
What three molecules make up the thin filament?
- 1. Actin
- 2. Tropomyosin
- 3. Troponin
What are thin filaments made of?
What are the proteins that make up the thin filaments of myosin?
What is the globular core domain of tropomyosin?
What are the properties of actin?
How does thin filament regulation work?
What is the protein meshwork in the Z disk?
How many tropomyosin molecules are in a 38 nm repeat?
See 4 more
About this website
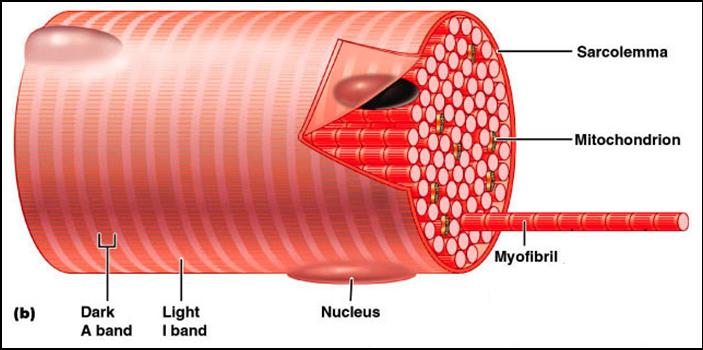
What are the 3 proteins in the thin filaments?
Tn exists as a complex of three component proteins: troponin C (TnC), troponin I (TnI) and troponin T (TnT). Each of the three proteins is a regulator of muscle contraction and plays distinct roles in the thin filament.
What are thin filaments made of?
Thin filaments (TFs) are comprised of F-actin, the troponin complex (Tn), and tropomyosin (Tm). Tn itself is a multiprotein complex comprised of the TnI (e.g., inhibitory) subunit, the TnC (e.g., Ca2+ binding) subunit, and TnT—the subunit which links the Tn complex to the Tm cable.
What proteins make up thick and thin filaments?
The thick filaments are composed of myosin, and the thin filaments are predominantly actin, along with two other muscle proteins, tropomyosin and troponin.
What is the main component of thin filaments quizlet?
The main component of the thin filaments is a protein called actin. Actin molecules join together forming chains twisted into a helix configuration. These molecules are very important to the contraction mechanism of muscles because each actin molecule has a single "myosin-binding site" (not illustrated above).
Which protein makes up the thick filaments quizlet?
The thick filaments are composed of a protein called myosin. The thin filaments are composed mainly of the protein actin along with two other muscle proteins, tropomyosin and troponin.
Is myosin A thin filament?
Most of the cytoplasm consists of myofibrils, which are cylindrical bundles of two types of filaments: thick filaments of myosin (about 15 nm in diameter) and thin filaments of actin (about 7 nm in diameter).
Which of the following proteins is not found in thin filaments?
c) Myosin is not a component of the thin filament in skeletal muscle.
What contains both thick and thin filaments?
The sarcomere is the basic contractile unit for both striated and cardiac muscle and is made up of a complex mesh of thick filaments, thin filaments, and a giant protein titin.
What is the main component of thin sheet?
The thin filament contains several important contractile regulatory proteins (Figure 4). The main component is the actin filament, which is formed from the polymerization of globular actin molecules.
What are the thin filaments and their characteristics?
The thin filaments are approximately 7-9 nm in diameter. They are attached to the z discs of the striated muscle. Each thin filament is made up of three proteins: (1) actin, (2) troponin, and (3) tropomyosin. Actin though is the main protein component of the thin filament.
What are thin filaments called?
major reference. In muscle: Thin filament proteins. The thin filaments contain three different proteins—actin, tropomyosin, and troponin.
Is myosin A thin filament?
Most of the cytoplasm consists of myofibrils, which are cylindrical bundles of two types of filaments: thick filaments of myosin (about 15 nm in diameter) and thin filaments of actin (about 7 nm in diameter).
What is the difference between Thick Filament and Thin Filament?
3. It is bisected by a proteinaceous line called M-line. Thin Filament: 1. It is made up of proteins – actin, tropomyosin and troponin. 2. It lies both in A and I band.
Thin filament Definition & Meaning | Merriam-Webster Medical
The meaning of THIN FILAMENT is a myofilament of the one of the two types making up myofibrils that is about 5 nanometers (50 angstroms) in width and is composed chiefly of the protein actin.
Thin filament | definition of thin filament by Medical dictionary
thin filament: one of the contractile elements in muscular fibers and other cells; in skeletal muscle, the actin filaments are about 7.5 nm wide and 1 mcm long, and attach to the transverse Z filaments. Synonym(s): thin filament
What are the components of the thin filaments of a muscle cell?
Actin, Tropomyosin and troponin. Thin filament which is 7-8nm" in diameter is one of the two filaments vital for muscular contractions. It is composed of three proteins that are: Actin to The thin filaments are composed chiefly of actin proteins. That's why these filaments are also called as actin filaments. The actin molecules are arranged in to chains. This chains twist around each other ...
