What allowed you to measure the amount of catalase activity?
what allowed you to measure the amount of catalase activity? the bubble height reaction the reaction rate would, ,if another substance competed with catalase for the active site.
What does catalase do in the body?
What Is the Role of Catalase?
- Cellular function. Oxygen is crucial to life; however, when we use oxygen our bodies constantly produce free radicals. ...
- Catalase test. Catalase test is extensively used by microbiologists in the laboratory to recognize and differentiate between bacterial species.
- Grey hair. ...
- Food industry. ...
- Cleaning agent. ...
What are the benefits of catalase?
The Health Benefits of Catalase
- Powerful Antioxidant Support. Catalases are perhaps the single most efficient enzymes found in the cells of the human body. ...
- Possible Anti-Aging and Anti-Degenerative Effects. Catalase is currently being studied for its applications on extending lifespan and vitality. ...
- Promotes Longevity
- Fat Reduction. ...
- Supports DNA Integrity. ...
What is the function of catalase in the human body?
What is the function of catalase in the human body? Catalase is one of the most important antioxidant enzymes. As it decomposes hydrogen peroxide to innocuous products such as water and oxygen, catalase is used against numerous oxidative stress-related diseases as a therapeutic agent.

What are the 4 factors that affect enzyme activity?
Several factors affect the rate at which enzymatic reactions proceed - temperature, pH, enzyme concentration, substrate concentration, and the presence of any inhibitors or activators.
What are the 7 factors that affect enzyme action?
Table of ContentsFactor # 1. Temperature:Factor # 2. Hydrogen Ion Concentration (pH):Factor # 3. Water:Factor # 4. Concentration of the Substrate:Factor # 5. Enzyme Concentration:Factor # 6. Inhibitors:Factor # 7. Accumulation of End-Products:
What inhibits catalase activity?
IT is well known that the activity of catalase is greatly inhibited by very small concentrations of potassium cyanide, hydrogen sulphide and especially hydroxylamine.
What 6 factors affect enzyme activity?
The six factors are: (1) Concentration of Enzyme (2) Concentration of Substrate (3) Effect of Temperature (4) Effect of pH (5) Effect of Product Concentration and (6) Effect of Activators.
What factors affect catalysis?
Factors that disrupt protein structure include temperature and pH; factors that affect catalysts in general include reactant or substrate concentration and catalyst or enzyme concentration.
How did temperature affect catalase activity?
Temperature has an effect on both the structure of the catalase itself and the hydrogen bonds it is designed to cleave. As the temperature increases toward the optimum point, hydrogen bonds loosen, making it easier for catalase to act on hydrogen peroxide molecules.
Does vitamin C inhibit catalase?
The new study shows that an enzyme called catalase is the central route for removing hydrogen peroxide generated by decomposing vitamin C. The researchers discovered that cells with lower amounts of catalase activity were more susceptible to damage and death when they were exposed to high amounts of vitamin C.
How does alcohol affect catalase activity?
Interestingly catalase activity increases in lower concentration of ethanol exposure, and decreased in higher concentration. Superoxide dismutase activity was also increased on ethanol exposure.
Does alcohol inhibit catalase?
Catalase (fungal source) was found to be essentially completely inhibited by wine concentrations of ethanol. The inhibition is noncompetitive and apparently involves the binding of the ethanol with the enzyme in the compound I form, thereby inhibiting the catalatic reaction.
Why does pH affect enzyme activity?
The effect of pH Within the enzyme molecule, positively and negatively charged amino acids will attract. This contributes to the folding of the enzyme molecule, its shape, and the shape of the active site. Changing the pH will affect the charges on the amino acid molecules.
What factors affect enzyme activity quizlet?
Terms in this set (6)Temperature. As temperature increases, the reaction rate increases, but if the temperature passes the optimal range, the enzyme will stop functioning.pH. Each enzyme has a specific pH. ... Enzyme Concentration. ... Substrate Concentration. ... Presence of Inhibitors. ... Presence of Activators.
