What is an early deceleration?
Early Decelerations- Explained. Early decelerations are a benign decrease in heart rate of a fetus from the normal baseline heart rate that occurs only during contractions and signals that the fetal head is compressed during contractions. The baby has a normal baseline heart rate. A deceleration causes a decrease in heart rate from the baseline.
Are decels normal with contractions?
- TimesMojo Are Early Decelerations Normal? Early decelerations are caused by fetal head compression during uterine contraction, resulting in vagal stimulation and slowing of the heart rate. Are Decels normal with contractions? Decelerations represent a reduction in fetal heart rate of more than 15 beats per minute (bpm) in bandwidth amplitude.
What is early deceleration of the uterus?
Early deceleration is defined as a symmetrical decrease and return of fetal heart rate (FHR) that is associated with a uterine contraction. The decrease is gradual and defined by the onset of deceleration to a nadir of 30 seconds or longer, with the nadir occurring at the same time as the peak of the uterine contraction.
What are decelerations in labor?
Decelerations are temporary decreases in the fetal heart rate (FHR) during labor. Hon and Quilligan first described three types of decelerations (early, variable, and late) in 1967 based on the shape and timing of decelerations relative to uterine contractions.[1]

What do early decelerations indicate?
Early decelerations can happen when the baby's head is compressed. This often happens during later stages of labor as the baby is descending through the birth canal. They may also occur during early labor if the baby is premature or in a breech position. This causes the uterus to squeeze the head during contractions.
What is the classic cause of early decelerations?
Early decelerations are caused by fetal head compression during uterine contraction, resulting in vagal stimulation and slowing of the heart rate.
What are late Decels?
Late decelerations. Late decelerations are characterized by a gradual decrease and return to baseline of the fetal heart rate associated with uterine contractions. The deceleration is delayed in timing, with the nadir of the deceleration occurring after the peak of the contraction.
What are early and late decelerations?
Early decelerations are benign and uniform in shape. They begin near the onset of a uterine contraction, and their lowest point occurs at the same time as the peak of the contraction. Late decelerations are also uniform in shape; however, their onset and return to baseline are gradual.
What are three 3 potential causes of early decelerations?
For example, early decelerations are caused by the compression of the baby's head during uterine contractions....What Causes Deceleration?A decrease in blood flow to the brain.A low heart rate.Low blood pressure.
What causes Decels during labor?
They are caused by decreased blood flow to the placenta and can signify an impending fetal acidemia. Typically, late decelerations are shallow, with slow onset and gradual return to normal baseline.
What are the nursing interventions for early decelerations?
As long as the FHR stays within normal range (110–160 bpm), early decelerations are nothing to worry about. They are typically caused by the compression of the head in the birth canal. When observing early decelerations, no interventions are needed, and the nurse should continue to monitor the patient.
What to do with fetal decelerations?
Interventions for late decelerations are:Lower the head of the bed and turn the mom on her left side to take the pressure off the vena cava and allow blood flow to the heart and to the lungs. ... Re-oxygenation or the reintroduction of oxygen to the baby by giving oxygen to the mother.
What is early deceleration quizlet?
What is early deceleration? Gradual onset. Onset of deceleration to nadir> 30 seconds. Return to baseline FHR at end of contraction and mirrors the contraction.
Which characteristics describe early decelerations quizlet?
Early decelerations are the fetus' response to fetal head compression; these are considered benign, and interventions are not necessary. Variable decelerations are associated with umbilical cord compression. Late decelerations are associated with uteroplacental insufficiency.
What is the cause of variable decelerations?
Common causes of variable decelerations include vagal reflex triggered by head compression during pushing and cord compression such as that caused by short cord, nuchal cord, body entanglement, prolapsed cord, decreased amniotic fluid, and fetal descent.
What causes fetal late decelerations?
They are caused by decreased blood flow to the placenta and can signify an impending fetal acidemia. Typically, late decelerations are shallow, with slow onset and gradual return to normal baseline. The usual cause of the late deceleration is uteroplacental insufficiency.
