See more

Is glycerol and glucose same?
Glycerol is superior to glucose for ε-PL production according to batch and fed-batch fermentations by Streptomyces sp. M-Z18 in this study. To elaborate this difference, physiological metabolism of Streptomyces sp. M-Z18 on glycerol has compared with glucose during batch fermentation.
Is glycerol made of glucose?
Glycerol is synthesized from glucose via the glycolytic pathway through reduction of dihydroxyacetone-P by glycerol dehydrogenase, yielding sn-glycerol-3P8.
What is the relationship between glycerol and glucose?
Glycerol is an important intermediate of glucose and lipid metabolism by virtue of its ability to support glycogenesis in various systems, as well as serving as a precursor for the synthesis of triglycerides (TG) and other glycerolipids (Rognstad et al.
What type of sugar is glycerol?
polyolGlycerin(e)/glycerol Glycerin (sometimes spelled glycerine), or glycerol, is a sweet, syrupy liquid that is about 75% as sweet as sucrose. It is chemically categorized as a polyol with 4.32 kcal/g. The FDA classifies glycerin as a Generally Recognized as Safe food additive.
How much glucose is produced from glycerol?
After 62-86 h of starvation, glycerol Ra rose to 5.32 +/- 0.58 mumol. kg-1. min-1, and 68% of glycerol was converted to glucose. This accounted for 21.6% of total glucose production.
What is glycerol made of?
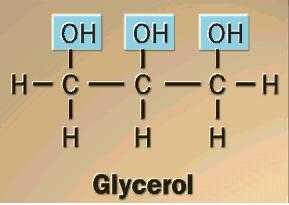
Glycerol is a trihydroxy sugar alcohol with three carbon atoms and three hydroxyl groups. The presence of multiple hydroxyl groups and carbon atoms makes it an organic polyol compound with the IUPAC name of 1, 2, 3 – Propanetriol.
Does glycerol raise blood sugar?
Glycerin belongs to a special category of carbohydrates called polyols, which also includes sugar alcohols like sorbitol and erythritol. Like sugar alcohols, which I've talked about before, glycerin tastes sweet but it is not metabolized as sugar in the body and doesn't cause a rise in blood sugar.
What is glycerol used for in the body?
In humans, glycerol allows ATP production through gluconeogenesis. Glycerol is a gluconeogenic substance, which can be metabolized in sufficient time to provide energy during intensive exercise (Kavouras et al., 1998).
What is glycerol used for?
Glycerol is used as an emollient, humectant, solvent, and lubricant in many products in the personal care industry such as toothpaste, mouthwashes, shaving cream, and soaps [15]. Furthermore, due to its hygroscopic properties glycerol is used in the pharmaceutical industry to prevent the drying of creams and ointments.
What is an example of glycerol?
Glycerol is also called glycerine (or glycerin). Nevertheless, the term “glycerol” is often used to indicate the presence of the compound as an ingredient of a product whereas “glycerine” (or glycerin) often pertains to the product name. For instance, the glycerin syrup is 99.7% glycerol.
When should I take glycerol?
In summary, glycerol ingestion before, during or following exercise is likely to improve the hydration state of the endurance athlete.
Should I take glycerol?
Glycerol seems to be safe for most adults. When taken by mouth, glycerol can cause side effects including headaches, dizziness, bloating, nausea, vomiting, thirst, and diarrhea. Glycerol may not be safe when injected intravenously (by IV). Red blood cells might get seriously damaged.
How do you make glycerol?
Glycerol can be produced by using different processes and feedstocks. For example, it can be obtained by propylene synthesis via several pathways [8], by hydrolysis of oil or by transesterification of fatty acids/oils.
Is glycerol a carbohydrate?
As used in foods, glycerol is categorized by the U.S. Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics as a carbohydrate. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) carbohydrate designation includes all caloric macronutrients excluding protein and fat.
What is the difference between glycogen and glycerol?
