
How did Enron misrepresent itself financially?
How did Enron misrepresent itself financially? Basically, they used "Special Purpose Entities" (SPEs) to improve the public's perception of their financial statements. An SPE allows the company to "boost" their performance by hiding certain losses and liabilities on the SPEs balance sheets and income statements, which Enron then did not have to report.
What Enron did wrong?
Top officials at Enron abused their power and privileges, manipulated information, engaged in inconsistent treatment of internal and external constituencies, put their own interests above those of their employees and the public, and failed to exercise proper oversight or shoulder responsibility for ethical failings.
What did Enron do illegally?
What did Enron do illegally? Enron executives used fraudulent accounting practices to inflate the company’s earnings and hide its debt to its subsidiaries. The SEC, rating agencies, and investment banks have also been accused of negligence, and in some cases outright fraud, making the fraud possible. Who was responsible for Enron’s demise?
What did Enron actually do?
What did the Enron company do? Enron was an energy-trading and utilities company based in Houston, Texas, that perpetrated one of the biggest accounting frauds in history. Enron's executives employed accounting practices that falsely inflated the company's revenues and, for a time, made it the seventh-largest corporation in the United States.
See more
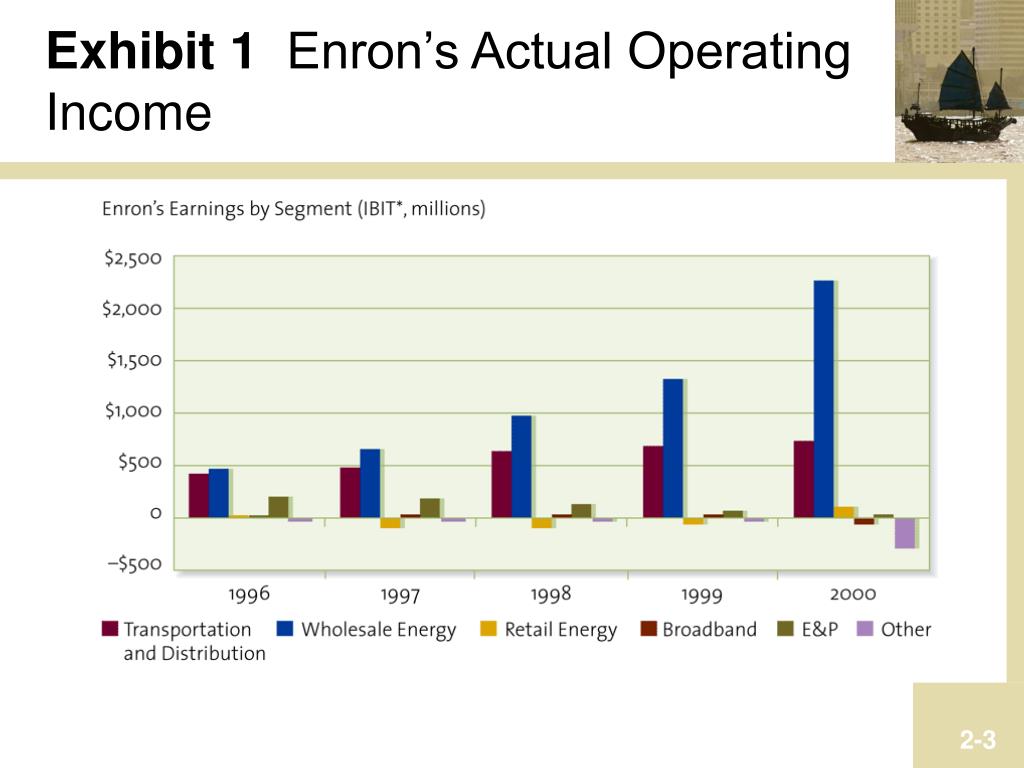
What accounting firm did Enron take down?
Arthur AndersenEnron and the Fall of Arthur Andersen Enron's fall 2001 collapse wound up taking down the accounting firm Arthur Andersen, too. The firm was indicted for having approved Enron's books, and went out of business. Critics say the government should have indicted responsible individuals, rather than the entire firm.
Who was affected by the Enron scandal?
