
Resistance to Beta-Lactam Antibiotics
| Class | Drug | Antimicrobial spectrum |
| Natural penicillin | Penicillin V | Streptococcus species and oral cavity an ... |
| Penicillinase-resistant penicillin | Cloxacillin (Tegopen) | Methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aur ... |
| Penicillinase-resistant penicillin | Dicloxacillin (Dynapen) | Methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aur ... |
| Penicillinase-resistant penicillin | Nafcillin (Unipen) * | Methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aur ... |
Why do beta lactams work so well?
β-lactam antibiotics are bactericidal, and act by inhibiting the synthesis of the peptidoglycan layer of bacterial cell walls. The peptidoglycan layer is important for cell wall structural integrity, especially in Gram-positive organisms, being the outermost and primary component of the wall.
What is a role of beta lactamase inhibitor?
Beta-lactamase inhibitors are drugs that are co-administered with beta-lactam antimicrobials to prevent antimicrobial resistance by inhibiting serine beta-lactamases, which are enzymes that inactivate the beta-lactam ring, which is a common chemical structure to all beta-lactam antimicrobials.
How do beta lactamase inhibitors work?
- Tebipenem is the first carbapenem to be administered orally in the form of tebipenem-pivoxil. ...
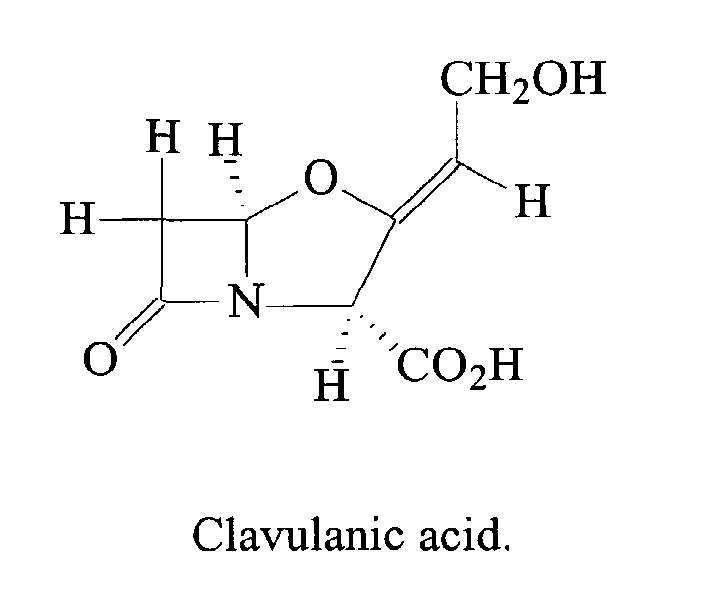
- Clavulanic acid or clavulanate, usually combined with amoxicillin ( Augmentin) or ticarcillin ( Timentin)
- Sulbactam, usually combined with ampicillin ( Unasyn) or cefoperazone ( Sulperazon)
- Tazobactam, usually combined with piperacillin ( Zosyn and Tazocin)
What can bacteria produce beta lactamase?
Beta-lactamases are enzymes produced by bacteria that break open the beta-lactam ring, inactivating the beta-lactam antibiotic. Some beta-lactamases are encoded on mobile genetic elements (eg, plasmids); others are encoded on chromosomes. There are numerous different types of beta-lactamases.

What do beta-lactam antibiotics do?
β-Lactam antibiotics inhibit bacteria by binding covalently to PBPs in the cytoplasmic membrane. These target proteins catalyze the synthesis of the peptidoglycan that forms the cell wall of bacteria. Alterations of PBPs can lead to β-lactam antibiotic resistance.
Why beta-lactam inhibitors are used with antibiotics?
Once administered, beta-lactam antibiotics act by inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis, which kills the bacteria. However, in resistant bacteria, the beta-lactamase enzyme binds to the beta-lactam ring within the antibiotic and breaks it down, thus inactivating the antibiotic.
What is the purpose of β lactamase inhibitors?
Beta-lactamase inhibitors are medications that are used ubiquitously in modern medicine due to their ability to combat bacterial antimicrobial resistance mechanisms. Antimicrobial resistance poses an enormous global public health challenge.
What drugs are beta lactams?
Beta-lactam antibiotics include penicillins, cephalosporins and related compounds. As a group, these drugs are active against many gram-positive, gram-negative and anaerobic organisms.
What is beta lactam?
β-lactam antibiotics ( beta- lactam antibiotics) are antibiotics that contain a beta-lactam ring in their molecular structure. This includes penicillin derivatives ( penams ), cephalosporins and cephamycins ( cephems ), monobactams, carbapenems and carbacephems. Most β-lactam antibiotics work by inhibiting cell wall biosynthesis in ...
How do -lactam antibiotics work?
Most β-lactam antibiotics work by inhibiting cell wall biosynthesis in the bacterial organism and are the most widely used group of antibiotics. Until 2003, when measured by sales, more than half of all commercially available antibiotics in use were β-lactam compounds. The first β-lactam antibiotic discovered, penicillin, ...
