
In biological terms, a mutagen is the agent of a substance that brings about a permanent alteration to the physical composition of a DNA gene. For better understanding, let's start from the DNA. The DNA may be a genetic material- a polynucleotide chain made of the long chain of A, T, G, and C.
What are the two main types of mutagens?
In biological terms, a mutagen is the agent of a substance that brings about a permanent alteration to the physical composition of a DNA gene. For better understanding, let's start from the DNA. The DNA may be a genetic material- a polynucleotide chain made of the long chain of …
What are some common mutagens?
Jan 19, 2022 · A mutagen is a chemical or agent that causes DNA damage that results in DNA mutation that results in the modification of the DNA sequence. All cell genetic information is encoded by a cell's DNA by a standard pattern of nucleic acid bases.
What does a mutagen cause?
Nov 04, 2019 · What are mutagens Definition of mutagens Types of mutagens Physical Radiation Heat Chemical Base analogs Alkylating agents intercalating agents Metal... Physical Radiation Heat Radiation Heat Chemical Base analogs Alkylating agents intercalating agents Metal ions Base analogs Alkylating agents ...
Which is considered a chemical mutagen?
Oct 18, 2021 · These agents are known as AS mutagens, and they act by altering cell's DNA sequence. Many mutagens, by virtue of their or structure, can slip through both cell and nuclear membranes and interact with DNA directly, usually resulting in damage.
What is an example of a biological mutagen?
Anything that causes a mutation (a change in the DNA of a cell). DNA changes caused by mutagens may harm cells and cause certain diseases, such as cancer. Examples of mutagens include radioactive substances, x-rays, ultraviolet radiation, and certain chemicals.
How do biological mutagens cause mutations?
A mutagen is a substance or agent that causes DNA impairment that results in the alteration of the DNA sequence. This alteration of the DNA sequence is known as mutation.Jan 13, 2022
What is biological mutagenesis?
Mutagenesis is the formation of mutations in DNA molecules. There are a variety of mutations that can occur in DNA, such as changes in the DNA sequence or rearrangement of the chromosomes. Such mutations may occur spontaneously, as a result of 'mistakes' that occur during DNA replication or mitosis.
What are the three types of mutagens?
Mutations are caused by environmental factors known as mutagens. Types of mutagens include radiation, chemicals, and infectious agents. Mutations may be spontaneous in nature.Mar 4, 2022
What are non biological mutagens?
Naturally occurring mutagens☆ Examples are the pyrrolizidine alkaloids, cycasin, a range of mycotoxins produced by various fungi, and at least two unidentified toxic agents in bracken.
What are some examples of chemical mutagens?
Most chemical mutagens are alkylating agents and azides. Physical mutagens include electromagnetic radiation, such as gamma rays, X rays, and UV light, and particle radiation, such as fast and thermal neutrons, beta and alpha particles.
What is mutation and mutagen?
Mutations. Definition. A Mutation occurs when a DNA gene is damaged or changed in such a way as to alter the genetic message carried by that gene. A Mutagen is an agent of substance that can bring about a permanent alteration to the physical composition of a DNA gene such that the genetic message is changed.
How many types of mutagens are there?
Mutagens can be classified into 3 types based on their origin.
What is Crispr biology?
CRISPR (/ˈkrɪspər/) (an acronym for clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats) is a family of DNA sequences found in the genomes of prokaryotic organisms such as bacteria and archaea. These sequences are derived from DNA fragments of bacteriophages that had previously infected the prokaryote.
Is cigarette smoke a mutagen?
Tobacco smoke produces mutagenic urine, and it is a human somatic-cell mutagen, producing HPRT mutations, SCEs, microsatellite instability, and DNA damage in a variety of tissues.
Are all carcinogens mutagens?
A carcinogen is any agent that directly increases the incidence of cancer. Most, but not all carcinogens are mutagens. Carcinogens that do not directly damage DNA include substances that accelerate cell division, thereby leaving less opportunity for cell to repair induced mutations, or errors in replication.Apr 9, 2022
Are viruses mutagens?
It was shown that the mutagenic element of a virus is its nucleic acid; viral proteins completely lack mutagenic properties.
1. What are Mutagens in Biology?
In biological terms, a mutagen is the agent of a substance that brings about a permanent alteration to the physical composition of a DNA gene. For...
2. What are the Most Popular Types of Mutagens as per the Effects?
Teratogens: Teratogens are the class of the mutagens, which causes congenital malformations. X-rays, valproate, and toxoplasma are standard physica...