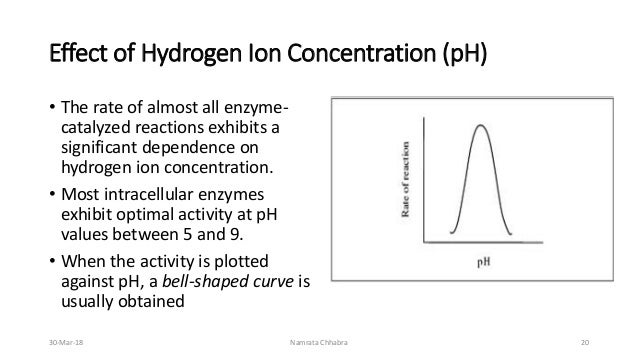
What is the effect of pH on enzyme activity?
Enzyme activity is at its maximum value at the optimum pH. As the pH value is increased above or decreased below the optimum pH the enzyme activity decreases.
What factors affect enzyme activity quizlet?
Terms in this set (6)Temperature. As temperature increases, the reaction rate increases, but if the temperature passes the optimal range, the enzyme will stop functioning.pH. Each enzyme has a specific pH. ... Enzyme Concentration. ... Substrate Concentration. ... Presence of Inhibitors. ... Presence of Activators.
What are the factors affecting enzyme activity Class 11?
Enzyme activity is affected by factors such as temperature, pH, the concentration of substrates, presence of inhibitors, allosteric regulators, etc.
What are the factors affecting the rate of enzyme reaction?
Some of the factors affecting the enzyme activity are pH, temperature, the concentration of enzymes, the concentration of substrate. Provision of a specific pH range, the optimum temperature is important for enzyme activity, else it can lose its ability to bind to a substrate.
What are the 3 types of enzyme inhibitors?
There are three basic types of enzyme inhibition: competitive, noncompetitive, and uncompetitive.
What happens when the temperature of catalase is low?
If the temperature is low, then this can result in there being insufficient thermal energy to meet the activation energy of the reaction – the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide by catalase. If the temperature is increased then the higher kinetic energy will result in more successful collisions between catalase enzymes and hydrogen peroxide substrates. At the optimal temperature – which is 37°C for catalase, then the rate of enzyme activity will be at its peak. Both high and low temperatures (approximately 10°C either side of the optimum) will cause enzyme stability to decrease – since the change in thermal energy will disrupt the hydrogen bonds within the enzyme. This can cause denaturation, following the loss of shape of the active site.
What pH is the best for catalase?
The prediction made at the start of the experiment was that the optimum pH for catalase activity was to be somewhere between pH 6 and 8. In the context of the experiment the prediction was that between pH 6 and 8, the time taken for the paper disc to rise would be lowest on average (due to faster H 2 O 2 decomposition). At extremely high pH levels, the charge of the enzyme will be altered. This changes protein solubility and overall shape. This change in shape of the active site diminishes its ability to bind to the substrate, thus annulling the function of the enzyme (catalase in this case). This process of denaturing only occurs when the enzyme is operating in an environment outside of its optimum range. It is hypothesised that the optimum range for catalase in this IA is between pH 6 and pH 8.
How to remove catalase from a disc?
Remove and shake off any clearly excess catalase solution from the disc. Drop the disc into the beaker of hydrogen peroxide from the consistent height of the top of the beaker, and start the stopwatch as soon as the disc hits the surface of the solution for the first time.
How much catalase to put in a beaker?
Pour 50ml of catalase solution at 0.1% concentration into a large beaker – for dipping the paper discs.
What is the chemical that breaks down hydrogen peroxide?
Hydrogen Peroxide (H 2 O 2) is a toxic substance in the human body, which is often said to be created ‘by accident’ in respiration. The catalase enzyme breaks it down into Hydrogen (H2) and Oxygen (O2). This is an example of the liver performing its function of using specialized enzymes to help it break down toxic substances and thus make them safer for the body to process.
What temperature was used to measure catalase?
In order to increase the temperature of the catalase to the required ‘optimum’ level, a water bath – measured electronically to be 37°C was used. This was monitored throughout the experiment to avoid any unwanted fluctuations. Windows were also covered with blinds to prevent any increase in the general temperature of the laboratory as a result of the sunny conditions outside.
What temperature should catalase be at?
