MACRS depreciation is calculated by the double declining balance method, using depreciation that is exactly double that of straight-line depreciation. With straight-line depreciation, an asset with a five year useful life will be depreciated 20% each year. Under MACRS depreciation, the first year depreciation will be 40%; since the half-year convention applies, however, the actual deprecation is only 20%.
How to calculate depreciation using MACRS?
To calculate depreciation using MACRS, you’ll need the following info:
- The depreciation system you need to use – GDS or ADS
- The property classification of your asset
- The cost basis of the asset
- The convention
- The depreciation method
What are the disadvantages of straight line depreciation?
Disadvantages of using straight-line depreciation. The following are a few disadvantages that using the straight-line depreciation method can have: It bases calculations on guesstimates. One downside of using the straight-line depreciation method is that it bases the useful life calculation used in this formula on a guesstimate.
What is the recovery period under MACRS depreciation?
MACRS Recovery Periods Under the General Depreciation System (GDS) Depreciable assets, except for buildings, fall within a three-year, five-year, seven-year, 10-year, 15-year, or 20-year recovery period under the general depreciation system (GDS). However, the actual recovery period shown in the MACRS depreciation tables show a recovery period ...
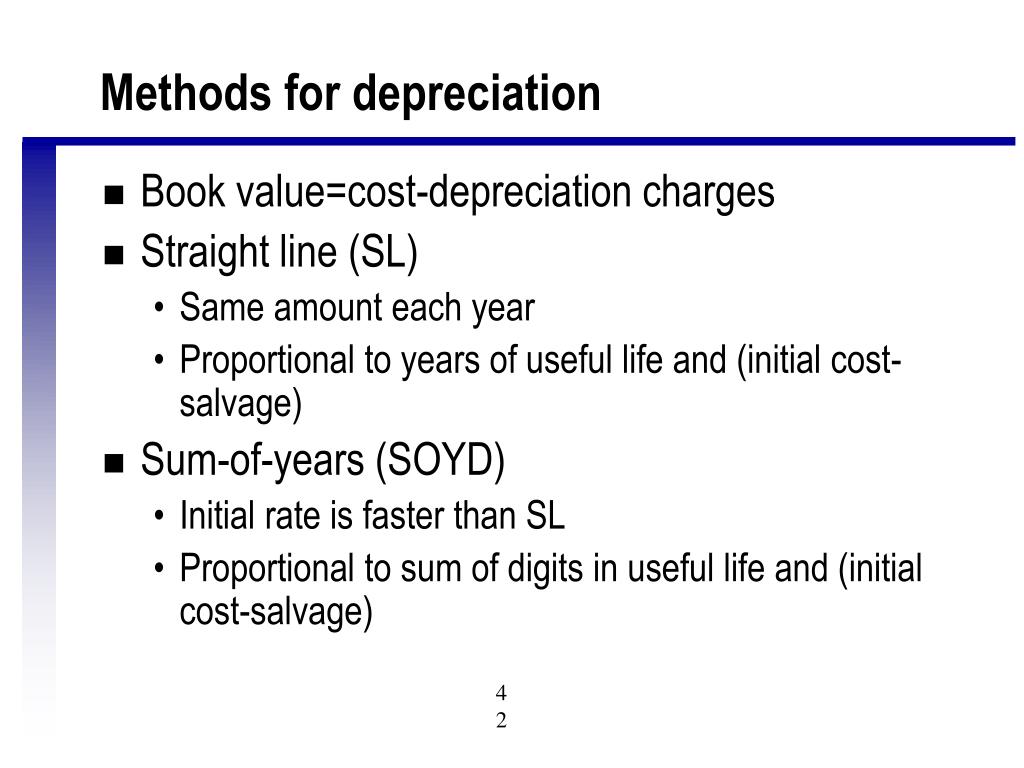
What is the formula for a straight line depreciation method?
The straight-line method of calculating straight-line depreciation has the following steps:
- Determine the initial cost of the asset at the time of purchasing.
- Determine the salvage value of the asset Salvage Value Of The Asset Salvage value or scrap value is the estimated value of an asset after its useful life is over. ...
- Determine the useful or functional life of the asset
- Calculate the depreciation rate, i.e., 1/useful life
Can you use MACRS straight line depreciation?
In fact, straight-line is the only option available for intangible assets, which can't use MACRS nor Section 179. If you opt for straight-line depreciation: It must be applied to all your assets in the same class.