Further, thousands and thousands of workers have lost their jobs. Some 4,000 Enron employees were let go after the company declared bankruptcy. The AFL-CIO estimates that 28,500 workers have lost their jobs from Enron, WorldCom and accounting firm Arthur Andersen alone.
What happened to Arthur Andersen accounting?
CHICAGO, Aug, 31, 2002 — -- After 89 years in business, Arthur Andersen LLP on Saturday ended its role as auditor of public companies. The Chicago-based company was convicted in June of obstruction of justice for shredding and doctoring documents related to Enron audits.
What happened between Enron and Arthur Andersen?
The controversy extended to Arthur Andersen, which was accused of overlooking significant sums of money that had not been represented on Enron's books. Arthur Andersen was later found guilty on federal charges that it obstructed justice by destroying thousands of documents related to Enron.
Who went to jail Enron?
Jeffrey Keith Skilling (born November 25, 1953) is a convicted American felon best known as the CEO of Enron Corporation during the Enron scandal. In 2006, he was convicted of federal felony charges relating to Enron's collapse and eventually sentenced to 24 years in prison.
What ruined Enron reputation?
Many went sour in the early months of 2001 as Enron's stock price and debt rating imploded because of loss of investor and creditor trust. Methods the company used to disclose (or creatively obscure) its complicated financial dealings were erroneous and, in the view of some, downright deceptive.
Who were the original Big 6 accounting firms?
There is a brief overview in the prologue about how mergers led to the emergence of the Big Six – Arthur Andersen, Coopers & Lybrand, Deloitte & Touche, Ernst & Young, KPMG Peat Marwick, and Price Waterhouse.
What is the Big 5 accounting firms?
Big FiveArthur Andersen.Deloitte & Touche.Ernst & Young.KPMG.PricewaterhouseCoopers.
What caused Arthur Andersen failure?
Enron Corporation is an American Energy Company based in Houston, Texas whereas Arthur Andersen was then one of the five largest audit and accountancy partnerships in the world, based in Chicago. The scandal happened as a result of accounting and auditing irregularities leading to a loss of $74 billion.
What happened to the Big 5 accounting firms?
The big 5 accounting firms were the largest accounting firms in the world until 2002. They were formed from the big eight accounting firms. They were formed from many smaller member firms and would later go on to create the big 4 firms. They ceased being the 8 biggest accounting firms in the world in 1989.
Who was the whistleblower in Enron?
Sherron Watkins'Justice was served': Enron whistleblower reflects on 20th anniversary of company's collapse. Sherron Watkins was an Enron VP when she warned boss Ken Lay of an impending "implosion." HOUSTON, Texas — Enron's energy empire crumbled exactly 20 years ago in gleaming downtown towers that now house Chevron.
Did Enron pay off Arthur Andersen?
Enron paid Andersen $27 million for nonaudit services, including tax and consulting work, compared with $25 million for audit services, making Enron one of its biggest clients. "We would marvel at the amounts of money we were spending" with Andersen, says a former Enron analyst, whose job was to streamline costs.
What were the consequences of the Enron scandal?
What effects did the Enron scandal have? The Enron scandal resulted in a wave of new regulations and legislation designed to increase the accuracy of financial reporting for publicly traded companies. The Sarbanes-Oxley Act (2002) imposed harsh penalties for destroying, altering, or fabricating financial records.
How did Enron affect the business world?
That was a watershed for the U.S. public.” The company's collapse sent ripples through the financial system, with the government introducing a set of stringent regulations for auditors, accountants and senior executives, huge requirements for record keeping, and criminal penalties for securities laws violations.
What did Enron do that was unethical?
Enron faced an ethical accounting scandal in 2001 after using “mark-to-market” accounting to fake their profits and misused special purpose entities, or SPEs. Enron worked to make their losses seem less than they actually were, and “cooked the books” to make their income look much higher than it was.
What was the main reason of Enron's failure?
Overall, poor corporate governance and a dishonest culture that nurtured serious conflicts of interests and unethical behaviour in Enron are identified as significant findings in this paper.
When did Enron file for bankruptcy?