At the optimal temperature – which is 37°C for catalase, then the rate of enzyme activity will be at its peak. Both high and low temperatures (approximately 10°C either side of the optimum) will cause enzyme stability to decrease – since the change in thermal energy will disrupt the hydrogen bonds within the enzyme.
How to test for amylase?
2) Place the amylase into the first starch test tube and stir for several seconds; once amylase is placed into the test tube, immediately begin the stop watch.
Why does crushing liver and potato produce a faster reaction with longer oxygen columns than the cubic pieces?
Crushing both the liver and potato produced a faster reaction with longer oxygen columns than the cubic pieces because this increased the surface area of the catalase. This increase in surface area allowed a greater percentage of catalase to react with the H 22 solution and produce a much more vigorous result.
Why is hydrogen peroxide broken down?
Hydrogen peroxide is naturally produced in organisms as a by-product of oxygen metabolism and needs to be broken down because high levels of it are extremely toxic. [7] H 22 > O 2 + H 2 O (catalyzed by catalase) Amylase, a carbohydrase, catalyzes the hydrolysis of starch.
Which produces more oxygen bubbles: liver or potato?
Both of the sources produced vigorous and visible reactions. The liver however produced a larger column of oxygen bubbles than the potato. (Liver: 8 cm and Potato: 5 cm) (see table 1.0)
Why does boiling liver cause no reaction?
As for the variable of temperature, boiling the liver caused it to yield no reaction because it was denatured.
Why does catalase stop working?
A change in pH to a mixture of hydrogen peroxide and catalase will cause the catalase to stop working properly because catalase is an enzyme and since they are very specific it can only function under certain pH and temperature conditions.
Does water affect catalase?
Since water is a neutral pH it does not have affect on the catalase since the pH of the hydrogen peroxide was not changed. The bubbles prove that the catalase was working since they are a product of the reaction between the hydrogen peroxide and catalase.
Does ammonia affect catalase activity?
There are a lot of bubbles created, which is a product of the reaction between hydrogen peroxide and catalase, so it seems the ammonia did not affect the catalase activity.
What is the role of catalase in càtabolism?
Catalase is involved in càtabolism means breakdown of large molecules in to small molecules
What is the pH level of catalase?
Enzyme pH levels also change the shape of the active site and affect the rate of enzyme activity. Each enzyme has its own optimal range of pH in which it works most effectively. In humans, catalase works only between pH 7 and pH 11. If the pH level is lower than 7 or higher than 11, the enzyme becomes denaturated and loses its structure. The liver sustains a neutral pH of about 7, which creates the best environment for catalase and other enzymes.
Why is pH important in catalytic reactions?
An optimal pH is required for maintaining the state of ionization of specific amino acid residues at catalytic site and for stabilization of the three-dimensional native conformation of enzyme. The correct state of ionization of active site and native conformation of enzyme are necessary for a catalytic process to take place. When the pH of a reaction is changed below or above the optimum pH, it causes a decrease in reaction velocity by influencing the state of ionization of active site and native conformation of enzyme. Extremes of pH on either side cause denaturation of enzymes.
What is the function of amylase?
Amylase is a functional protein whose function as for every enzyme is dependent on its three dimensional structure (confirmation). pH affects the protonation of various amino acids in protein chain thereby affecting intermolecular and intramoley hydrogen bonding and thus confirmation of the enzyme.
Why do enzymes go faster when heated?
Enzymes are a special case because proteins will denature (and lose their activity) when the temperature gets high enough. So typically the rate goes up dramatically until denaturation occurs — and then the rate goes down dramatically. See the graph below.
How does pH affect ionization?
Specifically, pH can have an effect on the state of ionization (ionization is the process by which an atom or a molecule acquires a negative or positive charge by gaining or losing electrons to form ions) of acidic or basic amino acids. If the state of ionization of an amino acid in a protein is altered, then the ionic bonds which help to give them their 3D shape also becomes altered, which could result in an enzyme becoming inactive.
How does pH affect enzymes?
Enzymes are very complex shaped structures. The pH of the surroundings affects the shape of the enzymes. If the enzymes are not the right shape they cannot breakdown the substrate. The more out of shape they are, the worse they fit