
Key takeaways:
- Diseconomy of scale is when, after an organization scales its operations to produce a higher quantity of products, the cost to produce each individual product increases.
- Diseconomies of scale are the opposite of economies of scale, which is when the price to produce a single unit decreases in response to increased output.
What Are Diseconomies of Scale?
What is technical diseconomy?
What causes a diseconomy of scale?
Why are there organizational diseconomies of scale?
How does output affect logistics?
When economies of scale no longer function for a firm, does the firm see an increase in costs?
What is the second situation?
See 4 more
About this website

What are diseconomies of scope quizlet?
What are diseconomies of scale? Diseconomies of scale occur when a firm increases output and this leads to an increase in average cost of production.
Why do diseconomies of scope occur?
An overcrowding effect within an organization is often the leading cause of diseconomies of scale. This happens when a company grows too quickly, thinking that it can achieve economies of scale in perpetuity.
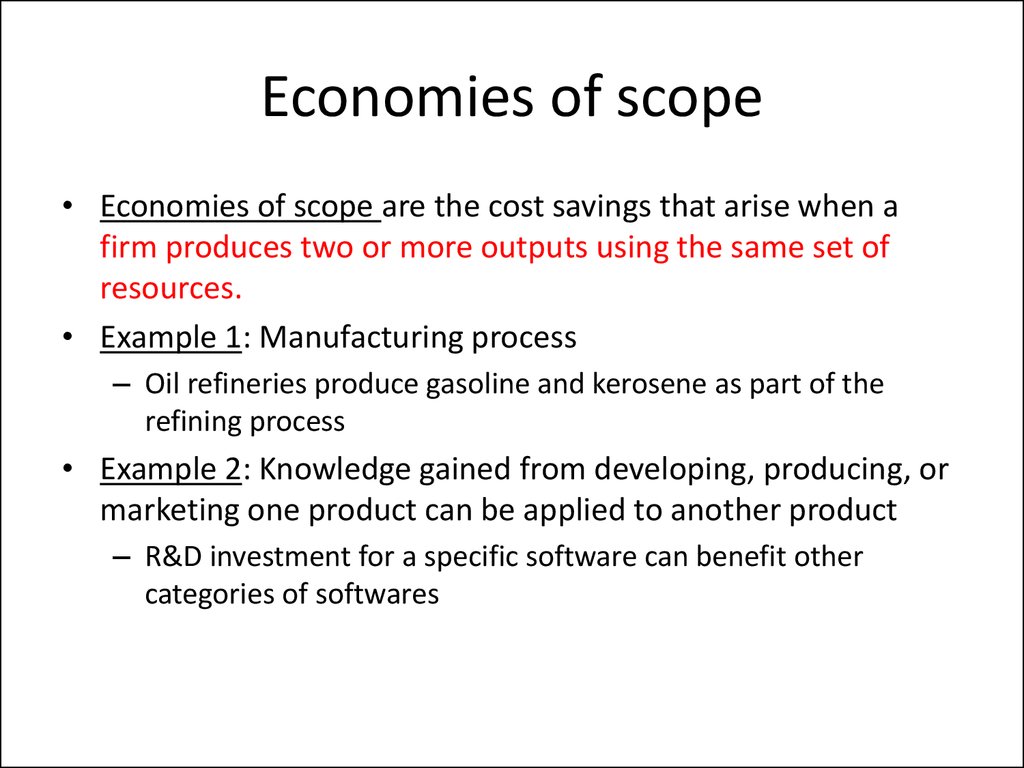
What is economies of scope meaning?
Economies of scope is an economic principle in which a business's unit cost to produce a product will decline as the variety of its products increases. In other words, the more different-but-similar goods you produce, the lower the total cost to produce each one will be.
What are the 3 types of diseconomies of scale?
Here are the five types of internal diseconomies of scale:Technical diseconomies of scale. Inefficiencies in the production process can cause technical diseconomies. ... Organizational diseconomies of scale. ... Purchasing diseconomies. ... Competitive diseconomies. ... Financial diseconomies.
What are the 3 reasons for diseconomies of scale?
Causes of Diseconomies of ScaleCommunication Breakdown. Communication is important in any organization, especially in managing economies of scale. ... Reduced Motivation. As the business grows, the employee base increases, which can make them feel isolated and thus less motivated. ... Lack of Coordination and Loss of Direction.
What could cause diseconomies of scale?
Diseconomies of scale are caused by either internal factors which are controlled by a company or external factors which are outside of the company's control. Diseconomies of scale may occur due to organizational issues, technical problems in the production process, or limitations on resources used in production.
What are the types of economies of scope?
Economies of scope can result from goods that are co-products or complements in production, goods that have complementary production processes, or goods that share inputs to production.
What are economies of scope provide examples?
