
Why are secondary pollutants harder to control?
What are some examples of air pollutants?
What is PM 2.5?
How is PM formed?
See 1 more
About this website

Is SO2 a primary or secondary pollutant?
SO2, along with nitrogen oxides (NOx), is a primary contributor to acid rain. Acid rain is a term for rain, snow, fog, and hail that contain sulfuric and nitric acids formed by the chemical reaction of SO2 and NOx with water, oxygen, and other chemicals in the atmosphere.
What are 3 secondary pollutants?
Examples of a secondary pollutant include ozone, which is formed when hydrocarbons (HC) and nitrogen oxides (NOx) combine in the presence of sunlight; NO2, which is formed as NO combines with oxygen in the air; and acid rain, which is formed when sulfur dioxide or nitrogen oxides react with water.
What are the primary and secondary pollutants?
Primary air pollutants: Pollutants that are formed and emitted directly from particular sources. Examples are particulates, carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxide, and sulfur oxide. Secondary air pollutants: Pollutants that are formed in the lower atmosphere by chemical reactions.
What are the 3 primary pollutant gases?
Types of primary pollutants include: Nitrogen oxides (NOx) Carbon monoxide (CO) Volatile organic compounds (VOCs)
What are the 5 secondary pollutants?
Different types of secondary pollutants include:Ozone (O3)Sulfuric acid and nitric acid (component of acid rain)Particulate matter.Nitrogen dioxide (NO2)Peroxyacyl nitrates (PANs)and more.
Is o3 a secondary pollutant?
Ground-level ozone is a colorless and highly irritating gas that forms just above the earth's surface. It is called a "secondary" pollutant because it is produced when two primary pollutants react in sunlight and stagnant air.
What are the 5 primary pollutants?
These six pollutants are carbon monoxide, lead, nitrogen oxides, ground-level ozone, particle pollution (often referred to as particulate matter), and sulfur oxides.
Which one is not a secondary pollutant?
Detailed Solution. The correct answer is Sulphur dioxide.
Which is not a primary pollutant?
Which of these is NOT a primary pollutant? Explanation: Ozone is not a primary pollutant since it is formed by the photo-chemical reaction of oxygen with the UV rays and not directly discharged into the atmosphere by a source.
Is co2 a secondary pollutant?
Carbon dioxide(CO2) is a primary air pollutant emitted directly from a source. Carbon dioxide is one of the main pollutants with regard to air pollution. It is a primary pollutant, which means it is emitted into the environment directly by human and natural sources.
What is a secondary air pollutant?
Secondary air pollution is pollution caused by reactions in air already polluted by primary emissions (from factories, automobiles and so forth). An example of secondary air pollution is photochemical smog.
Which of the following is secondary air pollutant?
Thus ozone is known as secondary air pollutant .
What is a secondary air pollutant?
Secondary air pollution is pollution caused by reactions in air already polluted by primary emissions (from factories, automobiles and so forth). An example of secondary air pollution is photochemical smog.
Is co2 a secondary pollutant?
Carbon dioxide(CO2) is a primary air pollutant emitted directly from a source. Carbon dioxide is one of the main pollutants with regard to air pollution. It is a primary pollutant, which means it is emitted into the environment directly by human and natural sources.
Is lead a secondary pollutant?
There are many types of primary pollutants, including carbon oxides, nitrogen oxides, sulfur oxides, particulates, lead, and volatile organic compounds. Secondary pollutants form from chemical reactions that occur when pollution is exposed to sunlight.
Is ammonia a secondary pollutant?
The major primary pollutants are Oxides of Sulphur, Oxides of Nitrogen, Oxides of Carbon, Particulate Matter, Methane, Ammonia, Chlorofluorocarbons, Toxic metals etc. The secondary pollutants are not emitted directly.
Difference Between Primary and Secondary Pollutants
Primary vs Secondary Pollutants . With industrialization and urbanization, lot of pollutants are released to the environment. It is important to know about the pollutants, their effects and how they are released to the environment in order to minimize their harmful effects.