Why use straight line instead of MACRS?
Straight-Line over the MACRS Recovery Period The straight-line method over the modified accelerated cost recovery system recovery period depreciates assets at a slower rate than the double declining method. Using this method allows businesses to depreciate assets by the number of years in the recovery period.
What type of depreciation is MACRS?
The MACRS or the Modified Accelerated Cost Recovery System places fixed assets into classes that have set devaluation periods. It is a depreciation method used for tax purposes in the U.S. As any other depreciation method, it allows to expense a part of the asset value over its useful life.
What is alternative MACRS straight line depreciation?
Alternative Depreciation System (ADS) is a method of calculating the depreciation of certain types of assets in special circumstances. The ADS method calculates depreciation using a straight-line method over a longer period of time relative to GDS; therefore, it reduces the depreciation expense recorded each year.
Can you switch from MACRS to straight line?
The standard method of depreciation for federal income tax purposes is called the Modified Accelerated Cost Recovery System, or MACRS. Essentially, a MACRS depreciation schedule will begin with a declining balance method, then switch to a straight line schedule to finish the schedule.
Why would a firm prefer to use MACRS rather than straight line depreciation for tax purposes?
MACRS allows for faster depreciation in the early years of an asset's life and slows in later years. Given the choice, a firm would prefer to use MACRS, because it facilitates the realization of cash flows sooner than straight-line depreciation.
What is MACRS 5 year depreciation?
An asset is to be depreciated with MACRS using a 5-year recovery period. The first year of recovery is based on double-declining-balance depreciation for one-half year. Verify by an appropriate calculation that r1 for this recovery period is 20.00%.
What is MACRS 7 year property?
7-year property. 7 years. Office furniture and fixtures, agricultural machinery and equipment, any property not designated as being in another class, natural gas gathering lines.
How do you use MACRS for depreciation?
Steps for How to Calculate MACRS DepreciationDetermine the Basis. The basis is simply how much you pay for your purchase, including: ... Determine Your Property's Class. ... Determine Your Depreciation Method. ... Choose Your MACRS Depreciation Convention. ... Determine Your Percentage.
What advantage does MACRS provide over straight line depreciation?
MACRS allows for greater accelerated depreciation over longer time periods. This is beneficial since faster acceleration allows individuals and businesses to deduct greater amounts during the first few years of an asset's life, and relatively less later.
Which depreciation method is used for IRS purposes?
The method used by most taxpayers is the Modified Accelerated Cost Recovery System (MACRS). MACRS provides a uniform method for all taxpayers to compute the depreciation.
Is straight line depreciation required by GAAP?
The straight line method of depreciation is the simplest method of depreciation. Using this method, the cost of a tangible asset is expensed by equal amounts each period over its useful life. The idea is that the value of the assets declines at a constant rate over its useful life. This method is approved by GAAP.
Which is better straight-line or MACRS?
The MACRS depreciation method allows for larger deductions in the early years of an asset's life, and lower deductions in later years. This contrasts significantly with straight-line depreciation, wherein you claim the same tax deduction each year, until the end of the asset's usable life.
Why is straight-line depreciation better?
Straight line is the most straightforward and easiest method for calculating depreciation. It is most useful when an asset's value decreases steadily over time at around the same rate.
What are the advantages of straight-line depreciation?
Straight line method is easy to understand, and has less probability of having errors during the asset life. It also expenses equal amount of depreciation every year.
Why would a company choose straight-line depreciation?
Straight line depreciation is often chosen by default because it is the simplest depreciation method to apply. You take the asset's cost, subtract its expected salvage value, divide by the number of years it's expect to last, and deduct the same amount in each year.
How many MACRS depreciation methods are there?
Based on the IRS, there are four MACRS depreciation methods. Three of them cover in the GDS system and the last method under the ADS system.
What is MACRS depreciation?
MACRS (the full form is Modified Accelerated Cost Recovery System) is a depreciation method for tax purposes used in the United States , and it allows for taking a higher depreciation deduction in the earlier years and less in the later years. It aims to maximize deductions using accelerated depreciation to encourage capital investments. However, MACRS depreciation tables are not advisable for depreciation expenses for audited financial statements as these rules ignore the useful life of the asset and salvage value.
What is modified acceleration cost recovery system?