Economies of scope is an economic theory stating that average total cost of production decrease as a result of increasing the number of different goods produced. For example, a gas station that sells gasoline can sell soda, milk, baked goods, etc.
How do you determine economies of scope?
0:352:29Economies of Scope: Determining if it Exists - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clip2 represent the different types of goods here. And we want to see if economies of scope occur. GivenMore2 represent the different types of goods here. And we want to see if economies of scope occur. Given this functional form of this cost function. So the firm would like to produce 10 units of good one
Which is the best example of diseconomies of scale?
Diseconomies of Scale ExamplesPoor Communication. As a firm grows, it acquires more workers and creates more departments. ... Inefficient Management. ... Motivation. ... Higher Costs of Resources. ... Greater Levels of debt and interest.
What is the meaning of diseconomies of scale?
In economics, the term diseconomies of scale describes the phenomenon that occurs when a firm experiences increasing marginal costs per additional unit of output. It is the opposite of economies of scale.
How many types of diseconomies of scale are there?
There are two main categories of diseconomies of scale: internal and external. While internal diseconomies of scale result from factors within the company's control, external diseconomies of scale occur due to factors outside of a company's influence.
Diseconomies of Scale: Types, How They Work and Examples
Updated August 24, 2022 | Published February 22, 2021. Updated August 24, 2022. Published February 22, 2021
Diseconomies of Scale - Definition, Examples, Causes - WallStreetMojo
Diseconomies of Scale Example. Below is an example of diseconomies of scale. Paul Mitchell, EY Global Mining & Metal advisory, mentions that the size and complexities of mining operations result in diseconomies of scale created when the mining industry had to ramp up Ramp Up Ramp Up in economics refers to the boosting of a company’s production. read more production in response to high prices.
What is a diseconomy of scale and how does this occur? - Investopedia
Erika Rasure, is the Founder of Crypto Goddess, the first learning community curated for women to learn how to invest their money—and themselves—in crypto, blockchain, and the future of ...
What Are Diseconomies of Scale?
Diseconomies of scale happen when a company or business grows so large that the costs per unit increase. It takes place when economies of scale no longer function for a firm. With this principle, rather than experiencing continued decreasing costs and increasing output, a firm sees an increase in costs when output is increased.
What is technical diseconomy?
Technical diseconomies of scale involve physical limits on handling and combining inputs and goods in process. These can include overcrowding and mismatches between the feasible scale or speed of different inputs and processes.
What causes a diseconomy of scale?
Diseconomies of scale may result from technical issues in a production process, organizational management issues, or resource constraints on productive inputs.
Why are there organizational diseconomies of scale?
Organizational diseconomies of scale can happen for many reasons, but overall, they arise because of the difficulties of managing a larger workforce. Several problems can be identified with diseconomies of scale. First, communication becomes less effective.
How does output affect logistics?
As output increases, the logistical costs of transporting goods to distant markets can increase enough to offset any economies of scale. A similar example is the depletion of a critical natural resource below its ability to reproduce itself in a tragedy of the commons scenario. As the resource becomes ever more scarce and ultimately runs out, the cost to obtain it increases dramatically.
When economies of scale no longer function for a firm, does the firm see an increase in costs?
With this principle, rather than experiencing continued decreasing costs and increasing output, a firm sees an increase in costs when output is increased.
What is the second situation?
The second situation arises when there is a higher level of operational waste, due to a lack of proper coordination.
Economies of Scope Definition
The economies of scope definition revolves around the idea that a company producing a greater range of products or services in tandem is more cost-efficient for the company rather than producing each item individually.
Types of economies of scope
There are two main types of economies of scope: economies of scope and diseconomies of scope.
Economies of Scope Formula
The economies of scope formula determines whether a firm producing two goods at the same time can generate more output than two single firms producing each of the goods individually. The economies of scope formula is based on how much of the production cost is saved when two or more products are produced simultaneously rather than individually.
What is the economic concept of scope?
Economies of Scope Economies of scope is an economic concept that refers to the decrease in the total cost of production when a range of products are produced together rather than separately. Law of Supply.
What are the diseconomies of scale?
What are Diseconomies of Scale? Diseconomies of scale occur when an additional production unit of output increases marginal costs. Fixed and Variable Costs Cost is something that can be classified in several ways depending on its nature. One of the most popular methods is classification according.
How does a small business affect employees?
A small business employs a few individuals with a personal connection to the business and a close working relationship with the owner and management. A large workforce with less interaction with the top management can easily lose focus, leading to reduced profitability and diseconomies of scale. Diminishing employee motivation and loyalty often leads to decreased productivity levels and an influx of marginal costs.
What are the challenges of expansion?
Many businesses face challenges when undergoing an expansion, as there are increases in workload and clients to serve. Effective cost control under changing business circumstances is difficult and may mean a reduction in profitability if production is increased.
Why do managers and supervisors have a hard time organizing operations?
