What are the three types of loose connective tissue?
The three types of loose connective tissue include adipose, areolar and basement membrane. There are two types of adipose; brown and white, and they function to keep the body warm and provide energy. Areolar is the most abundant of the types of loose connective tissue.
What is the function of loose connective tissue?
Loose connective tissue functions to attach epithelial tissue to the tissue that is underneath it. Loose connective tissue also allows the body to move without overextending. Loose connective tissue contains the salts and water needed by local tissue. Certain types of loose connective tissue act as an insulator and store energy.
Where is loose connective tissue located in the skin?
It is located under the epidermis and dermis layers of the skin. What are the 3 types of loose connective tissue? The three types of loose connective tissue include adipose, areolar and basement membrane. There are two types of adipose; brown and white, and they function to keep the body warm and provide energy.
What is unsourced connective tissue?
Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Loose connective tissue is a category of connective tissue which includes areolar tissue, reticular tissue, and adipose tissue. Loose connective tissue is the most common type of connective tissue in vertebrates. It holds organs in place and attaches epithelial tissue to other underlying tissues.
Does loose connective tissue have blood vessels?
Loose connective tissue is not particularly tough, but surrounds blood vessels and provides support to internal organs.
Is connective tissue avascular or vascular?
Epithelial and connective tissue are generally avascular, which means they lack a blood supply. While, Muscle and nervous tissue are vascular tissues, which means they have a strong blood supply.
What type of tissue is loose connective?
Fascia is loose connective tissue that surrounds and interpenetrates all components of the human body including muscles, nerves, blood vessels, and organs.
Which connective tissue is highly vascularized?
Bone is a highly vascularized connective tissue.
Which types of tissues are vascular?
There are two major types of vascular tissues: (1) xylem and (2) phloem.
Which of the following tissues is not vascular?
Epithelial tissues do not contain blood vessels and as such are avascular.
What's the difference between loose and dense connective tissue?
Loose connective tissue works to hold organs in place and is made up of extracellular matrix and collagenous, elastic and reticular fibers. Dense connective tissue is what makes up tendons and ligaments and consist of a higher density of collagen fibers.
Why is it called loose connective tissue?
Loose connective tissue Chief cells are the fibroblasts. However, immune system cells are also present. Collagen fibers are the principal fibers of the ECM. They are sparsely distributed within the ECM, which is why this tissue type is called 'loose'.
What are three types of loose connective tissue?
The three main types of loose connective fibers include collagenous, elastic, and reticular fibers.Collagenous fibers are made of collagen and consist of bundles of fibrils that are coils of collagen molecules. ... Elastic fibers are made of the protein elastin and are stretchable.More items...•
Which cell layers of the skin are vascularized?
The dermis is found beneath the basement membrane of the epidermis and is the main structural component of the skin. The dermis consists of a richly vascularized and highly innervated connective tissue that supports the epidermis and the skin appendages (hair follicles, sebaceous glands and sweat glands).
Is dense irregular connective tissue vascularized?
The other types of connective tissues are adipose, elastic, cartilage, bone, and blood. Unlike bones and adipose tissue that are vascular, the dense connective tissues are poorly vascularized; the cartilage, in turn, entirely lacks blood vessels.
Is connective tissue vascular if so are there any exceptions?
Most connective tissues are well vascularized, but there are exceptions. Tendons and ligaments have poor blood supply and cartilages are avascular. Therefore, these structures heal very slowly.
Which of the 4 major categories of tissue is avascular?
1. All epithelial tissue is avascular, acquiring nutrients through diffusion or absorption. 2. The four primary tissue types are epithelium, connective tissue, muscle and nervous tissue.
Which type of connective tissue is avascular quizlet?
Cartilage is a type of connective tissue that is avascular.
What is avascular in the body?
Overview. Avascular necrosis is the death of bone tissue due to a lack of blood supply. Also called osteonecrosis, it can lead to tiny breaks in the bone and cause the bone to collapse. The process usually takes months to years. A broken bone or dislocated joint can stop the blood flow to a section of bone.
Are ligaments avascular?
Tendons and ligaments have a very poor blood supply meaning that they do not have any blood vessels that travel through them, which is what makes them very strong and resistant to stretch.
What is loose connective tissue?
Loose connective tissue. Loose connective tissue is common and the most widely distributed connective tissue in animals. It is important to know for further studying of the different organ’s structures of animals’ bodies.
Where are loose connective tissues located?
Location of loose connective tissues. Usually, you will find the loose connective tissue beneath many epithelial tissues (lining epithelium). It provides the support and vascular supply and allows easy movement, shifting different organs of animals’ bodies. #1. In between layers of smooth muscles of any hollow organs.
What is the thickest fiber in the loose connective tissue?
