
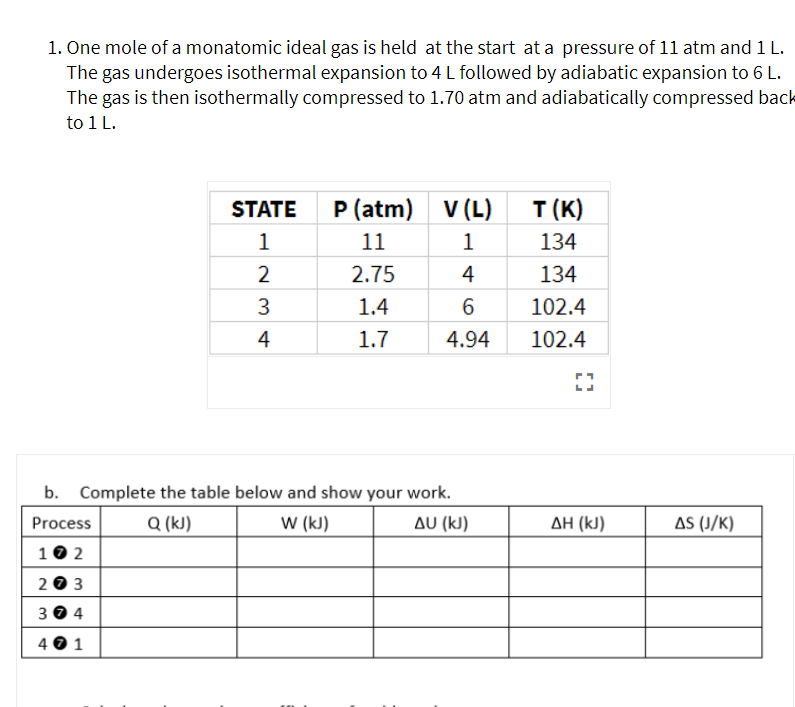
What is meant by a 'monatomic' gas?
Monatomic gas, gas composed of particles (molecules) that consist of single atoms, such as helium or sodium vapour, and in this way different from diatomic, triatomic, or, in general, polyatomic gases.
Which gas is monatomic at room temperature?
The noble gases of Group 8A (He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe, and Rn) are all gases at room temperature (as the name of the group implies); since they are all unreactive, monatomic elements, their boiling points are extremely low. Below is a table of the melting points, boiling points, and densities of the elements:
What are some examples of monatomic gases?
Gases that are made up of molecules that consist of a single atom are known as monatomic gases. Gases such as helium or sodium vapor are examples of monatomic gases. They can be quite easily distinguished from diatomic or polyatomic gases. In this article, we will learn more about monatomic gases, gas law, important formulae, and noble gases.
Why are noble gases monoatomic?
The noble gases are monatomic gases as they are unreactive in nature which is a property of these gases. They do find applications in daily life like: Helium is used in filling balloons as their density is lower than that of the air. Neon is used for creating advertising signs as they glow when electricity flows through it.
Are ideal gases diatomic?
A Diatomic Ideal Gas In a diatomic gas, it has a total of three translational kinetic energy modes and two rotational energy modes (hence, the 5/2).
Is gas diatomic or monatomic?
monatomicThe noble gases and mercury occur as monatomic species, whereas all other gases and bromine are diatomic molecules. All of the gaseous elements (other than the monatomic noble gases) are molecules. Within the same group (1, 15, 16 and 17), the lightest elements are gases.
Which gas is monatomic?
monatomic gas, gas composed of particles (molecules) that consist of single atoms, such as helium or sodium vapour, and in this way different from diatomic, triatomic, or, in general, polyatomic gases.
Are all gases monatomic?
What are Monatomic Gases? Monatomic is a combination of two words “mono” and “atomic” means a single atom. This term is used in both Physics and Chemistry and is applied to the gases as a monatomic gas. In the gaseous phase at sufficiently high temperatures, all the chemical elements are monatomic gases.
Is hydrogen gas a monatomic gas?
Monatomic gas is the gas that has molecules containing a single atom only while diatomic gas has the molecule containing two atoms. Similarly, triatomic gas contains molecules with three atoms. The hydrogen gas exists as a diatomic molecule, as it contains two atoms of hydrogen.
Are noble gases diatomic?
-All the elements contain 8 electrons in their valence shell and form a stable atom thus not reacting with other elements to form diatomic molecules. -Thus, the statement noble gas molecules are diatomic is not true.
Which one is not monoatomic?
Iodine is not a monoatomic elements. It is diatomic element.
Are all noble gases monatomic?
- All the noble gases are monatomic. The examples include He (Helium), Ne (Neon), Ar (Argon), Xe (Xenon), Ra (Radon). Thus, we can say that all the noble gases are monatomic. So, the correct answer is option (B).
Which of the following is monatomic?
The noble gases are monatomic gases. Examples: Helium, Radon, Neon, Xenon, Argon, Krypton.
What are the 7 monatomic elements?
List of Monatomic Elementshelium (He)neon (Ne)argon (Ar)krypton (Kr)xenon (Xe)radon (Rn)oganesson (Og)
Are all metals monoatomic?
