
Precautions
Levothyroxine was first made in 1927. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines, which lists the most effective and safe medicines needed in a health system.
What is levothyroxine?
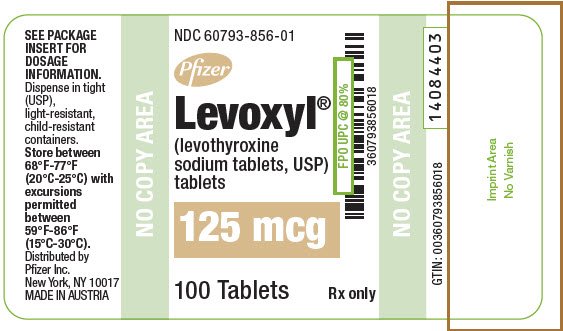
Levothyroxine sodium tablets USP are round, colored, scored and debossed with following debossing details on one side and break-line on other side. They are supplied as follows: Levothyroxine sodium tablets are contraindicated in patients with uncorrected adrenal insufficiency [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.3 )].
What do levothyroxine sodium tablets look like?
The typical dosage is 1.6 mcg/kg/day. Dosages are usually less than 200 mcg/day. The dosage is based on weight and thyroid hormone levels. The typical starting dosage is 12.5–25 mcg/day. Your doctor will adjust your dosage every 6–8 weeks, based on your thyroid hormone lab results. Your dosage is based on your needs and thyroid hormone levels.
What is the typical dosage of levothyroxine?
More... Are you on Levothyroxine and Still Experiencing Hypothyroid Symptoms? It's never normal for you to experience hypothyroid symptoms despite taking your thyroid medication. The entire goal of using thyroid medication is to resolve this deficiency and to improve your quality of life (1). But, what exactly is Levothyroxine?
Are You on levothyroxine and still experiencing hypothyroid symptoms?

Is it OK to cut levothyroxine in half?
Take this medicine in the morning on an empty stomach, at least 30 to 60 minutes before eating breakfast. Swallow the capsule whole. Do not cut, chew, or crush it. If your child is unable to swallow the tablet, you may crush and mix it in 1 to 2 teaspoons (5 to 10 milliliters) of water.
Are Synthroid tablets scored?
This medicine is a blue, round, partially scored, tablet imprinted with "FLINT" and "150".
Can I split Armour thyroid pills?
Another strategy to mitigate the potential side effects of Armour thyroid is to split your dose and take it multiple times throughout the day. This is a strategy employed successfully by many people taking all types of thyroid medications (including pure T3 medications and even T4 medications).
What does levothyroxine 50mg look like?
Tablet. White, uncoated, biconvex tablets engraved on one face with “LT” and “50” on the other. Recommended clinical indications: Control of hypothyroidism, congenital hypothyroidism in infants, acquired hypothyroidism in children and juvenile myxoedema.
Can I split Synthroid pills?
A Food and Drug Administration study found that the thyroid drug levothyroxine should not be cut even when tablets are scored (AAPS PharmSciTech, September 2010).
What happens if you crush levothyroxine?
Swallow capsules whole; do not cut, crush, or attempt to dissolve in water. The Levoxyl-branded tablet may rapidly swell and disintegrate, and cause choking or gagging if it becomes stuck in your throat.
Why should you not cut pills in half?
Don't use a kitchen knife or scissors. Split pills one at a time because some medications lose their effectiveness if exposed to the air after they are split.
Why is Armour Thyroid not recommended?
Due to the potential drug interaction between both natural and prescribed thyroid hormone and testosterone supplements, patients should be discouraged from self-administration of thyroid or anabolic steroids. Due to the lack of standardization in the T3 content, the use of Armour Thyroid should be avoided.
Can we use half tablet?
If your tablet has a score line on it, typically it's OK to split it. Extended-release tablets, capsules, and pills with special coatings on the outside usually can't be split or opened. Always check with a pharmacist before splitting any pills. They can tell you if cutting your pill is safe.
Why does my levothyroxine look different?
There are two main reasons that your pills may not look the same. It's the same medication and dose, just a different manufacturer. With generic medications, several manufacturers could make the same drug, but each could produce it in a different color and form.
Is 50 mcg levothyroxine too much?
