ball bearing momentum of the balls system is conserved. Therefore it is not an example of perfectly inelastic collision.
What items are considered inelastic?
Inelastic products are usually necessities without acceptable substitutes. The most common goods with inelastic demand are utilities, prescription drugs, and tobacco products. Businesses offering such products maintain greater flexibility with prices because demand remains constant even if prices increase or decrease.
What value is considered inelastic?
An inelastic demand is one in which the change in quantity demanded due to a change in price is small. If the formula creates an absolute value greater than 1, the demand is elastic. In other words, quantity changes faster than price. If the value is less than 1, demand is inelastic.
Is a car hitting a wall elastic or inelastic?
When given a push and allowed to collide with a wall, one car bounces off with only a small reduction in speed ("elastic" collison) whereas the other car comes nearly to a complere stop ("inelastic" collision).
What is an example of an inelastic material?
There are two main subcategories of inelastic materials: brittle (material that cracks or fractures easily without much stretching, such as glass) and ductile (material that can be drawn, stretched, or compressed into a deformed shape without breaking, such as silly putty at room temperature).
What happens if two bumper cars collide head on in a fairground?
If two bumper cars collide head-on in a fairground and both cars come to a stop due to the collision, kinetic energy is obviously not conserved . Is momentum conserved even though both cars stop?
Is kinetic energy a scalar quantity?
No. Kinetic energy is a scalar quantity so there is no balancing out of the different directions. Both cars were moving and had kinetic energy before the collision. Both cars are at rest and have no kinetic energy after. previous. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
Is a collision elastic?
If kinetic energy before is the same as after, then the collision is elastic. Interactions between molecules are examples of perfectly elastic collisions. In most other cases (eg snooker balls), collisions are not perfectly elastic - some kinetic energy is lost. But this must be tested by calculation. Remember that kinetic energy can be calculated ...
Is momentum conserved in a collision?
As in all collisions, momentum is conserved in this example. But calculations comparing kinetic energy before and after the collision show kinetic energy is not conserved. This is an inelastic collision. If kinetic energy before is the same as after, then the collision is elastic.
Is there momentum after a collision?
Yes, although there is no momentum after the collision, there was no total momentum before the collision. Momentum is a vector quantity. The positive momentum of one car must have been balanced out by the negative momentum of the other car.
What happens when there is a collision between two objects?
In these situations, the original kinetic energy is sometimes lost in the form of heat or sound, both of which are the results of the vibration of atoms at the point of collision.
What is the term for a collision that happens when kinetic energy is lost?
Perfectly Inelastic Collisions. While an inelastic collision occurs anytime that kinetic energy is lost during the collision, there is a maximum amount of kinetic energy that can be lost. In this sort of collision, called a perfectly inelastic collision, the colliding objects actually end up "stuck" together.
What type of collision is kinetic energy conserved?
This type of collision is called "inelastic.". In contrast, a collision in which kinetic energy is conserved throughout the collision is called an elastic collision. In theory, elastic collisions involve two or more objects colliding with no loss of kinetic energy, and both objects continuing to move as they did before the collision.
What is the kinetic energy of a car that crashes into a tree called?
At the same time, the impact results in a crashing noise. From a physics perspective, the car's kinetic energy changed drastically; much of the energy was lost in the form of sound (the crashing noise) and heat (which dissipates quickly). This type of collision is called "inelastic."
What is the effect of a bullet into wood?
A classic example of this occurs when shooting a bullet into a block of wood. The effect is known as a ballistic pendulum. The bullet goes into the wood and starts the wood moving, but then "stops" within the wood.
Is a collision in the real world elastic?
But of course, this doesn't really happen: any collision in the real world results in some form of sound or heat being given off, which means at least some kinetic energy is lost. For real-world purposes, though, some cases, such as two billiard balls colliding, are considered to be approximately elastic.
Is momentum conserved in collisions?
Though kinetic energy is not conserved in these collisions, momentum is still conserved and therefore the equations for momentum can be used to determine the motion of the various components of the collision.
What is an inelastic collision?
An inelastic collision, in contrast to an elastic collision, is a collision in which kinetic energy is not conserved due to the action of internal friction . In collisions of macroscopic bodies, some kinetic energy is turned into vibrational energy of the atoms, causing a heating effect, and the bodies are deformed.
What is the most common form of collision?
Partially inelastic collisions are the most common form of collisions in the real world. In this type of collision, the objects involved in the collisions do not stick, but some kinetic energy is still lost. Friction, sound and heat are some ways the kinetic energy can be lost through partial inelastic collisions.
Why are gas molecules inelastic?
The molecules of a gas or liquid rarely experience perfectly elastic collisions because kinetic energy is exchanged between the molecules' translational motion and their internal degrees of freedom with each collision. At any one instant, half the collisions are – to a varying extent – inelastic ...
How does kinetic energy lose in a collision?
In such a collision, kinetic energy is lost by bonding the two bodies together. This bonding energy usually results in a maximum kinetic energy loss of the system.
How many images per second is a bouncing ball?
A bouncing ball captured with a stroboscopic flash at 25 images per second. Each impact of the ball is inelastic, meaning that energy dissipates at each bounce. Ignoring air resistance, the square root of the ratio of the height of one bounce to that of the preceding bounce gives the coefficient of restitution for the ball/surface impact.