What is early deceleration?
Early deceleration is defined as a symmetrical decrease and return of fetal heart rate (FHR) that is associated with a uterine contraction. The decrease is gradual and defined by the onset of deceleration to a nadir of 30 seconds or longer, with the nadir occurring at the same time as the peak of the uterine contraction. In most instances, the onset, nadir, and recovery of the deceleration coincide with the onset, peak, and end of the contraction. [2]
What is a deceleration in labor?
Decelerations are temporary decreases in the fetal heart rate (FHR) during labor. Hon and Quilligan first described three types of decelerations (early, variable, and late) in 1967 based on the shape and timing of decelerations relative to uterine contractions.[1] Intrapartum FHR monitoring allows for the identification of changes associated with fetal distress that allows for early intervention.
Do early decelerations affect oxygenation?
As early decelerations are not associated with decreased fetal oxygenation or metabolic acidosis, they do not require any treatment. However, it is crucial to continue to monitor FHR tracings throughout labor to recognize any patterns that may be a concern regarding changes in the acid-base status of the fetus.
What is early deceleration?
Early decelerations are a benign decrease in heart rate of a fetus from the normal baseline heart rate that occurs only during contractions and signals that the fetal head is compressed during contractions.
How does the mirror of early decelerations and contractions work?
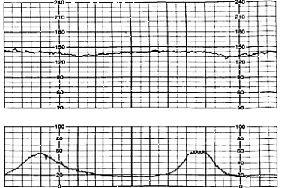
This shows how the mirror of early decelerations and contractions. It mirrors it pretty much exactly. It mirrors the inverse waveform of the contraction. So as you see an upside-down U on the contraction waveform, you will see a right-side-up U on the heart rates. So they really mirror each other inversely.
What happens at the end of a contraction?
By the end of the contraction, the baby's heart rate returns to baseline. Early decelerations, like late, have a gradual, rather than abrupt, decrease from the baseline. Early decelerations are mirror images of the contractions, meaning they mimic the contraction. When the contraction occurs, some deceleration occurs.
What happens when the heart rate is decelerated?
When the contraction occurs, some deceleration occurs. As the contraction gets stronger, the heart rate decelerates more. When the peak is of the contraction is reached, this causes the greatest deceleration (biggest drop in heart rate).
What happens during the peak of a baby's contraction?
During the peak of the contraction is the time when the baby's head normally gets squeezed the most, generally against the woman's pelvis or soft tissues, such as the cervix. Fetal head compression briefly increases intracranial pressure, causing the vagus nerve to slow the heart rate.
Do early decelerations cause oxygenation?
Early decelerations don't cause any compromise to the status of the fetus, such as oxygenation or anything. Therefore, it requires no medical intervention. So now that you know what early decelerations are and what causes it, let's see how to interpret them on a graph. Below is a graph showing early decelerations.
Do decelerations occur during contraction?
As stated before, early decelerations pretty much mimic the contraction. So decelerations occur all along the duration of the contraction. As the contraction begins, decelerations begin. First the decelerations are mild, but as the contraction increases in amplitude, the decelerations continue in amplitude (decreasing the heart rate).
What is early deceleration?from learningaboutelectronics.com
Early decelerations are a benign decrease in heart rate of a fetus from the normal baseline heart rate that occurs only during contractions and signals that the fetal head is compressed during contractions.
Why do babies decel?from flo.health
One explanation for early decels is the compression of your baby’s head, as opposed to a case of fetal hypoxia.
How does the mirror of early decelerations and contractions work?from learningaboutelectronics.com
This shows how the mirror of early decelerations and contractions. It mirrors it pretty much exactly. It mirrors the inverse waveform of the contraction. So as you see an upside-down U on the contraction waveform, you will see a right-side-up U on the heart rates. So they really mirror each other inversely.
Why do babies decelerate so early?from flo.health
One explanation for early decels is the compression of your baby’s head, as opposed to a case of fetal hypoxia. Despite the fact that early decelerations tend to be benign in nature, your doctor should still carefully monitor your fetus. This is because they’ll still have an increased likelihood of developing fetal hypoxia.