Adults usually start with a dose between 50 micrograms and 100 micrograms taken once a day. This may be increased gradually over a few weeks to between 100 micrograms and 200 micrograms taken once a day. Some people, such as over-50s or people with heart disease, may start on a lower dose.
How do you know if levothyroxine is too high?
Symptoms of too much levothyroxine can include anxiety, diarrhea, depression, elevated heartbeat, elevated blood pressure, fatigue, irritability, difficulty concentrating, difficulty sleeping, being overheated, and unprompted or unintentional weight loss.
What increments does Synthroid come in?
Synthroid is available in 25-microgram (mcg) strength intervals, as follows: 25 mcg, 50 mcg, 75 mcg, 100 mcg, 125 mcg, 150 mcg, 175 mcg, and 200 mcg....The following strengths are also available:88 mcg.112 mcg.137 mcg.300 mcg.
Is there a big difference between Synthroid and levothyroxine?
Levothyroxine and Synthroid contain the same active (main) ingredient, levothyroxine, which is human-made T4. Levothyroxine is the generic name for Synthroid. However, there can be small differences in the amount of T4 between Synthroid and some of its generic versions.
What are the rules for taking Synthroid?
Take levothyroxine once a day in the morning, ideally at least 30 minutes before having breakfast or a drink containing caffeine, like tea or coffee. Food and caffeinated drinks can both stop your body taking in levothyroxine properly so it does not work as well.
Why does my levothyroxine look different?
There are two main reasons that your pills may not look the same. It's the same medication and dose, just a different manufacturer. With generic medications, several manufacturers could make the same drug, but each could produce it in a different color and form.
How long before taking levothyroxine sodium?
Administer Levothyroxine sodium tablets at least 4 hours before or after drugs known to interfere with Levothyroxine sodium absorption [see Drug Interactions (7.1)] .
How much TSH is suppressed?
Generally, TSH is suppressed to below 0.1 IU per litre, and this usually requires a Levothyroxine sodium tablets dose of greater than 2 mcg per kg per day. However, in patients with high-risk tumors, the target level for TSH suppression may be lower.
What are the symptoms of overdosage?
In addition, confusion and disorientation may occur. Cerebral embolism, shock, coma, and death have been reported. Seizures occurred in a 3-year-old child ingesting 3.6 mg of Levothyroxine. Symptoms may not necessarily be evident or may not appear until several days after ingestion of Levothyroxine sodium.
When to start levothyroxine sodium?
Start Levothyroxine sodium tablets at the full daily dose in most pediatric patients. Start at a lower starting dose in newborns (0 to 3 months) at risk for cardiac failure and in children at risk for hyperactivity (see below). Monitor for clinical and laboratory response [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)] .
Where is T4 absorbed?
The majority of the Levothyroxine sodium dose is absorbed from the jejunum and upper ileum. The relative bioavailability of Levothyroxine sodium tablets, compared to an equal nominal dose of oral Levothyroxine sodium solution, is approximately 93%. T4 absorption is increased by fasting, and decreased in malabsorption syndromes and by certain foods such as soybeans. Dietary fiber decreases bioavailability of T4. Absorption may also decrease with age. In addition, many drugs and foods affect T4 absorption [see Drug Interactions (7)] .
Does thyroid hormone increase metabolism?
Thyroid hormone increases metabolic clearance of glucocorticoids. Initiation of thyroid hormone therapy prior to initiating glucocorticoid therapy may precipitate an acute adrenal crisis in patients with adrenal insufficiency. Treat patients with adrenal insufficiency with replacement glucocorticoids prior to initiating treatment with Levothyroxine sodium [see Contraindications (4)] .
Can levothyroxine be used for myxedema?
Use of oral thyroid hormone drug products is not recommended to treat myxedema coma. Administer thyroid hormone products formulated for intravenous administration to treat myxedema coma.