Primary and Secondary Air Pollutants- And Their Examples - CivilNotePpt
Examples of secondary air pollutants: 1) Ozone 2) Formaldehyde 3) PAN (Peroxy acetyl nitrate) 4) Photochemical smog 5) Formation of acid mists (H2SO4) due to the reaction of sulphur dioxide and dissolved oxygen. when water droplets are present in the atmosphere . Read More: Objectives of Air Conditioning
Major Examples of Primary Pollutants in Our Environment - Ways2GoGreen
My name is Clay Miller and I’m an advocate for oceans, beaches and state parks. I enjoy all things outdoors such as gardening and hiking. A graduate of the University of Kentucky (Go Wildcats!!), I’m also a huge fan of the Pittsburgh Steelers.
What Are The Differences Between Primary And Secondary Pollutants?
Effects Of Primary And Secondary Pollutants . Researchers have identified a link between primary pollutants and global climate change. Additionally, secondary pollutants are known to cause a number of negative impacts on the environment as well.
Examples of Secondary Pollutants and How They’re Formed - YourDictionary
Examples of Secondary Air Pollutants. In chemistry, you know that when you mix one chemical with another, it forms a new substance.That’s exactly what happens with secondary pollutants. The byproducts individuals and factories release into the air from burning fossil fuels, such as burning coal to make electricity, mix with the atmosphere in the air to create new compounds.
Why are secondary pollutants harder to control?
Secondary pollutants are harder to control because they have different ways of synthesizing and the formation are not well understood. They form naturally in the environment and cause problems like photochemical smog.
What are some examples of air pollutants?
Examples are particulates, carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxide, and sulfur oxide. Secondary air pollutants: Pollutants that are formed in the lower atmosphere by chemical reactions. The two examples are ozone and secondary organic aerosol ...
What is PM 2.5?
PM 2.5 (also known as fine fraction particles) is generally defined as those particles with an aerodynamic diameter of 2.5 microns or less. Sources of fine particles include all types of combustion activities (motor vehicles, power plants, wood burning, etc.) and certain industrial processes.
How is PM formed?
Other PM may be formed in the air from the chemical change of gases. They are indirectly formed when gases from burning fuels react with sunlight and water vapor. The sources can be from fuel combustion in motor vehicles, at power plants, and in other industrial processes. Clean Air Day (Winter)
Why are secondary pollutants harder to control?
Secondary pollutants are harder to control because they have different ways of synthesizing and the formation are not well understood. They form naturally in the environment and cause problems like photochemical smog.
What are some examples of air pollutants?
Examples are particulates, carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxide, and sulfur oxide. Secondary air pollutants: Pollutants that are formed in the lower atmosphere by chemical reactions. The two examples are ozone and secondary organic aerosol ...
What is PM 2.5?
PM 2.5 (also known as fine fraction particles) is generally defined as those particles with an aerodynamic diameter of 2.5 microns or less. Sources of fine particles include all types of combustion activities (motor vehicles, power plants, wood burning, etc.) and certain industrial processes.
How is PM formed?
