
What are the examples of monopolistic competition?
Example of Monopolistic Competition. There are usually a large numbers of independent firms competing in the market. The most common example of monopolistic competition is fast food burger companies like Burger King and McDonald. These two companies are almost selling similar product but depends on consumers which they like the most.
Who are monopolistic competitors?
Monopolistic competition involves many firms competing against each other, but selling products that are distinctive in some way. Examples include stores that sell different styles of clothing; restaurants or grocery stores that sell different kinds of food; and even products like golf balls or beer that may be at least somewhat similar but differ in public perception because of advertising and brand names.
What is monopolistic competition characterized by?
Monopolistic competition is characterized by large number of firms and low entry barriers. The restaurant, legal assistance, and clothing industries are each illustrations of monopolistic competition A monopolistically competitive firm has a highly elastic demand curve
Is the banking industry monopolistic competition?
Yes, In the United States, banking is a local monopoly. The US constitution prevented states from issuing their own money and from taxing trade between states. So one important source of revenue was banks.
What is monopolistic competition?
How do companies compete in a monopolistic market?
Why is freedom to exit due to continued economic losses important?
How do monopolistic competitive companies waste resources?
Why is collusion between companies impossible?
What happens to economic profits in the short run?
What is competition with other companies?
See 4 more
About this website
What is monopolistic competition?
Monopolistic competition is a type of market structure where many companies are present in an industry, and they produce similar but differentiated products. None of the companies enjoy a monopoly, and each company operates independently without regard to the actions of other companies.
How do companies compete in a monopolistic market?
Companies compete based on product quality, price, and how the product is marketed. Companies in a monopolistic competition make economic profits in the short run, but in the long run, they make zero economic profit. The latter is also a result of the freedom of entry and exit in the industry.
Why is freedom to exit due to continued economic losses important?
The freedom to exit due to continued economic losses lead s to an increase in prices and profits, which eliminates economic losses. In addition, companies in a monopolistic market structure are productively and allocatively inefficient as they operate with existing excess capacity.
How do monopolistic competitive companies waste resources?
Monopolistic competitive companies waste resources on selling costs, i.e., advertising and marketing to promote their products. Such costs can be utilized in production to reduce production costs and possibly lower product prices.
Why is collusion between companies impossible?
Because of the large number of companies, each player keeps a small market share and is unable to influence the product price. Therefore, collusion between companies is impossible. In addition, monopolistic competition thrives on innovation and variety.
What happens to economic profits in the short run?
Such a scenario inevitably eliminates economic profit and gradually leads to economic losses in the short run.
What is competition with other companies?
Competition with other companies is thus based on quality, price, and marketing. Quality entails product design and service. Companies able to increase the quality of their products are, therefore, able to charge a higher price and vice versa.
Short-Run Decisions on Output and Price
Long-Run Decisions on Output and Price
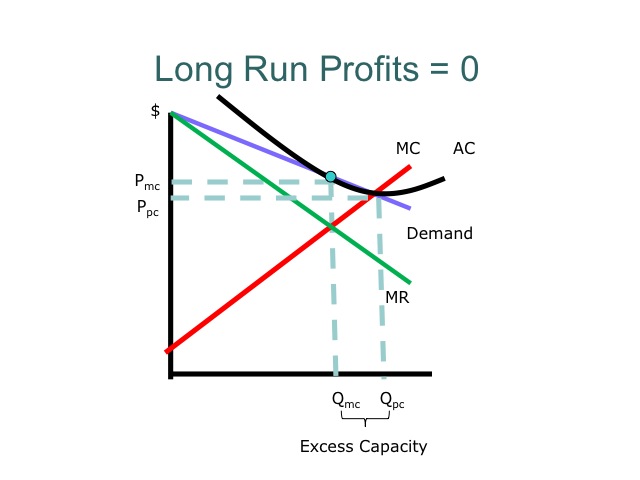
- In the long run, companies in monopolistic competition still produce at a level where marginal cost and marginal revenue are equal. However, the demand curve will have shifted to the left due to other companies entering the market. The shift in the demand curve is a result of reduced demand for an individual company’s products due to increased competition. Such an action red…
Monopolistic Competition vs. Perfect Competition
- Companies in monopolistic competition produce differentiated products and compete mainly on non-price competition. The demand curves in individual companies for monopolistic competition are downward sloping, whereas perfect competition demonstrates a perfectly elastic demand schedule. However, there are two other principal differences worth mentioning – excess capacit…
Inefficiencies in Monopolistic Competition
- The equilibrium output at the profit maximization level (MR = MC) for monopolistic competition means consumers pay more since the price is greater than marginal revenue.
- As indicated above, monopolistic competitive companies operate with excess capacity. They do not operate at the minimum ATC in the long run. Production capacity is not at full capacit…
- The equilibrium output at the profit maximization level (MR = MC) for monopolistic competition means consumers pay more since the price is greater than marginal revenue.
- As indicated above, monopolistic competitive companies operate with excess capacity. They do not operate at the minimum ATC in the long run. Production capacity is not at full capacity, resulting i...
- Monopolistic competitive companies waste resources on selling costs, i.e., advertising and marketing to promote their products. Such costs can be utilized in production to reduce production costs a...
- Since companies do not operate at excess capacity, it leads to unemploymentand social despondency in society.
Limitations of Monopolistic Competition Market Structure
- Companies with superior brands and high-quality products will consistently make economic profits in the real world.
- Companies entering the market will take a long time to catch up, and their products will not match those of the established companies for their products to be considered close substitutes. New comp...
Additional Resources
- Thank you for reading CFI’s guide to Monopolistic Competition. To keep learning and developing your knowledge of financial analysis, we highly recommend the additional resources below: 1. Aggregate Supply and Demand 2. Barriers to Entry 3. Legal Monopoly 4. Oligopoly