On December 2, 2001, Enron filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy protection. Many Enron executives were indicted on a variety of charges and were later sentenced to prison. Arthur Andersen came under intense scrutiny and eventually lost a majority of its clients.
Who is the chief financial officer of Enron?
One of his brightest recruits was Andrew Fastow, who quickly rose through the ranks to become Enron’s chief financial officer. Fastow oversaw the financing of the company through investments in increasingly complex instruments, while Skilling oversaw the building of its vast trading operation.
What is the Enron scandal?
Enron scandal. Former Enron employees sitting with their belongings after layoffs by the bankrupt energy-trading company. David J. Phillip/AP. Enron was founded in 1985 by Kenneth Lay in the merger of two natural-gas -transmission companies, Houston Natural Gas Corporation and InterNorth, Inc.; the merged company, HNG InterNorth, ...
What did Enron do under Skilling?
Under Skilling’s leadership, Enron soon dominated the market for natural-gas contracts, and the company started to generate huge profits on its trades. Skilling also gradually changed the culture of the company to emphasize aggressive trading.
What was the damage to Enron's reputation?
The damage to its reputation was so severe that it was forced to dissolve itself. In addition to federal lawsuits, hundreds of civil suits were filed by shareholders against both Enron and Andersen. Joseph Berardino, then CEO of Arthur Andersen, testifying during a congressional hearing on the Enron scandal, 2002.
Who was the CEO of Arthur Andersen?
Joseph Berardino, then CEO of Arthur Andersen, testifying during a congressional hearing on the Enron scandal, 2002. Scott J. Ferrell/Congressional Quarterly/Alamy. The scandal resulted in a wave of new regulations and legislation designed to increase the accuracy of financial reporting for publicly traded companies.
When did Enron go bankrupt?
At Enron's peak, its shares were worth $90.75; just prior to declaring bankruptcy on Dec. 2, 2001, they were trading at $0.26. 1. To this day, many wonder how such a powerful business, at the time one of the largest companies in the United States, disintegrated almost overnight.
How Did Enron Hide Its Debt?
Fastow and others at Enron orchestrated a scheme to use off-balance-sheet special purpose vehicles (SPVs), also known as special purposes entities (SPEs ), to hide its mountains of debt and toxic assets from investors and creditors. 2 The primary aim of these SPVs was to hide accounting realities rather than operating results.
What is an Enron to SPV transaction?
The standard Enron-to-SPV transaction would be the following: Enron would transfer some of its rapidly rising stock to the SPV in exchange for cash or a note. The SPV would subsequently use the stock to hedge an asset listed on Enron's balance sheet. In turn, Enron would guarantee the SPV's value to reduce apparent counterparty risk.
How does Enron write off its assets?
In Enron's case, the company would build an asset, such as a power plant, and immediately claim the projected profit on its books, even though the company had not made one dime from the asset. If the revenue from the power plant was less than the projected amount, instead of taking the loss, the company would then transfer the asset to an off-the-books corporation where the loss would go unreported. This type of accounting enabled Enron to write off unprofitable activities without hurting its bottom line.
What was the Enron trading business in 2000?
CEO Jeffrey Skilling hid the financial losses of the trading business and other operations of the company using mark-to-market accounting. 10 This technique measures the value of a security based on its current market value instead of its book value. This can work well when trading securities, but it can be disastrous for actual businesses.
How much debt did Enron have in 2000?
Enron had losses of $591 million and had $690 million in debt by the end of 2000. The final blow was dealt when Dynegy (NYSE: DYN), a company that had previously announced it would merge with Enron, backed out of the deal on Nov. 28. By Dec. 2, 2001, Enron had filed for bankruptcy. 16 .
What is the story of Enron 2021?
Updated Jun 1, 2021. The story of Enron Corporation depicts a company that reached dramatic heights only to face a dizzying fall. The fated company's collapse affected thousands of employees and shook Wall Street to its core.
What happened to Enron?
Energy-trading company Enron collapsed after a major accounting fraud scheme was revealed in 2001. In October of that year, the company admitted that it had overstated earnings dating back to 1997. In December, after being investigated by the Securities and Exchange Commission, it filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy protection. Enron’s bankruptcy filing was the largest in U.S. history at the time, CNN reported. In 2008, a class-action lawsuit filed by shareholders and investors was settled in federal court, and it was ruled that the banks involved in the accounting fraud scheme would have to pay out $7.2 billion.