How does penicillin work?
Penicillin and most other β-lactam antibiotics act by inhibiting penicillin-binding proteins, which normally catalyze cross-linking of bacterial cell walls. In the absence of β-lactam antibiotics (left), the cell wall plays an important role in bacterial reproduction.
What enzyme hydrolyzes the -lactam ring of an antibiotic?
If the bacterium produces the enzyme β-lactamase or the enzyme penicillinase, the enzyme will hydrolyse the β-lactam ring of the antibiotic, rendering the antibiotic ineffective. (An example of such an enzyme is New Delhi metallo-beta-lactamase 1, discovered in 2009.)
How many people have anaphylaxis from a -lactam antibiotic?
Anaphylaxis will occur in approximately 0.01% of patients.
What are the structural features of -lactam antibiotics?
The first is known as "Woodward's parameter", h, and is the height (in angstroms) of the pyramid formed by the nitrogen atom of the β-lactam as the apex and the three adjacent carbon atoms as the base. The second is called "Cohen's parameter", c, and is the distance between the carbon atom of the carboxylate and the oxygen atom of the β-lactam carbonyl. This distance is thought to correspond to the distance between the carboxylate- binding site and the oxyanion hole of the PBP enzyme. The best antibiotics are those with higher h values (more reactive to hydrolysis) and lower c values (better binding to PBPs).
What is the first antibiotic?
The first β-lactam antibiotic discovered, penicillin, was isolated from a rare variant of Penicillium notatum (since renamed Penicillium chrysogenum). Bacteria often develop resistance to β-lactam antibiotics by synthesizing a β-lactamase, an enzyme that attacks the β-lactam ring. To overcome this resistance, β-lactam antibiotics can be given ...
What is a beta lactam?
Beta-lactams are antibiotics that have a beta-lactam ring nucleus. Subclasses include. All beta-lactams bind to and inactivate enzymes required for bacterial cell wall synthesis.
What are beta-lactamases encoded on?
Some beta-lactamases are encoded on mobile genetic elements (eg, plasmids); others are encoded on chromosomes. There are numerous different types of beta-lactamases. They are not all active against all beta-lactam antibiotics and so are broadly classified into several main groups based on their affinity for particular beta-lactams: ...
What are the extended spectrum beta-lactamases?
Extended-spectrum beta-lactamases: Extended-spectrum penicillins (eg, piperacillin), most cephalosporins, monobactams. Metallo-beta-lactamases: Carbapenems plus all other beta-lactams, except the monobactam aztreonam (note, these enzymes are not inhibited by beta-lactamase inhibitors)
What are some examples of beta-lactamase inhibitors?
Examples include. Clavulanate, sulbactam, tazobactam: These drugs block penicillinases but not AmpC or carbapenemases.
What is the name of the enzyme that produces penicillin?
Penicillinases are narrow-spectrum enzymes produced by a variety of organisms including staphylococci such as Staphylococcus aureus. Serine carbapenemases, such as plasmid-mediated Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase (KPC), are produced most often by K. pneumoniae but have also been reported among other Enterobacteriaceae. ...
Which drugs block ESBLs?
Avibactam, relebactam, vaborbactam: These drugs block ESBLs, most serine carbapenemases including KPC, and AmpC but not the metallo-beta-lactamases. Avibactam: This drug also blocks some OXA carbapenemases.
Is there a beta lactamase inhibitor?
There are no currently available beta-lactamase inhibitors active against metallo-beta-lactamases (MBLs), such as NDM-1 (New Delhi MBL-1), VIMs (Verona integron–encoded MBLs), and IMP (imipenem)-types, which can inactivate all beta-lactam antibiotics except for aztreonam .
What are beta lactams?
Beta-lactams are antibiotics that have a beta-lactam ring nucleus. Subclasses include. Cephalosporins and cephamycins (cephems) Clavams. Carbapenems. Monobactams. Penicillins. All beta-lactams bind to and inactivate enzymes required for bacterial cell wall synthesis.
What are beta-lactamases encoded on?
Some beta-lactamases are encoded on mobile genetic elements (eg, plasmids); others are encoded on chromosomes. There are numerous different types of beta-lactamases. They are not all active against all beta-lactam antibiotics and so are broadly classified into several main groups based on their affinity for particular beta-lactams: ...
What are the extended spectrum beta-lactamases?
Extended-spectrum beta-lactamases: Extended-spectrum penicillins (eg, piperacillin), most cephalosporins, monobactams. Metallo-beta-lactamases: Carbapenems plus all other beta-lactams, except the monobactam aztreonam (note, these enzymes are not inhibited by beta-lactamase inhibitors) Penicillinases: Narrow-spectrum penicillins.
What are some examples of beta-lactamase inhibitors?
Examples include. Clavulanate, sulbactam, tazobactam: These drugs block penicillinases but not AmpC or carbapenemases.
What is the name of the enzyme that produces penicillin?
