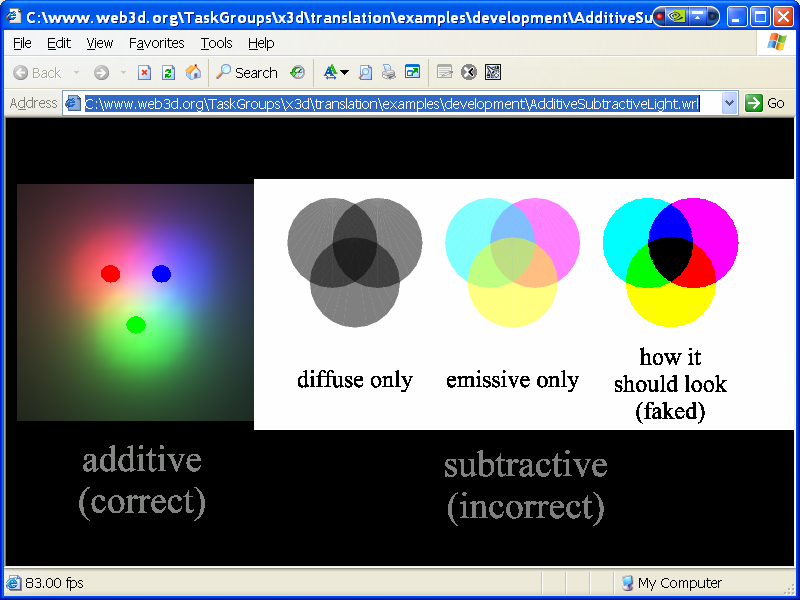
The additive color mode is primarily used when shades of light are used to create colors, while the subtractive mode is used when white light, such as sunlight, reflects off an object. Is light an additive? When we add all of the different wavelengths of sunlight, we see white light rather than many individual colors.
What is the difference between additive and subtractive color?
The additive color mode is primarily used when shades of light are used to create colors, while the subtractive mode is used when white light, such as sunlight, reflects off an object. Confused yet? Let’s jump in.
What is a subtractive color in photography?
Subtractive Color (CMYK) On the other hand, subtractive colors are created by completely or partially absorbing (or subtracting) some light wavelengths and reflecting others. Subtractive colors begin as white. As you add filters to the white light, such as ink, this white light takes on the appearance of color.
Is the sky additive or subtractive in color?
The colors of the trees, grass, rocks, land - these are subtractive colors (light is bouncing off these objects). The sky and sun - these are additive colors (light sources).
What is additive color and how does it work?
Additive color refers to how we see color in light itself. Our modern understanding of light and color begins with the experiments conducted by Sir Isaac Newton, who used a prism to split white light into the visible spectrum of colors. The key discovery here was the light is not merely revealing color which is already there; it is the color.

Is light an additive?
When we add all of the different wavelengths of sunlight, we see white light rather than many individual colors. It is called additive because all of the wavelengths still reach our eyes. It is the combination of different wavelengths that creates the diversity of colors.
Does light use a subtractive or additive color model?
Additive colorAdditive color models use light to display color while subtractive models use printing inks. Colors perceived in additive models are the result of transmitted light. Colors perceived in subtractive models are the result of reflected light.
Are colors of light additive?