The thin filaments of smooth muscles - PubMed
Contraction in vertebrate smooth and striated muscles results from the interaction of the actin filaments with crossbridges arising from the myosin filaments. The functions of the actin based thin filaments are (1) interaction with myosin to produce force; (2) regulation of force generation in respo …
What are thin filaments made of?
Thin filaments are made up of two helically arranged filamentous polymers of the protein actin together with a long filamentous protein tropomyosin that lies in the grooves of the helix as well as an associated globular protein troponin, found at intervals along the filament. From: Encyclopedia of the Neurological Sciences (Second Edition), 2014.
What are the proteins that make up the thin filaments of myosin?
Thin filaments are a polymer of actin with tightly bound regulatory proteins troponin and tropomyosin ( Fig. 39.4 ). When the cytoplasmic Ca 2+ concentration is low, troponin and tropomyosin inhibit the actin-activated adenosine triphosphatase (ATPase) of myosin. Tropomyosin, a 40-nm long coiled-coil of two α-helical polypeptides (see Fig. 3.10 ), binds laterally to seven contiguous actin subunits as well as head to tail to neighboring tropomyosins, forming a continuous strand along the whole thin filament. Troponin (TN) consists of three different subunits called TNC, TNI, and TNT (see Table 39.1 ). TNT anchors one troponin complex to each tropomyosin coiled-coil. TNC is a dumbbell-shaped protein with four EF-hand motifs to bind divalent cations similar to calmodulin (see Fig. 3.12 and Chapter 26 ). In resting muscle, the C-terminal globular domain of TNC binds two Mg 2+ ions and an α-helix of TNI, while the low-affinity sites in the N-terminal globular domain of TNC are empty. Ca 2+ binding to the low-affinity sites (two in fast skeletal muscle; one in slow muscle) during muscle activation exposes a new binding site for TNI. The resulting conformational change in TNI allows tropomyosin to move away from the myosin-binding sites on the actin filament.
What is the globular core domain of tropomyosin?
Troponin has a long tail and a globular core domain containing the calcium binding subunit troponin C (TnC), part of the inhibitory domain (TnI), and part of the tropomyosin binding domain (TnT). The structure of the core domain has been determined at high resolution, 20,21 but its orientation on the thin filament remains controversial and the detailed interactions between the protein components that are responsible for calcium regulation have not been fully characterized. It is clear, however, both from electron microscopy studies of isolated filaments and X-ray studies of muscle, that binding of Ca 2+ ions to TnC leads to motion of tropomyosin towards the center of the groove between the two strands of the actin in the thin filament. 22–24 This azimuthal motion of tropomyosin uncovers the binding site for myosin on actin, enabling the interaction between those two proteins that drives muscle contraction. This general scheme is often referred to as the steric blocking model of muscle regulation. A detailed description of thin filament structure and the molecular mechanisms that regulate its interaction with myosin is presented in Chapter 4.13.
What are the properties of actin?
Actin has three particularly important properties: (i) the ability to polymerize to form long filaments (conversion of monomeric G-actin to polymeric F-actin ), (ii) the ability to bind myosin and activate its MgATPase activity, and (iii) the ability to bind tropomyosin and regulatory proteins. G-actin binds 1 mol of ATP/mol, which is hydrolyzed as the G-actin polymerizes to form F-actin. Actin also contains 1 mol of bound divalent cation/mol, probably Mg 2+ in vivo.
How does thin filament regulation work?
Thin filament regulation occurs by modulating the access to the myosin binding actin domains and myosin ATPase inhibition by actin-associated proteins. The phosphorylation of the low molecular heat shock proteins HSP27 and HSP20 plays an important role in modulating contraction and relaxation. Under relaxed conditions the myosin binding domains on actin filaments are blocked. Upon stimulation by a contractile agonist, the tertiary associations of actin binding proteins with actin filaments are disrupted by Ca2+ /CaM binding and by PKCα and Ca 2+ /CaM-dependent protein kinase phosphorylation. Myosin heads can now bind actin and myosin ATPase activation results in cross-bridge cycling and smooth muscle contraction.
What is the protein meshwork in the Z disk?
A protein meshwork in the Z disk anchors the barbed end of each thin filament ( Fig. 39.5 ). Some crosslinks between actin filaments consist of α-actinin, a short rod with actin-binding sites on each end (see Fig. 33.17 ). At least a half dozen structural proteins stabilize the Z disk through interactions with α-actinin, actin, and titin. Some of these proteins also have signaling functions.
How many tropomyosin molecules are in a 38 nm repeat?
Tropomyosin is almost entirely α-helical coiled coil, and binds in the groove between the two actin strands of the thin filament, so that there are two tropomyosin molecules in every 38-nm repeat of the filament. Sign in to download full-size image. Figure 3.
What is the thin filament?