When did Enron declare bankruptcy?
When energy-trading company Enron declared bankruptcy in 2001, it was the largest bankruptcy filing in U.S. history. The company’s demise was tinged with scandal, as it was revealed that Enron execs were pocketing millions while knowingly overstating the company’s earnings to shareholders through fraudulent accounting.
How did Madoff's Ponzi scheme work?
The way his Ponzi scheme worked is that he would use funds from new investors to pay off promised returns to older investors. But when clients requested $7 billion in returns, Madoff only had about $200 million to $300 million in the fund, Business Insider reported. Madoff was ultimately charged with 11 counts of fraud, money laundering, perjury and theft and sentenced to 150 years in prison.
What happened to Texaco in the 1980s?
In the 1980s, oil giant Texaco got hit with a giant civil lawsuit by Pennzoil for interfering in the latter company’s imminent acquisition of the Getty Oil Company. The court ruled that Pennzoil was owed punitive damages of $10.5 billion (though Texaco ended up paying only $3 billion). In 1987, Texaco filed for bankruptcy protection. Roughly a year later, the company was acquired by Chevron.
How much money did Israel drain from Bayou?
Then, in 2004, Israel drained Bayou’s accounts of $161 million over the course of six days and wired the money to different banks in an attempt to hide the stolen funds from authorities. An SEC suit filed in 2005 alleged that over the course of the fund’s existence, Israel and his CFO had misappropriated millions of dollars for their personal use, CNN reported. Israel pleaded guilty to fraud in 2005 and Bayou filed for bankruptcy the following year.
When did GM shut down the Hummer?
Inspired by the Humvee military vehicle, Hummers had a cult following of off-road vehicle lovers before GM shut the brand down in 2010. The gas-guzzling vehicles were always shunned by environmentalists, but even fans of the car stopped buying them when gas prices rose above $4 a gallon in 2008. Sales of the Hummer dropped from 27,000 vehicles in 2008 to just 9,000 in 2009, CBS News reported. GM discontinued the brand after a deal to sell it to a Chinese company fell through.
When did Woolworths close?
stores for good in 1997. The company’s department stores had been moving from stand-alone stores to malls, but the setup costs were higher than what the stores were making in returns, according to The Woolworths Museum. Fortunately, the F.W. Woolworth Company spent much of the ’60s, ’70s and ’80s buying out specialty stores, including Foot Locker, so the company continues to live on through its other properties.
When did Enron go bankrupt?
In November 2001, the business for the first time admitted and made the revelation that it inflated its income levels by $586 million. Also that it has been doing so since 1997. On 2 nd December 2001, the business files for bankruptcy and the stock prices end up flat at $0.26 per share.
When did Enron become a company?
The year was 1985 , and Enron was incorporated as the merger of Houston Natural Gas company and Internorth Ince. In 1995, the business was recognized as the most innovative business by the Fortune, and it made it successful run for the next six years.
Why is the Enron Scandal Important?
The Enron scandal is significant in terms of learning perspectives for both new financial professionals and experienced professionals. The scandal tells us why strong corporate governance is the key to success for any business to sustain and drive profitable business. Additionally, it draws insights as to how accounting policies should not be used and applied. Any misuse can have drastic results or impacts on the health of the business.
What is the Enron scandal?
The Enron Scandal involves Enron duping the regulators by resorting to off-the-books accounting practices and incorporating fake holding. The company utilized special purpose vehicles to hide its toxic assets and big amounts of debts from the investors and creditors.
What was the Enron Corporation?
Conclusion. The Enron corporation was formed as the merger of Houston’s natural gas company and inter-north incorporation. After the merger, it grew rapidly and was regarded as the most innovative company. However, it resorted to bad accounting practices.
When was Enron formed?
The year was 1985 , and Enron was incorporated as the merger of Houston Natural Gas company and Internorth Ince. In 1995, the business was recognized as the most innovative business by the Fortune, and it made it successful run for the next six years. In 1998, Andrew Fastow became the CFO of the business, and the CFO created SPVs to conceal the financial losses of the Enron. During the period of 2000, the shares of Enron traded at the price levels of $90.56.