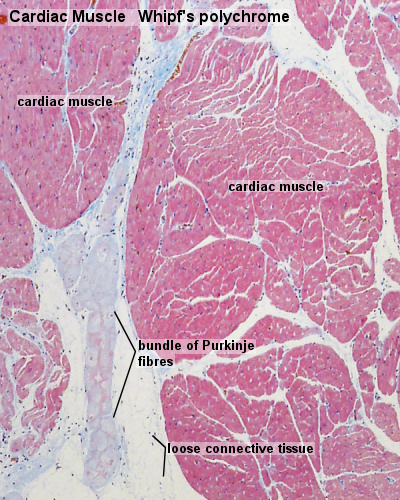
The amount and orientation of these fibers vary widely and depend on the particular tissue’s location and specific functions. The pink collagen fibers (in routine staining) are the thickest, most extensive and most numerous fibers in the loose connective tissue structure that courses in different directions.
What type of connective tissue is loosely arranged?
You will find all kinds of fibers (collagen, reticular and elastic fibers) that loosely arranged.
Where are connective tissue cells found?
Numerous connective tissue cells are found in the loose connective tissue histology where fibroblast and macrophages are more. Fibroblast is the most common flatten or fusiform in shaped with slender processes. These cells contain oval nucleus with prominent nuclei and are actively responsible for forming fibers and ground substances.
Where is reticular connective found?
Reticular connective may be found in the muscles fibers, blood vessels, nerves, and different epithelial structures of the body.
What is the basic tissue that provides structural and mechanical support to other tissues and organs of an animal's body?
Connective tissue is the fundamental tissue that provides structural and mechanical support to other tissues and organs of an animal’s body. Based on the variation of quantity and arrangement of fibers within the matrix, the ideal connective tissue is classified into two main types – loose connective tissue and dense connective tissue .
What is Loose Connective Tissue?
Loose connective tissue is the tissue that contains and attaches to organs. It is called loose connective tissue because its extracellular matrix is organized into loose strands and cells that are interwoven together and look like a loose weave. Loose connective tissue is different from other connective tissue. The extracellular matrix of loose connective tissue is arranged more loosely, hence the name, whereas dense connective tissue has an extracellular matrix that is densely packed together.
Why is loose connective tissue called loose?
Loose connective tissue is called loose because it contains fewer fibers than what is seen in dense connective tissue. The fibers are organized in a manner where they are loosely scattered throughout the tissue. Loose connective tissue is the most abundant of the connective tissues in the body. It is widespread and, as such, is found throughout the body. Loose connective tissue has fibers so widely placed that it allows the tissue to be flexible.
What is the most abundant fiber in loose connective tissue?
Loose connective tissue is the tissue that connects organs to other tissues in the body. Collagenous fibers are the most abundant fiber in loose connective tissue. Elastic fibers are the fibers that contain elastin. Reticular fibers are interwoven fibers of collagen. The two types of adipose tissue, or fat tissue, are brown adipose tissue, present during fetal and infant stages of life, and white adipose tissue, the tissue that acts as an insulator and brings energy to the body. Areolar tissue is the most abundant of the connective tissue in the body. The basement membrane is the thin, dense membrane that separates the body into compartments. The two types of cells that make up the loose connective tissue are fixed cells, also called resident cells that reside in the connective tissue at all times, and wandering cells, also called transient cells which are cells that move in and out of the loose connective tissue.
Why are elastic fibers called elastic fibers?
Elastic fibers get their name because they contain the protein elastin. Elastin allows the elastic fibers to stretch to many times their size and return to their original size afterward. The fibroblasts produce it in the extracellular matrix as well as smooth muscle and epithelial cells. Thus, elastic fibers can be found in every part of the body that stretches, such as the skin and ligaments of the vertebral column. Elastic fibers are interwoven with collagen fibers to give them some strength to prevent stretching to the point of tearing.
Where is the areolar connective tissue located?
It is sturdier than adipose tissue but still flexible. Areolar connective tissue is predominantly found in the layer under the dermis of the skin. The fibers in areolar connective tissue are loosely organized and allow fluid to flow through it. The cells in the epithelial tissue get their nutrients from the fluid that flows through the areolar connective tissue. The fibers can also be more densely packed in some areas of the body, such as the mucus membranes. The areolar connective tissue is a mesh of collagenous and elastic fibers.
Where are reticular fibers found?
These fibers are found most abundantly in areas where a new extracellular matrix is being formed, such as the sites of wound healing and scar tissue formation. The reticular fibers are also found close to some of the body's soft organs, where they provide support to the blood vessels, cells, and nerves of the tissue in the organ.
Is fat a connective tissue?
No. Fat is a type of loose connective tissue. There are two types of fat or adipose tissue in the body. They are brown fat and white fat.
What is the composition of loose connective tissue?
It is a pliable, mesh-like tissue with a fluid matrix and functions to cushion and protect body organs . Fibroblasts are widely dispersed in this tissue; they are irregular branching cells that secrete strong fibrous proteins and proteoglycans as an extracellular ...
Which type of connective tissue holds organs in place and attaches epithelial tissue to other underlying?
Loose connective tissue is the most common type of connective tissue in vertebrates. It holds organs in place and attaches epithelial tissue to other underlying tissues. For example, it forms telae, such as the tela submucosa and tela subserosa, which connect mucous and serous membranes to the muscular layer.
