Is Staphylococcus a heterotrophy or heterotroph?
When comes to carbon source, Staphylococcus is a heterotrophy (12). That is to say, it attains its carbon source by utilization of organic substances such as sucrose for synthesis of metabolites (19). To summarize, Staphylococcus should be one of the members of the microbial group, Chemo-organotrophic heterotrophs.
Are all bacteria autotrophs?
All Bacteria are not autotrophs, some of them are heterotrophs. Some types of bacteria use energy in the form of light to prepare their own food same as the process of photosynthesis.These bacteria do not come in the category of autotrophs because they all rely on others, not able to make food by themselves.
Is Staphylococcus aureus a bacteria?
The bacterial genus, Staphylococcus, will be isolated and identified in this project. This genus has been chosen to review because of its abundance on the skin of mammals and the pathogenic nature of one of its member, Staphylococcus aureus.
What is a heterotroph?
A heterotroph is an organism that eats other plants or animals for energy and nutrients. The term stems from the Greek words hetero for “other” and trophe for “nourishment.” Organisms are characterized into two broad categories based upon how they obtain their energy and nutrients: autotrophs and heterotrophs.
Is Staphylococcus aureus a Chemoheterotroph?
Staphylococcus is a catalase-positive Gram-positive coccus that is normally arranged in clusters. It is a facultatively anaerobic chemoheterotroph commonly found on skin and mucous membranes. Important species in this genus include S. aureus (an opportunistic pathogen) and S.
What type of organism is Staphylococcus aureus?
Staphylococcus aureus is a gram-positive bacteria that cause a wide variety of clinical diseases. Infections caused by this pathogen are common both in community-acquired and hospital-acquired settings.
What is the energy source for Staphylococcus aureus?
As for other pathogens, the synthesis and acquisition of certain nutrients are critical to support the infection capacity of S. aureus, glucose being one of the preferred carbon sources of this bacterium.
Is Staphylococcus aureus unicellular or multicellular?
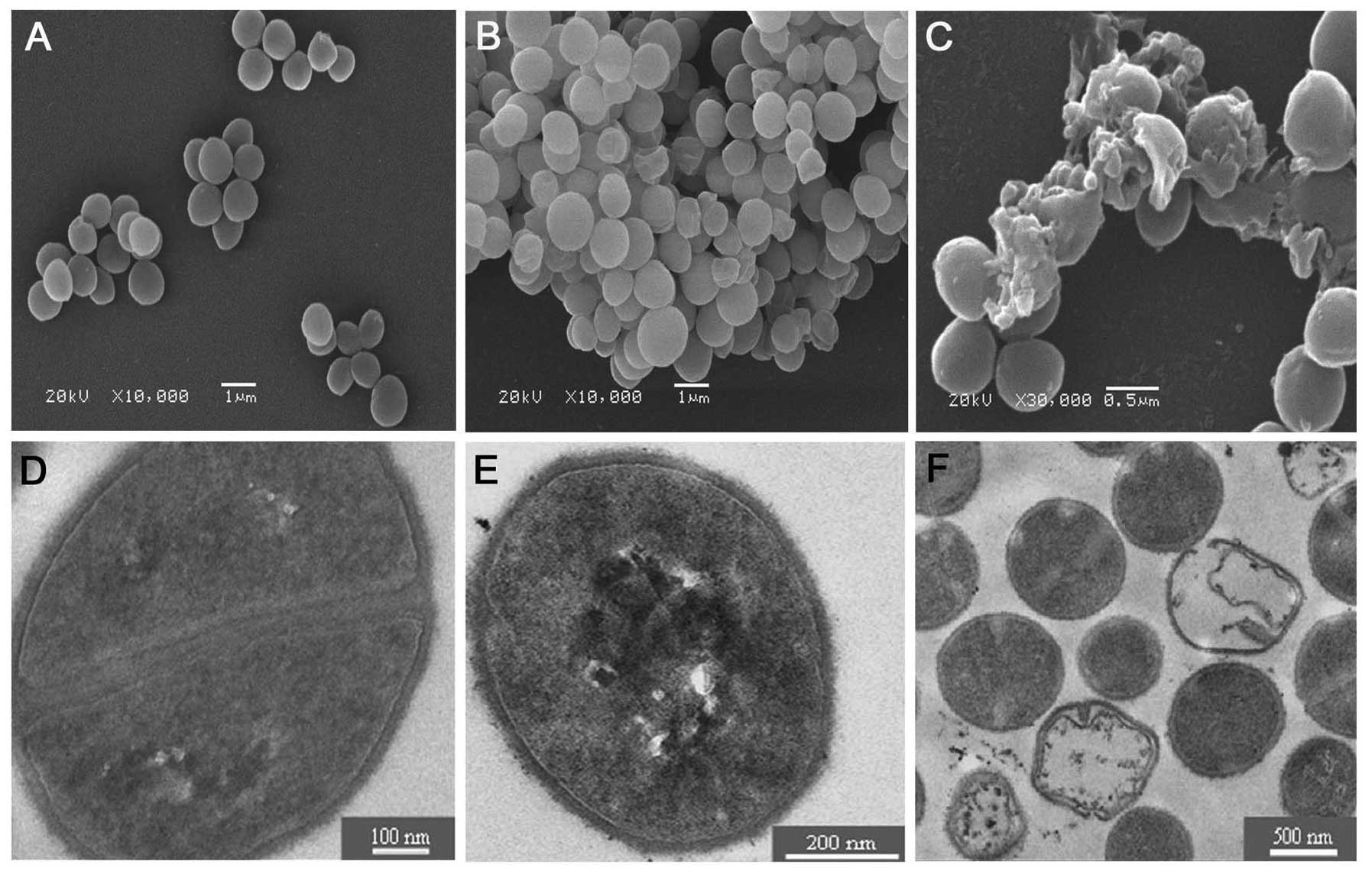
Staphylococcus aureus multicellular aggregates contain distinct cell types. (A) Fluorescence microscopy image fields of S. aureus cells harboring transcriptional fusions of biofilm-associated ica/spa genes and planktonic psmα/β agr-related genes and, the transcriptional fusion of the housekeeping gene dnaA.