Glycogen is a byproduct of breaking down carbohydrates, while glycerol is a byproduct of breaking down fats. Both are relatively easily converted from these states to glucose. Glycerol has no nitrogen, while glycogen does. Glycerol is a simple polyol compound.
Is glycerol a sugar alcohol?
Common names for sugar alcohols are erythritol, glycerol, isomalt, lactitol, maltitol, mannitol, sorbitol, xylitol, and hydrogenated starch hydrolysates (HSH).
What Is The Difference Between Glucose, Glycogen And Glycerol?
What is the difference between glucose, glycogen and glycerol? Are you sure that you want to delete this answer? Best Answer: Glucose is a simple carbohydrate, or sugar. It is important because cells in an organism use it as a source of energy. Turning glucose into energy is called respiration. Humans that do not have enough glucose have low blood sugar levels. Its chemical formula is C6H12O6. This means it has 6 carbon atoms, 12 hydrogen atoms, and 6 oxygen atoms bonded together. Glycogen (commonly known as animal starch although this name is inaccurate) is a polysaccharide that is the principal storage form of glucose in animal cells. Glycogen is found in the form of granules in the cytosol in many cell types, and plays an important role in the glucose cycle. Glycogen forms an energy reserve that can be quickly mobilized to meet a sudden need for glucose, but one that is less compact than the energy reserves of triglycerides. Only the glycogen stored in the liver can be made accessible to other organs. Glycerol (or glycerin, glycerine) is a compound consisting of a simple molecule. It is a colorless, odorless, viscous liquid that is widely used during the last step of preparing prescription drugs. Glycerol has three hydrophilic (water-loving) hydroxyl (oxygen-hydrogen) groups that are responsible for its solubility in water and its hygroscopic nature (which means it attracts water from the air). The glycerol backbone is central to all lipids known as triglycerides. Glycerol is sweet-tasting and of low toxicity. Upload failed. Please upload a file larger than 100 x 100 pixels We are experiencing some problems, please try again. You can only upload files of type PNG, JPG or JPEG. You can only upload files of type 3GP, 3GPP, MP4, MOV, AVI, MPG, MPEG or RM. You can only Continue reading >>
What is glycerin in a song?
Glycerol ( /lsrl/ ; [4] also called glycerine or glycerin; see spelling differences ) is a simple polyol compound. It is a colorless, odorless, viscous liquid that is sweet-tasting and non-toxic. The glycerol backbone is found in all lipids known as triglycerides . It is widely used in the food industry as a sweetener and humectant and in pharmaceutical formulations . Glycerol has three hydroxyl groups that are responsible for its solubility in water and its hygroscopic nature. [5] Although achiral , glycerol is prochiral with respect to reactions of one of the two primary alcohols. Thus, in substituted derivatives, the stereospecific numbering labels each carbon as either sn-1, sn-2, or sn-3. [6] [7] Glycerol is generally obtained from plant and animal sources where it occurs as triglycerides . Triglycerides are esters of glycerol with long-chain carboxylic acids. The hydrolysis, saponification , or transesterification of these triglycerides produces glycerol as well as the fatty acid derivative: Triglycerides (1) are treated with an alcohol such as ethanol (2) with catalytic base to give ethyl esters of fatty acids (3) and glycerol (4): Typical plant sources include soybeans or palm . Animal-derived tallow is another source. Approximately 950,000 tons per year are produced in the United States and Europe; 350,000 tons of glycerol were produced per year in the United States alone from 2000 to 2004. [8] The EU directive 2003/30/EC set a requirement that 5.75% of petroleum fuels are to be replaced with biofuel sources across all member states by 2010. It was projected in 2006 that by the year 2020, production would be six times more than demand, creating an excess of glycero Continue reading >>
Does E. coli need glucose?