What happens if Enron is compromised?
If the corporation was compromised, then the special economic entities won’t be able to hedge the deteriorating market price of such stocks. Additionally, the Enron corporation had held significant conflicts of interest with respect to the special purpose vehicles.
What was the Enron bankruptcy?
The bankruptcy of Enron was among the largest corporate bankruptcy in U.S. history. Another interesting aspect of the Enron scandal was its pervasiveness. The Enron scandal involved corruption at multiple levels, both inside and outside the company. Enron’s law firm was guilty of unethical behavior, as was Arthur Andersen, Enron’s accounting firm. ...
How did Enron's stock price fall?
When Enron executives were unable to provide satisfactory answers regarding the company’s finances and overall performance, Enron’s downward spiral commenced. Ultimately, Enron’s deceptive practices were brought to light and its stock price began to decline. The true financial picture of the company emerged, and it was far less bright than it had been portrayed to be. Enron’s stock price plummeted in record time. Enron’s top executives sold off more than $1 billion in stock prior to the price decline. Arthur Andersen shred tons and tons of documents as Enron was unraveling. These documents presumably would have provided evidence for Arthur Andersen’s collusion in Enron’s unethical activities.
How did Enron use mark to market?
Enron misused mark-to-market by deliberately misrepresenting the value of certain assets. For instance, Enron would list the value of a business deal at the time of its signing based on projected future profits. And in some cases, Enron continued to list the value of the deal even after the deal collapsed and failed to yield any profits. This led to Enron reporting a highly inaccurate financial picture of itself to the outside world. In many cases, this was done intentionally by Enron executives to manipulate the company’s stock price.
What was the most disastrous scandal in the history of corporate America?
For one, the fall of Enron was one of the most disastrous scandals in the history of corporate America. When the dust settled, thousands and thousands of employees had lost their jobs, pensions, and, in some cases, their professional reputations. The bankruptcy of Enron was among the largest corporate bankruptcy in U.S. history.
What is the purpose of Enron?
Enron’s main purpose behind these transactions was solely to hide debts and losses.
What was Enron's main purpose behind these transactions?
Enron’s main purpose behind these transactions was solely to hide debts and losses. This deceptive and unethical behavior came to the foreground when Enron’s executives faced prosecution following the company’s collapse.
Why do companies use different accounting methods?
Different companies use different accounting methods to keep track of their assets, liabilities and overall financial condition. Sometimes, a company prefers a particular method because of its industry.
Why did Enron fail?
The particular causes of Enron’s failure are complex. At one time Enron appears to have been a successful and innovative enterprise, principally engaged in trading and dealing in energy-related contracts. At some point it expanded by making substantial investments in a variety of large-scale projects. Although some of these were initially successful, others resulted in Enron incurring large economic losses. Then it appears to have embarked on covering up losses and manufacturing earnings. This succeeded for a time, but was ultimately unsustainable. These efforts allowed Enron to disguise the losses and not report debt for which it was contingently (and later actually) liable. They also apparently afforded certain Enron managers the opportunity of extracting personal gains at the expense of Enron’s stockholders.
What lesson should not be drawn from Enron?
One lesson that should not be drawn is that firms should be prevented from taking risks or incurring failure. That is an essential part of any competitive economy. The fact that Enron failed is not, by itself, a matter of concern.
What is the new administrative organization that would be charged with disciplining CPAs?
This oversight body, termed a “Public Regulatory Organization” (PRO) in a bill introduced by Representatives Oxley and Baker, would have the authority and responsibility to discipline CPAs who sign the financial statements of publicly traded corporations. Presumably, it would do its job better than the SEC, the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA), or state boards of accountancy that issue and can revoke CPA certificates, because at least two-thirds of the proposed PRO’s members would not be CPAs. Errant CPAs, indeed, might need more effective discipline and ought to pay a greater price than at present for permitting clients to deceive investors. However, we observe that the SEC, which has had the power to discipline CPAs who attest statements of registrants for a very long time, presumably is an organization independent of CPAs. Hence, we question the value of a new administrative agency that would do what the SEC can do now.