Usual Adult Dose for Hypothyroidism
Dosing should be individualized with consideration given to age, cardiovascular status, concomitant medical conditions (including pregnancy), and specific nature of condition; follow clinical response and laboratory parameters closely as dose is adjusted: INITIAL DOSES: Primary Hypothyroidism: For otherwise healthy individuals in whom growth and puberty are complete: Initial dose: 1.6 mcg/kg orally once a day -Adjust dose in 12.5 to 25 mcg increments every 4 to 6 weeks until clinically euthyroid and TSH returns to normal Individuals over 50 years and/or Patients with Cardiovascular Disease: Initial dose: 12.5 to 25 mcg orally once a day -Adjust dose at 6 to 8-weeks intervals until clinically euthyroid and TSH returns to normal Severe Longstanding Hypothyroidism: Initial dose: 12.5 to 25 mcg orally once a day -Adjust dose in increments of 12.5 to 25 mcg/day every 2 to 4 weeks until clinically euthyroid and TSH returns to normal MAINTENANCE DOSE: Approximately 1.6 mcg/kg/day is a full replacement dose MAXIMUM dose: 200 to 300 mcg/day (doses greater than 200 mcg/day are seldom needed; doses greater than 300 mcg/day are rarely needed and may indicate poor compliance, malabsorption, drug interactions, or a combination of these factors) Secondary (PITUITARY) OR Tertiary (HYPOTHALAMIC) Hypothyroidism: -Dosing as described above except serum free-T4 level will be used to monitor therapy; serum TSH levels are not a reliable measure and should not be used -Titrate until clinically euthyroid and serum free-T4 levels are restored to the upper half of the normal range Comments: -Dose should be individualized with regular monitoring of clinical status and laboratory parameters. -Peak effect of a given dose may not be attained for 4 to 6 weeks. -Not indicated for the treatment of hypothyroidism during the recovery phase of subacute thyroiditis. -Co-administered food and concomitant medications may significantly affect absorption; take on an empty stomach and at least 4 hours before or after drugs known to interfere with levothyroxine absorption. Use: As replacement therapy in primary (thyroidal), secondary (pituitary), and tertiary (hypothalamic) congenital or acquired hypothyroidism.
Usual Adult Dose for TSH Suppression
TSH levels should generally be suppressed to below 0.1 IU/L -A dose greater than 2 mcg/kg orally once a day is usually required to achieve this degree of suppression Comments: -Patients with high-risk tumors may target a greater level of TSH suppression, however, this is not well defined. -This drug is not indicated for suppression of benign thyroid nodules and nontoxic diffuse goiter in iodine-sufficient patients as there are no clinical benefits and overtreatment may induce hyperthyroidism. Use: As an adjunct to surgery and radioiodine therapy in the management of thyrotropin- dependent well-differentiated thyroid cancer..
Usual Adult Dose for Myxedema Coma
Parenteral Formulation: -Initial loading dose: 300 to 500 mcg IV once -Maintenance dose: 50 to 100 mcg IV once a day until patient can tolerate oral therapy Comment: -Age, general physical condition, cardiac risk factors, severity and duration of myxedema coma should be considered when determining the initial and maintenance dosages. -The relative bioavailability between oral and IV levothyroxine is estimated to be 48% to 74%; due to individual differences, TSH levels should be measured and doses adjusted accordingly. Use: For the treatment of myxedema coma..
Usual Geriatric Dose for Hypothyroidism
Initial dose: 12.5 to 25 mcg orally once a day -Adjust dose at 6 to 8-weeks intervals until clinically euthyroid and TSH returns to normal Maintenance dose: Full replacement doses may be less than 1 mcg/kg/day Maximum dose: 200 to 300 mcg/day (doses greater than 200 mcg/day are seldom needed; doses greater than 300 mcg/day are rarely needed and may indicate poor compliance, malabsorption, drug interactions, or a combination of these factors) Comments: -Dosing should be individualized with consideration given to age, cardiovascular status, concomitant medical conditions, and the specific nature of condition; follow clinical response and laboratory parameters closely as dose is adjusted. -Peak effect of a given dose may not be attained for 4 to 6 week; full recovery dose s. -Not indicated for the treatment of hypothyroidism during the recovery phase of subacute thyroiditis. -Co-administered food and concomitant medications may significantly affect absorption; take on an empty stomach and at least 4 hours before or after drugs known to interfere with levothyroxine absorption. Use: As replacement therapy in primary (thyroidal), secondary (pituitary), and tertiary (hypothalamic) congenital or acquired hypothyroidism.