Messages sorted by: [ date ] [ thread ] [ subject ] [ author ] Rich batch E. coli cultures often include glycerol, but the use of glucose is preferable in most fed batch media. This is due in part to the higher specific growth rates with glucose. The downside with glucose comes from the so called "bacterial crabtree effect": having too much glucose around causes the formation of large amounts of organic acids, usually acetate and lactate, when the bug cannot support a high enough level of aerobic metabolism to utilize what is present. The pH of the media goes down, acetate goes up and a lot of usable carbon goes up the flue as CO2. The key to using glucose to grow E. coli seems to be adding it at a rate which supports the high growth rate while avoiding an oversupply, this has led to fancy exponential feed schemes and control algorithims which gauge feed rate to dissolved O2,pH etc. Glycerol doesn't do this and thus enough to support a good cell density can be included in the begining of the culture with no real negative effect, save a slower growth rate. This can actually be a plus in typical batch cultures (ie shake flasks) so glycerol is usually the way to go.My $0.02.regards,Ted MicheliniInstitute of Molecular BiologyUniversity of Oregon tedm at darkwing.uoregon.edu Continue reading >>
Does Listeria monocytogenes use glycerol?
Lehrstuhl fr Mikrobiologie, Biozentrum, Universitt Wrzburg, D-97074 Wrzburg, Germany Listeria monocytogenes is able to efficiently utilize glycerol as a carbon source. In a defined minimal medium, the growth rate (during balanced growth) in the presence of glycerol is similar to that in the presence of glucose or cellobiose. Comparative transcriptome analyses of L. monocytogenes showed high-level transcriptional upregulation of the genes known to be involved in glycerol uptake and metabolism (glpFK and glpD) in the presence of glycerol (compared to that in the presence of glucose and/or cellobiose). Levels of expression of the genes encoding a second putative glycerol uptake facilitator (GlpF2) and a second putative glycerol kinase (GlpK2) were less enhanced under these conditions. GlpK1 but not GlpK2 was essential for glycerol catabolism in L. monocytogenes under extracellular conditions, while the loss of GlpK1 affected replication in Caco-2 cells less than did the loss of GlpK2 and GlpD. Additional genes whose transcription levels were higher in the presence of glycerol than in the presence of glucose and cellobiose included those for two dihydroxyacetone (Dha) kinases and many genes that are under carbon catabolite repression control. Transcriptional downregulation in the presence of glycerol (compared to those in the presence glucose and cellobiose) was observed for several genes and operons that are positively regulated by glucose, including genes involved in glycolysis, N metabolism, and the biosynthesis of branched-chain amino acids. The highest level of transcriptional upregulation was observed for all PrfA-dependent genes during early and late logarithmic growth in glycerol. Under these conditions, a low level of HPr-Ser-P and a high level of HPr-His-P were p Continue reading >>
Is postprandial blood glucose a predictor of cardiovascular events?
Postprandial Blood Glucose Is a Stronger Predictor of Cardiovascular Events Than Fasting Blood Glucose in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, Particularly in Women: Lessons from the San Luigi Gonzaga Diabetes Study
What is the role of glycerol in the plasma membrane?
The glycerol itself is plays an important role in the phospholipid bilayer, which is part of the plasma membrane. The bilayer is amphipathic (hydrophobic tails and hydrophilic head) which allows for our body and cells to function the way they do. We can get into the transport proteins associated with said amphipathic relationship, there is just so much to cover! I hope this helps though!
What is DHAP in biology?
Dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) is a glycolytic intermediate that can be converted to glucose via the gluconeogenic pathway.
Why is glucose used in exercise?
I know glucose is used to help diabetics who need a quick boost to help raise their blood sugars because it is much less complex that regular sugar.
Is glycerin an ingredient in face cream?
To me, glycerin is used as an emollient and is often listed as an ingredient in face creams. Definitely NOT something I would eat. I found this on the internet: (The compound glycerin and glycerol are somewhat related.)
What are the two types of carbohydrates?
They're each carbohydrates: glucose, a sugar; glycerol, a sugar alcohol.
Is gluconeol a precursor?
Glycerol is an important gluconeogenic precursor, and becomes the most important gluconeogenic precursor during starva tion.