The correct answer is Mono-atomic. All Kinds of Metals in nature are Mono-atomic & all types of gases are called diatomic. Atomicity: the present number of atoms in any molecule of an element is called its atomicity.
What are the three monatomic elements?
Monatomic elements are stable as individual atoms. Examples of monatomic elements include helium, neon, and argon.
What is monoatomic ideal gas?
monoatomic ideal gases usually show 3 degrees of freedom which are solely dedicated to translationa. Continue Reading. monoatomic means a molecule that is composed of a single atom. that is, it is stable by themselves and dont require to form any chemical bonds. noble gases are monoatomic gases.
What is ideal gas?
Lewis and Randall* define an ideal gas as one that has two behaviors: (1) Its energy is a function of temperature alone, which also means that it does not cool upon free expansion; (2) the relationship between the variables is PV =nRT. (p.
Why do gases behave like ideal gas models?
This is because the atoms/molecules are spaced widely apart so their interactions are minimal. Helium behaves most like the ideal model.
Why are noble gases considered monatomic?
They’re known as noble gases too and their reactivity is negligible (compared to other elements) because their octets are filled by default. Their non-bonding characteristic contributes towards their negligible reactivity (compared to other elements of-course) 105 views.
What are the particles that make up an ideal gas?
The particles forming an ideal gas are thought of as punctiform (point-like), and having no detailed structure. So, the real gases that best approximate this ideal model should be monatomic, and with atoms as small as possible. In practice, this corresponds to helium.
What is the smallest particle in an element?
An atom is the smallest particle of an element. It consists of one nucleus and its electrons and is an entity in molecules, compounds both ionic and covalent that involve the valence electrons. A monoatomic molecule is a neutral atom that exists by itself not bonded to other atoms.
What is the difference between H2O and NO2?
H2O= Water. (composed of two atoms of hydrogen and one atom of oxygen ) NO2=Nitrogen Dioxide. ( NO2 - composed of one atom of nitrogen and two atoms of oxygen ) SO2= Sulfur Dioxide. ( SO2 - composed of one atom of sulfur and two atoms of oxygen ) (3) Or it can be of three atoms of the same element.
What are Monatomic gases?
Monatomic gases are the gases with a single atom. They do not consist of rotational and energy vibrational components which make their thermodynamic behavior in the normal temperature range extremely simple. There are only three translational degrees of freedom in monatomic gases.
General gas law
The gas that follows a physical behavior by maintaining a particular idealized relation between temperature, pressure, and volume is known as a perfect or ideal gas. This law that they follow is known as general gas law. The law consists of both Boyle's law and the Charle's law’.
Noble gases
One of the properties of monatomic gases is that they are unreactive; noble gases also show similar properties. In monatomic gases, atoms are not hurdled to each other. Argon, krypton, and xenon are noble gases that are listed as monatomic gases.
Diatomic molecules
The molecules are made of only two atoms are known as diatomic. Nitrogen (78%) and oxygen (21%) are the two elements on the earth that have diatomic molecules.
Things to Remember
Gases that are made up of molecules that consist of a single atom are known as monatomic gases.
Sample questions
Ques. What are monatomic gases? How do they differentiate from diatomic ones? 2 marks
What is the ideal gas model?
The ideal gas model has also been used to model the behavior of electrons in a metal (in the Drude model and the free electron model ), and it is one of the most important models in statistical mechanics. If the pressure of an ideal gas is reduced in a throttling process the temperature of the gas does not change.
Why is the ideal gas concept useful?
The ideal gas concept is useful because it obeys the ideal gas law, a simplified equation of state, and is amenable to analysis under statistical mechanics. The requirement of zero interaction can often be relaxed if, for example, the interaction is perfectly elastic or regarded as point-like collisions.
What is the ideal quantum gas?
the ideal quantum Bose gas, composed of bosons, and. the ideal quantum Fermi gas, composed of fermions. The classical ideal gas can be separated into two types: The classical thermodynamic ideal gas and the ideal quantum Boltzmann gas.
What is the behavior of a real fluid?
Real fluids at low density and high temperature approximate the behavior of a classical ideal gas. However, at lower temperatures or a higher density, a real fluid deviates strongly from the behavior of an ideal gas, particularly as it condenses from a gas into a liquid or as it deposits from a gas into a solid.
What happens to the temperature of a gas when the pressure of an ideal gas is reduced in a thrott
If the pressure of an ideal gas is reduced in a throttling process the temperature of the gas does not change. (If the pressure of a real gas is reduced in a throttling process, its temperature either falls or rises, depending on whether its Joule–Thomson coefficient is positive or negative.)
Which law states that the internal energy of a fixed mass of ideal gas is a function only of its temperature?
The other equation of state of an ideal gas must express Joule's second law , that the internal energy of a fixed mass of ideal gas is a function only of its temperature. For the present purposes it is convenient to postulate an exemplary version of this law by writing:
Is a gas a liquid or a solid?
At some point of low temperature and high pressure, real gases undergo a phase transition, such as to a liquid or a solid.
Which elements are monatomic?