Usual Pediatric Dose for Hypothyroidism
0 to 3 months: 10 to 15 mcg/kg orally once a day 3 to 6 months: 8 to 10 mcg/kg orally once a day 6 to 12 months: 6 to 8 mcg/kg orally once a day 1 to 5 years: 5 to 6 mcg/kg orally once a day 6 to 12 years: 4 to 5 mcg/kg orally once a day 12 years or older and incomplete growth and puberty: 2 to 3 mcg/kg orally once a day 12 years or older with growth and puberty complete: 1.6 mcg/kg orally once a day Newborns (0 to 3 months) at Risk for Cardiac Failure: Consider a lower initial dose; increase dose every 4 to 6 weeks as needed based on clinical and laboratory response Pediatric Patients at Risk for Hyperactivity: Initial dose should be one-fourth the recommended full replacement dose; increase weekly by one-fourth to the full recommended replacement dose Comments: -Dose should be individualized with regular monitoring of clinical status and laboratory parameters; peak effect may not be attained for 4 to 6 weeks. -Not indicated for the treatment of hypothyroidism during the recovery phase of subacute thyroiditis. -Co-administered food and concomitant medications may significantly affect absorption; take on an empty stomach and at least 4 hours before or after drugs known to interfere with levothyroxine absorption. -The capsule formulation is indicated for patients 6 years or older as the capsule should be swallowed whole; see Other Comment/Administration Advice for specific administration instructions including instructions for those unable to swallow intact tablets. Use: For the treatment of congenital or acquired hypothyroidism..
Dose Adjustments
Myxedema Coma: Elderly and Patients with Cardiovascular Disease: IV use is associated with cardiac toxicity, therefore, doses at the lower end of the dose range should be used in these populations. Pregnancy: New Onset Hypothyroidism: -Patients with moderate to severe signs and symptoms of hypothyroidism: 1.6 mcg/kg orally once a day -Patients with mild hypothyroidism (TSH less than 10 mIU/L): 1 mcg/kg orally once a day -Evaluate TSH every 4 weeks and adjust dose until serum TSH is within trimester-specific range Preexisting Hypothyroidism: -Monitor TSH and free T4 as soon as pregnancy is confirmed and at least each trimester -Maintain TSH in trimester-specific reference range (primary hypothyroidism) -If serum TSH is above the normal trimester-specific range, increase by 12.5 to 25 mcg/day and measure TSH every 4 weeks until serum TSH is within the normal trimester-specific range -Reduce to pre-pregnancy dose immediately after delivery and measure serum TSH level 4 to 8 weeks postpartum to ensure dose is appropriate Therapeutic drug monitoring/range: -Primary Hypothyroidism: Monitor TSH -Secondary and Tertiary Hypothyroidism: Monitor serum free-T4 levels (maintain in the upper half of the normal range).
Precautions
US BOXED WARNING: NOT FOR TREATMENT OF OBESITY OR FOR WEIGHT LOSS -Thyroid hormones, either alone or with other agents, should not be used for the treatment of obesity or for weight loss. In euthyroid patients, doses within the range of daily hormonal requirements are ineffective for weight reduction.
What is oral levothyroxine used for?
Oral levothyroxine is primarily indicated for the treatment of primary, secondary, and tertiary hypothyroidism. Primary hypothyroidism is when the problem occurs in the thyroid gland. Secondary hypothyroidism is when the problem is in the pituitary gland, and there is a decrease in the production of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH).
What is the best treatment for levothyroxine overdose?
There is no antidote for the treatment of levothyroxine overdose. Treatment options include gastric lavage, activated charcoal, cholestyramine, glucocorticoids, beta-blockers, propylthiouracil, and supportive measures. [9]
Why should the clinician counsel the patient to use the same levothyroxine brand?
The clinician should counsel the patient to use the same levothyroxine brand because of the narrow therapeutic index. [23]
What is the T4 hormone?
Levothyroxine(T4) is a synthetic version of the body’s natural thyroid hormone: thyroxine(T4). Normally, the hypothalamus secretes thyrotropin-releasing hormone(TRH), which then stimulates the anterior pituitary to secrete thyroid-stimulating hormone(TSH), which subsequently stimulates the thyroid to secrete 80% thyroxine (T4) and 20% L-triiodothyronine(T3). 50% of thyroxine (T4) then gets converted to its active metabolite L-triiodothyronine (T3). The thyroid hormones then work by binding to thyroid receptor proteins contained within the cell nucleus. [7]
How long after levothyroxine do you monitor TSH?