Is glycerol a lipid?
Depending on the aspect you want to understand the glycerol molecule, I can only assume you are pertaining to lipids. Anyways, essentially glycerol includes an alcohol (hydroxyl group) with 3 Carbon and 3 OH molecules. This is highly important for aforementioned lipid because the molecule itself contains no affinity for water (this explains their hydrophobic interactions and nonpolar [hydrocarbon] affiliations). The hydrocarbon affiliations are due to fatty acid tails which contain a carboxyl group attached to an immense carbon skeleton, expanding on this topic, the glycerol and (3 fatty acids
Can Fats Be Turned Into Glycogen For Muscle?
It is not possible for fats to be converted directly into glycogen because they are not made up glucose, but it is possible for fats to be indirectly broken down into glucose, which can be used to create glycogen. Relationship Between Fats and Glycogen Fats are a nutrient found in food and a compound used for long-term energy storage in the body, while glycogen is a chain of glucose molecules created by the body from glucose for short-term energy storage and utilization. Dietary fats are used for a number of functions in the body, including maintaining cell membranes, but they are not used primarily as a source of fast energy. Instead, for energy the body relies mostly on carbohydrates, which are converted into glucose that is then used to form glycogen. Turning Fats Into Glucose Excess glucose in the body is converted into stored fat under certain conditions, so it seems logical that glucose could be derived from fats. This process is called gluconeogenesis, and there are multiple pathways the body can use to achieve this conversion. Gluconeogenesis generally occurs only when the body cannot produce sufficient glucose from carbohydrates, such as during starvation or on a low-carbohydrate diet. This is less efficient than producing glucose through the metabolizing of carbohydrates, but it is possible under the right conditions. Turning Glucose Into Glycogen Once glucose has been obtained from fats, your body easily converts it into glycogen. In gl Continue reading >>
What is the mechanism of glucose metabolism?
Gluconeogenesis is one of several main mechanisms used by humans and many other animals to maintain blood glucose levels, avoiding low levels (hypoglycemia). Other means include the degradation of glycogen (glycogenolysis) [1] and fatty acid catabolism.
How does fat become glycogen?
The amount of fat in the average diet and the amount of stored fat in the average body make the notion of converting that fat into usable energy appealing. Glycogen, a form of energy stored in muscles for quick use, is what the body draws on first to perform movements, and higher glycogen levels result in higher usable energy. It is not possible for fats to be converted directly into glycogen because they are not made up glucose, but it is possible for fats to be indirectly broken down into glucose, which can be used to create glycogen. Relationship Between Fats and Glycogen Fats are a nutrient found in food and a compound used for long-term energy storage in the body, while glycogen is a chain of glucose molecules created by the body from glucose for short-term energy storage and utilization. Dietary fats are used for a number of functions in the body, including maintaining cell membranes, but they are not used primarily as a source of fast energy. Instead, for energy the body relies mostly on carbohydrates, which are converted into glucose that is then used to form glycogen. Turning Fats Into Glucose Excess glucose in the body is converted into stored fat under certain conditions, so it seems logical that glucose could be derived from fats. This process is called gluconeogenesis, and there are multiple pathways the body can use to achieve this conversion. Gluconeogenesis generally occurs only when the body cannot produce sufficient glucose from carbohydrates, such as during starvation or on a low-carbohydrate diet. This is less efficient than producing glucose through the metabolizing of carbohydrates, but it is possible under the right conditions. Turning Glucose Into Glycogen Once glucose has been obtained from fats, your body easily converts it into glycogen. In gl Continue reading >>
How do plants use energy in their metabolism?