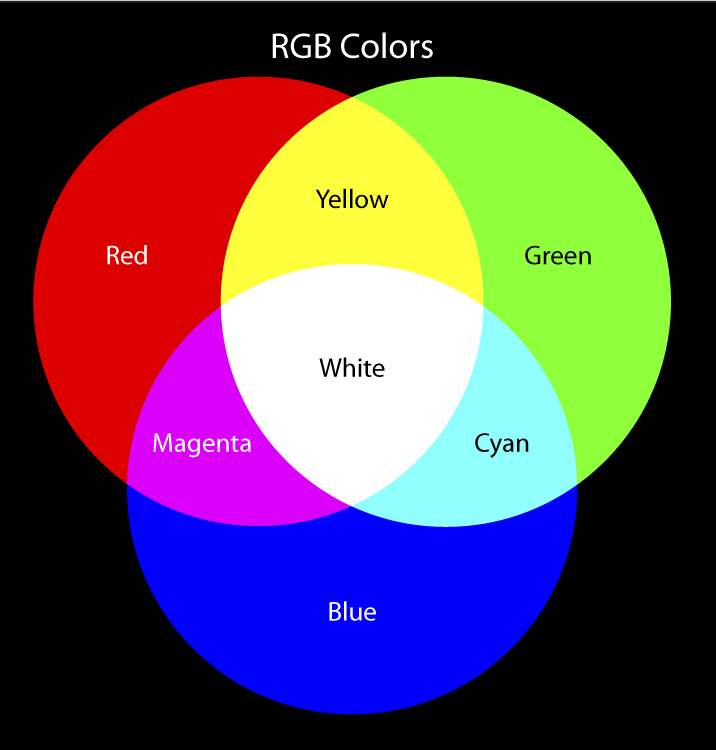
The additive color model describes how light produces color. The additive colors are red, green and blue, or RGB. Additive color starts with black and adds red, green and blue light to produce the visible spectrum of colors. As more color is added, the result is lighter.
Is pigment additive or subtractive?
subtractiveWhen you mix paints, the mixture of the pigments is a subtractive process. Red paint appears red because it absorbs (or subtracts) the shorter (blue) and medium (green) wavelengths and reflects primarily the longer (red) wavelengths.
What is the color system for lighting called?
Typically, these systems are known as CMY (Cyan, Magenta, Yellow) color mixing and consist of dichroic filters. Each of the three filters removes colors from the white source to reveal only the Cyan, Magenta or Yellow wavelengths.
What is an example of subtractive color?
The subtractive primaries of cyan, magenta, and yellow are the opposing colors to red, green, and blue. Televisions, mobile phones, tablets and computer monitors use the additive color system because they are emissive devices. They start with darkness and add red, green, and blue light to create the spectrum of colors.
Why is RGB additive?
The RGB color model is additive in the sense that the three light beams are added together, and their light spectra add, wavelength for wavelength, to make the final color's spectrum.
What is additive theory of light?
Color vision in humans is based on the additive color theory. This theory states that all perceivable colors can be made by mixing different amounts of red, green, and blue light, the primary colors of the additive color system.
Why is RGB called additive color?
RGB is called an additive color system because the combinations of red, green, and blue light create the colors that we perceive by stimulating the different types of cone cells simultaneously.
What is an example of additive color?
The most familiar example of colour reproduction by additive colour mixing is colour television in which all of the colours visible on screen are produced by a combination of light emitted by red, green and blue light sources (Nobbs, 2002).
Is RGB a subtractive color?
RGB is a system of additive color synthesis. The color display is obtained by the different light intensity of the primary colors: red, green and blue. This system is used for works intended for monitor display. CMYK is a system of subtractive color synthesis.
What are additive primary colors?
Primary Additive Colors Light is perceived as white by humans when all three cone cell types are simultaneously stimulated by equal amounts of red, green, and blue light. Because the addition of these three colors yields white light, the colors red, green, and blue are termed the primary additive colors.
Why are colored lights called additive colors?
Additive colors are created by adding colored light to black. On the other hand, subtractive colors are created by completely or partially absorbing (or subtracting) some light wavelengths and reflecting others. Subtractive colors begin as white.
What color schemes use additive colors?
Color vision in humans is based on the additive color theory. This theory states that all perceivable colors can be made by mixing different amounts of red, green, and blue light, the primary colors of the additive color system.
Why RGB is called an additive color model?
RGB is called an additive color system because the combinations of red, green, and blue light create the colors that we perceive by stimulating the different types of cone cells simultaneously.
What is the relationship between light and color?
Light is made up of wavelengths of light, and each wavelength is a particular colour. The colour we see is a result of which wavelengths are reflected back to our eyes. The visible spectrum showing the wavelengths of each of the component colours.