Managers and supervisors also experience a hard time organizing operations and ensuring that everyone is playing their part effectively. Businesses will be forced to hire or promote more supervisors to oversee the increased operations and monitor the performance of employees.
How to solve lack of coordination?
The ideal solution to the loss of direction and lack of coordination is to delegate tasks and decision-making to the junior levels in the organizational chart. Delegating tasks and responsibility not only saves time but also equips lower-level employees with better skills, rather than waiting for the higher levels of management to give direction on every task. Furthermore, delegation motivates junior employees to be innovative and creative since they move from being just executors of functions to owners of specific tasks.
What are Economies of Scope?
An economy of scope means that the production of one good reduces the cost of producing another related good. Economies of scope occur when producing a wider variety of goods or services in tandem is more cost effective for a firm than producing less of a variety, or producing each good independently. In such a case, the long-run average and marginal cost of a company, organization, or economy decreases due to the production of complementary goods and services.
Why do economies of scope occur?
Economies of scope can occur because the products are co-produced by the same process, the production processes are complementary, or the inputs to production are shared by the products.
How does economies of scope differ from economies of scale?
Economies of scope differ from economies of scale, in that the former means producing a variety of different products together to reduce costs while the latter means producing more of the same good in order to reduce costs by increasing efficiency. Economies of scope can result from goods that are co-products or complements in production, ...
What are some examples of economic scope?
Real-world examples of the economy of scope can be seen in mergers and acquisitions (M&A), newly discovered uses of resource byproducts (such as crude petroleum), and when two producers agree to share the same factors of production.
How can an aerospace manufacturer reduce its overall cost?
The manufacturer can reduce its overall costs by obtaining low cost access to skilled labor, and the engineering school can reduce its instructional costs by effectively outsourcing some instructional time to the manufacturer's training managers. The final goods being produced (airplanes and engineering degrees) might not seem to be direct complements or share many inputs, but producing them together reduces the cost of both.
Diseconomies of Scale - Key takeaways
Diseconomies of scale occur when a firm experiences an increase in its average cost as its total output increases.
Diseconomies of scale: definition
Diseconomies of scale point out the relationship between the average costs of a firm and its total output.
The diseconomies of scale graph
We can depict diseconomies of scale through a diagram, which we can see in figure 1 below.
Reasons for diseconomies of scale
There are many factors at play when a firm experiences diseconomies of scale. We will look at three of these reasons (Figure 2):
Types of diseconomies of scale
There are two main types of diseconomies of scale (Figure 3): internal diseconomies of scale and external diseconomies of scale.
What Are Diseconomies of Scale?
Diseconomies of scale happen when a company or business grows so large that the costs per unit increase. It takes place when economies of scale no longer function for a firm. With this principle, rather than experiencing continued decreasing costs and increasing output, a firm sees an increase in costs when output is increased.
What is technical diseconomy?
Technical diseconomies of scale involve physical limits on handling and combining inputs and goods in process. These can include overcrowding and mismatches between the feasible scale or speed of different inputs and processes.
What causes a diseconomy of scale?
Diseconomies of scale may result from technical issues in a production process, organizational management issues, or resource constraints on productive inputs.
Why are there organizational diseconomies of scale?
Organizational diseconomies of scale can happen for many reasons, but overall, they arise because of the difficulties of managing a larger workforce. Several problems can be identified with diseconomies of scale. First, communication becomes less effective.
How does output affect logistics?
As output increases, the logistical costs of transporting goods to distant markets can increase enough to offset any economies of scale. A similar example is the depletion of a critical natural resource below its ability to reproduce itself in a tragedy of the commons scenario. As the resource becomes ever more scarce and ultimately runs out, the cost to obtain it increases dramatically.
When economies of scale no longer function for a firm, does the firm see an increase in costs?
With this principle, rather than experiencing continued decreasing costs and increasing output, a firm sees an increase in costs when output is increased.
What is the second situation?
The second situation arises when there is a higher level of operational waste, due to a lack of proper coordination.
What Are Diseconomies of Scale?
Understanding Diseconomies of Scale
- The diagram below illustrates a diseconomy of scale. At point Q*, this firm is producing at the point of lowest average unit cost. If the firm produces more or less output, then the average cost per unit will be higher. To the left of Q*, the firm can reap the benefit of economies of scale to decrease average costs by producing more. To the right of Q*, the firm experiences diseconomi…
Special Considerations
- Diseconomies of scale specifically come about due to several reasons, but all can be broadly categorized as internal or external. Internal diseconomies of scale can arise from technical issues of production or organizational issues within the structure of a firm or industry. External diseconomies of scale can arise due to constraints imposed by the environment within which a f…
Types of Diseconomies of Scale
- Internal diseconomies of scale involve either technical constraints on the production process that the firm uses or organizational issues that increase costs or waste resources without any change to the physical production process.