Metabolism: Transformations and Interactions Chemical Reactions in the Body Plants use the sun’s energy to make carbohydrate from carbon dioxide and water. This is called photosynthesis. Humans and animals eat the plants and use the carbohydrate as fuel for their bodies. During digestion, the energy-yielding nutrients are broken down to monosaccharides, fatty acids, glycerol, and amino acids. After absorption, enzymes and coenzymes can build more complex compounds. In metabolism they are broken down further into energy (ATP), water and carbon dioxide. Chemical Reactions in the Body Metabolic reactions take place inside of cells, especially liver cells. Anabolism is the building up of body compounds and requires energy. Catabolism is the breakdown of body compounds and releases energy. Chemical Reactions in the Body Enzymes and coenzymes are helpers in reactions. Enzymes are protein catalysts that cause chemical reactions. Coenzymes are organic molecules that function as enzyme helpers. Cofactors are organic or inorganic substances that facilitate enzyme action. Breaking Down Nutrients for Energy The breakdown of glucose to energy starts with glycolysis to pyruvate. Pyruvate may be converted to lactic acid anaerobically (without oxygen) and acetyl CoA aerobically (with oxygen). Eventually, all energy-yielding nutrients enter the TCA cycle or tricarboxylic acid cycle (or Kreb’s cycle) and the electron transport chain. Breaking Down Nutrients for Energy Glucose Glucose-to-pyruvate is called glycolysis or glucose splitting. Pyruvate’s Options Anaerobic – lactic acid Aerobic – acetyl CoA Pyruvate-to-Lactate Oxygen is not available or cells lack sufficient mitochondria Lactate is formed when hydrogen is added to pyruvate. Liver cells recycle Continue reading >>
What is the process of converting glucose into glucose?
This process is called gluconeogenesis, and there are multiple pathways the body can use to achieve this conversion. Gluconeogenesis generally occurs only when the body cannot produce sufficient glucose from carbohydrates, such as during starvation or on a low-carbohydrate diet.
What is the pathway that produces glucose?
Glucone ogenesis. Not to be confused with Glycogenesis or Glyceroneogenesis. Simplified Gluconeogenesis Pathway Gluconeogenesis ( GNG) is a metabolic pathway that results in the generation of glucose from certain non-carbohydrate carbon substrates.
How does the body get energy from fat?
Your body is an amazing machine that is able to extract energy from just about anything you eat. While glucose is your body's preferred energy source, you can't convert fat into glucose for energy; instead, fatty acids or ketones are used to supply your body with energy from fat. Video of the Day Fat is a concentrated source of energy, and it generally supplies about half the energy you burn daily. During digestion and metabolism, the fat in the food you eat is broken down into fatty acids and glycerol, which are emulsified and absorbed into your blood stream. While some tissues -- including your muscles -- can use fatty acids for energy, your brain can't convert fatty acids to fuel. If you eat more fat than your body needs, the extra is stored in fat cells for later use. Fat has more than twice as many calories per gram as carbs and protein, which makes it an efficient form of stored energy. It would take more than 20 pounds of glycogen -- a type of carbohydrate used for fuel -- to store the same amount of energy in just 10 pounds of fat. Your Body Makes Glucose From Carbs Almost all the glucose in your body originated from carbohydrates, which come from the fruit, vegetables, grains and milk in your diet. When you eat these carb-containing foods, your digestive system breaks them down into glucose, which is then used for energy by your cells. Any excess glucose is converted into glycogen, then stored in your muscles and liver for later use. Once you can't store any more glucose or glycogen, your body stores any leftover carbs as fat. Glucose is your brain's preferred source of energy. However, when glucose is in short supply, your brain can use ketones -- which are derived from fat -- for fuel. Since your brain accounts for approximately one-fifth of your daily calori Continue reading >>
Is glucose fondant soft?
Glycerine is a natural softner. Glucose is a thicker version of corn syrup. They both make fondant more pliable and give it more strech. I don't know if they are interchangeable but I use both in the fondant receipe that I use.
Is Wilton glycerine food grade?
Make sure you're buying food-grade glycerine, like the Wilton bottles. Don't get the stuff from the drugstore that's used for other purposes, it might not be food grade.
Is glucose a liquid or liquid?
Glycerine is a colourless and odourless oil, glucose is a liquid sugar. I don't think they are interchangeable, all recipes for fondant i have seen call for both. HTH!