The depreciation based on Modified Accelerated Cost Recovery System (MACRS) is recognized in the company’s income tax return and used to determine taxable income by factoring in any tax credits and deductions that can be claimed on the property. Putting all together, classification & cost of asset, depreciation method and the period when the asset was placed into service determines the Modified Accelerated Cost Recovery System (MACRS).
What is the declining balance method?
Declining Balance Method In declining balance method of depreciation or reducing balance method, assets are depreciated at a higher rate in the initial years than in the subsequent years. A constant depreciation rate is applied to an asset’s book value each year, heading towards accelerated depreciation. read more
What is the depreciation rate for 7 years?
Using the rates mentioned by IRS, for a 7-year property gives us a depreciation rate of 14.29% for year 1 based on a 200% declining balance.
What are the different types of conventions for the period?
There are 3 types of conventions for the period: Property is placed in service or disposed of service. Non-residential real property, residential real property, and any railroad grading or tunnel bore only. The half-month of depreciation in the month the property was placed/ stopped in service.
How long is asset property?
Classification of asset property – it’s 5-year property.
How much is depreciated in the second year?
In the second year, the remaining 80% value of the asset — i.e., the original value less the first year's 20% depreciation — is depreciated by 40%, or 32% of the original asset value. The same procedure applies during the third, fourth, and fifth years, with the final half-year depreciation recorded in the sixth year.
What is a half year convention?
To accommodate different purchase dates during a fiscal year, the MACRS depreciation method provides for what's called a half-year convention. This means that no matter when an asset is purchased during a fiscal year, the business may depreciate that asset by the value of half a year. Thus the depreciation for an asset with a useful life ...
What is MACRS depreciation?
MACRS depreciation is the modified accelerated cost recovery system of depreciation. This depreciation method was implemented as part of the U.S. Tax Reform Act of 1986.
Why is higher depreciation used on a tax return?
Higher depreciation claimed on a tax return reduces earnings and the resulting tax due on those earnings. Businesses are permitted to use MACRS for tax purposes and other methods of depreciation on financial statements. These depreciation methods spread out depreciation over longer time periods, resulting in lower expenses and a higher level ...
Does the IRS allow a shift in depreciation methods?
The Internal Revenue Service allows a shift in depreciation methods only one time during the asset life. The calculation of MACRS depreciation includes the presumption that the company will switch to straight line depreciation at the point when it is advantageous to do so. The depreciation percentages included in the MACRS tables reflect this calculation. A detailed analysis of MACRS depreciation can be found in IRS Publication 946, including asset class lists and depreciation tables.
What Are the Different Ways to Calculate Depreciation?
In business there are many assets that are considered in the depreciable category after the accounting is done over them. Straight line method or also called as straight line depreciation method is one of the ways to gradually lessen the carrying amount of a fixed asset all over its useful span.
What is the straight line method for accelerated depreciation?
If a company elects not to use accelerated depreciation, it can instead use the straight-line method, where it depreciates an asset at the same standard rate throughout its useful life. All of the depreciation methods end up recognizing the same amount of depreciation, which is the cost of the fixed asset, less any expected salvage value. The only difference between the various methods is the speed with which depreciation is recognized.
How is depreciation calculated?
The deduction for depreciation is computed under one of two methods (declining balance switching to straight line or straight line) at the election of the taxpayer , with limitations. When companies invest in long-lived assets, instead of expensing those costs up front, those investments are capitalized and placed on the balance sheet. Management then needs to estimate the useful life of those assets and determine a depreciation method, such as accelerated or straight-line, among others. The other important type of accelerated depreciation is the “Sum-of-the-Years’ Digits” depreciation method, or SYD. This also focuses on the percentage of the asset’s cost you pay for the deduction expense, but takes into account how old the asset currently is.
What is accelerated depreciation?
For tax purposes, accelerated depreciation provides a way of deferring corporate income taxes by reducing taxable income in current years, in exchange for increased taxable income in future years. This is a valuable tax incentive that encourages businesses to purchase new assets. There are a lot of reasons businesses choose to use ...
Why do businesses use accelerated depreciation?
Some businesses, though, prefer an accelerated depreciation method that means paying higher expenses early on and lower expenses toward the end of the asset’s lifespan. Accelerated depreciation helps companies shield income from taxes — after all, the higher the depreciation expense, the lower the net income.
What are the most common depreciation methods?
The most common types of depreciation methods include straight-line, double declining balance, units of production, and sum of years digits.
What is the difference between accelerated and straight line depreciation?
The difference between accelerated and straight-line is the timing of the depreciation.