Why is subtractive mixing called additive mixing?
Additive and subtractive color mixing are so named because of the way different colors are achieved. As you might have guessed, additive color mixing involves adding color. Subtractive mixing involves taking color away. This post will explain it all in detail.
How is color created in subtractive mixing?
Additive and subtractive color mixing can be difficult to understand. It boils down to the source of light. If light is reaching your eye directly from the source, color is created through additive color mixing. We start with black and add color to create images. If the source is reflective light, color is achieved through subtractive mixing. We start with the color of the reflecting surface and subtract light from there.
What are the primary colors used in color mixing?
Understanding these two types of mixing explains why artists working with traditional media understand red, yellow and blue (RYB) as primary colors, while digital designers work with red, green and blue (RGB). A third color model used specifically for printing is called CMYK.
Why do we add color in additive models?
We add color in the additive model because we are starting with black. Again, remember that a deactivated computer screen looks black for lack of light emanating from it. We start with black and add color to generate something the eye can see. A piece of paper is not black because light reflects off it.
Is reflected light pure or unaltered?
Reflected light is not pure, unaltered light. It is altered by whatever surface it is reflecting off of. This suggests that the photoreceptors in the eyes don’t perceive reflected light quite the same way they perceive direct light. Without attempting to explain the biology, this is why the third primary color in reflected light is yellow rather than green. It also explains why blue and yellow create green in subtractive color mixing while red and green create yellow in additive mixing.
Why is subtractive color additive?
This is why it is referred to as additive color. With subtractive color, you see color because some wavelengths are being reflected and others are being absorbed ( subtracted ). When you mix all the subtractive colors together, you do not get white light; you get mud.
What Do Subtractive And Additive Colors Have In Common?
An interesting thing about subtractive and additive colors is that they both require light . With subtractive colors, light wavelengths are either reflecting off objects or being absorbed via pigmentation. Additive color is created by light itself.
What color is the secondary color of light?
Secondary Colors of Light: Cyan, magenta and yellow. If you mix green with red light, you get yellow light. If you mix blue with green light, you get cyan light. If you mix blue with red light, you get magenta light. When you mix (add) all the colors of light together, you get white light. This is why it is referred to as additive color. ...
What is subtractive color?
Subtractive color is how we see color in paints. It is the result of light either bouncing off or being absorbed by an object due to what is known as pigmentation. The light which bounces off the object is translated by our eyes and brain into the perception of color. This means that objects do not have an inherent color.
What would happen if there was no light?
So without light, color would not exist. It is light that allows us to experience the sensation of color. In a sense, light does not reveal color, it produces color.
Who discovered the color of light?
Our modern understanding of light and color begins with the experiments conducted by Sir Isaac Newton, who used a prism to split white light into the visible spectrum of colors. The key discovery here was the light is not merely revealing color which is already there; it is the color.
Is the sky subtractive or additive?
The colors of the trees, grass, rocks, land - these are subtractive colors (light is bouncing off these objects). The sky and sun - these are additive colors (light sources). The dilemma is that you are not able to use your paints (subtractive colors) to duplicate the effect of additive colors (a light source). This is a limitation of our paints.
What is subtractive color mixing?
Subtractive color mixing uses white light source with a series of filters to eliminate certain wavelengths of light. Typically, these systems are known as CMY (Cyan, Magenta, Yellow) color mixing and consist of dichroic filters. Each of the three filters removes colors from the white source to reveal only the Cyan, Magenta or Yellow wavelengths.
What are the benefits of automation lighting?
One of the biggest technological benefits to lighting designers is the ability to create a multitude of different colors from a single lighting fixture. Most automated lighting fixtures allow for color mixing capable of creating millions of different hues. This is achieved via two different methods known as Additive or Subtractive color mixing.
What colors can LED lights be used in?
The white LED can also be combined with colors to create pastels, such as pink (red and white) or lime (green and white). Some more complex additive color mix systems also use additional colors such as lime, amber and various shades of blue or green to allow for a greater spectrum of color.