What are the characteristics of Staphylococcus aureus?
S. aureus cells are Gram-positive and appear in spherical shape. They are often in clusters resembling bunch of grapes when observed under light microscope after Gram staining. The name 'Staphylococcus' was derived from Greek, meaning bunch of grapes ( staphyle ) and berry ( kokkos ) [1].
What is unique about Staphylococcus aureus?
S. aureus has long been recognized as one of the most important bacteria that cause disease in humans. It is the leading cause of skin and soft tissue infections such as abscesses (boils), furuncles, and cellulitis. Although most staph infections are not serious, S.
Does Staphylococcus aureus use glucose?
Glucose serves as an important carbohydrate for the growth of Staphylococcus aureus. Carbohydrates support the growth of S. aureus under anaerobic conditions and high nitric oxide stress (Richardson et al., 2008; Vitko et al., 2015).
Is Staphylococcus aureus aerobic or anaerobic?
facultative anaerobic bacteriumAlthough S. aureus is a facultative anaerobic bacterium, the growth rate was drastically reduced after the shift from aerobic to anaerobic growth conditions.
Is Staphylococcus aerobic or anaerobic?
Staphylococcus species are aerobically growing gram-positive cocci.
How do you classify Staphylococcus?
Staphylococcus is a genus of Gram-positive bacteria in the family Staphylococcaceae from the order Bacillales. Under the microscope, they appear spherical (cocci), and form in grape-like clusters. Staphylococcus species are facultative anaerobic organisms (capable of growth both aerobically and anaerobically).
How does Staphylococcus aureus reproduce?
Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) is a bacterium that reproduces through binary fission such that the daughter cells do not fully separate from the parents and cells form into clusters. S. aureus is a common member of human skin microflora, especially in the nose [1,2].
What is the difference between Staphylococcus and Staphylococcus aureus?
Staphylococcus aureus is a type of bacteria. It stains Gram positive and is non-moving small round shaped or non-motile cocci. It is found in grape-like (staphylo-) clusters. This is why it is called Staphylococcus.
What is the classification of staphylococci?
Staphylococcus is a genus of Gram-positive bacteria in the family Staphylococcaceae from the order Bacillales....StaphylococcusClass:BacilliOrder:BacillalesFamily:StaphylococcaceaeGenus:Staphylococcus Rosenbach 18847 more rows
What family does Staphylococcus belong to?
StaphylococcaceaeStaphylococcus / FamilyThe genus Staphylococcus is a member of a diverse group of the family Micrococcaceae that are capable of causing a wide array of diseases. They are characterized as typical catalase-positive, Gram-positive cocci that produce an array of extracellular and cell surface virulence factors.
What are Staphylococcus microorganisms?
Staphylococcus (staph) is a group of bacteria. There are more than 30 types. A type called Staphylococcus aureus causes most infections. Staph bacteria can cause many different types of infections, including: Skin infections, which are the most common types of staph infections.
What are the types of Staphylococcus?
Staph infections are caused by several different types of staph germs, including:methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA)vancomycin-intermediate Staphylococcus aureus (VISA)vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (VRSA)
What is the origin of Staphylococcus aureus?
Interesting Facts About Staphylococcus Aureus Infection: #1 The name Staphylococcus originates from Greek terms (staphyle and kokkos) which literally translate as a bunch of grapes. Over 30 types of Staphylococci bacteria cause infections in humans (typically skin infections which are limited to a small area of an individual’s skin, ...
What are the risk factors for staph infection?
#18 Some conditions may put you at higher risk of Staph infections, including: use of intravenous catheters; breastfeeding; surgical incisions; skin injuries or disorders; having type 2 diabetes mellitus; the use of injectable medications or drugs; having a weakened immune system;
What antibiotics are used for staph infection?
But, serious Staph infections require to be treated in hospital, usually with intravenous antibiotics. Antibiotics which are usually used include: vancomycin (it is a glycopeptide antibiotic); tetracycline; linezolid (com es as an oral suspens ion or as a tablet); clindamycin; trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole.