What is CR in math?
CR is the coefficient of restitution; if it is 1 we have an elastic collision; if it is 0 we have a perfectly inelastic collision, see below.
What happens when time is reversed?
With time reversed we have the situation of two objects pushed away from each other, e.g. shooting a projectile, or a rocket applying thrust (compare the derivation of the Tsiolkovsky rocket equation ).
What is the coefficient of restitution?
The coefficient of restitution is a number between 0 and 1 which describes where an interaction falls on the scale between perfectly inelastic (0) and perfectly elastic (1).
What is it called when a ball is dropped from a height above a surface?
Such collisions are simply called inelastic collisions .
How are modern vehicles designed?
Modern vehicles are designed to make use of both inelastic and elastic collisions in the event of an accident. The frame of a vehicle is designed to absorb energy in a collision through deformation of crumple zones built in to the structure of the vehicle. The interior passenger compartment however is designed to be strong so that damage to the occupants is minimized.
What is an elastic collision?
An elastic collision is a collision in which there is no net loss in kinetic energy in the system as a result of the collision. Both momentum and kinetic energy are conserved quantities in elastic collisions.
Why is kinetic energy conserved?
This is because the requirement that kinetic energy is conserved provides an additional constraint to our equations of motion. This allows us to solve problems in which we would otherwise have too many unknowns. Often the solution will be quite adequate because the collision is 'close enough' to perfectly elastic.
What is ballistic pendulum?
The ballistic pendulum is a practical device in which an inelastic collision takes place. Until the advent of modern instrumentation, the ballistic pendulum was widely used to measure the speed of projectiles.
Why is a trolley collision elastic?
They collide, bouncing off each other with no loss in speed. This collision is perfectly elastic because no energy has been lost.
What is perfect inelastic collision?
Perfectly Inelastic Collision. Andrew Zimmerman Jones is a science writer, educator, and researcher. He is the co-author of "String Theory for Dummies.". A perfectly inelastic collision—also known as a completely inelastic collision—is one in which the maximum amount of kinetic energy has been lost during a collision, ...
How to tell if a collision is inelastic?
In most cases, you can tell a perfectly inelastic collision because of the objects in the collision "stick" together, similar to a tackle in American football. The result of this sort of collision is fewer objects to deal with after the collision than you had before it, as demonstrated in the following equation for a perfectly inelastic collision between two objects. (Although in football, hopefully, the two objects come apart after a few seconds.)
When does a pendulum reach its maximum height?
Since you know that the pendulum reaches a maximum height when all of its kinetic energy turns into potential energy, you can use that height to determine that kinetic energy, use the kinetic energy to determine vf, and then use that to determine v1i - or the speed of the projectile right before impact.
What does v2i = 0 mean?
In this case, if the target is assumed to be the second object in the equation, then v2i = 0 represents the fact that the target is initially stationary.
Who is Andrew Zimmerman Jones?
Andrew Zimmerman Jones is a science writer, educator, and researcher. He is the co-author of "String Theory for Dummies.". our editorial process. Andrew Zimmerman Jones. Updated October 12, 2019. A perfectly inelastic collision—also known as a completely inelastic collision—is one in which the maximum amount of kinetic energy has been lost ...
How many grams are in a hockey puck?
Two ice hockey pucks of different masses are on a flat, horizontal hockey rink. The red puck has a mass of 15 grams, and is motionless; the blue puck has a mass of 12 grams, and is moving at 2.5 m/s to the left. It collides with the motionless red puck ( (Figure) ).
What happens to the kinetic energy of an object after an explosion?
Note that if the object is initially motionless, then the system (which is just the object) has no momentum and no kinetic energy. After the explosion, the net momentum of all the pieces of the object must sum to zero (since the momentum of this closed system cannot change). However, the system will have a great deal of kinetic energy after the explosion, although it had none before. Thus, we see that, although the momentum of the system is conserved in an explosion, the kinetic energy of the system most definitely is not; it increases. This interaction—one object becoming many, with an increase of kinetic energy of the system—is called an explosion.
Where does the initial momentum and initial kinetic energy of the system reside?
The initial momentum and initial kinetic energy of the system resides entirely and only in the second puck (the blue one ); the collision transfers some of this momentum and energy to the first puck.
Why is momentum conservation important?
Conservation of momentum is crucial to our understanding of atomic and subatomic particles because much of what we know about these particles comes from collision experiments.
What is the extreme case of an interaction?
The extreme case on the other end is if two or more objects approach each other, collide, and bounce off each other, moving away from each other at the same relative speed at which they approached each other. In this case, the total kinetic energy of the system is conserved. Such an interaction is called elastic.
What is the first possibility that a single object may break apart into two or more pieces?
These can be difficult to analyze if the number of fragments after the collision is more than about three or four; but nevertheless, the total momentum of the system before and after the explosion is identical.
What is the mass of a deuteron?
Formation of a Deuteron. A proton (mass 1.67 × 10−27kg 1.67 × 10 − 27 kg ) collides with a neutron (with essentially the same mass as the proton) to form a particle called a deuteron.