Thin filament which is 7 −8nm in diameter is one of the two filaments vital for muscular contractions. It is composed of three proteins that are: Actin → The thin filaments are composed chiefly of actin proteins. That's why these filaments are also called as actin filaments. The actin molecules are arranged in to chains.
What are the filaments of actin called?
That's why these filaments are also called as actin filaments . The actin molecules are arranged in to chains. This chains twist around each other like twisted double strand of pearls. Tropomyosin → Two strands of another protein twist around actin, This protein is tropomyosin.
What are thin filaments made of?
Thin filaments are made up of two helically arranged filamentous polymers of the protein actin together with a long filamentous protein tropomyosin that lies in the grooves of the helix as well as an associated globular protein troponin, found at intervals along the filament. From: Encyclopedia of the Neurological Sciences (Second Edition), 2014.
What are the proteins that make up the thin filaments of myosin?
Thin filaments are a polymer of actin with tightly bound regulatory proteins troponin and tropomyosin ( Fig. 39.4 ). When the cytoplasmic Ca 2+ concentration is low, troponin and tropomyosin inhibit the actin-activated adenosine triphosphatase (ATPase) of myosin. Tropomyosin, a 40-nm long coiled-coil of two α-helical polypeptides (see Fig. 3.10 ), binds laterally to seven contiguous actin subunits as well as head to tail to neighboring tropomyosins, forming a continuous strand along the whole thin filament. Troponin (TN) consists of three different subunits called TNC, TNI, and TNT (see Table 39.1 ). TNT anchors one troponin complex to each tropomyosin coiled-coil. TNC is a dumbbell-shaped protein with four EF-hand motifs to bind divalent cations similar to calmodulin (see Fig. 3.12 and Chapter 26 ). In resting muscle, the C-terminal globular domain of TNC binds two Mg 2+ ions and an α-helix of TNI, while the low-affinity sites in the N-terminal globular domain of TNC are empty. Ca 2+ binding to the low-affinity sites (two in fast skeletal muscle; one in slow muscle) during muscle activation exposes a new binding site for TNI. The resulting conformational change in TNI allows tropomyosin to move away from the myosin-binding sites on the actin filament.
What is the globular core domain of tropomyosin?
Troponin has a long tail and a globular core domain containing the calcium binding subunit troponin C (TnC), part of the inhibitory domain (TnI), and part of the tropomyosin binding domain (TnT). The structure of the core domain has been determined at high resolution, 20,21 but its orientation on the thin filament remains controversial and the detailed interactions between the protein components that are responsible for calcium regulation have not been fully characterized. It is clear, however, both from electron microscopy studies of isolated filaments and X-ray studies of muscle, that binding of Ca 2+ ions to TnC leads to motion of tropomyosin towards the center of the groove between the two strands of the actin in the thin filament. 22–24 This azimuthal motion of tropomyosin uncovers the binding site for myosin on actin, enabling the interaction between those two proteins that drives muscle contraction. This general scheme is often referred to as the steric blocking model of muscle regulation. A detailed description of thin filament structure and the molecular mechanisms that regulate its interaction with myosin is presented in Chapter 4.13.
What are the properties of actin?
Actin has three particularly important properties: (i) the ability to polymerize to form long filaments (conversion of monomeric G-actin to polymeric F-actin ), (ii) the ability to bind myosin and activate its MgATPase activity, and (iii) the ability to bind tropomyosin and regulatory proteins. G-actin binds 1 mol of ATP/mol, which is hydrolyzed as the G-actin polymerizes to form F-actin. Actin also contains 1 mol of bound divalent cation/mol, probably Mg 2+ in vivo.
How does thin filament regulation work?
Thin filament regulation occurs by modulating the access to the myosin binding actin domains and myosin ATPase inhibition by actin-associated proteins. The phosphorylation of the low molecular heat shock proteins HSP27 and HSP20 plays an important role in modulating contraction and relaxation. Under relaxed conditions the myosin binding domains on actin filaments are blocked. Upon stimulation by a contractile agonist, the tertiary associations of actin binding proteins with actin filaments are disrupted by Ca2+ /CaM binding and by PKCα and Ca 2+ /CaM-dependent protein kinase phosphorylation. Myosin heads can now bind actin and myosin ATPase activation results in cross-bridge cycling and smooth muscle contraction.
What is the protein meshwork in the Z disk?
A protein meshwork in the Z disk anchors the barbed end of each thin filament ( Fig. 39.5 ). Some crosslinks between actin filaments consist of α-actinin, a short rod with actin-binding sites on each end (see Fig. 33.17 ). At least a half dozen structural proteins stabilize the Z disk through interactions with α-actinin, actin, and titin. Some of these proteins also have signaling functions.
How many tropomyosin molecules are in a 38 nm repeat?
Tropomyosin is almost entirely α-helical coiled coil, and binds in the groove between the two actin strands of the thin filament, so that there are two tropomyosin molecules in every 38-nm repeat of the filament. Sign in to download full-size image. Figure 3.