How many people died from methicillin resistant staph?
#5 There were an estimated 5 million people in the United States colonized by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains.
How to prevent S. aureus?
aureus: don’t share any personal items, including sports equipment or towels; keep all skin injuries clean; bathe or shower once per day; wash your hands frequently and thoroughly with warm water and soap.
Do brown bears kill S. aureus?
where the bacterial infection has spread; the patient’s age. #23 Note – Siberian brown bears have a chemical in their saliva which has been found to kill S. aureus, according to a team of scientists affiliated with multiple institutions in the United States and Russia.
How many tRNA genes are in a staph aureus?
The Staphylococcus aureus strain NCTC 8325 complete circular genome map shows ~2,900 open reading frames, 61 tRNA genes, 3 structural RNAs, and 5 complete ribosomal RNA operons. This strain has about 33% G+C content and an average gene length of 824 nucleotides with 85% coding sequence, similar to other S. aureus strains. Half the coding sequence is located predominantly on one replichore and the second half is located predominantly on the other replichore.
Where are the genes for antibiotic resistance in Staphylococcus aureus?
aureus strains. The genes for antibiotic resistance in Staphylococcus aureus are located on plasmids or other similar structures.
What are the virulence factors of MRSA?
Virulence factors are encoded by phages, plasmids, pathogenicity islands and staphylococcus cassette chromosome. Increased resistance for antibiotics is encoded by a transposon (Tn 1546) that was inserted into a conjugated plasmid that also encoded resistance to other things including disinfectants. MRSA (Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus ), which is resistant to the antibiotic methicillin, expresses a modified penicillin-binding protein encoded by mecA gene. This was brought about by many evolutions thought horizontal gene transfer of mecA to a wide variety of methicillin susceptible S. aureus strains. The genes for antibiotic resistance in Staphylococcus aureus are located on plasmids or other similar structures.
What is the name of the bacteria that divides in two planes?
Staphylococci are spherical gram-positive bacteria, which are immobile and form grape-like clusters. They form bunches because they divide in two planes as opposed to their close relatives streptococci which form chains because they divide only in one plane. Colonies formed by S. aureus are yellow (thus the name aureus, ...
How does S. aureus evolve?
Evolution of this bacterium can occur through asymptomatic colonization and/or during the course of the caused disease.
Why is it important to understand the virulence mechanisms of S. aureus?
aureus especially the Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in order to successfully combat the pathogen. The increasing population of "super germs" and antibiotic resistant pathogens have increased pressure on researchers to find alternative, more effective ways of fighting these "super germs." DNA sequencing of this microbe has already isolated the source code of its' resistance to antibiotics, and further research will more than likely lead us to the path of our next artillery against this and many other pathogens.
When was S. aureus isolated?
In 1997 a strain of S. aureus resistant to vancomycin was isolated, and people are once again exposed to the threat of untreatable staphylococcus infection. MRSA strains are currently a very significant health care problem.
Abstract
Heterotrophic bacteria associated with two specimens of the marine sponge Erylus discophorus were screened for their capacity to produce bioactive compounds against a panel of human pathogens (Staphylococcus aureus wild type and methicillin-resistant S.
Substances
This research was supported by the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF) through the COMPETE - Operational Competitiveness Programme and national funds through FCT – Foundation for Science and Technology, under the projects PEst-C/MAR/LA0015/2013, PEst-OE/QUI/UI0612/2011 and PTDC/QUI-QUI/098053/2008.
What are protists?
Protists include all microscopic organisms that are not bacteria, not animals, not plants, and not fungi. Ex) Amoeba. Diatom. Euglena. Algae. 4. Fungi (Saccharomyces cerevisiae): Unicellular/Multicellular, and eukaryotic. It is heterotrophic. It reproduces sexually, and asexually.
Do fungi make their own food?
Unlike plants, fungi cannot make their own food. Most obtain their food from parts of plants that are not decaying in the soil. Ex) Mushroom. Mold. Yeast. Puffball. 5. Plantae (Cycas revoluta/Zea mays): Multicellular, and eukaryotic. It is autotrophic, and rarely heterotrophic.
Is a protist a heterotroph?
Protista (Paramecium caudatum/Chlamydomonas reinhardtii): Unicellular/Multicellular, and eukaryotic. It is Autotrophic/Heterotrophic. There are plant-like, animal-like, and fungi-like. It reproduces asexually. Protists include all microscopic organisms that are not bacteria, not animals, not plants, and not fungi. Ex) Amoeba.
Can archaebacteria be found?
2. Archaebacteria- Cannot be found. “ As of now, scientist do not know of any endangered species of archaebacteria. Its possible there are some, but we have not discovered any yet.”
Is Eubacteria heterotrophic or autotrophic?
It is Autotrophic/Heterotrophic. It reproduces asexually. Most Eubacteria are helpful. Some produce vitamins and foods like yogurt. Eubacteria are classified in their own kingdom because their chemical makeup is different.