How long does a deceleration last?from flo.health
Decelerations represent a reduction in fetal heart rate of more than 15 beats per minute (bpm) in bandwidth amplitude. They also last for longer than 15 seconds.
Are early decelerations a cause for concern?from flo.health
It’s not uncommon for a certain degree of hypoxemia (i.e., an abnormally low concentration of blood oxygen in your fetus) to occur in childbirth. However, the repetitive nature, duration, and intensity of the phenomenon determine the impact it will have on your baby. Their natural capacity for handling this type of strain also dictates the severity of their hypoxia.
How to know if a baby is decelerating?
The key to remembering if this an early deceleration is to see if the baby’s heart rate mirrors moms contraction and it does here. Plus look to see if the baby’s heart rate is staying within normal limits of 110-160 beats per minutes. The baby’s heart rate dips slightly at the same time the contraction starts and recovers to a normal range after mom’s contraction is over.
What is the coolest thing about labor?
It truly is a beautiful process from conception to birth and thereafter. One of the coolest things about the labor process is the monitoring of fetal heart tones. I think it is so neat that technology has advanced in such a way that we can monitor mother’s contractions and the fetal heart tones at the same time and it pops up on a monitor for the nurses/doctors to read. It is used to see how the baby is responding to mom’s contractions and to make sure the baby is getting enough oxygen or isn’t becoming distressed during the labor process.
How are early decelerations treated?
As early decelerations are not associated with decreased fetal oxygenation or metabolic acidosis, they do not require any treatment. However, it is crucial to continue to monitor FHR tracings throughout labor to recognize any patterns that may be a concern regarding changes in the acid-base status of the fetus.
Why are late decelerations bad?
Repeated late decelerations are a sign of fetal distress and are caused by fetal hypoxia. The degree to which the heart rate slows is not important. The timing of the deceleration is what must be carefully observed. Late decelerations must always be taken seriously.
Does fetal heart rate decrease with contractions?
During a contraction, the blood and oxygen supply to your baby drops for a short time. This is not a problem for most babies. But the heart rate of some babies gets slower. This change in heart rate can be seen on the external fetal monitor.
What is Type 2 deceleration?
Definitions (10) • Late deceleration (type II dip) Definition: onset 30-60 seconds after onset. of contractions, nadir & recovery all out. of phase.
What do variable decelerations indicate?
Variable decelerations of the fetal heart rate are the most common changes noted during continuous fetal monitoring. In general, they are presumed to represent a normal response to fetal baroceptor stimulation.
When do late decelerations occur?
Late decelerations occur when a fall in the level of oxygen in the fetal blood triggers chemoreceptors in the fetus to cause reflex constriction of blood vessels in nonvital peripheral areas in order to divert more blood flow to vital organs such as the adrenal glands, heart, and brain.
What is deceleration CTG?
Decelerations are transient episodes of decrease of FHR below the baseline of more than 15 bpm lasting at least 15 seconds.
How many types of deceleration are there in labor?from verywellhealth.com
There are three types of deceleration that may occur during labor. Each type is categorized by the timing of the deceleration during uterine contractions. 1
What Causes Deceleration?from verywellhealth.com
The cause of deceleration varies depending on the type. For example, early decelerations are caused by the compression of the baby’s head during uterine contractions. The compression causes vagal stimulation, which slows the fetal heart rate.
Why is my fetus decelerating?from verywellhealth.com
Late decelerations may indicate that a fetus has high levels of acid in the blood (a condition called impending fetal academia), which is often caused by a lack of oxygen. 1
How long does a variable deceleration last?from verywellhealth.com
A variable deceleration is a very quick decrease in fetal heart rate of 15 bpm or more, that lasts at least 15 seconds ( but may last up to two minutes) before the heart rate returns to baseline.
When does FHR slow down?from verywellhealth.com
The FHR begins to slow by midterm. By about 10 weeks of pregnancy, the FHR beings to slow to approximately twice the normal adult heart rate (which is about 60 to 100 bpm). The FHR can also slow down when the fetus is asleep.