What is nitroglycerin made of?
Nitroglycerin is an explosive material which is produced using glycerol. Glycerine. This is a commercial term. When there is more than 95% glycerol in a product, it is known as glycerin. Though the chemical term for such a sample should be glycerol, for the usage glycerine is commonly used.
What is glycerol used for?
Glycerol is a treatment for burns, bites, cuts, and psoriasis. Glycerol is humectants; therefore, it is used in moisturizers. Other than this, glycerol is used as an ingredient in our day-to-day used products like toothpaste, shaving cream, hair care products, mouthwashes, etc. In the food industry, this is used as a sweetener and solvent, ...
What is the name of the compound glycerin?
Glycerol is a polyol molecule with the molecular formula HOCH 2 CHOHCH 2 OH. According to the IUPAC nomenclature, glycerol is named as Propan-1, 2, 3-triol.
Is glycerin a compound?
However, glycerol is the chemical term which shows the exact compound in the sample. Glycerin is used for most of the uses as states above under glycerol. But since, glycerin doesn’t contain pure glycerol; it cannot be used for some of the purpose where pure glycerol is needed.
Is glycerin the same as glycerin?
Glycerol and glycerin are two terms that are confusing to many people and used interchangeably. Most of the time, both have the same usages. Although they seem to be the same, there is a difference between the two terms. Commonly we use the term glycerin, which is the commercial term for the compound glycerol, and there are few other differences between the two.
Is glycerol a triglyceride?
So glycerol is the backbone of a triglyceride. Since triglycerides are the compounds in soap, glycerol is useful in making soap. Moreover, this is widely used in pharmaceutical applications. It is used as a tablet-binding agent, to provide lubrication and as a laxative. Glycerol is a treatment for burns, bites, cuts, and psoriasis.
Is glycerol a polar molecule?
Because of the three-hydroxyl groups, glycerol molecule is highly polar. This makes them highly soluble in water and other polar solvents. Glycerol forms lipid with the combination of three fatty acids. The –OH group of glycerol and -COOH groups of fatty acids make ester bonds, and produce a triglyceride.
Why use glycerol in pressure gauges?
The excessive swinging of the needle can also damage internal gears or other components, causing premature wear. Glycerol, when poured into a gauge to replace the air space, reduces the harmonic vibrations that are transmitted to the needle, increasing the lifetime and reliability of the gauge.
What is the purpose of glycerol and water?
Glycerol and water are used to preserve certain types of plant leaves. As a sugar substitute, it has approximately 27 kilocalories per teaspoon (sugar has 20) and is 60% as sweet as sucrose. It does not feed the bacteria that form a dental plaque and cause dental cavities.
Why is glycerin soap used?
This kind of soap is used by people with sensitive, easily irritated skin because it prevents skin dryness with its moisturizing properties. It draws moisture up through skin layers and slows or prevents excessive drying and evaporation.
What is glycerol used for?
In food and beverages, glycerol serves as a humectant, solvent, and sweetener, and may help preserve foods. It is also used as filler in commercially prepared low-fat foods (e.g., cookies ), and as a thickening agent in liqueurs. Glycerol and water are used to preserve certain types of plant leaves.
Why is glycerol added to icing?
It is added to icing (frosting) to prevent it from setting too hard. As used in foods, glycerol is categorized by the U.S. Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics as a carbohydrate. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) carbohydrate designation includes all caloric macronutrients excluding protein and fat.
How does glycerol work?
It draws moisture up through skin layers and slows or prevents excessive drying and evaporation. Taken rectally, glycerol functions as a laxative by irritating the anal mucosa and inducing a hyperosmotic effect, expanding the colon by drawing water into it to induce peristalsis resulting in evacuation .
What is the source of glycerol?
glycerol. Triglycerides can be saponified with sodium hydroxide to give glycerol and fatty sodium salt or soap . Typical plant sources include soybeans or palm. Animal-derived tallow is another source.