Upon achieving the correct dosing of levothyroxine, monitor TSH levels 4 to 6 months after, and then every 12 months after that.
What is secondary hypothyroidism?
Secondary hypothyroidism is when the problem is in the pituitary gland (from adenomas to post-surgical intervention), and there is a decrease in the production of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). Tertiary hypothyroidism is very rare, and the problem is in the hypothalamus with decrease production of thyroid releasing hormone (TRH).
How does thyroid hormone work?
Once inside the nucleus, thyroid hormones work by directly influencing DNA transcription to increase body metabolism by increasing gluconeogenesis, protein synthesis, the mobilization of glycogen stores, and other more functions .
What is the name of the hormone that is secreted by the thyroid gland?
Levothyroxine is a synthetic form of thyroxine (T 4 ), an endogenous hormone secreted by the thyroid gland, which is converted to its active metabolite, L -triiodothyronine (T 3 ). T 4 and T 3 bind to thyroid receptor proteins in the cell nucleus and cause metabolic effects through the control of DNA transcription and protein synthesis. Like its naturally secreted counterpart, levothyroxine is a chiral compound in the L -form.
What foods interfere with thyroxine absorption?
Substances that reduce absorption are aluminium - and magnesium -containing antacids, simethicone, sucralfate, cholestyramine, colestipol, and polystyrene sulfonate. Grapefruit juice may delay the absorption of levothyroxine, but based on a study of 10 healthy people aged 20–30 (eight men, two women), it may not have a significant effect on bioavailability in young adults. A study of eight women suggested that coffee may interfere with the intestinal absorption of levothyroxine, though at a level less than eating bran. Certain other substances can cause adverse effects that may be severe. Combination of levothyroxine with ketamine may cause hypertension and tachycardia; and tricyclic and tetracyclic antidepressants increase its toxicity. Lithium, though, can cause hyperthyroidism (but most often hypothyroidism) by affecting iodine metabolism of the thyroid itself, thus inhibiting synthetic levothyroxine, as well. Soy, walnuts, fiber, calcium supplements, and iron supplements can also adversely affect absorption. A study found that cow's milk reduces levothyroxine absorption.
How long does it take for levothyroxine to work?
Levothyroxine is taken by mouth or given by intravenous injection. Maximum effect from a specific dose can take up to six weeks to occur. Side effects from excessive doses include weight loss, trouble tolerating heat, sweating, anxiety, trouble sleeping, tremor, and fast heart rate.
What is L-thyroxine used for?
It is used to treat thyroid hormone deficiency (hypothyroidism), including Hashimoto's disease and a severe form known as myxedema coma. It may also be used to treat and prevent certain types of thyroid tumors.
Why is TSH elevated with levothyroxine?
Poor compliance in taking the medicine is the most common cause of elevated TSH levels in people receiving appropriate doses of levothyroxine.
Where is levothyroxine absorbed?
Absorption of orally administered levothyroxine from the gastrointestinal tract ranges from 40 to 80%, with the majority of the drug absorbed from the jejunum and upper ileum. Levothyroxine absorption is increased by fasting and decreased in certain malabsorption syndromes, by certain foods, and with age.
When was levothyroxine first made?
Levothyroxine was first made in 1927. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Levothyroxine is available as a generic medication. In 2018, it was the second most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 105 million prescriptions.
How often should TSH be measured?
Patients with or at risk for hypothyroidism should undergo TSH evaluation every 4 weeks until midgestation and at least once near 30 weeks gestation (ATA [Alexander 2017]; De Groot 2012); re-assess TSH 2 to 4 weeks after initiation of therapy or dosage adjustment (ATA [Alexander 2017]). In patients who were initiated on levothyroxine during pregnancy, the necessity of continuing treatment should be evaluated; some patients will not require continued therapy. TSH should be measured 6 weeks after dosage adjustment or discontinuation (ATA [Alexander 2017]).
What is the name of the hormone that is secreted by the thyroid gland?