Is CMY a subtractive or additive color?
There are, of course, pros and cons to each of the color mixing systems. CMY systems use filters and mechanical devices, where RGB systems typically involve electronics and LEDs. More importantly, saturated colors tend to output less lumens with a subtractive CMY system, as it filters out more wavelengths. Alternately, with an additive RGB system, you are using the full output of emitters to produce the saturated color. For this reason, a deep blue or red is brighter with an additive system than a subtractive system.
What is the difference between additive and subtractive colors?
The difference lies in the word additive and subtractive themselves.... additive colors are colors which are "pure", i.e. colors add up to form white light. A RED light looks RED because it emits RED light. while subtractive colors are "impure". You perceive RED pigment to be RED because it reflects RED light and absorbs everything ...
What is additive color?
additivecolors are colors which are "pure", i.e. colors add up to form white light. A RED light looks RED because it emitsRED light.
What happens when you mix two colors of paint?
When u mix two paints or dyes, each of them absorbs some of the incident light, the result is that the mixture absorbs more than the initial colors (except if you mix with for ex. red paint with white paint of course!) and then the color shift goes in the opposite direction: you remove light, you create another color.
What happens when you superimpose two lights on paper?
However, when u project two lights on a piece of paper, you superimpose them, then u simply "add" light: there's more light, and the color that appears will be produced by the average of the two original lights. BUT, this optical average doesn't mean that the color will "look" so. For ex. if you superimpose Green & Red lights (both a bit yellowish), you get Yellow, which subjectively looks far from being an average of these two colors, but it is the color of their optical average!
Which color absorbs only one part of the light?
The only light that reflects off the surface and enters our eyes is the light that is not absorbed i.e. red. The primary colours are the colours that absorb only one part of the light e.g. cyan absorbs just red light, magenta absorbs just green light and yellow absorbs just blue light.
Is color a physical property?
I thinks that color questions, however fascinating, have little to do with physics, but let's admit for a while that color sensation is solely given by physical properties of light (its frequency) coming to your eye.
Do glossy magazines need white light?
By the way all the glossy magazines and books in full color printed with CMYK technology require not only white light but also white paper - CMYK pigments are transparent and filter first the incoming white light and than the rest of it reflected back to your eye from the white paper. Share. Improve this answer.
A Bit of Background
Additive vs. Subtractive Color
- There are two methods of producing color: additive and subtractive. The additive color mode is primarily used when shades of light are used to create colors, while the subtractive mode is used when white light, such as sunlight, reflects off an object. Confused yet? Let’s jump in.
Additive and Subtractive Colors in The Printing Process
- The differences between additive and subtractive color may seem subtle and unimportant for your everyday life – after all, color is color, right? Most of the time this is correct, but they are an important consideration when you’re designing for print. When you design something on your computer, your screen will display your design in an additive RGB color mode, but offset printing …
Adding It All Up
- Understanding additive and subtractive color may not help you decide which colors to use in your next creative project, but knowing how these two color modes differ is critical when you’re designing for print.
Additive Color Mixing in The Digital World
Subtractive Color Mixing in The Art World
- Subtractive color mixing is best understood by looking at it from the perspective of art. This takes us back to third grade art class. Remember being given a piece of white paper and a paint set? You were encouraged to paint your parents a beautiful picture with poster paints or watercolors. You had no idea you were practicing subtractive color mixing, did you? Remember that additive …
Why The Difference Between Additive and Subtractive Color Mixing Exists
- Hopefully, you are not totally confused by all of this. Perhaps you are wondering why there is a difference between additive and subtractive color mixing. It has to do with how the eye perceives color and light. Light emanating from a computer display goes directly to your eye. That light activates photo receptors, or cones, in your eye. It turns out that the human eye perceives red, gr…
Summary
- Additive and subtractive color mixing can be difficult to understand. It boils down to the source of light. If light is reaching your eye directly from the source, color is created through additive color mixing. We start with black and add color to create images. If the source is reflective light, color is achieved through subtractive mixing. We st...