Examples at standard conditions include the noble gases argon, krypton, and xenon, though all chemical elements will be monatomic in the gas phase at sufficiently high temperatures.
What does "monatomic" mean in chemistry?
Jump to navigation Jump to search. In physics and chemistry, "monatomic" is a combination of the words "mono" and "atomic", and means "single atom " . It is usually applied to gases: a monatomic gas is one in which atoms are not bound to each other.
What is the Avogadro number of a mole of atoms?
One mole of atoms contains an Avogadro number (. , where R is the gas constant. In an adiabatic process, monatomic gases have an idealised γ -factor ( Cp / Cv) of 5/3, as opposed to 7/5 for ideal diatomic gases where rotation (but not vibration at room temperature) also contributes. Also, for ideal monatomic gases:
What are noble gases?
When grouped together with the homonuclear diatomic gases such as nitrogen (N 2 ), the noble gases are called "elemental gases" or "molecular gases" to distinguish them from molecules that are also chemical compounds .
Is a noble gas a reactive species?
Noble gases have a full outer valence shell making them rather non-reactive species. While these elements have been described historically as completely inert, chemical compounds have been synthesized with all but neon and helium.
Homework Statement
5 moles of an idea gas at 300K at a pressure of 1.00 x 10^5 Pa is heated to 500K at constant pressure. The amount of heat transferred is 29.1kJ.
Homework Statement
5 moles of an idea gas at 300K at a pressure of 1.00 x 10^5 Pa is heated to 500K at constant pressure. The amount of heat transferred is 29.1kJ.
Overview
An ideal gas is a theoretical gas composed of many randomly moving point particles that are not subject to interparticle interactions. The ideal gas concept is useful because it obeys the ideal gas law, a simplified equation of state, and is amenable to analysis under statistical mechanics. The requirement of zero interaction can often be relaxed if, for example, the interaction is perfectly elastic or …
Types of ideal gas
There are three basic classes of ideal gas:
• the classical or Maxwell–Boltzmann ideal gas,
• the ideal quantum Bose gas, composed of bosons, and
• the ideal quantum Fermi gas, composed of fermions.
Classical thermodynamic ideal gas
The classical thermodynamic properties of an ideal gas can be described by two equations of state:
The ideal gas law is the equation of state for an ideal gas, given by:
P V = n R T {\displaystyle PV=nRT\,}
where
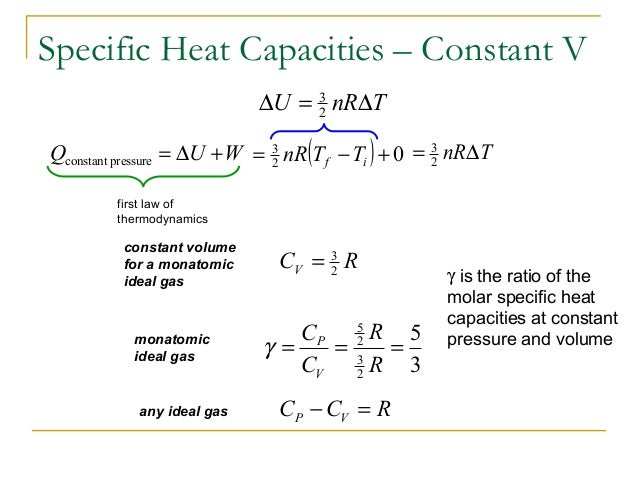
Heat capacity
The dimensionless heat capacity at constant volume is generally defined by
where S is the entropy. This quantity is generally a function of temperature due to intermolecular and intramolecular forces, but for moderate temperatures it is approximately constant. Specifically, the Equipartition Theorem predicts that the constant for a monatomic gas is ĉV = 3/2 while for a diatomic gas it is ĉV = 5/2 if vibrations are neglected (which is often an excellent appr…
Entropy
Using the results of thermodynamics only, we can go a long way in determining the expression for the entropy of an ideal gas. This is an important step since, according to the theory of thermodynamic potentials, if we can express the entropy as a function of U (U is a thermodynamic potential), volume V and the number of particles N, then we will have a complete statement of the thermodynamic behavior of the ideal gas. We will be able to derive both the ideal gas law and th…
Thermodynamic potentials
Expressing the entropy as a function of T, V, and N:
The chemical potential of the ideal gas is calculated from the corresponding equation of state (see thermodynamic potential):
where G is the Gibbs free energy and is equal to U + PV − TS so that:
The chemical potential is usually referenced to the potential at some standard pressure P so tha…
Speed of sound
The speed of sound in an ideal gas is given by the Newton-Laplace formula:
where the isentropic Bulk modulus
For an isentropic process of an ideal gas, , therefore
Here,
• γ is the adiabatic index (ĉP/ĉV)
Ideal quantum gases
In the above-mentioned Sackur–Tetrode equation, the best choice of the entropy constant was found to be proportional to the quantum thermal wavelength of a particle, and the point at which the argument of the logarithm becomes zero is roughly equal to the point at which the average distance between particles becomes equal to the thermal wavelength. In fact, quantum theory itself predicts the same thing. Any gas behaves as an ideal gas at high enough temperature and …