Levothyroxine (T 4) is a synthetic form of thyroxine, an endogenous hormone secreted by the thyroid gland. T 4 is converted to its active metabolite, L-triiodothyronine (T 3 ). Thyroid hormones (T 4 and T 3) then bind to thyroid receptor proteins in the cell nucleus and exert metabolic effects through control of DNA transcription and protein synthesis; involved in normal metabolism, growth, and development; promotes gluconeogenesis, increases utilization and mobilization of glycogen stores, and stimulates protein synthesis, increases basal metabolic rate
How many mcg/ml is a 500 mcg vial?
For products requiring further dilution, reconstitute vial for injection with 5 mL NS. Reconstituted concentrations for the 100 mcg, 200 mcg, and 500 mcg vials are 20 mcg/mL, 40 mcg/mL, and 100 mcg/mL, respectively. Shake well and use immediately after reconstitution (manufacturer labeling suggests reconstituted vial is stable for 4 hours); discard any unused portions.
How long after a meal can you take calcium?
Oral: Administer consistently in the morning on an empty stomach, at least 30 to 60 minutes before food. Alternatively, may consistently administer at night 3 to 4 hours after the last meal (AACE/ATA [Garber 2012]; ATA [Jonklaas 2014]). Do not administer within 4 hours of calcium- or iron-containing products or bile acid sequestrants.
What is pituitary thyrotropin?
Pituitary thyrotropin-stimulating hormone suppression: An adjunct to surgery and radioiodine therapy in the management of thyrotropin-dependent well-differentiated thyroid cancer.
How long does it take for a thyroid to heal?
Euthyroid: 6 to 7 days; Hypothyroid: 9 to 10 days; Hyperthyroid: 3 to 4 days
How to store tirosint?
Oral solution (Tirosint): Store in original container (closed aluminum pouch) at 25°C (77°F); excursions are permitted between 15°C and 30°C (59°F and 86°F). Keep ampules in pouch until ready to use; after opening the pouch, all ampules in the pouch should be used within 15 days.
What is levothyroxine?
Levothyroxine is a prescription drug. It comes as a tablet or capsule you take by mouth. It also comes as an injectable solution that’s only given by a healthcare provider.
How does levothyroxine work?
Levothyroxine works by providing the thyroid hormone that your thyroid gland would produce if it were working normally.
What is the name of the drug that is used to treat thyroid cancer?
Brand names: Levoxyl, Synthroid, and Unithroid. Levothyroxine comes in three forms: an oral tablet, an oral capsule, and an injectable solution. Levothyroxine oral tablet is used to treat hypothyroidism. It’s also used to treat goiter and certain types of thyroid cancer.
Why is levothyroxine less effective?
When levothyroxine is less effective: When you take levothyroxine with certain drugs, it may not work as well to treat your condition. This is because the amount of levothyroxine in your body may be decreased. Examples of these drugs include:
What are some examples of drugs that can be taken with levothyroxine?
Examples of these drugs include: The antidepressant sertraline. If you take sertraline with levothyroxine, your doctor might need to increase your levothyroxine dosage to keep it working well for you. Rifampin and anti-seizure drugs such as carbamazepine and phenobarbital. Calcium carbonate or ferrous sulfate.
How long before taking levothyroxine?
Take levothyroxine at least 4 hours before or after taking these medications to help make sure that levothyroxine works properly. Colesevelam, cholestyramine, colestipol, kayexalate, or sevelamer. Take levothyroxine at least 4 hours before taking these medications to help make sure that levothyroxine works properly.
Does levothyroxine cause bleeding?
Taking these drugs with levothyroxine may increase your risk of bleeding. Your doctor may need to decrease the dosage of your blood thinner if you’re also taking levothyroxine. Ketamine. Taking this drug with levothyroxine may increase your risk of high blood pressure and fast heart rate.
Do you need T3 medication?
By now you might be asking, do I need to be on medication containing T3?
What is LT4 thyroid?
This thyroid medication contains the inactive thyroid hormone T4 ( also known as LT4 and Thyroxine ). If you are taking this medication to treat your sluggish thyroid, ...
What happens if you take levothyroxine and you don't feel better?