Penicillinases are narrow-spectrum enzymes produced by a variety of organisms including staphylococci such as Staphylococcus aureus. Serine carbapenemases, such as plasmid-mediated Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase (KPC), are produced most often by K. pneumoniae but have also been reported among other Enterobacteriaceae. ...
Which drugs block ESBLs?
Avibactam, relebactam, vaborbactam: These drugs block ESBLs, most serine carbapenemases including KPC, and AmpC but not the metallo-beta-lactamases. Avibactam: This drug also blocks some OXA carbapenemases.
Is there a beta lactamase inhibitor?
There are no currently available beta-lactamase inhibitors active against metallo-beta-lactamases (MBLs), such as NDM-1 (New Delhi MBL-1), VIMs (Verona integron–encoded MBLs), and IMP (imipenem)-types, which can inactivate all beta-lactam antibiotics except for aztreonam .
What is beta-lactamase inhibitor?
Beta-lactamase inhibitors are a class of medicine that block the activity of beta-lactamase enzymes (also called beta-lactamases), preventing the degradation of beta-lactam antibiotics. They tend to have little antibiotic activity on their own. Beta-lactamase enzymes are produced by certain strains of the following bacteria: Bacteroides species, ...
Which bacteria produce beta-lactamases?
Beta-lactamase enzymes are produced by certain strains of the following bacteria: Bacteroides species, Enterococcus species, Hemophilus influenzae, Moraxella catarrhalis, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, and Staphylococcus species, either constitutively or on exposure to antimicrobials. Beta-lactamases cleave the beta-lactam ring ...
What are the active ingredients in beta-lactamase inhibitors?
The activity of the beta-lactams: amoxicillin, ampicillin, piperacillin, and ticarcillin, can be restored and widened by combining them with a beta-lactamase inhibitor. Clavulanic acid, sulbactam, and tazobactam are all beta-lactamase inhibitors.
Which antimicrobials are naturally resistant to beta-lactamases?
Some antimicrobials (eg, cefazolin and cloxacillin) are naturally resistant to certain beta-lactamases. The activity of the beta-lactams: amoxicillin, ampicillin, piperacillin, and ticarcillin, ...
Overview
β-lactam antibiotics (beta-lactam antibiotics) are antibiotics that contain a beta-lactam ring in their chemical structure. This includes penicillin derivatives (penams), cephalosporins and cephamycins (cephems), monobactams, carbapenems and carbacephems. Most β-lactam antibiotics work by inhibiting cell wall biosynthesis in the bacterial organism and are the most widely used gr…
Medical use
β-lactam antibiotics are indicated for the prevention and treatment of bacterial infections caused by susceptible organisms. At first, β-lactam antibiotics were mainly active only against Gram-positive bacteria, yet the recent development of broad-spectrum β-lactam antibiotics active against various Gram-negative organisms has increased their usefulness.
Adverse effects
Common adverse drug reactions for the β-lactam antibiotics include diarrhea, nausea, rash, urticaria, superinfection (including candidiasis).
Infrequent adverse effects include fever, vomiting, erythema, dermatitis, angioedema, pseudomembranous colitis.
Pain and inflammation at the injection site is also common for parenterally administered β-lacta…
Mechanism of action
β-lactam antibiotics are bactericidal, and act by inhibiting the synthesis of the peptidoglycan layer of bacterial cell walls. The peptidoglycan layer is important for cell wall structural integrity, especially in Gram-positive organisms, being the outermost and primary component of the wall. The final transpeptidation step in the synthesis of the peptidoglycan is facilitated by DD-transpeptidases, also kn…
Potency
Two structural features of β-lactam antibiotics have been correlated with their antibiotic potency. The first is known as "Woodward's parameter", h, and is the height (in angstroms) of the pyramid formed by the nitrogen atom of the β-lactam as the apex and the three adjacent carbon atoms as the base. The second is called "Cohen's parameter", c, and is the distance between the carbon atom of the carboxylate and the oxygen atom of the β-lactam carbonyl. This distance is thought t…
Modes of resistance
By definition, all β-lactam antibiotics have a β-lactam ring in their structure. The effectiveness of these antibiotics relies on their ability to reach the PBP intact and their ability to bind to the PBP. Hence, there are two main modes of bacterial resistance to β-lactams:
If the bacterium produces the enzyme β-lactamase or the enzyme penicillinase, t…
Nomenclature
β-lactams are classified according to their core ring structures.
• β-lactams fused to saturated five-membered rings:
• β-lactams fused to unsaturated five-membered rings:
• β-lactams fused to unsaturated six-membered rings:
Biosynthesis
To date, two distinct methods of biosynthesizing the β-lactam core of this family of antibiotics have been discovered. The first pathway discovered was that of the penams and cephems. This path begins with a nonribosomal peptide synthetase (NRPS), ACV synthetase (ACVS), which generates the linear tripeptide δ-(L-α-aminoadipyl)-L-cysteine-D-valine (ACV). ACV is oxidatively cyclized (two …