3. Name two chemical mutagens.
Nitrogen mustards and diethyl sulphate.
4. What are the effects of Mutagens?
The effects of mutagens are as follows:Mutagens alter DNA, causing problems with transcription and replication, and in extreme cases, cell death.St...
What is a mutagen?
Mutagens. “A mutagen is defined as any physical or chemical substance that can change the genetic material of an organism, thereby causing a mutation. ”. Mutations are natural, but the mutations brought about by the mutagens is above the natural background level. Furthermore, most mutations have the potential to cause cancer, hence, ...
What are the effects of mutagens?
In most cases, the mutagens can incite carcinogenic responses or impair functions of certain genes. Or they can completely ride a gene of its functionality, thereby causing various medical conditions.
When were mutagens first discovered?
The first ever instance of mutagens was linked to carcinogenic substances more than 2,000 years prior to the discovery of DNA. Though knowledge of radioactivity or carcinogens were non-existent during that time, its effects were clearly recorded throughout history.
Can mutagens cause hair loss?
Certain mutagens are highly toxic to proliferating cells and as a result, some are used to eradicate cancer cells. However, an obvious downside is that the mutagen can also affect the non-cancerous cells, leading to undesirable side effects such as hair loss.
Is benzene a mutagen?
Chemical mutagens: Elements such as arsenic, nickel and chromium are considered to be mutagens. Some organic compounds like benzene are also considered to be mutagenic in nature. Biological mutagens: Examples of biological mutagens involve transposons and viruses.
What is a mutagen?
Definition of mutagen: “Mutagens are the known agents either physical, chemical or biological causes mutations by altering the genotype or gene expression which results in genetic abnormality. ”. In other words, we can say, “Mutation causes by any agents is known as a mutagen.”. or.
What are the different types of mutagens?
Some of the common types of mutagens based on their effect are enlisted here: Teratogens: teratogens are the class of the mutagens which causes congenital malformations. X-rays, valproate and toxoplasma are common physicals, chemical and biological teratogens , respectively.
What is mutation in genetics?
In genetics, mutagen induced changes are known as mutation. The mutations are categorized under two broader categories; gene mutations and chromosomal mutations. The present topic is very important, in order to understand the mechanism of how genetic mutations originate in nature.
What happens when you heat DNA?
Heat is another mutagen that provokes mutations in our DNA. when we heat the DNA, over a certain degree (>95°C), the DNA becomes denatured- two single-stranded DNA is generated from the dsDNA. Also, extreme heat also damages DNA and breaks the phosphodiester bonds too.
What is DNA made of?
The DNA is a genetic material- a polynucleotide chain made up of the long chain of A, T, G, and C. The functional piece of DNA- a gene encodes a specific protein. If the sequence of a nucleotide within a gene is changed, the protein can not be formed or loss of function protein is formed. Read more on DNA: DNA story: The structure and function ...
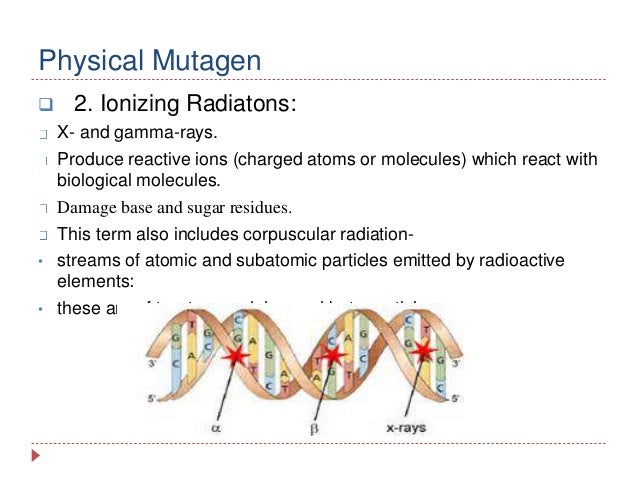
How does X-ray damage DNA?
At the molecular level, the lethal dose of X-ray (350-500 rems) breaks the phosphodiester bonds between the DNA and thus results in the strand breakages. It creates multiple strand breakage and results in the deletion of the portion of a DNA.
Is nitrogen mustard poisonous?
The first mutagenic effect of the nitrogen mustard was reported by charlotte Auerbach in 1942. (the nitrogen mustard is a poisonous gas used during the world war 1 and 2).
