What is the best insulation are value?
What R-Value For Attic Insulation?
- Zone 1 and 2: R-30 to R-49 is recommended.
- Zone 3: R-30 to R-60 is recommended.
- Zone 4 and 5: R-38 to R-60 is recommended.
- Zone 6 and 7: R-49 to R-60 is recommended.
Which insulation has the highest R-value?
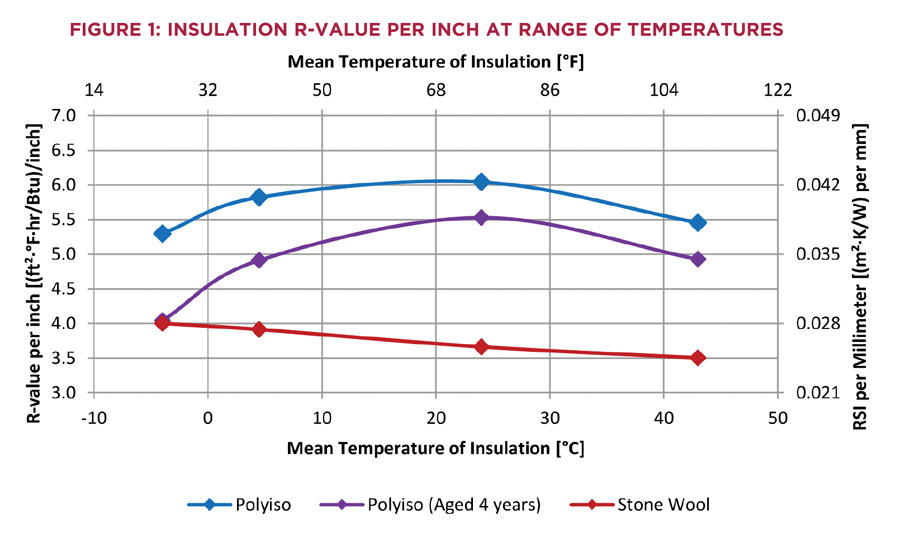
What insulation has the highest R-value? The insulation type with the highest R-value per inch is the rigid foam panels. In its rigid version, the polyurethane takes the form of rather light panels (density of 70 lbs / ft3).
Does fiberglass attic insulation really lose R-value?
Loose-fill fiberglass attic insulation was shown to lose up to half its R-value in a study from the early 1990s. [Photo credit: Energy Vanguard] When you get into the world of building science, it's inevitable that you'll hear about the Oak Ridge study proving that fiberglass insulation loses about half its R-value.
What is your value of rigid insulation?
What is R value of rigid insulation? With both rigid foam and fiberglass, the R–values are mostly determined by the thickness of the insulating material. Fiberglass insulation packs in more R–value per cubic inch than rigid foam insulation does. Rigid foam R–values range from R-1 for 1/4-inch thick sheathing panels to R-15 for 3-inch thick panels.

Which is better higher or lower R-value?
The R-value for insulation is a way to measure how much resistance the insulation has to heat flow. The higher the R-value, the more the resistance and the better the material is at insulating a home.
Is an R-value of 7 GOOD?
Basically, R values range from 1.5 to 7, and the higher the number is, the more effective the insulation sheet is at increasing thermal efficiency, and thereby, insulating your home.
Is higher R-value always better?
R-value measures how well building insulation can prevent the flow of heat into and out of the home. Higher R-value means greater insulation performance, and thus more savings on your next heating and cooling bill.
Is higher R-value better insulation?
An insulating material's resistance to conductive heat flow is measured or rated in terms of its thermal resistance or R-value -- the higher the R-value, the greater the insulating effectiveness. The R-value depends on the type of insulation, its thickness, and its density.
What R-value is considered weak?
If we wish to label the strength of the association, for absolute values of r, 0-0.19 is regarded as very weak, 0.2-0.39 as weak, 0.40-0.59 as moderate, 0.6-0.79 as strong and 0.8-1 as very strong correlation, but these are rather arbitrary limits, and the context of the results should be considered.
Is R60 attic insulation worth it?
Recommended R-Value Varies by State You need exactly as much as the area you live in determines. Here, where temps get pretty hot for much of the year, attics should have from R30 to R60 (average is R38). Those living up north want anything from R49 to R60. This helps insulate against the extreme cold weather.
Is R38 better than R30?
Example: R38 has a U of 1/R or 1/38=. 026 and R30 has a U of 1/30=. 033. So R38 is about 20% better.
How much better is R19 vs R13?
R-value is used to judge thermal insulation performance and the higher the number, the better the product's insulating ability. So R19 has better insulating ability than R13. Now R-Value ranges widely across products and home applications. Indeed you will see R60 in some places and R13 in others.
Can you put too much insulation?
It is possible to over-insulate your house so much that it can't breathe. The whole point of home insulation is to tightly seal your home's interior. But if it becomes too tightly sealed with too many layers of insulation, moisture can get trapped inside those layers. That's when mold starts to grow.
What R-value do I need for walls?
Depending on where you live and the part of your home you're insulating (walls, crawlspace, attic, etc.), you'll need a different R-Value. Typical recommendations for exterior walls are R-13 to R-23, while R-30, R-38 and R-49 are common for ceilings and attic spaces.