What is the first question about accounting standards?
The first question is whether the accounting standards (including disclosure) and auditing procedures were so deficient and misleading that informed decisions could not be made effectively and the losses incurred were magnified. In particular, the treatment of transactions with Special Purpose Entities sponsored by Enron, which were thinly capitalized (3% of assets) and involved severe conflicts of interest, has been widely criticized. At present, we do not know enough to determine the extent to which the problem is one of inadequate accounting standards or deficient application of the standards by Andersen. This clearly should be a focus of continued investigation.
Who was the auditor for Enron?
Long before federal prosecutors brought charges against Ken Lay and Jeffrey Skilling, they went after Enron's auditor, the Arthur Andersen Company. Andersen's partner in charge of the Enron account had ordered the wholesale shredding of Enron-related documents in the fall of 2001.
What happened to Enron and Arthur Andersen?
Enron and the Fall of Arthur Andersen. Enron's fall 2001 collapse wound up taking down the accounting firm Arthur Andersen, too . The firm was indicted for having approved Enron's books, and went out of business. Critics say the government should have indicted responsible individuals, rather than the entire firm.
What is Jeffrey Skilling convicted of?
Kenneth Lay, Jeffrey Skilling are convicted of fraud and conspiracy related to the firm's collapse.
Did Andersen fire the partner?
Andersen fired the partner, but that didn't stop then Deputy Attorney General Larry Thompson from seeking an indictment against the firm itself. Mr. LARRY THOMPSON (Former Deputy Attorney General): The indictment alleges that Andersen partners and others personally directed these efforts to destroy evidence.
Who is Larry Thompson?
Mr. LARRY THOMPSON (Former Deputy Attorney General): The indictment alleges that Andersen partners and others personally directed these efforts to destroy evidence.
Who makes NPR transcripts?
NPR transcripts are created on a rush deadline by Verb8tm, Inc. , an NPR contractor, and produced using a proprietary transcription process developed with NPR. This text may not be in its final form and may be updated or revised in the future. Accuracy and availability may vary.
Did Arthur Andersen get the death penalty?
The high court ruling came too late to save Andersen, which had shrunk from 28,000 employees to just 200. While Enron's top executives now face prison time, Arthur Andersen got the death sentence.
What went wrong with Enron?
What Really Went Wrong with Enron? On March 5, 2002, the Markkula Center for Applied Ethics convened a panel of four Santa Clara University business ethicists to discuss the Enron scandal. Panelists included Kirk O. Hanson, executive director of the Ethics Center and University Professor of Organizations and Society; Manuel Velasquez, ...
What are the causes of the Enron scandal?
I think that one of the obvious systemic causes of the Enron scandal is our legal and regulatory structure . First, current laws and SEC regulations allow firms like Arthur Andersen to provide consulting services to a company and then turn around and provide the audited report about the financial results of these consulting activities. This is an obvious conflict of interest that is built into our legal structure.
How long was the Enron board meeting in 1991?
Sloth: One of the most critical board meetings at Enron in 1991-where they were giving approval to set aside their ethics statements on behalf of these shenanigans with partnerships-that meeting lasted one hour. That's barely enough time to get a Coke.
How much did Fastow sell Enron?
Avarice: Fastow, the CFO, sold $36 million of his Enron investments before the company tanked. Lay had a whole bunch of sweetheart deals with family members. I'm sure tempted to call that greed….
When did Enron resign?
One of my friends, a former executive at Enron who resigned in 2000, described what the recruiting process was like…. They recruited just at the major business schools. They wined and dined the prospects. They promised them huge bonuses and fed those young egos as much as they would take.
Can Enron manage their own pension?
Third, most large companies like Enron are allowed to manage their own employee pension funds. Again, this is a conflict of interest built into our legal system because the company has an incentive to use these funds in ways that advantage the company even when they may disadvantage employees.
Does Enron pay its own auditors?
Second, a private company like Enron currently hires and pays its own auditors. This again is a conflict of interest built into our legal system because the auditor has an incentive not to issue an unfavorable report on the company that is paying him or her.