Other PM may be formed in the air from the chemical change of gases. They are indirectly formed when gases from burning fuels react with sunlight and water vapor. The sources can be from fuel combustion in motor vehicles, at power plants, and in other industrial processes. Clean Air Day (Winter)
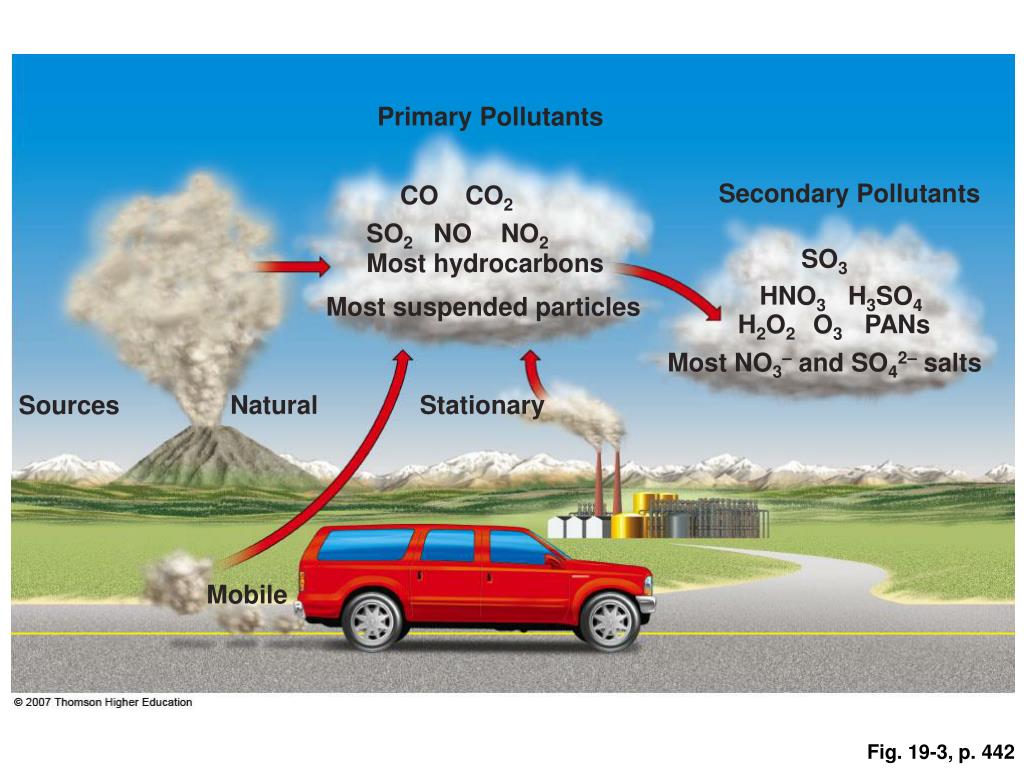
Primary Pollutants
Secondary Pollutants
- Secondary pollutants are formed when primary pollutants react with other gases or particles. Such transformations always occur in an open atmosphere. They can be just as harmful to people and the environment as primary pollutants. Secondary pollutants, unlike primary pollutants, do not become immediately visible in the materials they damage. Eventually, they build up to cause furt…
Categories of Pollutants
- Natural Pollutants (CO, SO2, Pb, Hg, trace elements, etc)
- Synthetic pollutants (pesticides, detergents, pharmaceuticals, organic acids, etc)
- Non-degradable pollutants (aluminum cans, mercurial salts, DDT, nuclear wastes, etc)
- Bio-degradable pollutants (phosphates, carbonates, nitrates, etc)
Sources of Primary and Secondary Pollutants
- 1. Stationary sources of pollutants Chimneys of power plants, manufacturing facilities, waste, etc are stationary sources of pollutants. 2. Natural sources of pollutants Forest fires, emissions from trees, volcanic eruptions, erosion activities, radioactive decay, methane, dust, etc are natural sources. 3. Anthropogenic activities Transportation, biomass burning, crop residue burning, indu…
Effects of Primary and Secondary Pollutants
- Air pollutants There are different effects of air pollutants on the environment. 1. Photochemical smog 2. Acid deposition (Acid rain) 3. Greenhouse effect 4. Ozone depletion, etc Water pollutants There are the following effects of water pollutants. 1. Eutrophication of aquatic ecosystem 2. Oxygen depletion 3. Metal toxicity 4. Heat, etc Soil pollutants Herbicides, insecticides, halogens, …
Concepts Berg
- What are the most dangerous primary and secondary pollutants? Both primary and secondary pollutants are dangerous. Although, primary pollutants exceed in hazards than secondary ones. What is a primary pollutant? Primary pollutants are emitted from a source. These pollutants may be chemicals, biological materials, or even radionuclides. Primary pollutants enter into the air, w…