Do early decelerations affect oxygenation?from ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
As early decelerations are not associated with decreased fetal oxygenation or metabolic acidosis, they do not require any treatment. However, it is crucial to continue to monitor FHR tracings throughout labor to recognize any patterns that may be a concern regarding changes in the acid-base status of the fetus.
How many types of deceleration are there in labor?
There are three types of deceleration that may occur during labor. Each type is categorized by the timing of the deceleration during uterine contractions. 1
What Causes Deceleration?
The cause of deceleration varies depending on the type. For example, early decelerations are caused by the compression of the baby’s head during uterine contractions. The compression causes vagal stimulation, which slows the fetal heart rate.
Why is my fetus decelerating?
Late decelerations may indicate that a fetus has high levels of acid in the blood (a condition called impending fetal academia), which is often caused by a lack of oxygen. 1
How long does a variable deceleration last?
A variable deceleration is a very quick decrease in fetal heart rate of 15 bpm or more, that lasts at least 15 seconds ( but may last up to two minutes) before the heart rate returns to baseline.
When does FHR slow down?
The FHR begins to slow by midterm. By about 10 weeks of pregnancy, the FHR beings to slow to approximately twice the normal adult heart rate (which is about 60 to 100 bpm). The FHR can also slow down when the fetus is asleep.
What happens when you have late decels?
However, when late decels occur in more than 50 percent of the contractions of your uterus, then fetal hypoxia is a plausible explanation. Your doctor will then take action to prevent medical complications for your newborn.
What causes late deceleration?
Usually, any process that causes the following conditions is capable of inducing late decelerations: 1 Maternal low blood pressure (or hypotension) 2 Excessive activity in your uterus 3 Reduced oxygen supply to your placenta
Why is my placenta decelerating?
Reduced oxygen supply to your placenta. Two of the most common late deceleration causes include an overactive uterus and hypotension due to epidural analgesia. This is the injection of an anesthetic into your spinal epidural space to eliminate pelvic pain during labor and delivery.
How long does it take for a deceleration to reach its lowest point?
Once deceleration starts, it takes about 20 to 30 seconds to reach its lowest point. When the timing of deceleration is delayed, it means that the lowest point is occurring past the peak of your uterine contraction. In the majority of cases, the beginning, low point, and recovery of late decelerations happen after the start, peak, ...
Is late deceleration dangerous?
One of many unusual FHR patterns observed during labor, late decelerations could be considered dangerous. They’re a sign of hampered blood flow to your placenta, which might trigger imminent fetal hypoxia (or a lack of oxygen for fetal tissues).
Can a doctor monitor late deceleration?
If your doctor identifies reversible causes, they’ll likely conduct other tests and closely monitor you. Also, you can take certain steps to treat late decelerations and improve fetal oxygen supply.
Can you give oxygen to a woman with late deceleration?
Your doctor might administer oxygen in response to late decelerations. However, there’s no clinical evidence suggesting its effectiveness when used alone in women with adequat e oxygen levels.

Fetal Heart Tone Monitoring of Decelerations For Nursing Students and Nurses
Quiz & Video on Fetal Heart Tone Decelerations
- After you read this article, be sure to take a Fetal Heart Tone Quizand test your knowledge on these decelerations.
Early Decelerations
- The picture above is known as an “early decelerations”. The top line is monitoring the baby’s heart rate and the bottom line is monitoring mom’s contractions. On the bottom line (mom’s contraction), you can see that the line start to go up and then down…….this means mom is having a contraction. The top line (baby’s heart rate) then responds to this...
Variable Decelerations
- This crazy looking strip is called “variable decelerations“. I remember it because the dips in the fetal heart tones look like V’s. The v’s remind me that this is a “variable deceleration”. Variable decelerations are NOT good! Notice that every time mom has a contraction the baby’s heart rate majorly decreases. Remember a normal fetal heart rate is 110-160 bpms. The cause of the decr…