What is a mutagen?
In genetics, a mutagen is a physical or chemical agent that permanently changes genetic material, usually DNA, in an organism and thus increases the frequency of mutations above the natural background level. As many mutations can cause cancer, such mutagens are therefore carcinogens, although not all necessarily are.
What were the first mutagens?
The first mutagens to be identified were carcinogens, substances that were shown to be linked to cancer. Tumors were described more than 2,000 years before the discovery of chromosomes and DNA; in 500 B.C., the Greek physician Hippocrates named tumors resembling a crab karkinos (from which the word "cancer" is derived via Latin), meaning crab. In 1567, Swiss physician Paracelsus suggested that an unidentified substance in mined ore (identified as radon gas in modern times) caused a wasting disease in miners, and in England, in 1761, John Hill made the first direct link of cancer to chemical substances by noting that excessive use of snuff may cause nasal cancer. In 1775, Sir Percivall Pott wrote a paper on the high incidence of scrotal cancer in chimney sweeps, and suggested chimney soot as the cause of scrotal cancer. In 1915, Yamagawa and Ichikawa showed that repeated application of coal tar to rabbit's ears produced malignant cancer. Subsequently, in the 1930s the carcinogen component in coal tar was identified as a polyaromatic hydrocarbon (PAH), benzo [a]pyrene. Polyaromatic hydrocarbons are also present in soot, which was suggested to be a causative agent of cancer over 150 years earlier.
How do mutagens affect DNA?
Mutagens can cause changes to the DNA and are therefore genotoxic. They can affect the transcription and replication of the DNA, which in severe cases can lead to cell death. The mutagen produces mutations in the DNA, and deleterious mutation can result in aberrant, impaired or loss of function for a particular gene, and accumulation of mutations may lead to cancer. Mutagens may therefore be also carcinogens. However, some mutagens exert their mutagenic effect through their metabolites, and therefore whether such mutagens actually become carcinogenic may be dependent on the metabolic processes of an organism, and a compound shown to be mutagenic in one organism may not necessarily be carcinogenic in another.
What are mutagens in science fiction?
In science fiction, mutagens are often represented as substances that are capable of completely changing the form of the recipient or granting them superpowers. Powerful radiations are the agents of mutation for the superheroes in Marvel Comics 's Fantastic Four, Daredevil, and Hulk, while in the Teenage Mutant Ninja Turtles franchise the mutagen is a chemical agent also called "ooze", and for Inhumans the mutagen is the Terrigen Mist. Mutagens are also featured in video games such as Cyberia, The Witcher, Metroid Prime: Trilogy, Resistance: Fall of Man, Resident Evil, Infamous, Freedom Force, Command & Conquer, Gears of War 3, StarCraft, BioShock, Fallout, and Maneater . In the "nuclear monster" films of the 1950s, nuclear radiation mutates humans and common insects often to enormous size and aggression; these films include Godzilla, Them!, Attack of the 50 Foot Woman, Tarantula!, and The Amazing Colossal Man .
How are rodents tested?
Rodents are usually used in animal test. The chemicals under test are usually administered in the food and in the drinking water, but sometimes by dermal application, by gavage, or by inhalation, and carried out over the major part of the life span for rodents. In tests that check for carcinogens, maximum tolerated dosage is first determined, then a range of doses are given to around 50 animals throughout the notional lifespan of the animal of two years. After death the animals are examined for sign of tumours. Differences in metabolism between rat and human however means that human may not respond in exactly the same way to mutagen, and dosages that produce tumours on the animal test may also be unreasonably high for a human, i.e. the equivalent amount required to produce tumours in human may far exceed what a person might encounter in real life.
Why are mutations silent?
Many mutations are silent mutations, causing no visible effects at all, either because they occur in non-coding or non-functional sequences, or they do not change the amino-acid sequence due to the redundancy of codons . Some mutagens can cause aneuploidy and change the number of chromosomes in the cell.
How are male mice treated?
Male mice are treated with chemicals under test, mated with females, and the females are then sacrificed before parturition and early fetal deaths are counted in the uterine horns . Transgenic mouse assay using a mouse strain infected with a viral shuttle vector is another method for testing mutagens.