What is the function of areolar connective tissue?
Function. Areolar connective tissue holds organs in place and attaches epithelial tissue to other underlying tissues. It also serves as a reservoir of water and salts for surrounding tissues. Almost all cells obtain their nutrients from and release their wastes into areolar connective tissue.
What are reticular fibers?
Reticular fibers: reticular fibers consist of one or more types of very thin collagen fibers. They join connective tissues to other tissues.
Where is the areolar tissue located?
The areolar tissue is found beneath the epidermis layer and is also underneath the epithelial tissue of all the body systems that have external openings. it makes the skin elastic and helps it to withstand pulling pain. It is also a component of the lamina propria of the digestive and respiratory tracts, the mucous membranes of reproductive and urinary systems, the stroma of glands, and the hypodermis of the skin. It is also found in the mesentery which is surrounding the intestine.
Why is loose connective tissue called loose connective tissue?
Loose connective tissue is named so because of the "weave" and type of its constituent fibers. These fibers form an irregular network with spaces between the fibers. The spaces are filled with ground substance. The three main types of loose connective fibers include collagenous, elastic, and reticular fibers.
Which is stronger, dense or loose connective tissue?
In comparison to loose connective tissue, dense tissue has a higher proportion of collagenous fibers to ground substance. It is thicker and stronger than loose connective tissue and forms a protective capsule layer around organs such as the liver and kidneys .
What is the ground substance in connective tissue?
The ground substance acts as a fluid matrix that suspends the cells and fibers within the particular connective tissue type. Connective tissue fibers and matrix are synthesized by specialized cells called fibroblasts. There are three main groups of connective tissues: loose connective tissue, dense connective tissue, and specialized connective tissue.
Why is spongy bone called cancellous bone?
Spongy bone, also called cancellous bone, gets its name because of its spongy appearance. The large spaces, or vascular cavities, in this type of bone tissue contain blood vessels and bone marrow. Spongy bone is the first bone type formed during bone formation and is surrounded by compact bone.
What is the insulating layer of fat tissue?
This image shows a sample of fat tissue with fat cells (adipocytes, blue) surrounded by fine strands of supportive connective tissue. Adipose tissue forms an insulating layer under the skin, storing energy in the form of fat. Steve Gschmeissner/Science Photo Library/Getty Images
What is the function of connective tissue?
As the name implies, connective tissue serves a connecting function: It supports and binds other tissues in the body. Unlike epithelial tissue, which has cells that are closely packed together, connective tissue typically has cells scattered throughout an extracellular matrix of fibrous proteins and glycoproteins attached to a basement membrane. The primary elements of connective tissue include a ground substance, fibers, and cells.
What are the three types of loose fibers?
The three main types of loose connective fibers include collagenous, elastic, and reticular fiber s. Collagenous fibers are made of collagen and consist of bundles of fibrils that are coils of collagen molecules. These fibers help to strengthen connective tissue. Elastic fibers are made of the protein elastin and are stretchable.
What are some examples of connective tissue?
They can be found all over the body. Bone, cartilage, fat, blood, and lymphatic tissue are all examples of connective tissue.
What are the fluid connective tissues that circulate in the body and help in interaction and communication among all the organs?
Blood and lymph are fluid connective tissues that circulate in the body and help in interaction and communication among all the organs.
What is the layer of connective tissue that connects muscles and other structures to the skin?
Loose connective tissues can be found all over the body, providing both support and elasticity. They, along with adipose tissues, form the subcutaneous layer beneath the skin, which connects muscles and other structures to the skin.
What is dense regular tissue?
Dense regular tissue: In this type of tissue, the orientation of fibres are regular. The collagen fibres are present between the running bundles of fibres parallelly. The regular arrangement enhances tensile strength and poses resistance to stretching in the direction of the orientation of fibre. Examples of dense regular tissue are tendons and ligaments. Tendons attach bones to skeletal muscles. Ligaments attach two bones together.
What tissue is found beneath the skin and helps to sustain the epithelium?
Areolar Tissue: It is found beneath the skin and helps to sustain the epithelium. Fibres, fibroblasts, mast cells, chromatocytes, adipocytes, and macrophages are spread irregularly. It wraps around blood and lymph veins, supports the organs in the abdominal cavity, and fills the gap between muscle fibres.
What are the four primary forms of tissue?
Epithelial, connective, muscular, and nerve tissue are the four primary forms of tissue in the body. All tissues and organs in the body rely on connective tissue for support, protection, and structure. Additionally, connective tissue stores fat, aids in the movement of nutrients and other substances between tissues and organs, and aids in the repair of injured tissue. Read on more about the origin of connective tissue, basic components of connective tissues, types and functions.
Which tissue is the most abundant and widely distributed in the body?
The most abundant and widely distributed tissue in the body is connective tissue. The embryo’s mesoderm is responsible for the formation of the connective tissues. It connects various tissues or organs and provides support to various structures of an animal body.
