
Full Answer
Why do enzymes work better at their optimum pH?
What cleaners should not be mixed?
- Baking Soda and Vinegar.
- Hydrogen Peroxide and Vinegar.
- Ammonia and Bleach.
- Vinegar and Bleach.
- Bleach and Rubbing Alcohol.
- Different Drain Cleaners.
- Mildew Stain Remover and Bleach.
- Bleach and Toilet Bowl Cleaner.
What pH would the enzymes be most effective?
Method
- Set up a Bunsen burner, heatproof mat, tripod and gauze.
- Place a beaker of water on the gauze and adjust the flame to keep the water at about 35°C.
- Now put two drops of iodine solution into each spot of a spotting tile.
- Add 2 cm3 of amylase enzyme solution to a test tube.
- Place 2 cm3 of starch solution into the same tube.
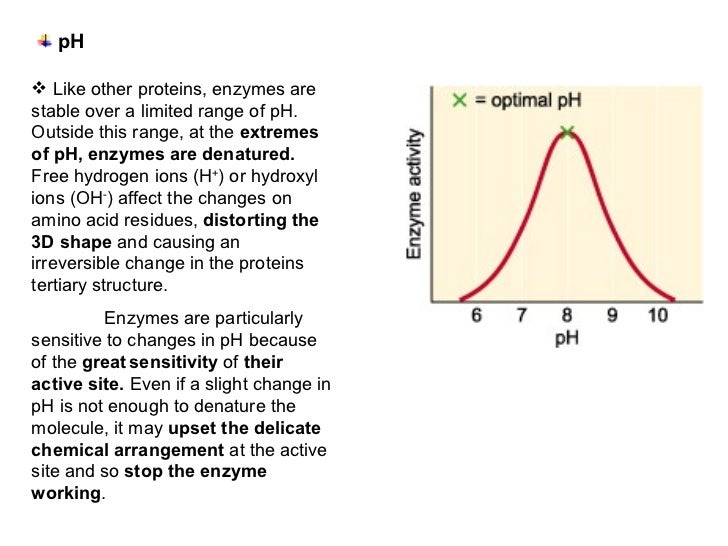
What does the optimum pH of an enzyme mean?
Under the optimum pH conditions, each enzyme showed the maximum activity. For example, the optimum pH of an enzyme that works in the acidic environment of the human stomach is lower than that of an enzyme that works in a neutral environment of human blood.
What is the optimal pH for most enzymes?
Most enzymes' optimum pH is neutral or close to neutral, like amylase found in saliva, which has an optimal pH = 6.8. Some enzymes prefer a more drastic pH, like pepsin, which can have an optimum pH of 1.7 to 2. Sometimes enzyme pH optima depends on where the enzyme is found.
Is saliva pH neutral?
pH and the Body. Bodily pH is not uniform, and if you think about it, that makes a lot of sense. Something like saliva is relatively neutral, in the 6.5-6.75 range. By comparison, gastric secretions like stomach acid are more acidic, and something like bile would be more alkaline. Where things go wrong in the body is generally when acidity levels ...
Can you use enzymes to support digestive health?
This can be a major concern if you are trying to use enzymes to support your digestive health or any other facet of health. Even if you use supplemental enzymes, if they are going into a body with a pH level that’s not suitable, chances are that you’re only going to see a fraction of the potential benefits, if any.
What are the effects of pH on enzymes?
Effects of pH. Enzymes are affected by changes in pH. The most favorable pH value - the point where the enzyme is most active - is known as the optimum pH. This is graphically illustrated in Figure 14. Extremely high or low pH values generally result in complete loss of activity for most enzymes. pH is also a factor in the stability of enzymes.
What happens when pH is low?
Extremely high or low pH values generally result in complete loss of activity for most enzymes. pH is also a factor in the stability of enzymes. As with activity, for each enzyme there is also a region of pH optimal stability.