Discovery of Mutagens
- The first ever instance of mutagens was linked to carcinogenic substances more than 2,000 years prior to the discovery of DNA. Though knowledge of radioactivity or carcinogens were non-existent during that time, its effects were clearly recorded throughout history. One of the well-documented cases of exposure to mutagens were miners working in poorly ventilated mines. Th…
Types of Mutagens
- Mutagens can be classified into 3 types based on their origin. They are as follows: 1. Physical mutagens: These include ionizing radiation, such as X-rays, gamma rays and alpha particles. Ultraviolet radiations can also behave as potential mutagens. 1. Chemical mutagens: Elements such as arsenic, nickel and chromium are considered to be mutagens. Some organic compound…
Effects of Mutagens
- Mutagens are substances that alter or change the genetic material of an organism, hence they are termed as genotoxic. In most cases, the mutagens can incite carcinogenic responses or impair functions of certain genes. Or they can completely ride a gene of its functionality, thereby causing various medical conditions. However, the effects of most mutagens cannot be substantiated fro…
Protection Against Mutagens
- As mentioned above, there are many types of mutagens. Exposure to physical mutagens obviously involves limiting or avoiding high-energy radiation. The effects of some chemical mutagens can be reduced through the help of antioxidants. Antioxidants are found in fruits and vegetables and are heralded as anticarcinogenic compounds. In other words, antioxidants inhibi…
Mutagens in Anti-Cancer Roles
- Certain mutagens are highly toxic to proliferating cells and as a result, some are used to eradicate cancer cells. However, an obvious downside is that the mutagen can also affect the non-cancerous cells, leading to undesirable side effects such as hair loss. For example, we do know that ionizing radiation can be carcinogenic, and can damage the cell’s DNA. But it is for the sam…
Discovery of Mutagens
- Carcinogens are the first-ever mutagens to be discovered about 2,000 years ago, even before the discovery of chromosomes and DNA. The discovery of tumors was solely described by the effects caused and there was no knowledge of mutagens at that time. It was in the eighteenth century that scientists started discovering and demonstrating the different types of mutagen and mutag…
Types of Mutagens
- Based on their nature, mutagens are classified into three types. They are, namely, physical, chemical, and biological mutagens. 1. Physical Mutagens:Physical Mutagens or physical mutagenic agents are of physical origin and include ionizing radiations (X -rays, gamma rays, alpha particles), ultraviolet(UV) radiations, and radioactive decay(decay heat). In general, heat a…
Protection Against Mutagens
- Some of the key measures that can be taken up for protection against Mutagens are listed below for your reference, 1. To protect against physical mutagens, it is best to limit or avoid exposure to heat and radiations of high energies, especially that of tobacco smoke and ultraviolet radiations of which the individual is more vulnerable to be exposed. 2. Antioxidants, a pivotal group of anticar…
Role of Mutagens in Anti-Cancer Therapy
- Certain mutagens are used in anti-cancer therapies due to them being highly harmful and toxic to proliferating cancer cells, hence helpful in the destruction of cancer cells.
- In chemotherapy, alkylating agents and intercalating agents are used for treatments. Examples of alkylating agents include cyclophosphamic and cis-platin, while that of intercalating agents include...
- Certain mutagens are used in anti-cancer therapies due to them being highly harmful and toxic to proliferating cancer cells, hence helpful in the destruction of cancer cells.
- In chemotherapy, alkylating agents and intercalating agents are used for treatments. Examples of alkylating agents include cyclophosphamic and cis-platin, while that of intercalating agents include...
- In radiation therapy, ionizing radiation is used for the treatments.
- It is the same property of mutagens being carcinogenic, which is used in anticancer therapies. A collective combination of mutagens, such as a combination of ionizing radiations and intercalating a...
Key Terms
- Mutagens: Mutagens are mutation-causing agents which are responsible for the alteration of genetic material in individual organisms. Examples of mutagens are heat, ionizing radiations, alkylating a...
- Mutation:Mutation is the alteration of base sequence in the genetic material resulting in genetic variations.
- Mutagens: Mutagens are mutation-causing agents which are responsible for the alteration of genetic material in individual organisms. Examples of mutagens are heat, ionizing radiations, alkylating a...
- Mutation:Mutation is the alteration of base sequence in the genetic material resulting in genetic variations.
- Carcinogens:Carcinogens or cancer-causing agents are a class of mutagens that affects the individual organism’s DNA and brings about genetic mutations causing cancer. Examples are X-rays, ultraviol...
- Transposons:Transposons or transposable elements are DNA sequences that are repetitive and can transpose within a genome, that is moving from a particular location of the genome …