If you are on Levothyroxine and NOT feeling better, then one or more of these things might be happening to you: You are not on a high enough dose. You are on the WRONG type of T4 thyroid medication. You are not absorbing thyroid hormone correctly. You are not getting enough T3 thyroid hormone. But the main question is:
What happens if you take levothyroxine?
If you are on Levothyroxine and NOT feeling better, then one or more of these things might be happening to you: 1 You are not on a high enough dose 2 You are on the WRONG type of T4 thyroid medication 3 You are not absorbing thyroid hormone correctly 4 You are not getting enough T3 thyroid hormone
What is the demand for thyroid hormone?
And the demand for thyroid hormone depends on multiple factors including how much stress we are under, how much inflammation we are suffering from, the type of medications we are using and so on.
What is the same medication that doctors give out?
Unfortunately, most Doctors give out the same medication: Levothyroxine or Synthroid.
What are the symptoms of hypothyroidism?
Chronic pain in the muscles and joints. Cold extremities (hands and feet) Chronic constipation. These are the symptoms I am referring to whenever I mention the 'symptoms of hypothyroidism' and these symptoms should be going away or reducing if you are taking thyroid medication such as Levothyroxine or Synthroid.
Indications and Usage For Levothyroxine
Levothyroxine is used to treat an underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism).
May Treat: Hypothyroidism · Adjunct to surgery or radiotherapy for thyroid carcinoma · Myxedema coma
Brand Names: Levothroid · Levoxyl · Synthroid · Unithroid · Tirosint and more
Drug Class: Thyroid Hormones - Synthetic T4 (Thyroxine)
Availability: Prescription sometimes needed
Pregnancy: Consult a doctor before using
Lactation: Does not adversely affect lactation
Levothyroxine Dosage and Administration
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Contraindications
Warnings and Precautions
- General Administration Information
Administer Levothyroxine sodium tablets as a single daily dose, on an empty stomach, one-half to one hour before breakfast. Administer Levothyroxine sodium tablets at least 4 hours before or after drugs known to interfere with Levothyroxine sodium tablets absorption [see Drug Interactio… - General Principles of Dosing
The dose of Levothyroxine sodium tablets for hypothyroidism or pituitary TSH suppression depends on a variety of factors including: the patient's age, body weight, cardiovascular status, concomitant medical conditions (including pregnancy), concomitant medications, co-administer…
Adverse Reactions
- Levothyroxine sodium tablets USP are round, colored, scored and debossed with following debossing details on one side and break-line on other side. They are supplied as follows:
Drug Interactions
- Levothyroxine sodium tablets are contraindicated in patients with uncorrected adrenal insufficiency [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Use in Specific Populations
- Cardiac Adverse Reactions in the Elderly and in Patients with Underlying Cardiovascular Disease
Over-treatment with Levothyroxine may cause an increase in heart rate, cardiac wall thickness, and cardiac contractility and may precipitate angina or arrhythmias, particularly in patients with cardiovascular disease and in elderly patients. Initiate Levothyroxine sodium tablets therapy in t… - Myxedema Coma
Myxedema coma is a life-threatening emergency characterized by poor circulation and hypometabolism, and may result in unpredictable absorption of Levothyroxine sodium from the gastrointestinal tract. Use of oral thyroid hormone drug products is not recommended to treat m…
Overdosage
- Adverse reactions associated with Levothyroxine sodium tablets therapy are primarily those of hyperthyroidism due to therapeutic overdosage [see Warnings and Precautions (5), Overdosage (10)]. They include the following: • 1. General:fatigue, increased appetite, weight loss, heat intolerance, fever, excessive sweating • 1. Central nervous system:headache, hyperactivity, nervo…
Levothyroxine Description
- Drugs Known to Affect Thyroid Hormone Pharmacokinetics
Many drugs can exert effects on thyroid hormone pharmacokinetics and metabolism (e.g., absorption, synthesis, secretion, catabolism, protein binding, and target tissue response) and may alter the therapeutic response to Levothyroxine sodium tablets (see Tables 2 to 5 below). - Antidiabetic Therapy
Addition of Levothyroxine sodium tablets therapy in patients with diabetes mellitus may worsen glycemic control and result in increased antidiabetic agent or insulin requirements. Carefully monitor glycemic control, especially when thyroid therapy is started, changed, or discontinued [s…