Does doubling insulation Double R-value?
ABOUT INSULATION The thermal barrier of a home should consist of a continuous layer of insulation on all sides—including the lowest floor, the exterior walls, and the ceiling or roof. Doubling the thickness of insulation will double the insulation's R-value, cutting heat loss in half.
Is higher R-value warmer?
A R-value (resistance-value) is a metric used to ratehow well a specific type of insulation can resist heat flow. The higher the R-value the warmer the pad.
What is a decent R-value?
Depending on where you live and the part of your home you're insulating (walls, crawlspace, attic, etc.), you'll need a different R-Value. Typical recommendations for exterior walls are R-13 to R-23, while R-30, R-38 and R-49 are common for ceilings and attic spaces.
What R-value is considered strong?
The relationship between two variables is generally considered strong when their r value is larger than 0.7. The correlation r measures the strength of the linear relationship between two quantitative variables. Pearson r: r is always a number between -1 and 1.
What does a 0.7 R-value mean?
Values between 0.7 and 1.0 (-0.7 and -1.0) indicate a strong positive (negative) linear relationship via a firm linear rule. The value of r squared is typically taken as “the percent of variation in one variable explained by the other variable,” or “the percent of variation shared between the two variables.”
Is an R-value of 11 good?
Floor Insulation: While there are additional considerations—such as venting and moisture problems—to take into account when you insulate under floors, the United States Department of Energy recommends an R-25 rating in cold climates and an R-11 in warmer parts of the country.
What is R Value?
R-Value is the measurement of how well a product resists conductive heat flow. If you’ve read our blog on the various sorts of heat flow, you’ll know that conduction is one of the 3 ways the warmth is often transferred (the other two are convection and radiation).
Why Is R-Value Important? How Does It Affect Energy Efficiency?
When it involves keeping your home warm and your energy bills manageable throughout the year, knowing the R-Value of products you select to place in your home and their cumulative effect on energy efficiency can assist you to save an excellent deal of cash within the short and future.
So Which is Better? A High R Value or a Low One?
Deciding if a better or lower R-Value is best for your home’s needs is all about context. Three main factors affect the type of R-Value you would possibly want to extend the energy efficiency of your home:
Should I Use the Same R-Value Throughout my Home?
With numerous different products on the market, it’s tricky to understand which should be used where, but there are some general rules of thumb that will help guide you.
How Eco Spray Can Help You Increase Your Energy Efficiency
At Eco Spray Insulation, the question of whether a better or lower R-Value is best depends on the house and its needs – but when it involves different types of insulation, we unequivocally believe that spray foam offers our customers the simplest in home insulation and R Values.
What Impacts Insulation R-Value?
R-Value isn’t set in stone, meaning there are things that can impact that number not only lowering it but essentially making your insulation ineffective.
Does Highest R-Value Mean the Best Insulation?
Do higher R-Values mean the material you’re considering is the best option for your home?
What insulation creates an air seal?
Foam is the only insulation option that creates that air seal, but now you’re probably wondering about code and that’s good.
What happens when insulation is not properly installed?
If there are gaps with no coverage or the material doesn’t fit perfectly and evenly where it is installed, then a space has been created for air movement. These gaps can also be created in traditional insulation materials over time as both fiberglass and cellulose are known to shift, settle, and sag as time goes on.
How to prove insulation performance?
Proving all of this is done by taking all of the insulation data, room assemblies, etc., and putting them into a program like REScheck or HERS Index.
What is the R value of insulation?
R-Value is the measurement of an insulation material’s thermal resistance.
Can spray foam pass code?
The thing is spray foam can pass code without hitting those R-Value numbers and it all comes down to how it performs. Inspectors don’t take the foam insulation contractors word for it, but they do take the word science. The insulation contractor has to prove to the inspector that the foam’s performance creates an air seal, has an aged R-Value, ...
Where does the r value come from? And what values can it take?
The " r value" is a common way to indicate a correlation value. More specifically, it refers to the (sample) Pearson correlation , or Pearson's r. The "sample" note is to emphasize that you can only claim the correlation for the data you have, and you must be cautious in making larger claims beyond your data.
What does it mean when a correlation is zero?
A perfect zero correlation means there is no correlation. For each type of correlation, there is a range of strong correlations and weak correlations. Correlation values closer to zero are weaker correlations, while values closer to positive or negative one are stronger correlation.
What are the levels of correlation?
Correlations can have different levels of strength 1 positive, 2 negative, or 3 non-existent
What is correlation in math?
Correlation is an abstract math concept, but you probably already have an idea about what it means. Here are some examples of the three general categories of correlation. As you eat more food, you will probably end up feeling more full. This is a case of when two things are changing together in the same way.
What to tweet when you read this far?
If you read this far, tweet to the author to show them you care. Tweet a thanks
What does comparing all values to the average do?
Intuitively, comparing all these values to the average gives us a target point to see how much change there is in one of the variables.
How do we normalize the amount of change in two variables?
In more technical terms, we normalize how much the two variables change together by how much each of the two variables change by themselves.
